深度学习网络模型——RepVGG网络详解、RepVGG网络训练花分类数据集整体项目实现
深度学习网络模型——RepVGG网络详解、RepVGG网络训练花分类数据集整体项目实现
- 0 前言
- 1 RepVGG Block详解
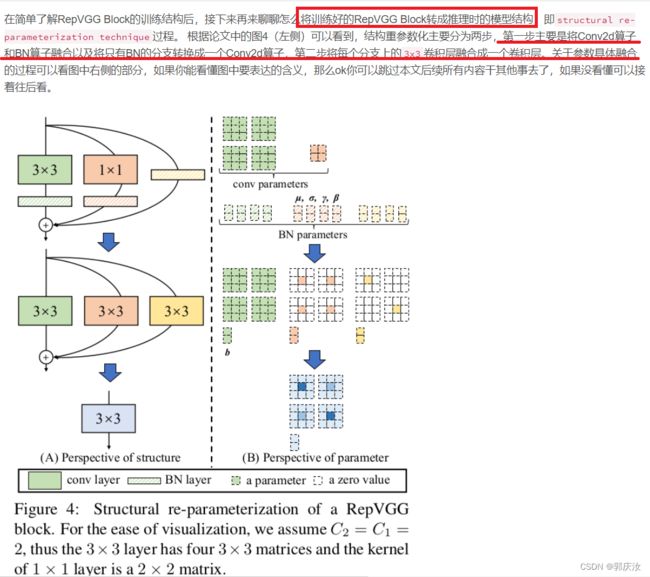
- 2 结构重参数化
-
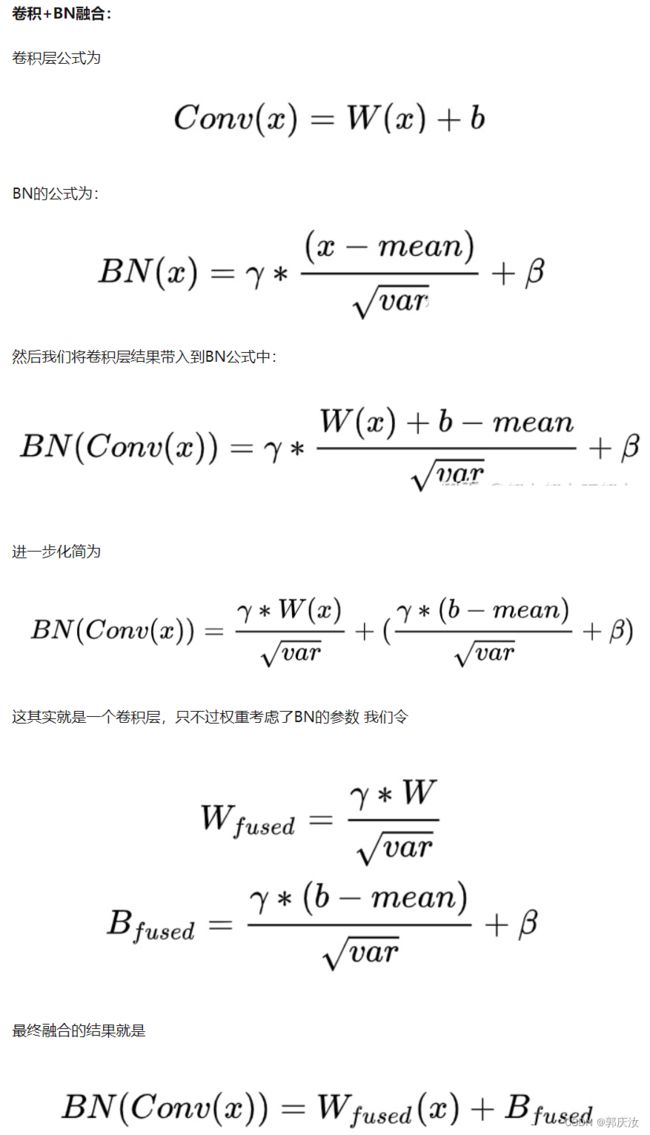
- 2.1 融合Conv2d和BN
- 2.2 Conv2d+BN融合实验(Pytorch)
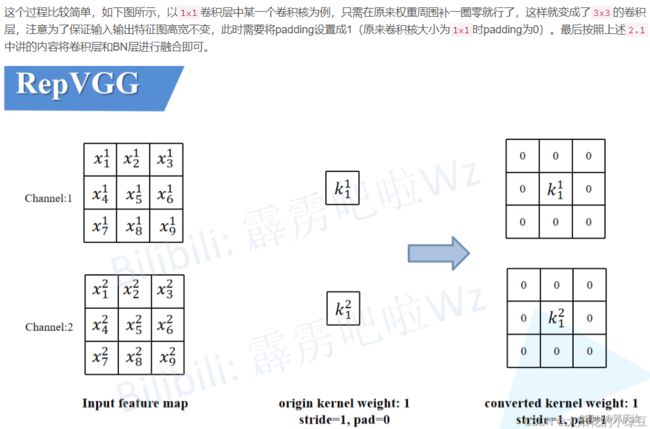
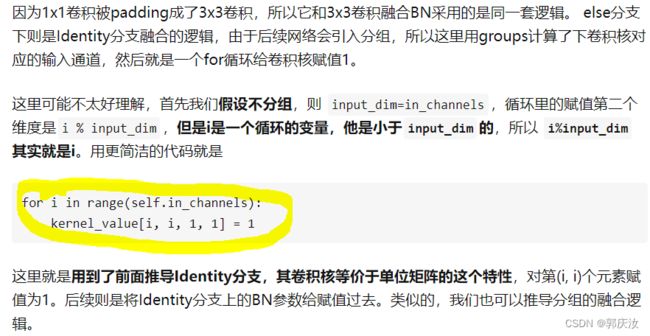
- 2.3 将1x1卷积转换成3x3卷积
- 2.4 将BN转换成3x3卷积
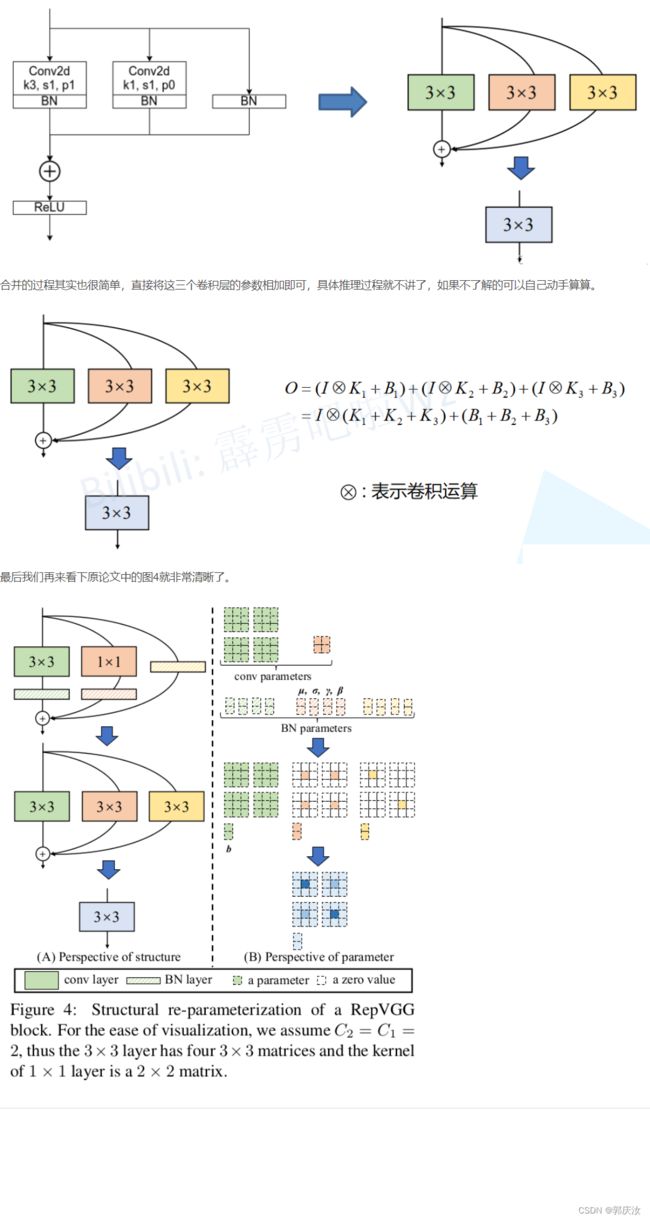
- 2.5 多分支融合
- 2.6 结构重参数化实验(Pytorch)
- 3 模型配置
- 4、RepVGG网络训练花分类数据集整体项目实现
-
- (1)模型构建:model.py
- (2)模型训练:train.py
- (3)模型推理测试:predict.py
- (5)整体项目代码
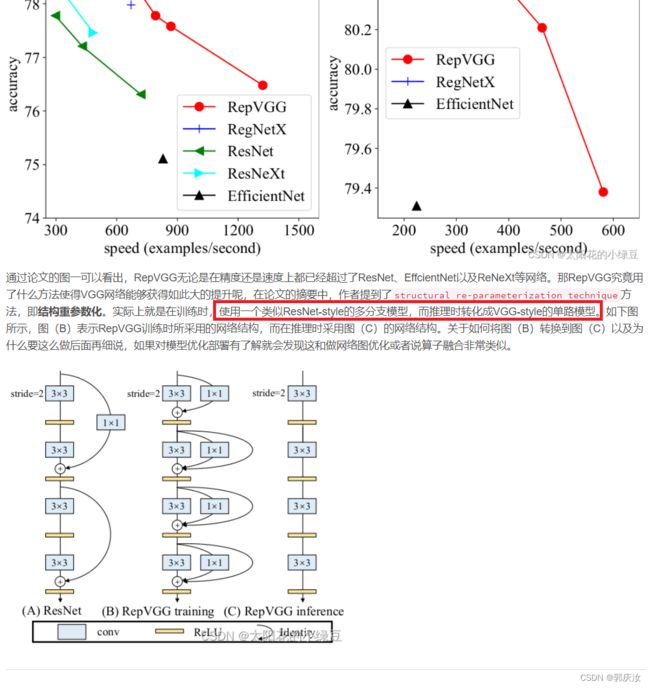
论文名称: RepVGG: Making VGG-style ConvNets Great Again
论文下载地址: https://arxiv.org/abs/2101.03697
官方源码(Pytorch实现): https://github.com/DingXiaoH/RepVGG
0 前言
1 RepVGG Block详解
2 结构重参数化
2.1 融合Conv2d和BN
2.2 Conv2d+BN融合实验(Pytorch)
from collections import OrderedDict
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
def main():
torch.random.manual_seed(0)
f1 = torch.randn(1, 2, 3, 3)
module = nn.Sequential(OrderedDict(
conv=nn.Conv2d(in_channels=2, out_channels=2, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=False),
bn=nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=2)
))
module.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
output1 = module(f1)
print(output1)
# fuse conv + bn
kernel = module.conv.weight
running_mean = module.bn.running_mean
running_var = module.bn.running_var
gamma = module.bn.weight
beta = module.bn.bias
eps = module.bn.eps
std = (running_var + eps).sqrt()
t = (gamma / std).reshape(-1, 1, 1, 1) # [ch] -> [ch, 1, 1, 1]
kernel = kernel * t
bias = beta - running_mean * gamma / std
fused_conv = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=2, out_channels=2, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1, bias=True)
fused_conv.load_state_dict(OrderedDict(weight=kernel, bias=bias))
with torch.no_grad():
output2 = fused_conv(f1)
print(output2)
np.testing.assert_allclose(output1.numpy(), output2.numpy(), rtol=1e-03, atol=1e-05)
print("convert module has been tested, and the result looks good!")
