实战项目:基于主从Reactor模型实现高并发服务器
项目完整代码仿mudou库one thread one loop式并发服务器实现: 仿muduo库One Thread One Loop式主从Reactor模型实现⾼并发服务器:通过模拟实现的⾼并发服务器组件,可以简洁快速的完成⼀个⾼性能的服务器搭建。并且,通过组件内提供的不同应⽤层协议⽀持,也可以快速完成⼀个⾼性能应⽤服务器的搭建(项⽬中提供HTTP协议组件的⽀持)。项目主要实现的是⼀个⾼并发服务器组件,因此当前的项⽬中并不包含实际的业务内容。 - Gitee.comhttps://gitee.com/niuniuzxy/mudou/tree/master/MudouItem--%E5%AE%8C%E6%95%B4%E7%89%88
项目简介
环境介绍
服务器部署:Linux-centos -- 2核2G的腾讯云服务器。
webbench模拟的客户端:Linux-centos -- 4核8G的虚拟机。
项目定位
a. 主从Reactor模型服务器,主Reactor线程只负责监听描述符,获取新建连接。这样就保证了新连接的获取比较高效,提高了服务器的并发性能。主Reactor获取到新连接后分发给子Reactor进行通信事件监控。
b.子(从)Reactor线程监控各自文件描述符下的读写事件,进行数据读写以及业务处理。
c.One Thread One Loop的思想就是把所有的操作都放到线程中进行,一个线程对应一个EventLoop。
功能模块划分
项目实现目标:带有协议支持的Reactor模型高性能服务器。模块划分如下:
1.Server模块:实现Reactor模型的TCP服务器。
2.协议模块:对于自主实现的Reactor模型服务器提供应用层协议支持,项目中支持的Http协议。
性能测试
测试环境
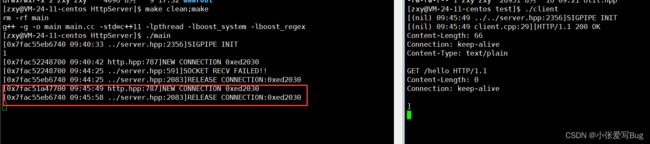
测试1:长连接测试
创建一个客户端持续给服务器发送数据,直到超过超时时间看看是否正常。
int main()
{
Socket cli_sock;
cli_sock.CreateClient(8085, "10.0.24.11");
std::string req = "GET /hello HTTP/1.1\r\nConnection: keep-alive\r\nContent-Length: 0\r\n\r\n";
while(1) {
assert(cli_sock.Send(req.c_str(), req.size()) != -1);
char buf[1024] = {0};
assert(cli_sock.Recv(buf, 1023));
DEBUG_LOG("[%s]", buf);
sleep(3);
}
cli_sock.Close();
return 0;
}客户端每三秒发送一次数据,刷新活跃度。长连接测试正常。
测试2:超时连接测试
创建一个客户端,给服务器发送一次数据后 不动了,查看服务器是否会正常的超时关闭连接。
int main()
{
Socket cli_sock;
cli_sock.CreateClient(8085, "10.0.24.11");
std::string req = "GET /hello HTTP/1.1\r\nConnection: keep-alive\r\nContent-Length: 0\r\n\r\n";
while(1) {
assert(cli_sock.Send(req.c_str(), req.size()) != -1);
char buf[1024] = {0};
assert(cli_sock.Recv(buf, 1023));
DEBUG_LOG("[%s]", buf);
sleep(15);
}
cli_sock.Close();
return 0;
}客户端发送一次数据后,超时时间内再无动作。非活跃连接正常超时关闭,测试正常。
测试3:不完整请求测试
给服务器发送一个数据,告诉服务器要发送1024字节的数据,但是实际发送的数据不足1024,查看服务器处理结果。
//不完整请求测试
int main()
{
Socket cli_sock;
cli_sock.CreateClient(8085, "10.0.24.11");
std::string req = "GET /hello HTTP/1.1\r\nConnection: keep-alive\r\nContent-Length: 100\r\n\r\nbitejiuyeke";
while(1) {
assert(cli_sock.Send(req.c_str(), req.size()) != -1);
