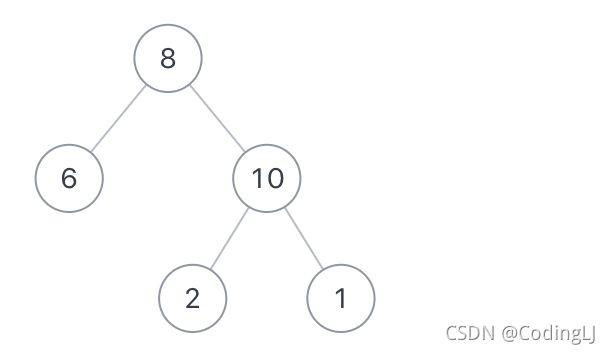
- C++11堆操作深度解析:std::is_heap与std::is_heap_until原理解析与实践
文章目录堆结构基础与函数接口堆的核心性质函数签名与核心接口std::is_heapstd::is_heap_until实现原理深度剖析std::is_heap的验证逻辑std::is_heap_until的定位策略算法优化细节代码实践与案例分析基础用法演示自定义比较器实现最小堆检查边缘情况处理性能分析与实际应用时间复杂度对比典型应用场景与手动实现的对比注意事项与最佳实践迭代器要求比较器设计C++标
- 冒泡、选择、插入排序:三大基础排序算法深度解析(C语言实现)
xienda
算法排序算法数据结构
在算法学习道路上,排序算法是每位程序员必须掌握的基石。本文将深入解析冒泡排序、选择排序和插入排序这三种基础排序算法,通过C语言代码实现和对比分析,帮助读者彻底理解它们的差异与应用场景。算法原理与代码实现1.冒泡排序(BubbleSort)工作原理:通过重复比较相邻元素,将较大元素逐步"冒泡"到数组末尾。voidbubbleSort(intarr[],intn){ for(inti=0;iarr[
- Leetcode 148. 排序链表
文章目录前引题目代码(首刷看题解)代码(8.9二刷部分看解析)代码(9.15三刷部分看解析)前引综合性比较强的一道题,要求时间复杂度必须O(logn)才能通过,最适合链表的排序算法就是归并。这里采用自顶向下的方法步骤:找到链表中点(双指针)对两个子链表排序(递归,直到只有一个结点,记得将子链表最后指向nullptr)归并(引入dummy结点)题目Leetcode148.排序链表代码(首刷看题解)c
- 全面触摸屏输入法设计与实现
长野君
本文还有配套的精品资源,点击获取简介:触摸屏输入法是针对触摸设备优化的文字输入方案,包括虚拟键盘、手写、语音识别和手势等多种输入方式。本方案通过提供主程序文件、用户手册、界面截图、示例图、说明文本和音效文件,旨在为用户提供一个完整的、多样的文字输入体验。开发者通过持续优化算法和用户界面,使用户在无物理键盘环境下也能高效准确地进行文字输入。1.触摸屏输入法概述简介在现代信息技术飞速发展的今天,触摸屏
- FPGA小白到项目实战:Verilog+Vivado全流程通关指南(附光学类岗位技能映射)
阿牛的药铺
算法移植部署fpga开发verilog
FPGA小白到项目实战:Verilog+Vivado全流程通关指南(附光学类岗位技能映射)引言:为什么这个FPGA入门路线能帮你快速上岗?本文设计了一条**"Verilog语法→工具链操作→光学项目实战→岗位技能对标"的阶梯式学习路径。不同于泛泛而谈的FPGA教程,我们聚焦光学类产品开发**核心能力(时序接口设计、图像处理算法移植、高速接口应用),通过3个递进式项目(从LED闪烁到图像边缘检测),
- PyTorch & TensorFlow速成复习:从基础语法到模型部署实战(附FPGA移植衔接)
阿牛的药铺
算法移植部署pytorchtensorflowfpga开发
PyTorch&TensorFlow速成复习:从基础语法到模型部署实战(附FPGA移植衔接)引言:为什么算法移植工程师必须掌握框架基础?针对光学类产品算法FPGA移植岗位需求(如可见光/红外图像处理),深度学习框架是算法落地的"桥梁"——既要用PyTorch/TensorFlow验证算法可行性,又要将训练好的模型(如CNN、目标检测)转换为FPGA可部署的格式(ONNX、TFLite)。本文采用"
- 算法学习笔记:17.蒙特卡洛算法 ——从原理到实战,涵盖 LeetCode 与考研 408 例题
在计算机科学和数学领域,蒙特卡洛算法(MonteCarloAlgorithm)以其独特的随机抽样思想,成为解决复杂问题的有力工具。从圆周率的计算到金融风险评估,从物理模拟到人工智能,蒙特卡洛算法都发挥着不可替代的作用。本文将深入剖析蒙特卡洛算法的思想、解题思路,结合实际应用场景与Java代码实现,并融入考研408的相关考点,穿插图片辅助理解,帮助你全面掌握这一重要算法。蒙特卡洛算法的基本概念蒙特卡
- 算法学习笔记:15.二分查找 ——从原理到实战,涵盖 LeetCode 与考研 408 例题
呆呆企鹅仔
算法学习算法学习笔记考研二分查找
