数据结构:力扣OJ题(每日一练)
本篇主要以理解结构为主!!!
题一:用队列实现栈
示例:
输入: ["MyStack", "push", "push", "top", "pop", "empty"] [[], [1], [2], [], [], []] 输出: [null, null, null, 2, 2, false] 解释: MyStack myStack = new MyStack(); myStack.push(1); myStack.push(2); myStack.top(); // 返回 2 myStack.pop(); // 返回 2 myStack.empty(); // 返回 False
思路一:
初始化:初始化队列Q1,Q2;入栈:先将要入栈的数据放入为空的队列中,都为空时,放入Q1;出栈:当要出栈时,将Q1的数据出列n-1个,此时的Q1就是栈要出栈的数据(每次出栈都进行一次第三步将为不为空的队列数据放n-1个到为空队列中));获取栈顶元素:访问不为空的队列最后一个元素;判断栈是否为空:两个队列均为NULL时为空;销毁栈:先将Q1,Q2用到的动态内存销毁,再销毁OBJ。
typedef int Qdatatype;
//队列结构
typedef struct Queuenode
{
struct Queuenode* next;
Qdatatype data;
}Qnode;
//队列
typedef struct Queue
{
Qnode* head;
Qnode* tail;
int size;
}Que;
//初始化
void QueueInit(Que* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
pq->size = 0;
}
//入列
void QueuePush(Que* pq, Qdatatype x)
{
assert(pq);
//开辟队列结构动态内存
Qnode* newnode = (Qnode*)malloc(sizeof(Qnode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
//第一次或N+1次
if (pq->tail == NULL)
{
pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->tail->next = newnode;
pq->tail = newnode;
}
pq->size++;
}
//出列
void QueuePop(Que* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
if (pq->head->next == NULL)
{
//就剩下一个
free(pq->head);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
else
{
//剩下两个及以上
Que * del = pq->head;
pq->head = pq->head->next;
free(del);
}
pq->size--;
}
// 获取队列头部元素
Qdatatype QueueFront(Que* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->head->data;
}
// 获取队列队尾元素
Qdatatype QueueBack(Que* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(!QueueEmpty(pq));
return pq->tail->data;
}
// 获取队列中有效元素个数
int QueueSize(Que* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->size;
}
// 检测队列是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果非空返回0
int QueueEmpty(Que* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->head == NULL;
}
//销毁
void QueueDestroy(Que* pq)
{
assert(pq);
while (pq->head)
{
Que* del = pq->head->next;
free(pq->head);
pq->head = del;
pq->size--;
}
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
//此处为题目开始!!!
typedef struct
{
Que Q1;
Que Q2;
} MyStack;
//栈的初始化
MyStack* myStackCreate()
{
MyStack* pts = (MyStack*)malloc(sizeof(MyStack));
QueueInit(&pts->Q1);
QueueInit(&pts->Q2);
return pts;
}
//入栈
void myStackPush(MyStack* obj, int x)
{
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->Q1))
QueuePush(&obj->Q1,x);
else
QueuePush(&obj->Q2,x);
}
//出栈
int myStackPop(MyStack* obj)
{
Que* empty = &obj->Q1;
Que* noempty = &obj->Q2;