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
2.3 将1x1卷积转换成3x3卷积
2.4 将BN转换成3x3卷积
2.5 多分支融合
2.6 结构重参数化实验(Pytorch)
import time
import torch.nn as nn
import numpy as np
import torch
def conv_bn(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, padding, groups=1):
result = nn.Sequential()
result.add_module('conv', nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels,
kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride, padding=padding,
groups=groups, bias=False))
result.add_module('bn', nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=out_channels))
return result
class RepVGGBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size=3,
stride=1, padding=1, dilation=1, groups=1, padding_mode='zeros', deploy=False):
super(RepVGGBlock, self).__init__()
self.deploy = deploy
self.groups = groups
self.in_channels = in_channels
self.nonlinearity = nn.ReLU()
if deploy:
self.rbr_reparam = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels,
kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride,
padding=padding, dilation=dilation, groups=groups,
bias=True, padding_mode=padding_mode)
else:
self.rbr_identity = nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=in_channels) \
if out_channels == in_channels and stride == 1 else None
self.rbr_dense = conv_bn(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=kernel_size,
stride=stride, padding=padding, groups=groups)
self.rbr_1x1 = conv_bn(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=1,
stride=stride, padding=0, groups=groups)
def forward(self, inputs):
if hasattr(self, 'rbr_reparam'):
return self.nonlinearity(self.rbr_reparam(inputs))
if self.rbr_identity is None:
id_out = 0
else:
id_out = self.rbr_identity(inputs)
return self.nonlinearity(self.rbr_dense(inputs) + self.rbr_1x1(inputs) + id_out)
def get_equivalent_kernel_bias(self):
kernel3x3, bias3x3 = self._fuse_bn_tensor(self.rbr_dense)
kernel1x1, bias1x1 = self._fuse_bn_tensor(self.rbr_1x1)
kernelid, biasid = self._fuse_bn_tensor(self.rbr_identity)
return kernel3x3 + self._pad_1x1_to_3x3_tensor(kernel1x1) + kernelid, bias3x3 + bias1x1 + biasid
def _pad_1x1_to_3x3_tensor(self, kernel1x1):
if kernel1x1 is None:
return 0
else:
return torch.nn.functional.pad(kernel1x1, [1, 1, 1, 1])
def _fuse_bn_tensor(self, branch):
if branch is None:
return 0, 0
if isinstance(branch, nn.Sequential):
kernel = branch.conv.weight
running_mean = branch.bn.running_mean
running_var = branch.bn.running_var
gamma = branch.bn.weight
beta = branch.bn.bias
eps = branch.bn.eps
else:
assert isinstance(branch, nn.BatchNorm2d)
if not hasattr(self, 'id_tensor'):
input_dim = self.in_channels // self.groups
kernel_value = np.zeros((self.in_channels, input_dim, 3, 3), dtype=np.float32)
for i in range(self.in_channels):
kernel_value[i, i % input_dim, 1, 1] = 1
self.id_tensor = torch.from_numpy(kernel_value).to(branch.weight.device)
kernel = self.id_tensor
running_mean = branch.running_mean
running_var = branch.running_var
gamma = branch.weight
beta = branch.bias
eps = branch.eps
std = (running_var + eps).sqrt()
t = (gamma / std).reshape(-1, 1, 1, 1)
return kernel * t, beta - running_mean * gamma / std
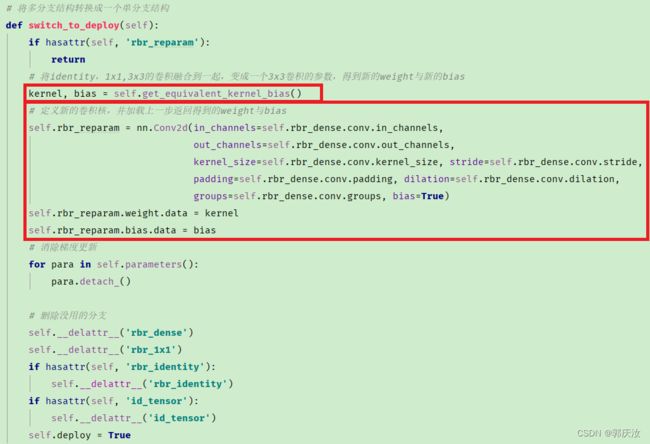
def switch_to_deploy(self):
if hasattr(self, 'rbr_reparam'):
return
kernel, bias = self.get_equivalent_kernel_bias()
self.rbr_reparam = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=self.rbr_dense.conv.in_channels,
out_channels=self.rbr_dense.conv.out_channels,
kernel_size=self.rbr_dense.conv.kernel_size, stride=self.rbr_dense.conv.stride,
padding=self.rbr_dense.conv.padding, dilation=self.rbr_dense.conv.dilation,
groups=self.rbr_dense.conv.groups, bias=True)
self.rbr_reparam.weight.data = kernel
self.rbr_reparam.bias.data = bias
for para in self.parameters():
para.detach_()
self.__delattr__('rbr_dense')
self.__delattr__('rbr_1x1')
if hasattr(self, 'rbr_identity'):
self.__delattr__('rbr_identity')
if hasattr(self, 'id_tensor'):
self.__delattr__('id_tensor')
self.deploy = True
def main():
f1 = torch.randn(1, 64, 64, 64)
block = RepVGGBlock(in_channels=64, out_channels=64)
block.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
output1 = block(f1)
start_time = time.time()
for _ in range(100):
block(f1)
print(f"consume time: {time.time() - start_time}")
# re-parameterization
block.switch_to_deploy()
output2 = block(f1)
start_time = time.time()
for _ in range(100):
block(f1)
print(f"consume time: {time.time() - start_time}")
np.testing.assert_allclose(output1.numpy(), output2.numpy(), rtol=1e-03, atol=1e-05)
print("convert module has been tested, and the result looks good!")