在计算机科学的查找算法中,二分查找以其高效性占据着重要地位。它利用数据的有序性,通过不断缩小查找范围,将原本需要线性时间的查找过程优化为对数时间,成为处理大规模有序数据查找问题的首选算法。二分查找的基本概念二分查找(BinarySearch),又称折半查找,是一种在有序数据集合中查找特定元素的高效算法。其核心原理是:通过不断将查找范围减半,快速定位目标元素。与线性查找逐个遍历元素不同,二分查找依赖
- Python 脚本最佳实践2025版
前文可以直接把这篇文章喂给AI,可以放到AI角色设定里,也可以直接作为提示词.这样,你只管提需求,写脚本就让AI来.概述追求简洁和清晰:脚本应简单明了。使用函数(functions)、常量(constants)和适当的导入(import)实践来有逻辑地组织你的Python脚本。使用枚举(enumerations)和数据类(dataclasses)等数据结构高效管理脚本状态。通过命令行参数增强交互性
- (Python基础篇)字典的操作
EternityArt
基础篇python开发语言
一、引言在Python编程中,字典(Dictionary)是一种极具灵活性的数据结构,它通过“键-值对”(key-valuepair)的形式存储数据,如同现实生活中的字典——通过“词语(键)”快速查找“释义(值)”。相较于列表和元组的有序索引访问,字典的优势在于基于键的快速查找,这使得它在处理需要频繁通过唯一标识获取数据的场景中极为高效。掌握字典的操作,能让我们更高效地组织和管理复杂数据,是Pyt
- LeetCode算法题:电话号码的字母组合
吱屋猪_
算法leetcodejava
题目描述:给定一个仅包含数字2-9的字符串,返回所有它能表示的字母组合。答案可以按任意顺序返回。给出数字到字母的映射如下(与电话按键相同)。注意1不对应任何字母。2->"abc"3->"def"4->"ghi"5->"jkl"6->"mno"7->"pqrs"8->"tuv"9->"wxyz"例如,给定digits="23",返回["ad","ae","af","bd","be","bf","cd
- 霍夫变换(Hough Transform)算法原来详解和纯C++代码实现以及OpenCV中的使用示例
点云SLAM
算法图形图像处理算法opencv图像处理与计算机视觉算法直线提取检测目标检测霍夫变换算法
霍夫变换(HoughTransform)是一种经典的图像处理与计算机视觉算法,广泛用于检测图像中的几何形状,例如直线、圆、椭圆等。其核心思想是将图像空间中的“点”映射到参数空间中的“曲线”,从而将形状检测问题转化为参数空间中的峰值检测问题。一、霍夫变换基本思想输入:边缘图像(如经过Canny边缘检测)输出:一组满足几何模型的形状(如直线、圆)关键思想:图像空间中的一个点→参数空间中的一个曲线参数空
- Java三年经验程序员技术栈全景指南:从前端到架构,对标阿里美团全栈要求
可曾去过倒悬山
java前端架构
Java三年经验程序员技术栈全景指南:从前端到架构,对标阿里美团全栈要求三年经验是Java程序员的分水岭,技术栈深度决定你成为“业务码农”还是“架构师候选人”。本文整合阿里、美团、滴滴等大厂招聘要求,为你绘制可落地的进阶路线。一、Java核心:从语法糖到JVM底层三年经验与初级的核心差异在于系统级理解,大厂面试常考以下能力:JVM与性能调优内存模型(堆外内存、元空间)、GC算法(G1/ZGC适用场
- 被动降噪的概念及编程实现
CodeByte
人工智能算法javascript编程
被动降噪是指通过编程技术和算法,对输入的数据进行处理,以减少或消除其中的噪声。噪声可以是各种形式的干扰,例如来自传感器、通信信号或其他外部源的干扰。在本文中,我们将探讨被动降噪的意义以及如何使用编程来实现这一目标。被动降噪的意义:噪声对数据的准确性和可靠性产生负面影响。在许多应用领域,例如图像处理、音频处理和信号处理中,噪声的存在可能导致数据质量下降,使得后续的分析和处理变得困难。因此,被动降噪技
- 传统检测响应慢?陌讯多模态引擎提速90+FPS实战
2501_92473147
算法计算机视觉目标检测
