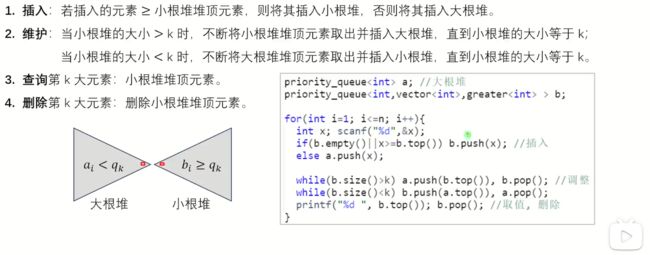
对顶堆算法
对顶堆可以动态维护一个序列上的第k大的数,由一个大根堆和一个小根堆组成,
- 小根堆维护前k大的数(包含第k个)
- 大根堆维护比第k个数小的数
[CSP-J2020] 直播获奖
题目描述
NOI2130 即将举行。为了增加观赏性,CCF 决定逐一评出每个选手的成绩,并直播即时的获奖分数线。本次竞赛的获奖率为 w % w\% w%,即当前排名前 w % w\% w% 的选手的最低成绩就是即时的分数线。
更具体地,若当前已评出了 p p p 个选手的成绩,则当前计划获奖人数为 max ( 1 , ⌊ p × w % ⌋ ) \max(1, \lfloor p \times w \%\rfloor) max(1,⌊p×w%⌋),其中 w w w 是获奖百分比, ⌊ x ⌋ \lfloor x \rfloor ⌊x⌋ 表示对 x x x 向下取整, max ( x , y ) \max(x,y) max(x,y) 表示 x x x 和 y y y 中较大的数。如有选手成绩相同,则所有成绩并列的选手都能获奖,因此实际获奖人数可能比计划中多。
作为评测组的技术人员,请你帮 CCF 写一个直播程序。
输入格式
第一行有两个整数 n , w n, w n,w。分别代表选手总数与获奖率。
第二行有 n n n 个整数,依次代表逐一评出的选手成绩。
输出格式
只有一行,包含 n n n 个非负整数,依次代表选手成绩逐一评出后,即时的获奖分数线。相邻两个整数间用一个空格分隔。
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
10 60
200 300 400 500 600 600 0 300 200 100
样例输出 #1
200 300 400 400 400 500 400 400 300 300
样例 #2
样例输入 #2
10 30
100 100 600 100 100 100 100 100 100 100
样例输出 #2
100 100 600 600 600 600 100 100 100 100
提示
样例 1 解释
数据规模与约定
各测试点的 n n n 如下表:
| 测试点编号 | n = n= n= |
|---|---|
| 1 ∼ 3 1 \sim 3 1∼3 | 10 10 10 |
| 4 ∼ 6 4 \sim 6 4∼6 | 500 500 500 |
| 7 ∼ 10 7 \sim 10 7∼10 | 2000 2000 2000 |
| 11 ∼ 17 11 \sim 17 11∼17 | 1 0 4 10^4 104 |
| 18 ∼ 20 18 \sim 20 18∼20 | 1 0 5 10^5 105 |
对于所有测试点,每个选手的成绩均为不超过 600 600 600 的非负整数,获奖百分比 w w w 是一个正整数且 1 ≤ w ≤ 99 1 \le w \le 99 1≤w≤99。
提示
在计算计划获奖人数时,如用浮点类型的变量(如 C/C++ 中的 float 、 double,Pascal 中的 real 、 double 、 extended 等)存储获奖比例 w % w\% w%,则计算 5 × 60 % 5 \times 60\% 5×60% 时的结果可能为 3.000001 3.000001 3.000001,也可能为 2.999999 2.999999 2.999999,向下取整后的结果不确定。因此,建议仅使用整型变量,以计算出准确值。
思路
模版题: k为i*w/100
- 使用一个大根堆x维护比第k个数小的数
- 使用一个小根堆y来维护前k大的数
代码
#include
priority_queue<int, vector<int>, greater<>> y;//小根堆,维护ai>=q;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int a;
cin >> a;
if (y.empty() || a >= y.top()) y.push(a);
else x.push(a);
int k = max((int) 1, i * w / 100);
while (y.size() > k) x.push(y.top()), y.pop();//保持小根堆有k个元素
while (y.size() < k) y.push(x.top()), x.pop();
cout << y.top() << " ";
}
}
signed main() {
IOS
#ifndef ONLINE_JUDGE
freopen("../test.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("../test.out", "w", stdout);
#endif
int _ = 1;
while (_--) solve();
return 0;
}
[ABC306E] Best Performances
题面翻译
题目描述:
给定长度为 N N N 的数列 A = ( A 1 , A 2 , … , A N ) A=(A_1,A_2,\dots,A_N) A=(A1,A2,…,AN),最开始所有项均为 0 0 0。
定义函数 f ( A ) f(A) f(A) 如下:
将 A A A 按照降序(即使得 A A A 为广义单调递减序列)排序得到 B B B。
则 f ( A ) = B 1 + B 2 + ⋯ + B K f(A)=B_1+B_2+\dots+B_K f(A)=B1+B2+⋯+BK,其中 B B B 为排序后的数列, K K K 为 A A A 中不为 0 0 0 的元素个数。
现在对该数列进行 Q Q Q 次更新。对于每次更新,按顺序执行以下操作,并输出此时的 f ( A ) f(A) f(A) 值:
将 A X i A_{X_i} AXi 更改为 Y i Y_i Yi。
题目描述
样例 #1
样例输入 #1
4 2 10
1 5
2 1
3 3
4 2
2 10
1 0
4 0
3 1
2 0
3 0
样例输出 #1
5
6
8
8
15
13
13
11
1
0
提示
- $ 1\ \le\ K\ \le\ N\ \le\ 5\ \times\ 10^5 $
- $ 1\ \le\ Q\ \le\ 5\ \times\ 10^5 $
- $ 1\ \le\ X_i\ \le\ N $
- $ 0\ \le\ Y_i\ \le\ 10^9 $
思路
可以使用对顶堆,这里涉及到修改操作,因此可以使用multiset维护方便一些
- a维护前k大为小根堆
- b维护比第k个数小的,大根堆
使用res来维护前k大的和。
代码
#include