使用cpp写一个json的解析器
使用cpp写一个json的解析器
地址:2.API 设计与实现_哔哩哔哩_bilibili
------------API设计--------------
1.json定义
JSON(JavaScript Object Notation, JS对象简谱)是一种轻量级的数据交换格式。它基于ECMAScript(European Computer Manufacturers Association, 欧洲计算机协会制定的js规范)的一个子集,采用完全独立于编程语言的文本格式来存储和表示数据。简洁和清晰的层次结构使得 JSON 成为理想的数据交换语言。 易于人阅读和编写,同时也易于机器解析和生成,并有效地提升网络传输效率。
JSON是一个标记符的序列。这套标记符包含六个构造字符、字符串、数字和三个字面名。
JSON是一个序列化的对象或数组。
JSON 基于两种结构:
名称/值对的集合。在不同的语言中,这是通过对象、记录、结构、字典、哈希表、键控列表或关联数组来实现的。
值的有序列表。在大多数语言中,这是以数组、向量、列表或序列的形式实现的。
在 JSON,他们采取以下形式:
对象是一组无序的名称/值对。对象以{左大括号开始,以}右大括号结束。每个名称后面跟着: 冒号,名称/值对之间用逗号分隔。
json的数据结构
object array string number "true " “false” “null”
定义json.h
使用map来表示object,使用vector来表示array,使用string来表示string字符串,number使用int和double来表示,"true " "false"用bool值来表示, "null"用空指针null表示。
#pragma once
#include json中字符串、数组、对象采用传入指针来节省空间,只需要传入首元素的地址。
定义json.cpp
首先实现对于初始化函数的定义
#include "json.h"
#include 注:初始化字符串、数组、对象时,由于传入的是一个指针,所以需要使用new来动态分配内存空间
测试初始化函数
#include 结果:运行编辑正常
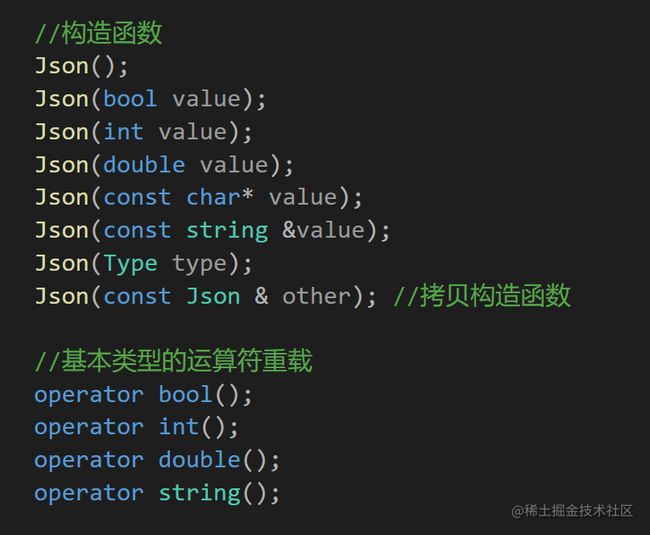
2.基本类型的运算符重载
目的:可以将创建的json的value对应的值赋值给基本类型的对象
在class json的json.h的里面添加基本类型运算符重载的声明
//基本类型的运算符重载
operator bool();
operator int();
operator double();
operator string();
添加位置如下:
在class json的json.cpp的里面添加基本类型运算符重载的定义
//基本类型的运算符重载
Json::operator bool()
{
if (m_type != json_bool)
{
throw new logic_error("type error, not bool value");
}
return m_value.m_bool;
}
Json::operator int()
{
if (m_type != json_int)
{
throw new logic_error("type error, not int value");
}
return m_value.m_int;
}
Json::operator double()
{
if (m_type != json_double)
{
throw new logic_error("type error, not double value");
}
return m_value.m_double;
}
Json::operator string()
{
if (m_type != json_string)
{
throw new logic_error("type error, not string value");
}
//string类型传入的是指针,返回字符串的时候需要对指针进行解引用
return *(m_value.m_string);
}
直接添加在json.cpp的尾部即可
验证基本类型的运算符重载
在main函数中添加
bool b = v2;
int i = v3;
double f = v4;
const string& s = v5;
3.测试数组类型的定义(按照数组索引的方式向数组中添加元素)
在class json的json.h的里面添加如下声明:
//测试数组类型的定义(按照数组索引的方式向数组中添加元素)
Json& operator [](int index);//重载[]
void append(const Json& other);//实现append追加
添加实现
Json& Json::operator [](int index)//重载[]
{
//判断other类型是否是数组类型
if (m_type != json_array)
{
m_type = json_array;
m_value.m_array = new vector<Json>();
}
if (index < 0)
{
throw new logic_error("array[] index < 0");
}
int size = (m_value.m_array)->size();
//如果index是大于size的,则需要扩容
if (index >= size)
{
//使用for循环进行扩容
for (int i = size; i <= index; i++)
{
//朝数组中添加空的json对象
(m_value.m_array)->push_back(Json());
}
}
return (m_value.m_array)->at(index);
}
void Json::append(const Json& other)//实现append追加
{
//判断other类型是否是数组类型
if (m_type != json_array)
{
m_type = json_array;
m_value.m_array = new vector<Json>();
}
//如果类型一致,追加数据
(m_value.m_array)->push_back(other);
}
将数组可视化输出
在class json的json.h的里面添加如下声明:
//将json返回的内容可视化
string str() const;
添加实现
//将json返回的内容可视化
string Json::str() const
{
stringstream ss;
switch (m_type)
{
case json_null:
ss << "null";
break;
case json_bool:
if (m_value.m_bool)
{
ss << "true";
}
else
{
ss << "false";
}
break;
case json_int:
ss << m_value.m_int;
break;
case json_double:
ss << m_value.m_double;