开篇痛点:实时目标检测在安防监控中的核心挑战在安防监控领域,实时目标检测是保障公共安全的关键技术。然而,传统算法如YOLOv5或开源框架MMDetection常面临两大痛点:误报率高(复杂光照或遮挡场景下检测不稳定)和响应延迟(高分辨率视频流处理FPS低于30)。实测数据显示,城市交通监控系统误报率达15%,导致安保资源浪费;客户反馈表明,延迟超100ms时,目标跟踪可能失效。这些问题源于算法泛化
- 反光衣识别漏检率 30%?陌讯多尺度模型实测优化
在建筑工地、交通指挥等场景中,反光衣是保障作业人员安全的重要装备,对其进行精准识别是智能监控系统的核心功能之一。但传统视觉算法在实际应用中却屡屡碰壁:强光下反光衣易与背景混淆、远距离小目标漏检率高达30%、复杂场景下模型泛化能力不足[实测数据来源:某智慧工地项目2024年Q1日志]。这些问题直接导致安全监控系统预警滞后,给安全生产埋下隐患。一、技术解析:反光衣识别的核心难点与陌讯算法创新反光衣识别
- 【GESP】C++三级真题 luogu-B4359 [GESP202506 三级] 分糖果
CoderCodingNo
GESPc++java开发语言
GESPC++三级,2025年6月真题,模拟算法,难度★★☆☆☆。本次三级题目个人感觉比较简单。题目题解详见:【GESP】C++三级真题luogu-B4359[GESP202506三级]分糖果|OneCoder【GESP】C++三级真题luogu-B4359[GESP202506三级]分糖果|OneCoderGESPC++三级,2025年6月真题,模拟算法,难度★★☆☆☆。本次三级题目个人感觉比较
- 【华为机试】HJ61 放苹果
不爱熬夜的Coder
算法华为机试golang华为golang算法面试
文章目录HJ61放苹果描述输入描述输出描述示例1示例2解题思路算法分析问题本质分析状态定义与转移递推关系详解动态规划表构建算法流程图示例推导过程代码实现思路时间复杂度分析关键优化点边界情况处理递归解法对比实际应用场景测试用例分析算法特点数学原理完整题解代码HJ61放苹果描述我们需要将m个相同的苹果放入n个相同的盘子中,允许有的盘子空着不放。求解有多少种不同的分法。输入描述输入两个整数m,n(0B[
- .NET中的安全性之数字签名、数字证书、强签名程序集、反编译
hezudao25
NET.netassembly加密算法referenceheader
本文将探讨数字签名、数字证书、强签名程序集、反编译等以及它们在.NET中的运用(一些概念并不局限于.NET在其它技术、平台中也存在)。1.数字签名数字签名又称为公钥数字签名,或者电子签章等,它借助公钥加密技术实现。数字签名技术主要涉及公钥、私钥、非对称加密算法。1.1公钥与私钥公钥是公开的钥匙,私钥则是与公钥匹配的严格保护的私有密钥;私钥加密的信息只有公钥可以解开,反之亦然。在VisualStud
- HashMap的Get(),Put()源码解析
Ttang23
哈希算法散列表算法
1、什么是HashMap?HashMap是Java中用于存储键值对(Key-Value)的集合类,它实现了Map接口。其核心特点是:无序性:不保证元素的存储顺序,也不保证顺序恒定不变。唯一性:键(Key)不能重复,若插入重复键会覆盖原有值。允许null:允许一个null键和任意数量的null值。非线程安全:相比HashTable,HashMap不支持同步,性能更高。2.核心数据结构:哈希表(Has
- C++STL-queue
s15335
C++STLc++开发语言
一.基本概念和数据结构里面的队列一样,只支持先进先出,队尾插,队头删。二.基本用法1.queue对象创建1.默认构造函数queueq1;2.拷贝构造函数queueq2(q1);2.queue赋值操作queueq1;queueq2;q2=q1;3.queue入队queueq;q.push(5);//5q.push(4);//54q.push(3);//543q.push(2);//5432q.pus
- zookeeper etcd区别
sun007700
zookeeperetcd分布式
ZooKeeper与etcd的核心区别体现在设计理念、数据模型、一致性协议及适用场景等方面。ZooKeeper基于ZAB协议实现分布式协调,采用树形数据结构和临时节点特性,适合传统分布式系统;而etcd基于Raft协议,以高性能键值对存储为核心,专为云原生场景优化,是Kubernetes等容器编排系统的默认存储组件。12架构与设计目标差异ZooKeeper。设计定位:专注于分
- 数据结构:导论