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
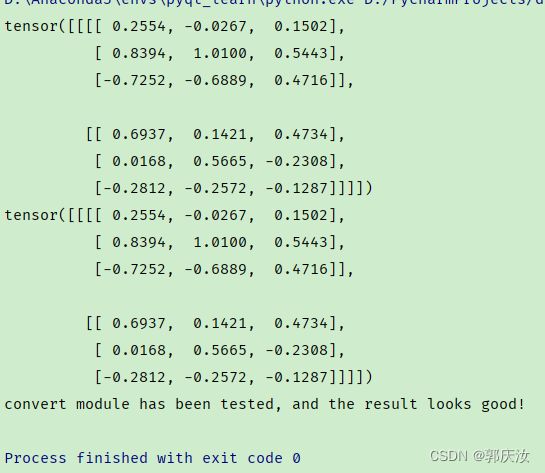
终端输出结果如下:
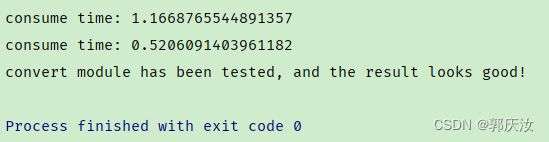
通过对比能够发现,结构重参数化后推理速度翻倍了,并且转换前后的输出保持一致。
3 模型配置
4、RepVGG网络训练花分类数据集整体项目实现
其中model.py是RepVGG模型实现代码,可以供选择的模型依次如下:
func_dict = {
'RepVGG-A0': create_RepVGG_A0,
'RepVGG-A1': create_RepVGG_A1,
'RepVGG-A2': create_RepVGG_A2,
'RepVGG-B0': create_RepVGG_B0,
'RepVGG-B1': create_RepVGG_B1,
'RepVGG-B1g2': create_RepVGG_B1g2,
'RepVGG-B1g4': create_RepVGG_B1g4,
'RepVGG-B2': create_RepVGG_B2,
'RepVGG-B2g2': create_RepVGG_B2g2,
'RepVGG-B2g4': create_RepVGG_B2g4,
'RepVGG-B3': create_RepVGG_B3,
'RepVGG-B3g2': create_RepVGG_B3g2,
'RepVGG-B3g4': create_RepVGG_B3g4,
'RepVGG-D2se': create_RepVGG_D2se, # Updated at April 25, 2021. This is not reported in the CVPR paper.
}
(1)模型构建:model.py
# --------------------------------------------------------
# RepVGG: Making VGG-style ConvNets Great Again (https://openaccess.thecvf.com/content/CVPR2021/papers/Ding_RepVGG_Making_VGG-Style_ConvNets_Great_Again_CVPR_2021_paper.pdf)
# Github source: https://github.com/DingXiaoH/RepVGG
# Licensed under The MIT License [see LICENSE for details]
# --------------------------------------------------------
import torch.nn as nn
import numpy as np
import torch
import copy
from se_block import SEBlock
import torch.utils.checkpoint as checkpoint
def conv_bn(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride, padding, groups=1):
result = nn.Sequential()
result.add_module('conv', nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels,
kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride, padding=padding, groups=groups, bias=False))
result.add_module('bn', nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=out_channels))
return result
class RepVGGBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size,
stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, padding_mode='zeros', deploy=False, use_se=False):
super(RepVGGBlock, self).__init__()
self.deploy = deploy
self.groups = groups
self.in_channels = in_channels
assert kernel_size == 3
assert padding == 1
padding_11 = padding - kernel_size // 2
self.nonlinearity = nn.ReLU()
if use_se:
# Note that RepVGG-D2se uses SE before nonlinearity. But RepVGGplus models uses SE after nonlinearity.
self.se = SEBlock(out_channels, internal_neurons=out_channels // 16)
else:
self.se = nn.Identity()
if deploy:
self.rbr_reparam = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride,
padding=padding, dilation=dilation, groups=groups, bias=True, padding_mode=padding_mode)
else:
self.rbr_identity = nn.BatchNorm2d(num_features=in_channels) if out_channels == in_channels and stride == 1 else None
self.rbr_dense = conv_bn(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=kernel_size, stride=stride, padding=padding, groups=groups)
self.rbr_1x1 = conv_bn(in_channels=in_channels, out_channels=out_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, padding=padding_11, groups=groups)
print('RepVGG Block, identity = ', self.rbr_identity)
def forward(self, inputs):
if hasattr(self, 'rbr_reparam'):
return self.nonlinearity(self.se(self.rbr_reparam(inputs)))
if self.rbr_identity is None:
id_out = 0
else:
id_out = self.rbr_identity(inputs)
return self.nonlinearity(self.se(self.rbr_dense(inputs) + self.rbr_1x1(inputs) + id_out))
# Optional. This may improve the accuracy and facilitates quantization in some cases.
# 1. Cancel the original weight decay on rbr_dense.conv.weight and rbr_1x1.conv.weight.
# 2. Use like this.
# loss = criterion(....)
# for every RepVGGBlock blk:
# loss += weight_decay_coefficient * 0.5 * blk.get_cust_L2()
# optimizer.zero_grad()
# loss.backward()
def get_custom_L2(self):
K3 = self.rbr_dense.conv.weight
K1 = self.rbr_1x1.conv.weight
t3 = (self.rbr_dense.bn.weight / ((self.rbr_dense.bn.running_var + self.rbr_dense.bn.eps).sqrt())).reshape(-1, 1, 1, 1).detach()
t1 = (self.rbr_1x1.bn.weight / ((self.rbr_1x1.bn.running_var + self.rbr_1x1.bn.eps).sqrt())).reshape(-1, 1, 1, 1).detach()
l2_loss_circle = (K3 ** 2).sum() - (K3[:, :, 1:2, 1:2] ** 2).sum() # The L2 loss of the "circle" of weights_ in 3x3 kernel. Use regular L2 on them.
eq_kernel = K3[:, :, 1:2, 1:2] * t3 + K1 * t1 # The equivalent resultant central point of 3x3 kernel.
l2_loss_eq_kernel = (eq_kernel ** 2 / (t3 ** 2 + t1 ** 2)).sum() # Normalize for an L2 coefficient comparable to regular L2.
return l2_loss_eq_kernel + l2_loss_circle
# This func derives the equivalent kernel and bias in a DIFFERENTIABLE way.
# You can get the equivalent kernel and bias at any time and do whatever you want,
# for example, apply some penalties or constraints during training, just like you do to the other models.
# May be useful for quantization or pruning.
def get_equivalent_kernel_bias(self):
kernel3x3, bias3x3 = self._fuse_bn_tensor(self.rbr_dense)
kernel1x1, bias1x1 = self._fuse_bn_tensor(self.rbr_1x1)
kernelid, biasid = self._fuse_bn_tensor(self.rbr_identity)
return kernel3x3 + self._pad_1x1_to_3x3_tensor(kernel1x1) + kernelid, bias3x3 + bias1x1 + biasid
def _pad_1x1_to_3x3_tensor(self, kernel1x1):
if kernel1x1 is None:
return 0
else:
return torch.nn.functional.pad(kernel1x1, [1,1,1,1])
def _fuse_bn_tensor(self, branch):
if branch is None:
return 0, 0
if isinstance(branch, nn.Sequential):
kernel = branch.conv.weight
running_mean = branch.bn.running_mean
running_var = branch.bn.running_var
gamma = branch.bn.weight
beta = branch.bn.bias
eps = branch.bn.eps
else:
assert isinstance(branch, nn.BatchNorm2d)
if not hasattr(self, 'id_tensor'):
input_dim = self.in_channels // self.groups
kernel_value = np.zeros((self.in_channels, input_dim, 3, 3), dtype=np.float32)
for i in range(self.in_channels):
kernel_value[i, i % input_dim, 1, 1] = 1
self.id_tensor = torch.from_numpy(kernel_value).to(branch.weight.device)
kernel = self.id_tensor
running_mean = branch.running_mean
running_var = branch.running_var
gamma = branch.weight
beta = branch.bias
eps = branch.eps
std = (running_var + eps).sqrt()
t = (gamma / std).reshape(-1, 1, 1, 1)
return kernel * t, beta - running_mean * gamma / std
def switch_to_deploy(self):
if hasattr(self, 'rbr_reparam'):
return
kernel, bias = self.get_equivalent_kernel_bias()
self.rbr_reparam = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=self.rbr_dense.conv.in_channels, out_channels=self.rbr_dense.conv.out_channels,
kernel_size=self.rbr_dense.conv.kernel_size, stride=self.rbr_dense.conv.stride,
padding=self.rbr_dense.conv.padding, dilation=self.rbr_dense.conv.dilation, groups=self.rbr_dense.conv.groups, bias=True)
self.rbr_reparam.weight.data = kernel
self.rbr_reparam.bias.data = bias
self.__delattr__('rbr_dense')
self.__delattr__('rbr_1x1')
if hasattr(self, 'rbr_identity'):
self.__delattr__('rbr_identity')
if hasattr(self, 'id_tensor'):
self.__delattr__('id_tensor')
self.deploy = True
class RepVGG(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_blocks, num_classes=1000, width_multiplier=None, override_groups_map=None, deploy=False, use_se=False, use_checkpoint=False):
super(RepVGG, self).__init__()