//assert(cli_sock.Send(req.c_str(), req.size()) != -1);
//assert(cli_sock.Send(req.c_str(), req.size()) != -1);
char buf[1024] = {0};
assert(cli_sock.Recv(buf,1023));
DEBUG_LOG("[%s]", buf);
sleep(3);
}
cli_sock.Close();
return 0;
}1. 如果数据只发送一次,服务器将得不到完整请求,就不会进行业务处理,客户端也就得不到响应,最终超时关闭连接。
 2. 连着给服务器发送了多次 小的请求, 服务器会将后边的请求当作前边请求的正文进行处理,而后边处理的时候有可能就会因为处理错误而关闭连接。
2. 连着给服务器发送了多次 小的请求, 服务器会将后边的请求当作前边请求的正文进行处理,而后边处理的时候有可能就会因为处理错误而关闭连接。
测试4:业务处理超时测试
业务处理超时,查看服务器的处理情况
当服务器达到了一个性能瓶颈,在一次业务处理中花费了太长的时间(超过了服务器设置的非活跃超时时间)
1. 在一次业务处理中耗费太长时间,导致其他的连接也被连累超时,其他的连接有可能会被拖累超时释放。假设现在 12345描述符就绪了, 在处理1的时候花费了30s处理完,超时了,导致2345描述符因为长时间没有刷新活跃度
1. 如果接下来的2345描述符都是通信连接描述符,如果都就绪了,则并不影响,因为接下来就会进行处理并刷新活跃度
2. 如果接下来的2号描述符是定时器事件描述符 定时器触发超时,执行定时任务,就会将345描述符给释放掉
2.1 这时一旦345描述符对应的连接被释放,接下来在处理345事件的时候就会导致程序崩溃(内存访问错误)
2.2 因此这时候,在本次事件处理中,并不能直接对连接进行释放,而应该将释放操作压入到任务池中,等到事件处理完了执行任务池中的任务的时候,再去释放。
int main()
{
signal(SIGCHLD, SIG_IGN);
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
pid_t pid = fork();
if (pid < 0) {
DEBUG_LOG("FORK ERROR");
return -1;
}else if (pid == 0) {
Socket cli_sock;
cli_sock.CreateClient(8085, "10.0.24.11");
std::string req = "GET /hello HTTP/1.1\r\nConnection: keep-alive\r\nContent-Length: 0\r\n\r\n";
while(1) {
assert(cli_sock.Send(req.c_str(), req.size()) != -1);
char buf[1024] = {0};
assert(cli_sock.Recv(buf, 1023));
DEBUG_LOG("[%s]", buf);
}
cli_sock.Close();
exit(0);
}
}
while(1) sleep(1);
return 0;
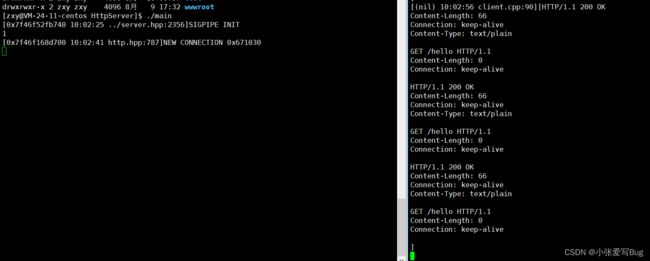
}测试5:一次发送多条数据测试
一次性给服务器发送多条数据,然后查看服务器的处理结果。
int main()
{
Socket cli_sock;
cli_sock.CreateClient(8085, "10.0.24.11");
std::string req = "GET /hello HTTP/1.1\r\nConnection: keep-alive\r\nContent-Length: 0\r\n\r\n";
req += "GET /hello HTTP/1.1\r\nConnection: keep-alive\r\nContent-Length: 0\r\n\r\n";
req += "GET /hello HTTP/1.1\r\nConnection: keep-alive\r\nContent-Length: 0\r\n\r\n";
while(1) {
assert(cli_sock.Send(req.c_str(), req.size()) != -1);
char buf[1024] = {0};
assert(cli_sock.Recv(buf, 1023));
DEBUG_LOG("[%s]", buf);
sleep(3);
}
cli_sock.Close();
return 0;
}每一条请求都应该得到正常处理。
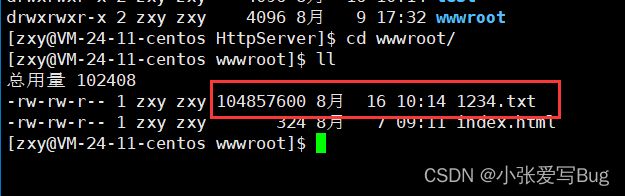