梁辰兴
数据结构学习笔记数据结构导论算法时间复杂度空间复杂度
目录一,数据结构的研究内容二,基本概念与术语(一)数据、数据元素、数据项与数据对象(二)数据结构(三)数据类型与抽象数据类型️三,抽象数据类型的表示与实现⚙️四,算法与算法分析⚖️(一)算法的定义及特性(二)评价算法优劣的基本标准⏱️(三)算法的时间复杂度(四)算法的空间复杂度章结一,数据结构的研究内容数据结构是计算机科学的核心基础,其研究内容可概括为三大维度:数据组织形式:探索如何将现实世界中的
- redis中什么是bigkey?会有什么影响?
Vic2334
redis
什么是bigkey?会有什么影响?bigkey是指key对应的value所占的内存空间比较大,例如一个字符串类型的value可以最大存到512MB,一个列表类型的value最多可以存储23-1个元素。如果按照数据结构来细分的话,一般分为字符串类型bigkey和非字符串类型bigkey。字符串类型:体现在单个value值很大,一般认为超过10KB就是bigkey,但这个值和具体的OPS相关。非字符串
- C++ 标准库 <numeric>
以下对C++标准库中头文件所提供的数值算法与工具做一次系统、深入的梳理,包括算法功能、示例代码、复杂度分析及实践建议。一、概述中定义了一组对数值序列进行累加、内积、差分、扫描等操作的算法,以及部分辅助工具(如std::iota、std::gcd/std::lcm等)。所有算法均作用于迭代器区间,符合STL风格,可与任意容器或原始数组配合使用。从C++17、20起,又陆续加入了并行友好的std::r
- 具身语义导航算法总揽
Shilong Wang
具身导航算法算法
端到端方法小脑大脑GNMNavDPNaVILAViNTNomadNavidStreamVLNMapNavNavGPTUni-NavidOctoNavNavGPT2模仿学习行为克隆BCDAgger模块化方法GOATVLFMSayPlanLM-NavETPNavVoroNavEmbodiedRAGVL-NavStairwaytoSuccess业内大佬北大王鹤NavidUni-NavidOctoNav吴
- android去除gps漂移代码,GPS漂移过滤算法
扇贝君
GPS漂移过滤算法基本思想:逐点过滤,再经过基础过滤后,进行判断运动状态,静止状态和运动中。如果静止,则使用电子围栏;如果运动,则先过滤大速度,再过滤加速度,然后过滤距离(包括超大距离,和速度相关距离)。对于要过滤的点,采用之前最近的可靠点,进行替换,同时,无效次数+1,如果后面是有效点,则无效次数-1,如果无效次数归0,认为这个点才是真正可靠点(无效次数为正时,都为要被替换的点)。如果遇到不定点
- 项目开发日记
框架整理学习UIMgr:一、数据结构与算法1.1关键数据结构成员变量类型说明m_CtrlsList当前正在显示的所有UI页面m_CachesList已打开过、但现在不显示的页面(缓存池)1.2算法逻辑查找缓存页面:从m_Caches中倒序查找是否已有对应ePageType页面,找到则重用。页面加载:从资源管理器ResMgr加载prefab并绑定控制器/视图组件。页面关闭:从m_Ctrls移除,添加
- 上位机知识篇---常见的文件系统
文件系统是操作系统用于管理和组织存储设备上文件的机制,它决定了文件的存储方式、命名规则、访问权限、数据结构等。以下是常见的文件系统及其应用场景、优势和劣势的详细介绍:一、Windows常用文件系统1.FAT32(FileAllocationTable32)基本特点:采用32位文件分配表,是FAT系列的升级版,支持最大单文件4GB,最大分区容量理论上为8TB(实际常用2TB以内)。应用场景:U盘、存
- 深度学习图像分类数据集—桃子识别分类
AI街潜水的八角
深度学习图像数据集深度学习分类人工智能
该数据集为图像分类数据集,适用于ResNet、VGG等卷积神经网络,SENet、CBAM等注意力机制相关算法,VisionTransformer等Transformer相关算法。数据集信息介绍:桃子识别分类:['B1','M2','R0','S3']训练数据集总共有6637张图片,每个文件夹单独放一种数据各子文件夹图片统计:·B1:1601张图片·M2:1800张图片·R0:1601张图片·S3:
- Java开发中,spring mvc 的线程怎么调用?