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->Q1))
{
empty = &obj->Q2;
noempty = &obj->Q1;
}
while(QueueSize(noempty) > 1)
{
QueuePush(empty,QueueFront(noempty));
QueuePop(noempty);
}
int tmp = QueueFront(noempty);
QueuePop(noempty);
return tmp;
}
//获取栈顶元素
int myStackTop(MyStack* obj)
{
if(!QueueEmpty(&obj->Q1))
{
return QueueBack(&obj->Q1);
}
else
{
return QueueBack(&obj->Q2);
}
}
//判断栈是否为空
bool myStackEmpty(MyStack* obj)
{
return QueueEmpty(&obj->Q1) && QueueEmpty(&obj->Q2);
}
//栈的销毁
void myStackFree(MyStack* obj)
{
QueueDestroy(&obj->Q1);
QueueDestroy(&obj->Q2);
free(obj);
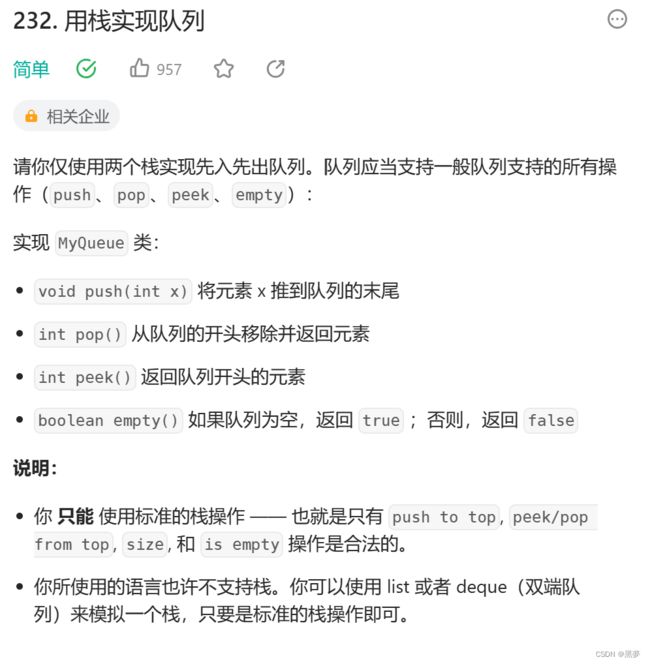
}题二:用栈实现队列
示例 1:
输入: ["MyQueue", "push", "push", "peek", "pop", "empty"] [[], [1], [2], [], [], []] 输出: [null, null, null, 1, 1, false]
思路一:
初始化:初始化栈IN,OUT;入列:将数据全部存放到IN栈上;出列:将进栈点的数据全部按栈的“先进后出”顺序放入出栈点,此时出栈的顺序就是出列。当出栈点为空时,再将进栈点数据存入。;获取列头元素:访问出栈点里的栈顶;判断栈是否为空:两个栈均为NULL时为空;销毁栈:先将IN,OUT用到的动态内存销毁,再销毁OBJ。
//约定类型方便更改类型
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top;
int capacity;
}SL;
//初始化
void SLInit(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
}
//入栈
void SLPush(SL* ps, STDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
//栈顶=容量说明需要扩容
if (ps->capacity == ps->top)
{
int newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * ps->capacity;
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a,sizeof(STDataType) * newcapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
ps->capacity = newcapacity;
ps->a = tmp;
}
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
//后缀++方便下一次入栈和打印栈顶
ps->top++;
}
//出栈
void SLPop(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
//为空情况“0”
assert(ps->top > 0);
//
--ps->top;
}
//获得栈顶元素
STDataType SLTTop(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
//为空情况“0”
assert(ps->top > 0);
int n = (ps->top) - 1;
return ps->a[n];
}
//获取栈中有效元素个数
int SLSize(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
//销毁栈
void SLDestroy(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
//开辟数组优势:一次全部释放
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->capacity = ps->top = 0;
}
// 检测栈是否为空,如果为空返回非零结果,如果不为空返回0
bool SLEmpty(SL* ps)
{
assert(ps);
//为“0”说明为NULL
if (ps->top == 0)
{
return true;
}
return false;
}
//题目从此处开始!!!
typedef struct
{
SL IN;
SL OUT;
} MyQueue;
//初始化
MyQueue* myQueueCreate()
{
MyQueue* obj = (MyQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyQueue));
SLInit(&obj->IN);
SLInit(&obj->OUT);
return obj;
}
//入列
void myQueuePush(MyQueue* obj, int x)
{
SLPush(&obj->IN,x);
}
//返回队列开头的元素
int myQueuePeek(MyQueue* obj)