测试6:大文件传输测试
大文件传输测试,给服务器上传一个大文件,服务器将文件保存下来,观察处理结果。上传的文件,和服务器保存的文件一致。
准备好一个测试文件,资源有限,创建一个100MB大小的log.txt。
int main()
{
Socket cli_sock;
cli_sock.CreateClient(8085, "10.0.24.11");
std::string req = "PUT /1234.txt HTTP/1.1\r\nConnection: keep-alive\r\n";
std::string body;
Util::ReadFile("./log.txt", body);
req += "Content-Length: " + std::to_string(body.size()) + "\r\n\r\n";
assert(cli_sock.Send(req.c_str(), req.size()) != -1);
assert(cli_sock.Send(body.c_str(), body.size()) != -1);
char buf[1024] = {0};
assert(cli_sock.Recv(buf, 1023));
DEBUG_LOG("[%s]", buf);
sleep(3);
cli_sock.Close();
return 0;
}文件上传成功:
收到的文件:
对比两个文件内容是否相同:
根据测试,文件传输也没有问题。
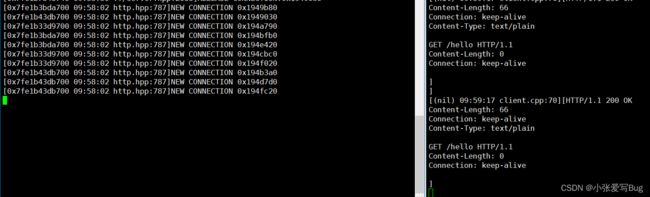
测试7:抗压力测试
通过测试工具模拟大量客户端向服务器发送连接请求。
服务器的环境如下
模拟20000个客户端同时向服务器发送请求,没有出现连接失败。
测试结论(参考)
性能测试环境:
服务端:2核2G带宽为1M的云服务器。
客户端:4核8G的虚拟机通过webbench工具模拟客户端,创建大量线程连接服务器,发送请求,在收到响应后关闭连接,开始下一个连接的建立。
测试结论:
服务器并发量:可以同时处理20000-30000个客户端的请求而不会出现连接失败。
QPS:(Query Per Second)每秒查询率107左右。
Reactor简介
Reactor模型简单分析
在高性能的I/O设计中,Reactor模型用于同步I/O。
优点:
1.响应快,不必为单个同步时间所阻塞(虽然Reactor本身依然是同步的);
2.可以最大程度的避免复杂的多线程及同步问题,并且避免了多线程/进程的切换开销。
可扩展性:可以方便地通过增加Reactor实例个数来充分利用CPU资源。
可复用性,Reactor模型本身与具体事件处理逻辑无关,具有很高的复用性。
3.Rector模型基于事件驱动,特别适合处理海量的I/O。
多Reactor多线程分析:多I/O多路复用+线程池(业务处理)
1. 在主Reactor中处理新连接请求事件,有新连接到来则分发到⼦Reactor中监控。
2. 在⼦Reactor中进⾏客⼾端通信监控,有事件触发,则接收数据分发给Worker线程池。
3. Worker线程池分配独⽴的线程进⾏具体的业务处理。⼯作线程处理完毕后,将响应交给⼦Reactor线程进⾏数据响应。
4. 优点:充分的利用了CPU多核资源,主从Reactor各自完成各自的任务。
核心模块及思路剖析
Server模块
Buffer模块
本模块主要提供的功能为数据的存储和取出。实现思想如下:
1.想要实现缓冲区首先要有一块内存空间,使用vector
2.一个读偏移记录当前读取数据的位置。一个写偏移记录当前的写入位置。
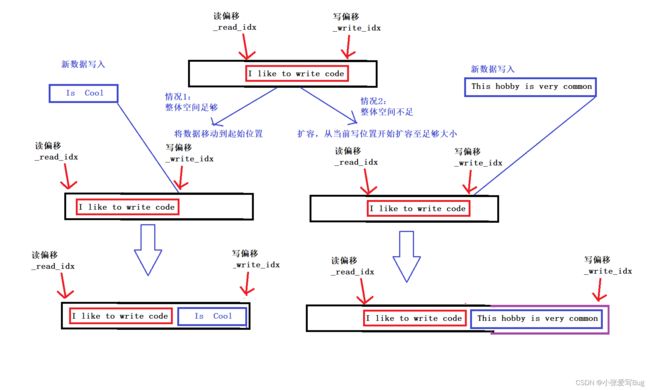
3.写入数据:从写偏移的位置开始写入,如果后续空间足够直接写。反之,扩容:这里的扩容比较特殊,可以从整体空闲空间(当数据被读取,读偏移会向后移动,前面的空间是空闲的状态)和写偏移后的空闲空间两种情况考虑,如果整体空间足够,将现有数据移动到起始位置。如果不够,扩容,从当前写位置开始扩容足够的大小。数据写入成功后,写偏移记得向后偏移。
2.读取数据:从当前读偏移开始读取,前提是有数据可读。可读数据的大小--写偏移和读偏移之间的数据。
#define BUFFER_SIZE 1024
//缓冲区模块
class Buffer
{
private:
std::vector _buffer;
//相对起始位置的偏移量
uint64_t _read_idx; //读偏移
uint64_t _write_idx; //写偏移
char *begin() { return &*_buffer.begin(); }
public:
Buffer() : _read_idx(0), _write_idx(0), _buffer(1024) {}