小麦麦子
springmvc
今天逛知乎,看到最近很多人都在问spring mvc 的线程http://www.maiziedu.com/course/java/ 的启动问题,觉得挺有意思的,那哥们儿问的也听仔细,下面的回答也很详尽,分享出来,希望遇对遇到类似问题的Java开发程序猿有所帮助。
问题:
在用spring mvc架构的网站上,设一线程在虚拟机启动时运行,线程里有一全局
- maven依赖范围
bitcarter
maven
1.test 测试的时候才会依赖,编译和打包不依赖,如junit不被打包
2.compile 只有编译和打包时才会依赖
3.provided 编译和测试的时候依赖,打包不依赖,如:tomcat的一些公用jar包
4.runtime 运行时依赖,编译不依赖
5.默认compile
依赖范围compile是支持传递的,test不支持传递
1.传递的意思是项目A,引用
- Jaxb org.xml.sax.saxparseexception : premature end of file
darrenzhu
xmlprematureJAXB
如果在使用JAXB把xml文件unmarshal成vo(XSD自动生成的vo)时碰到如下错误:
org.xml.sax.saxparseexception : premature end of file
很有可能时你直接读取文件为inputstream,然后将inputstream作为构建unmarshal需要的source参数。InputSource inputSource = new In
- CSS Specificity
周凡杨
html权重Specificitycss
有时候对于页面元素设置了样式,可为什么页面的显示没有匹配上呢? because specificity
CSS 的选择符是有权重的,当不同的选择符的样式设置有冲突时,浏览器会采用权重高的选择符设置的样式。
规则:
HTML标签的权重是1
Class 的权重是10
Id 的权重是100
- java与servlet
g21121
servlet
servlet 搞java web开发的人一定不会陌生,而且大家还会时常用到它。
下面是java官方网站上对servlet的介绍: java官网对于servlet的解释 写道
Java Servlet Technology Overview Servlets are the Java platform technology of choice for extending and enha
- eclipse中安装maven插件
510888780
eclipsemaven
1.首先去官网下载 Maven:
http://www.apache.org/dyn/closer.cgi/maven/binaries/apache-maven-3.2.3-bin.tar.gz
下载完成之后将其解压,
我将解压后的文件夹:apache-maven-3.2.3,
并将它放在 D:\tools目录下,
即 maven 最终的路径是:D:\tools\apache-mave
- jpa@OneToOne关联关系
布衣凌宇
jpa
Nruser里的pruserid关联到Pruser的主键id,实现对一个表的增删改,另一个表的数据随之增删改。
Nruser实体类
//*****************************************************************
@Entity
@Table(name="nruser")
@DynamicInsert @Dynam
- 我的spring学习笔记11-Spring中关于声明式事务的配置
aijuans
spring事务配置
这两天学到事务管理这一块,结合到之前的terasoluna框架,觉得书本上讲的还是简单阿。我就把我从书本上学到的再结合实际的项目以及网上看到的一些内容,对声明式事务管理做个整理吧。我看得Spring in Action第二版中只提到了用TransactionProxyFactoryBean和<tx:advice/>,定义注释驱动这三种,我承认后两种的内容很好,很强大。但是实际的项目当中
- java 动态代理简单实现
antlove
javahandlerproxydynamicservice
dynamicproxy.service.HelloService
