SpringBoot中使用@ConfigurationProperties进行配置绑定
文章目录
-
-
-
- 使用Java读取.properties文件的内容并封装成JavaBean
- 使用SpringBoot的@ConfigurationProperties进行配置绑定
-
- @ConfigurationProperties
- @ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mycar")
-
- @Component+@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mycar")
- @EnableConfigurationProperties+@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mycar")
-
-
使用Java读取.properties文件的内容并封装成JavaBean
- 新建Maven项目:demo1。
- 修改pom.xml,添加依赖。
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0modelVersion>
<groupId>com.examplegroupId>
<artifactId>demo1artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOTversion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parentartifactId>
<version>2.6.1version>
parent>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8maven.compiler.target>
properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-webartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
<version>1.18.12version>
<scope>providedscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>commons-beanutilsgroupId>
<artifactId>commons-beanutilsartifactId>
<version>1.9.4version>
dependency>
dependencies>
project>
- 新建类com.example.boot.bean.Car。
package com.example.boot.bean;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Data
public class Car {
private String brand;
private Integer price;
}
- resources下新建配置文件application.properties。
brand=BYD
price=100000
- 新建控制器com.example.boot.controller.DemoController。
package com.example.boot.controller;
import com.example.boot.bean.Car;
import org.apache.commons.beanutils.BeanUtils;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
@Controller
public class DemoControlller {
@RequestMapping("/car")
@ResponseBody
public Car car() {
Car car = new Car();
try {
car = getProperties();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (InvocationTargetException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IllegalAccessException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
return car;
}
}
public Car getProperties() throws IOException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
Car car = new Car();
Properties pps = new Properties();
pps.load(new FileInputStream("src/main/resources/application.properties"));
Map<String,String> map = new HashMap<>();
Enumeration enumeration = pps.propertyNames();
while(enumeration.hasMoreElements()){
String strKey = (String) enumeration.nextElement();
String strValue = pps.getProperty(strKey);
map.put(strKey,strValue);
System.out.println(strKey + "=" + strValue);
}
BeanUtils.populate(car,map);
return car;
}
}
这里使用Java读取application.properties文件中的内容,并通过BeanUtils将它封装到JavaBean中(pom配置文件中添加了依赖commons-beanutils)。
- 新建主启动类com.example.boot.MainApplication。
package com.example.boot;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class MainApplication {
public static void main(String[] args){
SpringApplication.run(MainApplication.class,args);
}
}
使用SpringBoot的@ConfigurationProperties进行配置绑定
在Spring项目中,可能会有大量的参数配置在application.properties或application.yml中,以前会通过Java读取配置文件中的内容来获取这些参数,见上面的例子,琐碎且繁杂,而SpringBoot提供的@ConfigurationProperties注解可以帮助我们轻松地获取到它们。不信?往下看。
@ConfigurationProperties
- 修改com.example.boot.bean.Car。
package com.example.boot.bean;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Data
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties
public class Car {
private String brand;
private Integer price;
}
注意两点。
第一点:@Component,将Car标注为普通组件,添加到SpringBoot容器中。注意哈,只有加入到SpringBoot容器中的组件,才能使用SpringBoot提供的强大功能。
@Component,标注为普通组件
@Controller,标注为控制层组件
@Service,标注为服务层组件
@Repository,标注为持久层组件
第二点:@ConfigurationProperties,可以将自动为属性注入配置值。
application.properties中配置的brand=BYD,BYD自动成为Car的brand属性的默认值;application.properties中配置的price=100000,100000自动成为Car的price属性的默认值。
- 修改com.example.boot.controller.DemoController。
package com.example.boot.controller;
import com.example.boot.bean.Car;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
public class DemoControlller {
@Autowired
private Car car;
@RequestMapping("/car")
@ResponseBody
public Car car() {
return car;
}
}
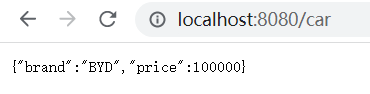
- 启动应用,访问接口localhost:8080/car。

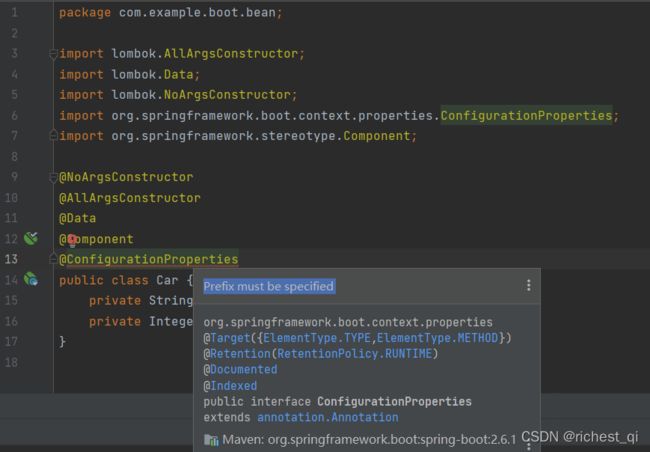
如上图所示,使用@ConfigurationProperties时必须指定prefix属性(不过,刚刚我们没有指定,运行也并没有报错,指定prefix属性是最佳实践)。那我们就来最佳实践一把。
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “mycar”)
@Component+@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “mycar”)
- 修改application.properties,加了前缀
mycar。
mycar.brand=BYD
mycar.price=100000
- 修改com.example.boot.bean.Car,
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mycar")。
package com.example.boot.bean;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Data
@Component
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mycar")
public class Car {
private String brand;
private Integer price;
}
- com.example.boot.controller.DemoController。
package com.example.boot.controller;
import com.example.boot.bean.Car;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
public class DemoControlller {
@Autowired
private Car car;
@RequestMapping("/car")
@ResponseBody
public Car car() {
return car;
}
}
上面提到,需要将Car添加到SpringBoot容器中,才能使用SpringBoot的@ConfigurationProperties注解进行配置绑定。
刚刚介绍了@Component+@ConfigurationProperties这一解决方案。
下面介绍另一种解决方案:@EnableConfigurationProperties+@ConfigurationProperties。
@EnableConfigurationProperties+@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = “mycar”)
- 新建com.example.boot.config.MyConfig。
package com.example.boot.config;
import com.example.boot.bean.Car;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(Car.class)
public class MyConfig {
}
@EnableConfigurationProperties(Car.class)的作用有两个,一个是,使能属性配置功能或者配置绑定功能;另一个是,将Car注册为SpringBoot容器中的组件。
- com.example.boot.bean.Car。
package com.example.boot.bean;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
@NoArgsConstructor
@AllArgsConstructor
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "mycar")
public class Car {
private String brand;
private Integer price;
}
- com.example.boot.controller.DemoController。
package com.example.boot.controller;
import com.example.boot.bean.Car;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ResponseBody;
@Controller
public class DemoControlller {
@Autowired
private Car car;
@RequestMapping("/car")
@ResponseBody
public Car car() {
return car;
}
}
- 重启应用,访问接口localhost:8080/car,得到预期结果。