break;
case json_string:
//字符串需要包含引号
ss << '\"' << *(m_value.m_string) << '\"';
break;
case json_array:
ss << '[';
//遍历数组显示
for (auto it = (m_value.m_array)->begin(); it != (m_value.m_array)->end(); it++)
{
//元素之间添加逗号分割
if (it != (m_value.m_array)->begin())
{
ss << ",";
}
ss << it->str();
}
ss << ']';
break;
case json_object:
ss << '{';
//遍历map显示
for (auto it = (m_value.m_object)->begin(); it != (m_value.m_object)->end(); it++)
{
//元素之间添加逗号分割
if (it != (m_value.m_object)->begin())
{
ss << ",";
}
//first是string类型,需要加“”
ss << '\"' << it->first << '\"' << ':' << it->second.str();
}
ss << '}';
break;
default:
break;
}
return ss.str();
}
测试
//测试将数组元素可视化输出
cout << arr.str() << endl;
4.测试map类型的定义(按照按照键索引的方式)
在class json的json.h的里面添加如下声明:
//测试map类型的定义(按照键索引的方式)
Json& operator [](const char * key);//重载[]
Json& operator [](const string & key);//重载[]
void operator= (const Json& other); //重载=
void copy(const Json& other);//拷贝函数的抽象
void clear(); //对动态分配的内存进行释放
添加实现
//测试map类型的定义(按照键索引的方式)
//c风格
Json& Json::operator [](const char* key)//重载[]
{
string name(key);
return (*(this))[name];
}
//c++风格
Json& Json::operator [](const string& key)//重载[]
{
//类型判断
if (m_type != json_object)
{
clear();
m_type = json_object;
m_value.m_object = new map<string, Json>();
}
return (*(m_value.m_object))[key];
}
void Json::operator= (const Json& other) //重载=
{
clear();
copy(other);
}
void Json::copy(const Json& other)//拷贝函数的抽象
{
//将参数的type传入
m_type = other.m_type;
//根据类型的不同进行不同的初始化
switch (m_type)
{
case json_null:
break;
case json_bool:
m_value.m_bool = other.m_value.m_bool;
break;
case json_int:
m_value.m_int = other.m_value.m_int;
break;
case json_double:
m_value.m_double = other.m_value.m_double;
break;
//采用浅拷贝来提高效率,只传入指针
case json_string:
m_value.m_string = other.m_value.m_string;
break;
case json_array:
m_value.m_array = other.m_value.m_array;
break;
case json_object:
m_value.m_object = other.m_value.m_object;
break;
default:
cout << "请传入Json类型的数据!!!" << endl;
break;
}
}
void Json::clear() //对动态分配的内存进行释放
{
//根据类型的不同进行不同的初始化
switch (m_type)
{
//对于没有进行动态内存分配的
case json_null:
break;
case json_bool:
m_value.m_bool = false;
break;
case json_int:
m_value.m_int = 0;
break;
case json_double:
m_value.m_double = 0.0;
break;
//采用浅拷贝来提高效率,只传入指针
case json_string:
delete m_value.m_string;
break;
case json_array:
{
for (auto it = (m_value.m_array)->begin(); it != (m_value.m_array)->end(); it++)
{
it->clear();
}
delete m_value.m_array;
break;
}
case json_object:
{
for (auto it = (m_value.m_object)->begin(); it != (m_value.m_object)->end(); it++)
{
(it->second).clear();
}
delete m_value.m_object;
break;
}
default:
break;
}
//将类型置空
m_type = json_null;
}
这个步骤当中,将拷贝函数抽象出来成为copy()函数。在copy的过程中需要考虑内存泄漏的问题,于是写clear()函数,在动态分配内存之后及时回收内存。
同样,上一节中对于数组的重载操作中同样需要放置内存泄露。
Json& Json::operator [](int index)//重载[]
{
//判断other类型是否是数组类型
if (m_type != json_array)
{
clear();
m_type = json_array;
m_value.m_array = new vector<Json>();
}
if (index < 0)
{
throw new logic_error("array[] index < 0");
}
int size = (m_value.m_array)->size();
//如果index是大于size的,则需要扩容
if (index >= size)
{
//使用for循环进行扩容
