系统发布时BeanCopyUtils.copyAppointFields导致空指针
一、引言
今天在发布的时候产生了空指针,根据堆栈显示BeanCopyUtils.copyAppointFields的时候产生了空指针,这里说明下这个工具类和方法是公司内部封装的,用于指定部分字段进行复制。
作者看到堆栈第一反应就是这个工具类有问题,作者和leader讨论了下,觉得是有可能的,下面介绍下排查过程和原理。
二、排查过程
一开始其实是吧log里面打出来的json拷贝到本地运行了一下,总要先检查自己的代码,再去看底层
1、堆栈
从堆栈可以看到具体报错的地方,可以找到源码查看
2、工具类源码
开发人使用了两个hashmap进行缓存,存储类的getset方法,如果没有缓存过会进入缓存方法,有的同学可能从这就知道了,问题就出在两个hashmap,后面我们再说这个
private static Map, MethodAccess> methodMap = new HashMap, MethodAccess>();
private static Map, Map> methodIndexMap = new HashMap<>();
if (source == null || target == null) {
log.error("BeanCopyUtils Process", "source or target is null, {}, {}", source, target);
return;
}
if (methodMap.get(source.getClass()) == null || methodMap.get(target.getClass()) == null) {
cache(source, target);
} 使用synchronized防止并发设置,然后懒汉模式在判断一次,最后存储到缓存
private synchronized static void cache(Object source, Object target) {
if (methodMap.get(source.getClass()) == null) {
cacheMethodIndex(source.getClass());
}
if (methodMap.get(target.getClass()) == null) {
cacheMethodIndex(target.getClass());
}
}
protected synchronized static void cacheMethodIndex(Class clazz) {
if (methodMap.get(clazz) != null) {
return;
}出问题的地方是在从缓存取出字段对应get方法的时候爆了空指针
Map sourceMethodIndexMap = methodIndexMap.get(source.getClass());
for (String field : sourceFieldList) {
Integer getMethodIndex = sourceMethodIndexMap.get(GET + StringUtils.capitalize(field)); 这里说明存储类对应的字段方法映射sourceMethodIndexMap的时候get的就是null,但是这里通过synchronized保证了并发,看代码一下子还看不出来问题。
作者有思考了一会,它是先判断了一遍get != null然后再取值,这是两步操作,当=null的时候还要经过一段缓存才能再次get。这期间如果发生hash冲突导致链表或者红黑树的node移动,那么get的时候就会是null;
3、验证
有了方向就需要去验证,那么需要写一段验证代码,代码要满足:
1、hash冲突之后会在entry形成链表或者红黑树节点移动
2、并发设置与取值
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("key", "value");
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
// 线程1执行put操作
executorService.execute(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
map.put("key" + i, "value" + i);
}
});
// 线程2执行get操作
executorService.execute(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
if (map.get("key" + i) != null) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
String value = map.get("key" + i);
if (value == null) {
System.out.println("get方法返回null,key=" + ("key" + i));
}
}
}
});
executorService.shutdown();
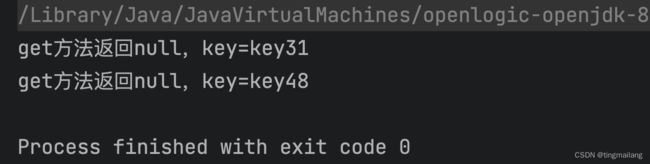
} 看一下运行结果,验证了猜测的方向
三、原理与解决
知道原理才能谈解决,不然就是人云亦云
1、原理
作者这里只介绍一种简单情况,便于理解,左图形成链表之后,根据key获取对应node的value的时候是不为null,但是到了右图的时候,链表在重新连接,这时候就是null了
2、解决
解决方案其实很简单,就是把hashmap换成ConcurrentHashMap,因为Doug Lea创作Concurrent包的时候做了并发互斥,在数据改动的时候会在ConcurrentHashMap里面通过分段锁阻塞读。Java 8中的ConcurrentHashMap使用了一种新的实现方式,即CAS+Synchronized来替代了旧版本中的分段锁实现。这种新的实现方式可以更好地利用现代CPU的硬件特性,提高并发性能。
有的同学可能说,那我只要并发的地方用到hashmap的地方都换成ConcurrentHashMap不就好了吗?
是的,大多数情况直接替换就可以,极少数追求性能并且控制好风险的情况下用hashmap可以减少分段锁的性能。
另外对于研发人员最重要的是知其然也知其所以然,如果Doug Lea没有创作Concurrent包,没有ConcurrentHashMap,要知道怎么排查解决。如果ConcurrentHashMap在极端情况下出现了新的问题,要知道怎么排查解决。
就像作者之前经常说的k8s、systemd、mq等等问题,开源社区或者中间件运维团队都是说升级就可以解决,那是解决吗?那是人云亦云,他们自己都不清楚为什么,那么开源社区的问题都是谁解决的,就需要每个研发人员对所有底层抱有质疑,并且尝试去解决。
不存在系统、框架、中间件是完全没有问题的!
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConcurrentHashMap map = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
map.put("key", "value");
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(2);
// 线程1执行put操作
executorService.execute(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
map.put("key" + i, "value" + i);
}
});
// 线程2执行get操作
executorService.execute(() -> {
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
if (map.get("key" + i) != null) {
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
String value = map.get("key" + i);
if (value == null) {
System.out.println("get方法返回null,key=" + ("key" + i));
}
}
}
});
executorService.shutdown();
} 四、总结
表象的发布问题牵扯到底层其实是一件好事,解决之后就可以一劳永逸的解决问题,排查过程还可以锻炼研发人员的思考、总结能力。
还是那句话,这里都是作者的理解,欢迎有不同想法的同学进行讨论。