{
//为空,将IN列元素放到OUT上
if(SLEmpty(&obj->OUT))
{
while(!SLEmpty(&obj->IN))
{
SLPush(&obj->OUT,SLTTop(&obj->IN));
SLPop(&obj->IN);
}
}
return SLTTop(&obj->OUT);
}
//从队列的开头移除并返回元素
int myQueuePop(MyQueue* obj)
{
int top = myQueuePeek(obj);
SLPop(&obj->OUT);
return top;
}
//判断队列是否为空
bool myQueueEmpty(MyQueue* obj)
{
//SLEmpty返回值为true或false
return SLEmpty(&obj->IN) == true && SLEmpty(&obj->OUT) == true;
}
//销毁
void myQueueFree(MyQueue* obj)
{
SLDestroy(&obj->IN);
SLDestroy(&obj->OUT);
free(obj);
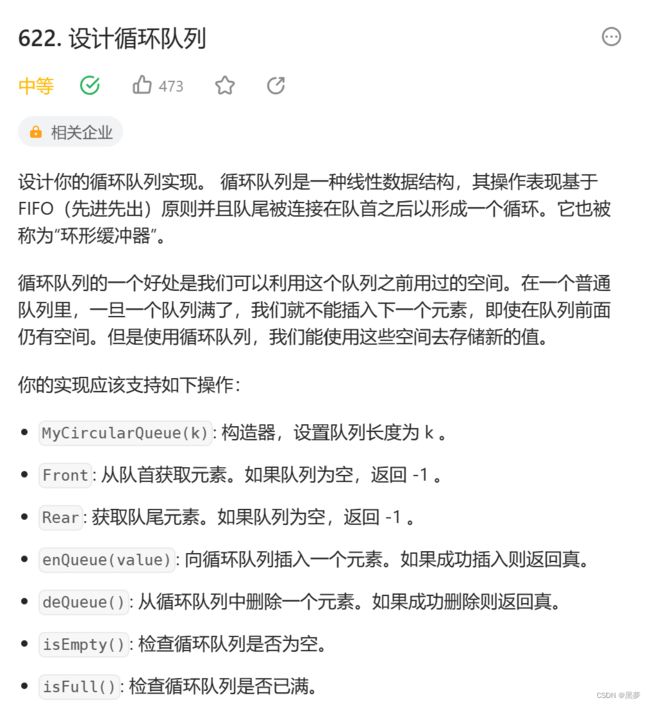
}题三:设计循环队列
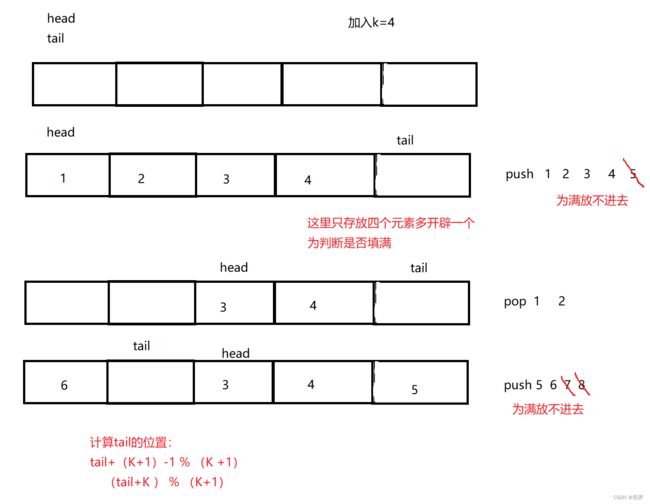
示例: MyCircularQueue circularQueue = new MyCircularQueue(3); // 设置长度为 3 circularQueue.enQueue(1); // 返回 true circularQueue.enQueue(2); // 返回 true circularQueue.enQueue(3); // 返回 true circularQueue.enQueue(4); // 返回 false,队列已满 circularQueue.Rear(); // 返回 3 circularQueue.isFull(); // 返回 true circularQueue.deQueue(); // 返回 true circularQueue.enQueue(4); // 返回 true circularQueue.Rear(); // 返回 4
思路一:
初始化:初始化队列head,tail,k,以及所需开辟的空间;入列:队列不为满时,将值输入;出列:判断队列不为空时,删除;获取列顶元素:访问head节点值;获取列顶元素:访问tail节点值;判断队列是否为空:head=tail时;销毁队列:先将a的动态内存销毁,再销毁OBJ。
typedef struct
{
int k;
int head;//头
int tail;//尾
int* a;//值
} MyCircularQueue;
//初始化
MyCircularQueue* myCircularQueueCreate(int k)
{
MyCircularQueue* obj = (MyCircularQueue*)malloc(sizeof(MyCircularQueue));
obj->a = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*(k+1));
obj->head = obj->tail = 0;
obj->k = k;
return obj;
}
//判断队列是否为空
bool myCircularQueueIsEmpty(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{
return obj->head == obj->tail;
}
//是否队列是否满
bool myCircularQueueIsFull(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{
return (obj->tail+1) % (obj->k+1) == obj->head;
}
//插入一个元素
bool myCircularQueueEnQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj, int value)
{
if(myCircularQueueIsFull(obj))
return false;
obj->a[obj->tail] = value;
obj->tail++;
obj->tail %= (obj->k+1);
return true;
}
//删除一个元素
bool myCircularQueueDeQueue(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
return false;
obj->head++;
obj->head = obj->head % (obj->k+1);
return true;
}
//从队首获取元素
int myCircularQueueFront(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
return -1;
else
return obj->a[obj->head];
}
//获取队尾元素
int myCircularQueueRear(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{
if(myCircularQueueIsEmpty(obj))
return -1;
else
return obj->a[(obj->tail + obj->k) % (obj->k+1)];
}
//销毁
void myCircularQueueFree(MyCircularQueue* obj)
{
free(obj->a);
free(obj);
}