for (int i = size; i <= index; i++)
{
//朝数组中添加空的json对象
(m_value.m_array)->push_back(Json());
}
}
return (m_value.m_array)->at(index);
}
测试
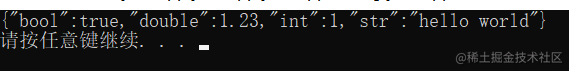
//3.对象的相关功能
Json obj;
obj["bool"] = true;
obj["int"] = 1;
obj["double"] = 1.23;
obj["str"] = "hello world";
//测试对象的键值对输出
cout << obj.str() << endl;
5.迭代器相关设置
定义迭代器
在class json的json.h的里面添加如下声明:
//迭代器相关设置
//定义迭代器
typedef vector<Json>::iterator iterator;
iterator begin()
{
return (m_value.m_array)->begin();
}
iterator end()
{
return (m_value.m_array)->end();
}
目前仅定义了迭代器的起始和结束位置,后续可考虑增加更多的功能。
测试
//4.迭代器相关功能
Json arr;
arr[0] = true;
arr[1] = 1;
arr[2] = 1.23;
arr[3] = "hello world";
for (auto it = arr.begin(); it != arr.end(); it++)
{
cout << (*it).str() << endl;
}
6.运算符重载的拓展
重载== 和!=
在class json的json.h的里面添加如下声明:
bool operator== (const Json& other); //重载==
bool operator!= (const Json& other); //重载!=
添加实现
bool Json::operator== (const Json& other) //重载==
{
if (m_type != other.m_type)
{
return false;
}
switch (m_type)
{
case json_null:
return true;
case json_int:
return m_value.m_int == other.m_value.m_int;
case json_double:
return m_value.m_double == other.m_value.m_double;
case json_string:
return *(m_value.m_string) == *(other.m_value.m_string);
case json_array:
{
if ((m_value.m_array)->size() != (other.m_value.m_array)->size())
{
return false;
}
return m_value.m_array == other.m_value.m_array;
}
case json_object:
{
return m_value.m_object == other.m_value.m_object;
}
default:
return false;
}
}
bool Json::operator!= (const Json& other) //重载!=
{
return !(*(this) == other);
}
7.其他函数实现
在class json的json.h的里面添加如下:
//类型判断
bool isNull() const { return m_type == json_null; }
bool isBool() const { return m_type == json_bool; }
bool isInt() const { return m_type == json_int; }
bool isDouble() const { return m_type == json_double; }
bool isString()const { return m_type == json_string; }
bool isArray() const { return m_type == json_array; }
bool isobject() const { return m_type == json_object; }
//函数类型的显示转换
bool asBool() const;
int asInt() const;
double asDouble() const;
string asString() const;
添加实现
//函数类型的显示转换
bool Json::asBool() const
{
if (!isBool())
{
throw new logic_error("type error, not bool value");
}
return m_value.m_bool;
}
int Json::asInt() const
{
if (!isInt())
{
throw new logic_error("type error, not int value");
}
return m_value.m_int;
}
double Json::asDouble() const
{
if (!isDouble())
{
throw new logic_error("type error, not double value");
}
return m_value.m_double;
}
string Json::asString() const
{
if (!isString())
{
throw new logic_error("type error, not string value");
}
return *(m_value.m_string);
}
索引判断
//判断索引或者是key是否存在
bool has(int index);
bool has(const char* key);
bool has(const string& key);
//判断索引或者是key是否存在
bool Json::has(int index)
{
if (m_type != json_array)
{
return false;
}
int size = (m_value.m_array)->size();
return(index >= 0 && index < size);
}
bool Json::has(const char* key)
{
string name(key);
return has(name);
}
bool Json::has(const string& key)
{
if (m_type != json_object)
{
return false;
}
return ((m_value.m_object)->find(key) != (m_value.m_object)->end());
