【并发编程JUC】Future和CompletableFuture机制
场景题
面试的时候当面试官提出一个场景题,比如有一个翻译接口,同时调用百度、网易、谷歌的三个翻译接口,使用返回的第一个的翻译。这个时候一般的想法可能是,先串行执行。然后异步获取。但是其实都知道这样性能非常慢。
Future
如果直接使用Future的方式,我们知道Future的get接口是阻塞的,也就是在执行调用三方接口的返回结果的时候,需要阻塞等待结果。
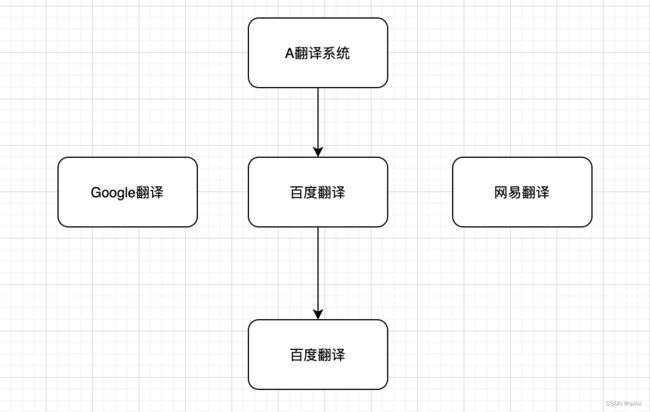
其实整体的耗时就是取决于最短的三方接口响应,如果百度、网易、google分别是200、300、400毫秒,那么程序需要阻塞200毫秒。
FutureTask<Integer> futureTask = new FutureTask<Integer>(() -> {
Thread.sleep(10000);
System.out.println("调用三方翻译接口");
return 1024;
});
new Thread(futureTask).start();
Integer integer = futureTask.get(); //会阻塞
Integer integer = futureTask.get(1, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
while (true) {
if (futureTask.isDone()) {
System.out.println("完成任务");
break;
} else {
System.out.println("执行中,稍等.");
}
}
Integer x = futureTask.get();
System.out.println(x);
所以在实际的生产环境中,并不会使用get()。而是使用get超时机制,或者使用自定义的isDone() 轮询处理的方式。避免因为一个接口导致整体链路的阻塞。
如果想要异步获取结果,通常都会以轮询的方式去获取结果尽量不要阻塞
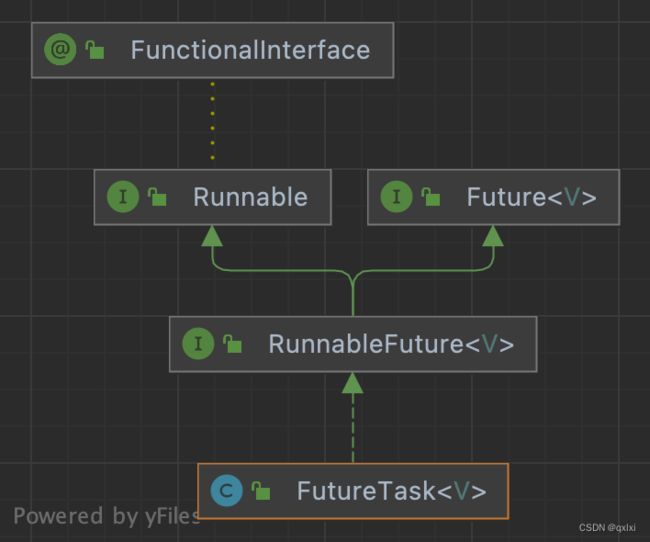
因为Future的继承图是来自Runable,所以启动线程的方式也是通过new Thread的方式开启。
CompletableFuture
为了解决上述Future的阻塞问题点,以及可以实现真正意义上的异步并发编程,所以引入了CompleablteFuture。
创建方式
## 无 返回值
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable,
Executor executor) {
return asyncRunStage(screenExecutor(executor), runnable);
}
public static CompletableFuture<Void> runAsync(Runnable runnable) {
return asyncRunStage(asyncPool, runnable);
}
## 有返回值
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier) {
return asyncSupplyStage(asyncPool, supplier);
}
public static <U> CompletableFuture<U> supplyAsync(Supplier<U> supplier,
Executor executor) {
return asyncSupplyStage(screenExecutor(executor), supplier);
}
其中executor可以进行自定义的线程池。没有指定Executor的方法,直接使用默认的ForkJoinPool.commonPool() 作为它的线程池执行异步代码。
CompletionStage
CompletionStage描述的是每个子任务,主要包含四个接口,thenApply、thenAccept、thenRun、thenCompose。
描述串行关系
CompletionStage<R> thenApply(fn);
CompletionStage<R> thenApplyAsync(fn);
CompletionStage<Void> thenAccept(consumer);
CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptAsync(consumer);
CompletionStage<Void> thenRun(action);
CompletionStage<Void> thenRunAsync(action);
CompletionStage<R> thenCompose(fn);
CompletionStage<R> thenComposeAsync(fn);
案例
CompletableFuture<java.lang.String> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
return "helloword";
}).thenApply(s -> s + "qq");
需要一个执行完毕,在执行另一个。
描述AND关系
CompletionStage<R> thenCombine(other, fn);
CompletionStage<R> thenCombineAsync(other, fn);
CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptBoth(other, consumer);
CompletionStage<Void> thenAcceptBothAsync(other, consumer);
CompletionStage<Void> runAfterBoth(other, action);
CompletionStage<Void> runAfterBothAsync(other, action);
描述 OR 汇聚关系
CompletionStage applyToEither(other, fn);
CompletionStage applyToEitherAsync(other, fn);
CompletionStage acceptEither(other, consumer);
CompletionStage acceptEitherAsync(other, consumer);
CompletionStage runAfterEither(other, action);
CompletionStage runAfterEitherAsync(other, action);
异常处理
CompletionStage exceptionally(fn);
CompletionStage<R> whenComplete(consumer);
CompletionStage<R> whenCompleteAsync(consumer);
CompletionStage<R> handle(fn);
CompletionStage<R> handleAsync(fn);
案例
CompletableFuture<Integer> completableFuture = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " 异步调用三方");
try {
Thread.sleep(TimeUnit.SECONDS.toSeconds(10));
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
return 1;
}).thenApply(f -> {
return f + 10;
}).whenComplete((v, e) -> {
if (e == null) {
System.out.println("计算结果为:" + v);
}
}).exceptionally(e -> {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
});