//获取当前写位置的地址
char *WriteAddres() { return begin() + _write_idx; }
//获取当前读位置的地址
char *ReadAddres() { return begin() + _read_idx; }
//获取写之后的空间大小
uint64_t WriteAfterSize() { return _buffer.size() - _write_idx; }
//获取读之前空间大小
uint64_t ReadBeforeSize() { return _read_idx; }
//将写位置向后移动指定长度
void WriteMovesBack(int len){
assert(len <= WriteAfterSize());
_write_idx += len;
}
//将读位置向后移动指定长度
void ReadMovesBack(int len){
assert(len <= (_write_idx - _read_idx));
_read_idx += len;
}
//获取可读数据大小
uint64_t MayReadSize() { return _write_idx - _read_idx; }
//确保可写空间足够(移动+扩容)
void EnsureSpaceEnough(uint64_t len){
if (len <= WriteAfterSize())return;
else if (len <= WriteAfterSize() + ReadBeforeSize()) {
//可读数据整体向前挪动
uint64_t res = MayReadSize();
std::copy(ReadAddres(), ReadAddres() + res, begin());
//更新读偏移地址和写偏移地址
_read_idx = 0;
_write_idx = res;
}
else{
//早写偏移后扩容
_buffer.resize(len + _write_idx);
}
}
void Write(const void *data, int len)
{
if (len == 0)
return;
//要保证空间足够
EnsureSpaceEnough(len);
const char *d = (const char *)data;
//将数据拷贝进去
std::copy(d, d + len, WriteAddres());
}
void WritePush(const void *data, int len)
{
Write(data, len);
WriteMovesBack(len);
}
void WriteString(const std::string str)
{
Write(str.c_str(), str.size());
}
void WriteStringPush(const std::string str)
{
WriteString(str);
WriteMovesBack(str.size());
}
void WriteBuffer(Buffer buf)
{
Write(buf.ReadAddres(), buf.MayReadSize());
}
void WriteBufferPush(Buffer buf)
{
WriteBuffer(buf);
WriteMovesBack(buf.MayReadSize());
}
//读
void Read(void *buf, int len)
{
if (len == 0)
return;
//要读取的长度,不能超过可读长度
//assert(len <= MayReadSize());
//将数据拷贝到buf中
std::copy(ReadAddres(), ReadAddres() + len, (char *)buf);
}
void ReadPop(void *buf, int len)
{
Read(buf, len);
ReadMovesBack(len);
}
std::string ReadString(int len)
{
//std::cout << len << ": " << MayReadSize() << std::endl;
assert(len <= MayReadSize());
std::string str;
str.resize(len);
Read(&str[0], len);
return str;
}
std::string ReadStringPop(int len)
{
assert(len <= MayReadSize());
std::string str = ReadString(len);