assert len(width_multiplier) == 4
self.deploy = deploy
self.override_groups_map = override_groups_map or dict()
assert 0 not in self.override_groups_map
self.use_se = use_se
self.use_checkpoint = use_checkpoint
self.in_planes = min(64, int(64 * width_multiplier[0]))
self.stage0 = RepVGGBlock(in_channels=3, out_channels=self.in_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1, deploy=self.deploy, use_se=self.use_se)
self.cur_layer_idx = 1
self.stage1 = self._make_stage(int(64 * width_multiplier[0]), num_blocks[0], stride=2)
self.stage2 = self._make_stage(int(128 * width_multiplier[1]), num_blocks[1], stride=2)
self.stage3 = self._make_stage(int(256 * width_multiplier[2]), num_blocks[2], stride=2)
self.stage4 = self._make_stage(int(512 * width_multiplier[3]), num_blocks[3], stride=2)
self.gap = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(output_size=1)
print("----------------------------",num_classes)
self.linear = nn.Linear(int(512 * width_multiplier[3]), num_classes)
def _make_stage(self, planes, num_blocks, stride):
strides = [stride] + [1]*(num_blocks-1)
blocks = []
for stride in strides:
cur_groups = self.override_groups_map.get(self.cur_layer_idx, 1)
blocks.append(RepVGGBlock(in_channels=self.in_planes, out_channels=planes, kernel_size=3,
stride=stride, padding=1, groups=cur_groups, deploy=self.deploy, use_se=self.use_se))
self.in_planes = planes
self.cur_layer_idx += 1
return nn.ModuleList(blocks)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.stage0(x)
for stage in (self.stage1, self.stage2, self.stage3, self.stage4):
for block in stage:
if self.use_checkpoint:
out = checkpoint.checkpoint(block, out)
else:
out = block(out)
out = self.gap(out)
out = out.view(out.size(0), -1)
out = self.linear(out)
return out
optional_groupwise_layers = [2, 4, 6, 8, 10, 12, 14, 16, 18, 20, 22, 24, 26]
g2_map = {l: 2 for l in optional_groupwise_layers}
g4_map = {l: 4 for l in optional_groupwise_layers}
def create_RepVGG_A0(deploy=False, use_checkpoint=False,num_classes=None):
return RepVGG(num_blocks=[2, 4, 14, 1], num_classes=num_classes,
width_multiplier=[0.75, 0.75, 0.75, 2.5], override_groups_map=None, deploy=deploy, use_checkpoint=use_checkpoint)
def create_RepVGG_A1(deploy=False, use_checkpoint=False):
return RepVGG(num_blocks=[2, 4, 14, 1], num_classes=1000,
width_multiplier=[1, 1, 1, 2.5], override_groups_map=None, deploy=deploy, use_checkpoint=use_checkpoint)
def create_RepVGG_A2(deploy=False, use_checkpoint=False):
return RepVGG(num_blocks=[2, 4, 14, 1], num_classes=1000,
width_multiplier=[1.5, 1.5, 1.5, 2.75], override_groups_map=None, deploy=deploy, use_checkpoint=use_checkpoint)
def create_RepVGG_B0(deploy=False, use_checkpoint=False):
return RepVGG(num_blocks=[4, 6, 16, 1], num_classes=1000,
width_multiplier=[1, 1, 1, 2.5], override_groups_map=None, deploy=deploy, use_checkpoint=use_checkpoint)
def create_RepVGG_B1(deploy=False, use_checkpoint=False):
return RepVGG(num_blocks=[4, 6, 16, 1], num_classes=1000,
width_multiplier=[2, 2, 2, 4], override_groups_map=None, deploy=deploy, use_checkpoint=use_checkpoint)
def create_RepVGG_B1g2(deploy=False, use_checkpoint=False):
return RepVGG(num_blocks=[4, 6, 16, 1], num_classes=1000,
width_multiplier=[2, 2, 2, 4], override_groups_map=g2_map, deploy=deploy, use_checkpoint=use_checkpoint)
def create_RepVGG_B1g4(deploy=False, use_checkpoint=False):
return RepVGG(num_blocks=[4, 6, 16, 1], num_classes=1000,
width_multiplier=[2, 2, 2, 4], override_groups_map=g4_map, deploy=deploy, use_checkpoint=use_checkpoint)
def create_RepVGG_B2(deploy=False, use_checkpoint=False):
return RepVGG(num_blocks=[4, 6, 16, 1], num_classes=1000,
width_multiplier=[2.5, 2.5, 2.5, 5], override_groups_map=None, deploy=deploy, use_checkpoint=use_checkpoint)
def create_RepVGG_B2g2(deploy=False, use_checkpoint=False):
return RepVGG(num_blocks=[4, 6, 16, 1], num_classes=1000,
width_multiplier=[2.5, 2.5, 2.5, 5], override_groups_map=g2_map, deploy=deploy, use_checkpoint=use_checkpoint)
def create_RepVGG_B2g4(deploy=False, use_checkpoint=False):
return RepVGG(num_blocks=[4, 6, 16, 1], num_classes=1000,
width_multiplier=[2.5, 2.5, 2.5, 5], override_groups_map=g4_map, deploy=deploy, use_checkpoint=use_checkpoint)
def create_RepVGG_B3(deploy=False, use_checkpoint=False):
return RepVGG(num_blocks=[4, 6, 16, 1], num_classes=1000,
width_multiplier=[3, 3, 3, 5], override_groups_map=None, deploy=deploy, use_checkpoint=use_checkpoint)
def create_RepVGG_B3g2(deploy=False, use_checkpoint=False):
return RepVGG(num_blocks=[4, 6, 16, 1], num_classes=1000,
width_multiplier=[3, 3, 3, 5], override_groups_map=g2_map, deploy=deploy, use_checkpoint=use_checkpoint)
def create_RepVGG_B3g4(deploy=False, use_checkpoint=False):
return RepVGG(num_blocks=[4, 6, 16, 1], num_classes=1000,
width_multiplier=[3, 3, 3, 5], override_groups_map=g4_map, deploy=deploy, use_checkpoint=use_checkpoint)
