Vue第一部分(5):计算属性和过滤器
计算属性
在插值表达式中可以直接使用js表达式,这是非常方便的。但是如果表达式的内容很复杂,就会影响代码可读性,而且后期维护起来也不方便,例如下面的场景:需要统计多个商品的总价。
代码如下:
<div id="app">
<h2>总价:{{products.reduce((total,p)=>{return total+p.price*p.count;},0)}}h2>
div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
products:[
{
name: 'iPhone 7',
price: 7199,
count: 2
},
{
name: 'iPad',
price: 2888,
count: 1
}
]
}
})
script>
Vue中提供了计算属性,来替代复杂的表达式。通过给Vue实例添加选项computed来定义计算属性:
<div id="app">
<h2>总价:{{products.reduce((total,p)=>{return total+p.price*p.count;},0)}}h2>
<h2>总价:{{totalPrice}}h2>
div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
products:[
{
name: 'iPhone 7',
price: 7199,
count: 2
},
{
name: 'iPad',
price: 2888,
count: 1
}
]
},
computed:{
totalPrice(){
return this.products.reduce((total,p)=>{return total+p.price*p.count;},0);
}
}
})
script>
计算属性本质就是方法,但是一定要返回数据。然后页面渲染时,可以把这个方法当成一个变量来使用。
过滤器
过滤器的作用是对数据进行格式化,比如字母全部大写、日期格式化输出、货币前添加货币符号等场景。Vue.js支持在{{ }}插值的尾部添加一个管道符“(|)”对数据进行过滤。过滤的规则,通过给Vue实例添加选项filters来设置。
<div id="app">
<h2>使用过滤器字母全大写:{{str | toUpperCase}}h2>
<h2>使用过滤器日期格式化:{{date | dateFormat}}h2>
<h2>货币格式化输出:{{money | moneyFormat("¥")}}h2>
div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
str:"hello filter",
date:new Date(),
money:1000.0
},
filters:{
toUpperCase(value){
return value.toUpperCase();
},
dateFormat(value){
let year = value.getFullYear();
let month = value.getMonth();
let day = value.getDay();
let hours = value.getHours();
let seconds = value.getSeconds();
let minutes = value.getMinutes();
return `${year}-${month}-${day} ${hours}:${seconds}:${minutes}`;
},
moneyFormat(value,symbol){
return symbol+" "+value;
}
}
})
script>
说明:还可以将过滤器定义为全局过滤器。
Vue.filter('过滤器名称', function (value[,param1,...] ) {
//逻辑代码
})
计算属性和过滤器的异同
相同点:
- 都基于原始属性值进行变换
- 都可以在{{}}中调用
不同点:
- 计算属性可以基于多个原始属性,而过滤器只对一个原始属性操作
- 计算属性通常用于复杂的逻辑计算,而过滤器用于简单的数据格式化输出
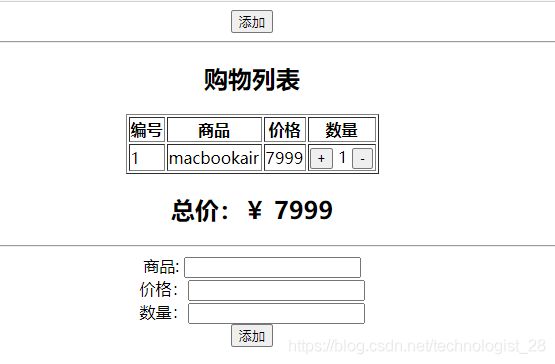
案例:购物车
<body>
<div id="app">
<div style="text-align: center;">
<button @click="addFormShow = true;">添加button>
div>
<hr>
<div v-if="shoppingList.length > 0">
<h2 style="text-align:center">购物列表h2>
<table align="center" border="1">
<thead>
<tr>
<th>编号th>
<th>商品th>
<th>价格th>
<th>数量th>
tr>
thead>
<tbody>
<tr v-for="(item,index) in shoppingList">
<td>{{index+1}}td>
<td>{{item.name}}td>
<td>{{item.price}}td>
<td>
<button @click="increment(index)">+button>
<span>{{item.count}}span>
<button @click="decrement(index)">-button>
td>
tr>
tbody>
table>
<h2 style="text-align: center;">总价:{{totalPrice | priceFormat}}h2>
div>
<div v-else>
<h2 style="text-align: center;">购物车空空如也h2>
div>
<hr>
<div style="text-align: center;" v-show="addFormShow">
<form action="" @submit.prevent="addItem">
商品: <input type="text" v-model="shoppingItem.name"> <br>
价格:<input type="number" v-model="shoppingItem.price"> <br>
数量:<input type="number" v-model="shoppingItem.count"> <br>
<input type="submit" value="添加">
form>
div>
div>
<script>
const vm = new Vue({
el:"#app",
data:{
addFormShow:false,
shoppingItem:{},
shoppingList:[
{
name:"macbookair",
price:7999.0,
count:1
}
]
},
methods:{
increment(i){
this.shoppingList[i].count++;
},
decrement(i){
if(this.shoppingList[i].count <= 1){
this.shoppingList.splice(i,1);
}else{
this.shoppingList[i].count--;
}
},
addItem(){
let item = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(this.shoppingItem));
this.shoppingList.push(item);
this.shoppingItem={};
}
},
computed:{
totalPrice(){
return this.shoppingList.reduce((total,item)=>total+item.price*item.count,0);
}
},
filters:{
priceFormat(value){
return "¥ "+value;
}
}
})
script>
body>