ReadMovesBack(len);
return str;
}
//查找换行字符
char *FindCRLF(){
char *res = (char *)memchr(ReadAddres(), '\n', MayReadSize());
}
//获取一行数据
std::string GetLine(){
char *pos = FindCRLF();
if (pos == nullptr)
return "";
return ReadString(pos - ReadAddres() + 1);
}
std::string GetLinePop(){
std::string str = GetLine();
ReadMovesBack(str.size());
return str;
}
//清空缓冲区
void Clear(){
_write_idx = 0;
_read_idx = 0;
}
}; TimeQueue模块
介绍:实现固定时间,执行定时任务的模块 --- 定时任务管理器。向该模块添加一个任务,任务将在固定时间后被执行,同时也可以对定时任务进行刷新,延迟该任务执行,当然也可以通过接口取消定时任务。
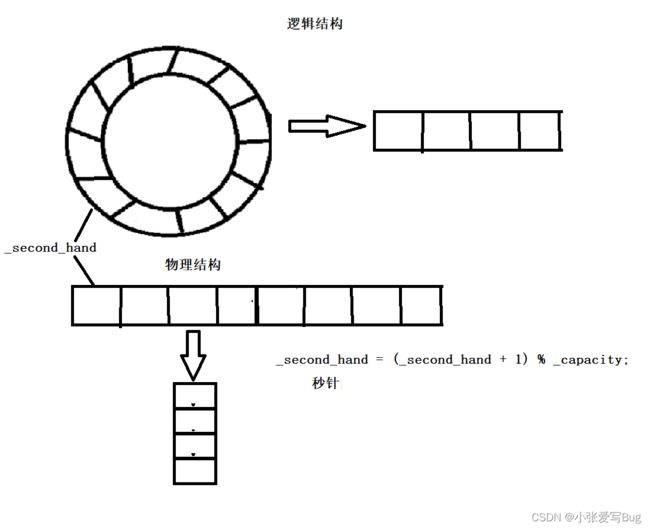
时间轮思想:
如上图所示,时间轮的实现通过定义数组模拟,并且有一个秒针指向数组的起始位置,这个指针向后走,走到哪里代表哪里的任务要被执行,假设我们要一个任务5秒后执行,只需要将任务添加到_second_hand + 5的位置,秒针每秒向后走一步,5秒后秒针指向对应的位置,定时任务执行。
需要注意的是,在同一时间,可能会有大批量的定时任务。因此我们只需要在数组对应的位置下拉一个数组即可。这样就可以在同一时刻添加多个任务了。
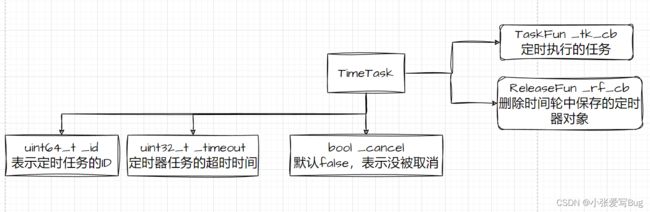
定时器任务类
//定时器任务类
using TaskFun = std::function;
using ReleaseFun = std::function;
class EventLoop;
class TimerTask
{
private:
uint64_t _id; //标识定时器任务,确保该任务能被找到
uint32_t _timeout; //定时器任务的超时 时间
bool _cancel; //默认false,表示没被取消
TaskFun _task_co; //定时执行的任务
ReleaseFun _release;
public:
TimerTask(int id, uint64_t timeout, const TaskFun co)
: _id(id), _timeout(timeout), _task_co(co), _cancel(false){}
~TimerTask(){
if (_cancel == false)
_task_co();
}
void CancelAlter() { _cancel = true; }
void SetRelease(const TaskFun &co) { _release = co; }
uint32_t GetTimeout() { return _timeout; }
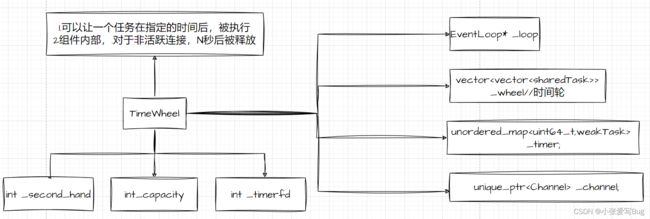
}; a.该模块主要是对Connection对象的生命周期进行管理,对非活跃连接进行超时后的释放。
b.该模块内部包含有一个timerfd: linux系统提供的定时器。
c.该模块内部含有一个Channel对象:实现对timerfd的事件就绪回调处理。
//时间轮类
using sharedTask = std::shared_ptr;
using weakTask = std::weak_ptr;
class TimeWheel
{
private:
int _second_hand; //秒针走到哪里,任务就在哪里执行
int _capacity; //时间轮的最大容量
std::vector> _wheel; //时间轮
std::unordered_map _timer;
EventLoop *_eloop;
int _timerfd;
std::unique_ptr _channel;
private:
//移除weaktask
void RemoveTimer(uint64_t id)
{
auto it = _timer.find(id);
if (it != _timer.end())
{
//找到了,移除
_timer.erase(it);
}
}
static int CreateTimerfd()
{
int timerfd = timerfd_create(CLOCK_MONOTONIC, 0);