}
----------paser设计------------
1.构造函数Parser()以及加载函数load()的定义
paser.h
#pragma once
#include 首先定义构造函数Parser()以及加载函数load()
实现
#include "Parser.h"
using namespace yazi::json;
//构造函数
Parser::Parser() : m_str(""),m_idx(0)
{
}
void Parser::load(const string& str)
{
m_str = str;
m_idx = 0;
}
构造函数就是简单的给空字符串和0值的索引。
2.parse()函数实现(核心)
框架搭建
在Parser.h中添加声明
//解析函数(核心)
Json parse();
private:
//解析不同类型的私有函数
Json parse_null();
Json parse_bool();
Json parse_number();
string parse_string();
Json parse_array();
Json parse_object();
//跳过空白字符
void skip_white_space();
//获取下一个字符
char get_next_token();
cpp文件添加实现
#include "Parser.h"
using namespace yazi::json;
//构造函数
Parser::Parser() : m_str(""),m_idx(0)
{
}
void Parser::load(const string& str)
{
m_str = str;
m_idx = 0;
}
//解析函数(核心)
Json Parser::parse()
{
//获取字符
char ch = get_next_token();
//对获取的字符进行判断
switch (ch)
{
case 'n':
return parse_null();
case 't':
case 'f':
return parse_bool();
case '-':
case '0':
case '1':
case '2':
case '3':
case '4':
case '5':
case '6':
case '7':
case '8':
case '9':
return parse_number();
case '"' :
return Json(parse_string());
case '[':
return parse_array();
case '{':
return parse_object();
default:
break;
}
}
//跳过空白字符
void Parser::skip_white_space()
{
while (m_str[m_idx] == ' ' || m_str[m_idx] == '\n' || m_str[m_idx] == '\r' || m_str[m_idx] == '\t')
{
m_idx++;
}
}
//获取下一个字符
char Parser::get_next_token()
{
skip_white_space();
char ch = m_str[m_idx];
m_idx++;
return ch;
//return m_str[m_idx++]
}
//解析不同类型的私有函数
//返回空值
Json Parser::parse_null()
{
return Json();
}
Json Parser::parse_bool()
{
return Json();
}
Json Parser::parse_number()
{
return Json();
}
string Parser::parse_string()
{
return "";
}
Json Parser::parse_array()
{
return Json();
}
Json Parser::parse_object()
{
return Json();
}
对于类型返回值暂时返回空值用于测试代码框架和逻辑
测试
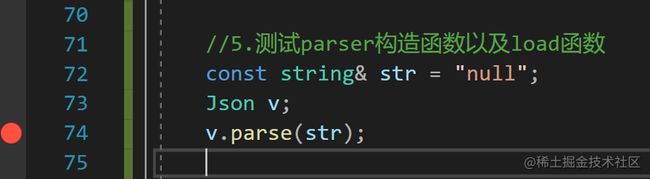
在json-cpp-cpp中添加测试代码:
//5.测试parser构造函数以及load函数
const string& str = "null";
Json v;
v.parse(str);
由于测试时使用的是空值,故返回的值为空,能正常编译说明parse()函数框架逻辑没问题,下一步开始加内容。
添加parse的具体函数内容
首先是parse_null内容的添加
这个地方写抛异常会报错说没有类型说明符,原因是没有把logic_error的头文件#include 引入
Json Parser::parse_null()
{
if (m_str.compare(m_idx, 4, "null") == 0)
{
return Json();
}
throw new logic_error("pause null error");
}
下面调试一下这段代码:
在parse函数调用的地方打断点

上图可以看见在进入parse_null()函数之后,我们的m_idx会变成1,是因为我们在get_next_token()函数中对m_idx进行了加1操作,故我们在parse()的switvh语句执行case之前将m_idx进行减1操作。这下就正确了:
定义对各种类型的解析:
Json Parser::parse_null()
{
if (m_str.compare(m_idx, 4, "null") == 0)
{
m_idx += 4;
return Json();
}
throw new logic_error("pause null error");
}
Json Parser::parse_bool()
{
if (m_str.compare(m_idx, 4, "true") == 0)
{
m_idx += 4;
return Json(true);
}
else if (m_str.compare(m_idx, 5, "false") == 0)
{
m_idx += 5;
return Json(false);
}
throw new logic_error("pause bool error");
}
Json Parser::parse_number()
{
//存开始的位置
int pos = m_idx;
//复数情况
if (m_str[m_idx] == '-')
{
//查看下一位是否是数字
m_idx++;
}
//不是数字的情况
if (m_str[m_idx] < '0' || m_str[m_idx] > '9')
{
throw new logic_error("pause number error");
}
//如果这一位是数字的话
while (m_str[m_idx] >= '0' && m_str[m_idx] <= '9')
{
m_idx++;
}
//排除小数的可能
if (m_str[m_idx] != '.')