package dynamicproxy.service;
public interface HelloService {
public void sayHello();
}
dynamicproxy.service.impl.HelloServiceImpl
package dynamicp
- JDBC连接数据库
百合不是茶
JDBC编程JAVA操作oracle数据库
如果我们要想连接oracle公司的数据库,就要首先下载oralce公司的驱动程序,将这个驱动程序的jar包导入到我们工程中;
JDBC链接数据库的代码和固定写法;
1,加载oracle数据库的驱动;
&nb
- 单例模式中的多线程分析
bijian1013
javathread多线程java多线程
谈到单例模式,我们立马会想到饿汉式和懒汉式加载,所谓饿汉式就是在创建类时就创建好了实例,懒汉式在获取实例时才去创建实例,即延迟加载。
饿汉式:
package com.bijian.study;
public class Singleton {
private Singleton() {
}
// 注意这是private 只供内部调用
private static
- javascript读取和修改原型特别需要注意原型的读写不具有对等性
bijian1013
JavaScriptprototype
对于从原型对象继承而来的成员,其读和写具有内在的不对等性。比如有一个对象A,假设它的原型对象是B,B的原型对象是null。如果我们需要读取A对象的name属性值,那么JS会优先在A中查找,如果找到了name属性那么就返回;如果A中没有name属性,那么就到原型B中查找name,如果找到了就返回;如果原型B中也没有
- 【持久化框架MyBatis3六】MyBatis3集成第三方DataSource
bit1129
dataSource
MyBatis内置了数据源的支持,如:
<environments default="development">
<environment id="development">
<transactionManager type="JDBC" />
<data
- 我程序中用到的urldecode和base64decode,MD5
bitcarter
cMD5base64decodeurldecode
这里是base64decode和urldecode,Md5在附件中。因为我是在后台所以需要解码:
string Base64Decode(const char* Data,int DataByte,int& OutByte)
{
//解码表
const char DecodeTable[] =
{
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0
- 腾讯资深运维专家周小军:QQ与微信架构的惊天秘密
ronin47
社交领域一直是互联网创业的大热门,从PC到移动端,从OICQ、MSN到QQ。到了移动互联网时代,社交领域应用开始彻底爆发,直奔黄金期。腾讯在过去几年里,社交平台更是火到爆,QQ和微信坐拥几亿的粉丝,QQ空间和朋友圈各种刷屏,写心得,晒照片,秀视频,那么谁来为企鹅保驾护航呢?支撑QQ和微信海量数据背后的架构又有哪些惊天内幕呢?本期大讲堂的内容来自今年2月份ChinaUnix对腾讯社交网络运营服务中心
- java-69-旋转数组的最小元素。把一个数组最开始的若干个元素搬到数组的末尾,我们称之为数组的旋转。输入一个排好序的数组的一个旋转,输出旋转数组的最小元素
bylijinnan
java
public class MinOfShiftedArray {
/**
* Q69 旋转数组的最小元素
* 把一个数组最开始的若干个元素搬到数组的末尾,我们称之为数组的旋转。输入一个排好序的数组的一个旋转,输出旋转数组的最小元素。
* 例如数组{3, 4, 5, 1, 2}为{1, 2, 3, 4, 5}的一个旋转,该数组的最小值为1。
*/
publ
- 看博客,应该是有方向的
Cb123456
反省看博客
看博客,应该是有方向的:
我现在就复习以前的,在补补以前不会的,现在还不会的,同时完善完善项目,也看看别人的博客.
我刚突然想到的:
1.应该看计算机组成原理,数据结构,一些算法,还有关于android,java的。
2.对于我,也快大四了,看一些职业规划的,以及一些学习的经验,看看别人的工作总结的.