if (timerfd < 0)
{
ERROR_LOG("Timerfd create error");
exit(-1);
}
struct itimerspec itime;
itime.it_value.tv_sec = 1;
itime.it_value.tv_nsec = 0;
itime.it_interval.tv_sec = 1;
itime.it_interval.tv_nsec = 0;
timerfd_settime(timerfd, 0, &itime, NULL);
return timerfd;
}
int ReadTimefd()
{
uint64_t timer = 0;
int ret = read(_timerfd, &timer, 8);
if (ret < 0)
{
ERROR_LOG("Read Time Error");
exit(-1);
}
return timer;
}
//秒针向后走
void RunTimerTask()
{
//DEBUG_LOG("%d",_second_hand);
_second_hand = (_second_hand + 1) % _capacity;
_wheel[_second_hand].clear();
}
void OnTime()
{
//根据超时的次数,对应的执行任务
uint64_t timer = ReadTimefd();
for (int i = 0; i < timer; ++i)
{
RunTimerTask();
}
}
//添加定时器
void TimerAddInLoop(uint64_t id, uint32_t timeout, const TaskFun &co)
{
//DEBUG_LOG("我添加了一个定时任务");
sharedTask st(new TimerTask(id, timeout, co));
st->SetRelease(std::bind(&TimeWheel::RemoveTimer, this, id));
//id和st建立 kv的映射关系
_timer[id] = weakTask(st);
int pos = (_second_hand + timeout) % _capacity;
//DEBUG_LOG("%d:%d:%d:%d", _second_hand, timeout, pos, _capacity);
_wheel[pos].push_back(st);
}
//刷新(延迟)定时任务
void TimerRefreshInLoop(uint64_t id)
{
//先确定要刷新的任务是否存在
auto it = _timer.find(id);
if (it == _timer.end())
{
//没找到
std::cout << "要刷新的任务并不存在" << std::endl;
return;
}
//找到的情况下刷新任务
sharedTask st = it->second.lock();
int timeout = st->GetTimeout();
int pos = (timeout + _second_hand) % _capacity;
_wheel[pos].push_back(st);
}
void TimerCancelInLoop(uint16_t id)
{
auto it = _timer.find(id);
if (it == _timer.end())
{
return; //没找到
}
//找到的情况下刷新任务
sharedTask st = it->second.lock();
if (st)
st->CancelAlter();
}
public:
TimeWheel() {}
TimeWheel(EventLoop *loop)
: _second_hand(0), _capacity(60), _wheel(_capacity), _eloop(loop), _timerfd(CreateTimerfd()), _channel(new Channel(_eloop, _timerfd))
{
//设置读事件的回调函数
_channel->SetReadCallback(std::bind(&TimeWheel::OnTime, this));
//启动读事件监控
_channel->ReadStart();
}
//保证线程安全
void TimerAdd(uint64_t id, uint32_t timeout, const TaskFun &co);
void TimerRefresh(uint64_t id);
void TimerCancel(uint16_t id);
