Python教程(8)——一文弄懂Python字符串操作(下)
Python字符串操作
- 字符串常用方法
- 字符串更多方法介绍
字符串常用方法
字符串在编程中是一种不可或缺的数据类型,它在文本和字符数据时提供了丰富而强大的功能。掌握了字符串的使用方法,你能够更加便捷地进行文本处理、数据操作、用户交互等任务,从而提高编程效率和质量。
len():返回字符串的长度。
str1 = "Hello, World!"
length = len(str1)
print(length) # 输出:13
lower():将字符串中的所有字符转换为小写。
str2 = "Hello, World!"
lower_str = str2.lower()
print(lower_str) # 输出:hello, world!
upper():将字符串中的所有字符转换为大写。
str3 = "Hello, World!"
upper_str = str3.upper()
print(upper_str) # 输出:HELLO, WORLD!
strip():移除字符串两端的空白字符。
str4 = " Hello, World! "
stripped_str = str4.strip()
print(stripped_str) # 输出:Hello, World!
replace(old, new):将字符串中的指定部分替换为新的字符串。
str5 = "Hello, World!"
replaced_str = str5.replace("Hello", "Hi")
print(replaced_str) # 输出:Hi, World!
split(delimiter):将字符串按指定的分隔符切分成多个子串,并返回一个列表。
str6 = "Hello, World!"
splitted_list = str6.split(",")
print(splitted_list) # 输出:['Hello', ' World!']
join(iterable):将可迭代对象中的字符串元素拼接成一个字符串。
list7 = ["Hello", "World!"]
joined_str = " ".join(list7)
print(joined_str) # 输出:Hello World!
startswith(prefix):判断字符串是否以指定的前缀开始。
str8 = "Hello, World!"
starts_with = str8.startswith("Hello")
print(starts_with) # 输出:True
endswith(suffix):判断字符串是否以指定的后缀结束。
str9 = "Hello, World!"
ends_with = str9.endswith("World!")
print(ends_with) # 输出:True
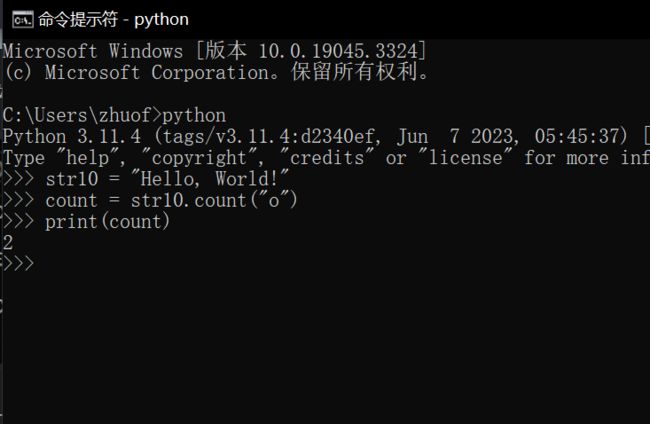
count(substring):返回指定子串在字符串中出现的次数。
str10 = "Hello, World!"
count = str10.count("o")
print(count) # 输出:2
isdigit():判断字符串是否只包含数字字符。
str11 = "12345"
is_digit = str11.isdigit()
print(is_digit) # 输出:True
isalpha():判断字符串是否只包含字母字符。
str12 = "Hello"
is_alpha = str12.isalpha()
print(is_alpha) # 输出:True
findstring):返回指定子串在字符串中第一次出现的索引,如果不存在返回-1。
str13 = "Hello, World!"
index = str13.find("World")
print(index) # 输出:7
字符串的相关方法可以说是非常重要的,在平时的编程中都是非常经常使用到的,需要重点掌握以上的相关方法。
字符串更多方法介绍
在Python当中,字符串的操作方法很多,有些是常用的,有些可能不会很经常的使用到,但是需要真遇见了,还是需要需要明白其中方法的意思,所以我特意整理了以下字符串中的方法
| 函数名 | 解释 |
|---|---|
| capitalize() | 将字符串首字母大写 |
| casefold() | 将字符串转换为小写并移除所有大小写特殊字符 |
| center(width, fillchar) | 返回一个指定宽度的字符串,并在两侧填充指定字符 |
| count(substring, start, end) | 统计子字符串在字符串中出现的次数 |
| encode(encoding, errors) | 使用指定的编码方式对字符串进行编码 |
| endswith(suffix, start, end) | 检查字符串是否以指定后缀结尾 |
| expandtabs(tabsize) | 将字符串中的制表符转换为空格 |
| find(substring, start, end) | 在字符串中查找子字符串,并返回索引 |
| format(*args, **kwargs) | 格式化字符串 |
| format_map(mapping) | 使用映射来格式化字符串 |
| index(substring, start, end) | 在字符串中查找子字符串,并返回索引(无匹配时引发异常) |
| isalnum() | 检查字符串是否只包含字母和数字字符 |
| isalpha() | 检查字符串是否只包含字母字符 |
| isdecimal() | 检查字符串是否只包含十进制数字字符 |
| isdigit() | 检查字符串是否只包含数字字符 |
| isidentifier() | 检查字符串是否是一个合法的标识符 |
| islower() | 检查字符串是否全为小写字母 |
| isnumeric() | 检查字符串是否只包含数值字符 |
| isprintable() | 检查字符串是否全部为可打印字符 |
| isspace() | 检查字符串是否只包含空白字符 |
| istitle() | 检查字符串是否为标题化(所有单词首字母大写) |
| isupper() | 检查字符串是否全为大写字母 |
| join(iterable) | 在可迭代对象的每个元素之间插入字符串 |
| ljust(width, fillchar) | 返回一个指定宽度的左对齐字符串,右侧填充指定字符 |
| lower() | 将字符串转换为小写字母 |
| lstrip(characters) | 移除字符串左边指定的字符 |
| maketrans(x, y, z) | 创建字符映射转换表 |
| partition(separator) | 根据指定的分隔符将字符串分成三部分 |
| replace(old, new, count) | 替换字符串中的指定内容 |
| rfind(substring, start, end) | 从右侧开始查找子字符串,并返回索引 |
| rindex(substring, start, end) | 从右侧开始查找子字符串,并返回索引(无匹配时引发异常) |
| rjust(width, fillchar) | 返回一个指定宽度的右对齐字符串,左侧填充指定字符 |
| rpartition(separator) | 根据指定的分隔符将字符串分成三部分(从右边开始) |
| rsplit(separator, maxsplit) | 从右侧开始以指定分隔符分割字符串 |
| rstrip(characters) | 移除字符串右边指定的字符 |
| split(separator, maxsplit) | 以指定分隔符分割字符串 |
| splitlines(keepends) | 按照行分隔符分割字符串,并返回一个包含各行作为元素的列表 |
| startswith(prefix, start, end) | 检查字符串是否以指定前缀开头 |
| strip(characters) | 移除字符串两侧指定的字符 |
| swapcase() | 将字符串中的大小写字母互换 |
| title() | 将字符串转换为首字母大写的标题格式 |
| translate(mapping) | 使用指定的映射表转换字符串 |
| upper() | 将字符串转换为大写字母 |
| zfill(width) | 在字符串左侧填充0直到达到指定宽度 |
以上几乎涵盖了所有字符串操作的方法,当然可能会有一些遗漏,欢迎指出
更多精彩内容,请关注同名公众:一点sir(alittle-sir)