def create_RepVGG_D2se(deploy=False, use_checkpoint=False):
return RepVGG(num_blocks=[8, 14, 24, 1], num_classes=1000,
width_multiplier=[2.5, 2.5, 2.5, 5], override_groups_map=None, deploy=deploy, use_se=True, use_checkpoint=use_checkpoint)
func_dict = {
'RepVGG-A0': create_RepVGG_A0,
'RepVGG-A1': create_RepVGG_A1,
'RepVGG-A2': create_RepVGG_A2,
'RepVGG-B0': create_RepVGG_B0,
'RepVGG-B1': create_RepVGG_B1,
'RepVGG-B1g2': create_RepVGG_B1g2,
'RepVGG-B1g4': create_RepVGG_B1g4,
'RepVGG-B2': create_RepVGG_B2,
'RepVGG-B2g2': create_RepVGG_B2g2,
'RepVGG-B2g4': create_RepVGG_B2g4,
'RepVGG-B3': create_RepVGG_B3,
'RepVGG-B3g2': create_RepVGG_B3g2,
'RepVGG-B3g4': create_RepVGG_B3g4,
'RepVGG-D2se': create_RepVGG_D2se, # Updated at April 25, 2021. This is not reported in the CVPR paper.
}
def get_RepVGG_func_by_name(name):
return func_dict[name]
# Use this for converting a RepVGG model or a bigger model with RepVGG as its component
# Use like this
# model = create_RepVGG_A0(deploy=False)
# train model or load weights_
# repvgg_model_convert(model, save_path='repvgg_deploy.pth')
# If you want to preserve the original model, call with do_copy=True
# ====================== for using RepVGG as the backbone of a bigger model, e.g., PSPNet, the pseudo code will be like
# train_backbone = create_RepVGG_B2(deploy=False)
# train_backbone.load_state_dict(torch.load('RepVGG-B2-train.pth'))
# train_pspnet = build_pspnet(backbone=train_backbone)
# segmentation_train(train_pspnet)
# deploy_pspnet = repvgg_model_convert(train_pspnet)
# segmentation_test(deploy_pspnet)
# ===================== example_pspnet.py shows an example
def repvgg_model_convert(model:torch.nn.Module, save_path=None, do_copy=True):
if do_copy:
model = copy.deepcopy(model)
for module in model.modules():
if hasattr(module, 'switch_to_deploy'):
module.switch_to_deploy()
if save_path is not None:
torch.save(model.state_dict(), save_path)
return model
(2)模型训练:train.py
本次我训练是轻量级的级别的模型RepVGG-A0使用官方预训练模型,测试集达到86%准确率,可能模型比较浅的原因,官方预训练模型连接如下:
RepVGG官方预训练模型
提取码:rvgg
在训练过程中根据自己需求导入不同深度级别模型

如下代码位置为分类的类别数:
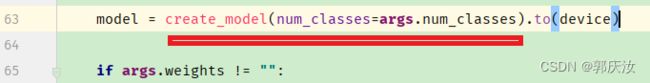
模型训练整体代码:
train.py
import os
import argparse
import torch
import torch.optim as optim
from torch.utils.tensorboard import SummaryWriter
from torchvision import transforms
from my_dataset import MyDataSet
from model import create_RepVGG_A0 as create_model
from utils import read_split_data, create_lr_scheduler, get_params_groups, train_one_epoch, evaluate
def main(args):
device = torch.device(args.device if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
print(f"using {device} device.")
if os.path.exists("weights_") is False:
os.makedirs("weights_")
tb_writer = SummaryWriter()
train_images_path, train_images_label, val_images_path, val_images_label = read_split_data(args.data_path)
img_size = 224
data_transform = {
"train": transforms.Compose([transforms.RandomResizedCrop(img_size),
transforms.RandomHorizontalFlip(),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])]),
"val": transforms.Compose([transforms.Resize(int(img_size * 1.143)),
transforms.CenterCrop(img_size),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize([0.485, 0.456, 0.406], [0.229, 0.224, 0.225])])}
# 实例化训练数据集
train_dataset = MyDataSet(images_path=train_images_path,
images_class=train_images_label,
transform=data_transform["train"])
# 实例化验证数据集
val_dataset = MyDataSet(images_path=val_images_path,
images_class=val_images_label,
transform=data_transform["val"])
batch_size = args.batch_size
nw = min([os.cpu_count(), batch_size if batch_size > 1 else 0, 8]) # number of workers
print('Using {} dataloader workers every process'.format(nw))
train_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(train_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True,
pin_memory=True,
num_workers=nw,
collate_fn=train_dataset.collate_fn)
val_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(val_dataset,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=False,
pin_memory=True,
num_workers=nw,
collate_fn=val_dataset.collate_fn)
model = create_model(num_classes=args.num_classes).to(device)
if args.weights != "":
assert os.path.exists(args.weights), "weights_ file: '{}' not exist.".format(args.weights)
weights_dict = torch.load(args.weights, map_location=device)["model"]
# 删除有关分类类别的权重
for k in list(weights_dict.keys()):
if "head" in k:
del weights_dict[k]
print(model.load_state_dict(weights_dict, strict=False))
if args.freeze_layers:
for name, para in model.named_parameters():
# 除head外,其他权重全部冻结
if "head" not in name:
para.requires_grad_(False)
else:
print("training {}".format(name))
# pg = [p for p in model.parameters() if p.requires_grad]
pg = get_params_groups(model, weight_decay=args.wd)
optimizer = optim.AdamW(pg, lr=args.lr, weight_decay=args.wd)
lr_scheduler = create_lr_scheduler(optimizer, len(train_loader), args.epochs,
warmup=True, warmup_epochs=1)
best_acc = 0.