bool HasTimer(uint16_t id)
{
auto it = _timer.find(id);
if (it == _timer.end())
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
~TimeWheel()
{
}
};
void TimeWheel::TimerAdd(uint64_t id, uint32_t timeout, const TaskFun &co)
{
_eloop->RunInLoop(std::bind(&TimeWheel::TimerAddInLoop, this, id, timeout, co));
}
void TimeWheel::TimerRefresh(uint64_t id)
{
_eloop->RunInLoop(std::bind(&TimeWheel::TimerRefreshInLoop, this, id));
}
void TimeWheel::TimerCancel(uint16_t id)
{
_eloop->RunInLoop(std::bind(&TimeWheel::TimerCancelInLoop, this, id));
} Any模块
Connection中需要设置协议处理的上下⽂来控制处理节奏。但是应⽤层协议有很多,这个协议接收解析上下⽂就不能有明显的协议倾向,它可以是任意协议的上下⽂信息,因此就需要⼀个通⽤的类型来保存各种不同的数据结构。
Any内部设计⼀个模板容器holder类,可以保存各种类型数据。因为在Any类中⽆法定义这个holder对象或指针,因为any也不知道这个类要保存什么类型的数据,因此⽆法传递类型参数。所以,定义⼀个基类placehoder,让holder继承于placeholde,⽽Any类保存⽗类指针即可。当需要保存数据时,则new⼀个带有模板参数的⼦类holder对象出来保存数据,然后让Any类中的⽗类指针,指向这个⼦类对象就搞定了。
class Any
{
private:
class holder
{
public:
virtual ~holder() {}
virtual const std::type_info &type() = 0;
virtual holder *clone() = 0;
};
template
class placeholder : public holder
{
public:
placeholder(const T &val) : _val(val) {}
// 获取子类对象保存的数据类型
virtual const std::type_info &type() { return typeid(T); }
// 针对当前的对象自身,克隆出一个新的子类对象
virtual holder *clone() { return new placeholder(_val); }
public:
T _val;
};
holder *_content;
public:
Any() : _content(NULL) {}
template
Any(const T &val) : _content(new placeholder(val)) {}
Any(const Any &other) : _content(other._content ? other._content->clone() : NULL) {}
~Any() { delete _content; }
Any &swap(Any &other)
{
std::swap(_content, other._content);
return *this;
}
// 返回子类对象保存的数据的指针
template
T *get()
{
//想要获取的数据类型,必须和保存的数据类型一致
assert(typeid(T) == _content->type());
return &((placeholder *)_content)->_val;
}
//赋值运算符的重载函数
template
Any &operator=(const T &val)
{
Any(val).swap(*this);
return *this;
}
Any &operator=(const Any &other)
{
Any(other).swap(*this);
return *this;
}
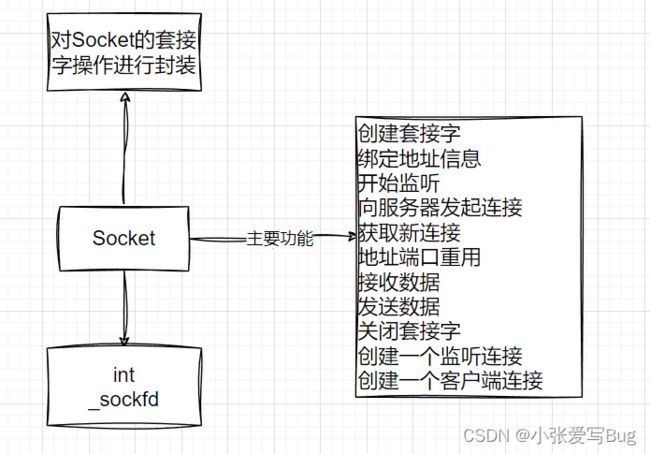
}; Socket模块
本模块对套接字操作进行封装,方便使用。对外提供各种操作接口。
#define MAX_SIZE 1024
//套接字模块
class Socket
{
private:
int _sockfd;