{
int i = atoi(m_str.c_str() + pos);
return Json(i);
}
//如果是浮点数执行下面
m_idx++;
//不是数字的情况
if (m_str[m_idx] < '0' || m_str[m_idx] > '9')
{
throw new logic_error("pause number error");
}
//如果这一位是数字的话
while (m_str[m_idx] >= '0' && m_str[m_idx] <= '9')
{
m_idx++;
}
double f = atof(m_str.c_str() + pos);
return Json(f);
}
string Parser::parse_string()
{
//暂存string
string out;
while (1)
{
//存放下一个字符
//这里不可以使用get_next_token(),因为函数会过滤转义字符和空格
char ch = m_str[m_idx++];
//对获取到的字符进行判断
if (ch == '"')
{
break;
}
//如果遇见了转义字符
if (ch == '\\')
{
ch = m_str[m_idx++];
switch (ch)
{
case '\n':
out += '\n';
break;
case '\r':
out += '\r';
break;
case '\t':
out += '\t';
break;
case '\b':
out += '\b';
break;
case '"':
out += "\\\"";
break;
case '\\':
out += "\\\\";
break;
case '\f':
out += "\f";
break;
case '\\u':
out += "\\u";
//\u后面跟了四个字符,也需要追加上去
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++)
{
out += m_str[m_idx++];
}
break;
default:
break;
}
}
else
{
out += ch;
}
}
return out;
}
Json Parser::parse_array()
{
Json arr(Json::json_array);
char ch = get_next_token();
//空数组的情况
if (ch == ']')
{
return arr;
}
//数组不为空
while (true)
{
arr.append(parse());
ch = get_next_token();
//m_idx--;
if (ch == ']')
{
break;
}
if (ch != ',')
{
throw new logic_error("parse array error");
}
skip_white_space();
}
return arr;
}
Json Parser::parse_object()
{
Json obj(Json::json_object);
char ch = get_next_token();
//空对象的情况
if (ch == '}')
{
return obj;
}
//对象不为空
while (true)
{
//解析key
ch = get_next_token();
//如果key不是引号的话,抛异常
if (ch != '"')
{
throw new logic_error("parse object error");
}
string key = parse_string();
//解析下一位是不是冒号(key:value)
ch = get_next_token();
//如果key不是引号的话,抛异常
if (ch != ':')
{
throw new logic_error("parse object error");
}
obj[key] = parse();
ch = get_next_token();
if (ch == '}')
{
break;
}
if (ch != ',')
{
throw new logic_error("parse object error");
}
skip_white_space();
}
return obj;
}
项目代码到这一步已经比较完善了,下一步是整个json的来测试我们的代码。
随便找个网页复制一段json下来

然后找json在线整理一下格式:
测试:
//使用json测试
ifstream fin("./test.json");
stringstream ss;
ss << fin.rdbuf();
const string& str = ss.str();
Json v;
v.parse(str);
//测试解析是否成功
int quality = v["data"]["quality"];
string from = v["data"]["from"];
//cout << v.str() << endl;
密密麻麻,那我们就输出一个小的结构来看一下吧:
例如
//使用json测试
ifstream fin("./test.json");
stringstream ss;
ss << fin.rdbuf();
const string& str = ss.str();
Json v;
v.parse(str);
//测试解析是否成功
int quality = v["data"]["quality"];
string from = v["data"]["from"];
解析成功!!!!!