for epoch in range(args.epochs):
# train
train_loss, train_acc = train_one_epoch(model=model,
optimizer=optimizer,
data_loader=train_loader,
device=device,
epoch=epoch,
lr_scheduler=lr_scheduler)
# validate
val_loss, val_acc = evaluate(model=model,
data_loader=val_loader,
device=device,
epoch=epoch)
tags = ["train_loss", "train_acc", "val_loss", "val_acc", "learning_rate"]
tb_writer.add_scalar(tags[0], train_loss, epoch)
tb_writer.add_scalar(tags[1], train_acc, epoch)
tb_writer.add_scalar(tags[2], val_loss, epoch)
tb_writer.add_scalar(tags[3], val_acc, epoch)
tb_writer.add_scalar(tags[4], optimizer.param_groups[0]["lr"], epoch)
if best_acc < val_acc:
torch.save(model.state_dict(), "./weights_/best_model.pth")
best_acc = val_acc
if __name__ == '__main__':
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser()
parser.add_argument('--num_classes', type=int, default=5)
parser.add_argument('--epochs', type=int, default=200)
parser.add_argument('--batch-size', type=int, default=256)
parser.add_argument('--lr', type=float, default=5e-4)
parser.add_argument('--wd', type=float, default=5e-2)
# 数据集所在根目录
parser.add_argument('--data-path', type=str,
default="./flower_photos")
# 预训练权重路径,如果不想载入就设置为空字符
parser.add_argument('--weights', type=str, default='',
help='initial weights_ path')
# 是否冻结head以外所有权重
parser.add_argument('--freeze-layers', type=bool, default=False)
parser.add_argument('--device', default='cuda:0', help='device id (i.e. 0 or 0,1 or cpu)')
opt = parser.parse_args()
main(opt)
(3)模型推理测试:predict.py
由于RepVGG是训练-推理解耦的,也即其训练时的网络结构和推理时的网络结构是不同的:训练阶段,网络包含了残差结构、不同大小的卷积核(33、11);而推理阶段,则只包含3*3卷积且为plain结构。需要将训练得到的模型进行相应的转化
# create model
from model import repvgg_model_convert, create_RepVGG_A0
train_model = create_RepVGG_A0(deploy=False,num_classes=5).to(device)
train_model.load_state_dict(torch.load("weights_/best_model.pth"))
deploy_model = repvgg_model_convert(train_model)
或者:
from model import repvgg_model_convert, create_RepVGG_A0
deploy_model = create_RepVGG_A0(deploy=True)
deploy_model.load_state_dict(torch.load('weights_/best_model.pth'))
import os
import json
import torch
from PIL import Image
from torchvision import transforms
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import os
os.environ["KMP_DUPLICATE_LIB_OK"]="TRUE"
def main():
device = torch.device("cuda:0" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
data_transform = transforms.Compose(
[transforms.Resize((224, 224)),
transforms.ToTensor(),
transforms.Normalize((0.5, 0.5, 0.5), (0.5, 0.5, 0.5))])
# load image
img_path = "test.jpg"
assert os.path.exists(img_path), "file: '{}' dose not exist.".format(img_path)
img = Image.open(img_path)
print(img)
plt.imshow(img)
# [N, C, H, W]
img = data_transform(img)
# expand batch dimension
img = torch.unsqueeze(img, dim=0)
# read class_indict
json_path = './class_indices.json'
assert os.path.exists(json_path), "file: '{}' dose not exist.".format(json_path)
with open(json_path, "r") as f:
class_indict = json.load(f)
# create model
from model import repvgg_model_convert, create_RepVGG_A0
train_model = create_RepVGG_A0(deploy=False,num_classes=5).to(device)
train_model.load_state_dict(torch.load("weights_/best_model.pth",map_location=torch.device('cpu')))
deploy_model = repvgg_model_convert(train_model)
deploy_model.eval()
with torch.no_grad():
# predict class
output = torch.squeeze(deploy_model(img.to(device))).cpu()
predict = torch.softmax(output, dim=0)
predict_cla = torch.argmax(predict).numpy()
print_res = "class: {} prob: {:.3}".format(class_indict[str(predict_cla)],
predict[predict_cla].numpy())
plt.title(print_res)
for i in range(len(predict)):
print("class: {:10} prob: {:.3}".format(class_indict[str(i)],
predict[i].numpy()))
plt.show()
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
(5)整体项目代码
整体项目已经传至CSDN!!!