为什么要写
- [开源与商业]做开源项目的人生活上一定要朴素,尽量减少对官方和商业体系的依赖
comsci
开源项目
为什么这样说呢? 因为科学和技术的发展有时候需要一个平缓和长期的积累过程,但是行政和商业体系本身充满各种不稳定性和不确定性,如果你希望长期从事某个科研项目,但是却又必须依赖于某种行政和商业体系,那其中的过程必定充满各种风险。。。
所以,为避免这种不确定性风险,我
- 一个 sql优化 ([精华] 一个查询优化的分析调整全过程!很值得一看 )
cwqcwqmax9
sql
见 http://www.itpub.net/forum.php?mod=viewthread&tid=239011
Web翻页优化实例
提交时间: 2004-6-18 15:37:49 回复 发消息
环境:
Linux ve
- Hibernat and Ibatis
dashuaifu
Hibernateibatis
Hibernate VS iBATIS 简介 Hibernate 是当前最流行的O/R mapping框架,当前版本是3.05。它出身于sf.net,现在已经成为Jboss的一部分了 iBATIS 是另外一种优秀的O/R mapping框架,当前版本是2.0。目前属于apache的一个子项目了。 相对Hibernate“O/R”而言,iBATIS 是一种“Sql Mappi
- 备份MYSQL脚本
dcj3sjt126com
mysql
#!/bin/sh
# this shell to backup mysql
#
[email protected] (QQ:1413161683 DuChengJiu)
_dbDir=/var/lib/mysql/
_today=`date +%w`
_bakDir=/usr/backup/$_today
[ ! -d $_bakDir ] && mkdir -p
- iOS第三方开源库的吐槽和备忘
dcj3sjt126com
ios
转自
ibireme的博客 做iOS开发总会接触到一些第三方库,这里整理一下,做一些吐槽。 目前比较活跃的社区仍旧是Github,除此以外也有一些不错的库散落在Google Code、SourceForge等地方。由于Github社区太过主流,这里主要介绍一下Github里面流行的iOS库。 首先整理了一份
Github上排名靠
- html wlwmanifest.xml
eoems
htmlxml
所谓优化wp_head()就是把从wp_head中移除不需要元素,同时也可以加快速度。
步骤:
加入到function.php
remove_action('wp_head', 'wp_generator');
//wp-generator移除wordpress的版本号,本身blog的版本号没什么意义,但是如果让恶意玩家看到,可能会用官网公布的漏洞攻击blog
remov
- 浅谈Java定时器发展
hacksin
java并发timer定时器
java在jdk1.3中推出了定时器类Timer,而后在jdk1.5后由Dou Lea从新开发出了支持多线程的ScheduleThreadPoolExecutor,从后者的表现来看,可以考虑完全替代Timer了。
Timer与ScheduleThreadPoolExecutor对比:
1.
Timer始于jdk1.3,其原理是利用一个TimerTask数组当作队列
- 移动端页面侧边导航滑入效果
ini
jqueryWebhtml5cssjavascirpt
效果体验:http://hovertree.com/texiao/mobile/2.htm可以使用移动设备浏览器查看效果。效果使用到jquery-2.1.4.min.js,该版本的jQuery库是用于支持HTML5的浏览器上,不再兼容IE8以前的浏览器,现在移动端浏览器一般都支持HTML5,所以使用该jQuery没问题。HTML文件代码:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<h
- AspectJ+Javasist记录日志
kane_xie
aspectjjavasist
在项目中碰到这样一个需求,对一个服务类的每一个方法,在方法开始和结束的时候分别记录一条日志,内容包括方法名,参数名+参数值以及方法执行的时间。
@Override
public String get(String key) {
// long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
// System.out.println("Be
- redis学习笔记
MJC410621
redisNoSQL
1)nosql数据库主要由以下特点:非关系型的、分布式的、开源的、水平可扩展的。
1,处理超大量的数据
2,运行在便宜的PC服务器集群上,
3,击碎了性能瓶颈。
1)对数据高并发读写。
2)对海量数据的高效率存储和访问。
3)对数据的高扩展性和高可用性。
redis支持的类型:
Sring 类型
set name lijie
get name lijie
set na
- 使用redis实现分布式锁
qifeifei
在多节点的系统中,如何实现分布式锁机制,其中用redis来实现是很好的方法之一,我们先来看一下jedis包中,有个类名BinaryJedis,它有个方法如下:
public Long setnx(final byte[] key, final byte[] value) {
checkIsInMulti();
client.setnx(key, value);
ret
- BI并非万能,中层业务管理报表要另辟蹊径
张老师的菜
大数据BI商业智能信息化
BI是商业智能的缩写,是可以帮助企业做出明智的业务经营决策的工具,其数据来源于各个业务系统,如ERP、CRM、SCM、进销存、HER、OA等。
BI系统不同于传统的管理信息系统,他号称是一个整体应用的解决方案,是融入管理思想的强大系统:有着系统整体的设计思想,支持对所有
- 安装rvm后出现rvm not a function 或者ruby -v后提示没安装ruby的问题
wudixiaotie
function
1.在~/.bashrc最后加入
[[ -s "$HOME/.rvm/scripts/rvm" ]] && source "$HOME/.rvm/scripts/rvm"
2.重新启动terminal输入:
rvm use ruby-2.2.1 --default
把当前安装的ruby版本设为默