public:
Socket() : _sockfd(-1){};
Socket(int fd) : _sockfd(fd){};
~Socket() { Close(); }
int GetFd() { return _sockfd; }
//创建套接字
bool Create()
{
_sockfd = socket(AF_INET, SOCK_STREAM, 0);
if (_sockfd < 0)
{
ERROR_LOG("socket error");
return false;
}
return true;
}
//信息绑定
bool Bind(const std::string &ip, uint64_t port)
{
struct sockaddr_in addr;
addr.sin_family = AF_INET;
addr.sin_port = htons(port);
addr.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(ip.c_str());
socklen_t len = sizeof(struct sockaddr_in);
int ret = bind(_sockfd, (struct sockaddr *)&addr, len);
if (ret < 0)
{
ERROR_LOG("bind error");
return false;
}
return true;
}
//监听套接字
bool Listen(int backlog = MAX_SIZE)
{
int ret = listen(_sockfd, backlog);
if (ret < 0)
{
ERROR_LOG("listen error");
return false;
}
return true;
}
bool Connect(const std::string &ip, uint64_t port)
{
struct sockaddr_in peer;
peer.sin_family = AF_INET;
peer.sin_port = htons(port);
peer.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(ip.c_str());
socklen_t len = sizeof(sockaddr_in);
int ret = connect(_sockfd, (struct sockaddr *)&peer, len);
if (ret < 0)
{
ERROR_LOG("Connect Errot!!!");
return false;
}
return true;
}
//获取链接
int Accept()
{
int newfd = accept(_sockfd, NULL, NULL);
if (newfd < 0)
{
ERROR_LOG("SOCKET ACCEPT FAILED!");
return -1;
}
return newfd;
}
//发送数据
size_t Send(const void *buf, size_t len, int flag = 0)
{
int ret = send(_sockfd, buf, len, flag);
if (ret < 0)
{
if (errno == EAGAIN || errno == EINTR)
{
return 0;
}
ERROR_LOG("SOCKET SEND ERROR!!");
return -1;
}
return ret;
}
size_t NonBlockSend(void *buf, size_t len)
{
return Send(buf, len, MSG_DONTWAIT);
}
//接收数据
size_t Recv(void *buf, size_t len, int flag = 0)
{
int ret = recv(_sockfd, buf, len, flag);
if (ret < 0)
{
//没有数据
if (errno == EAGAIN || errno == EINTR)
{
NORMAL_LOG("No Data wait....");
return 0;
}
ERROR_LOG("Socket Recv Error!!");
return -1;
}
return ret;
}
size_t NonBlockRecv(void *buf, size_t len)
{
//DEBUG_LOG("错误定位");
//std::cout<< len<Accept模块
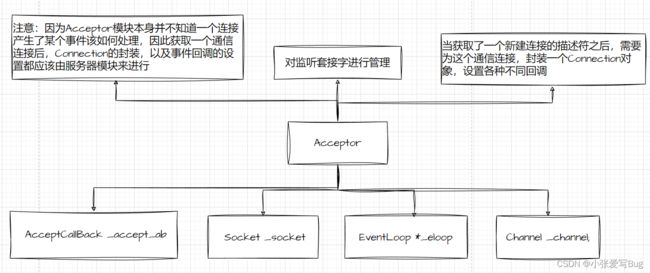
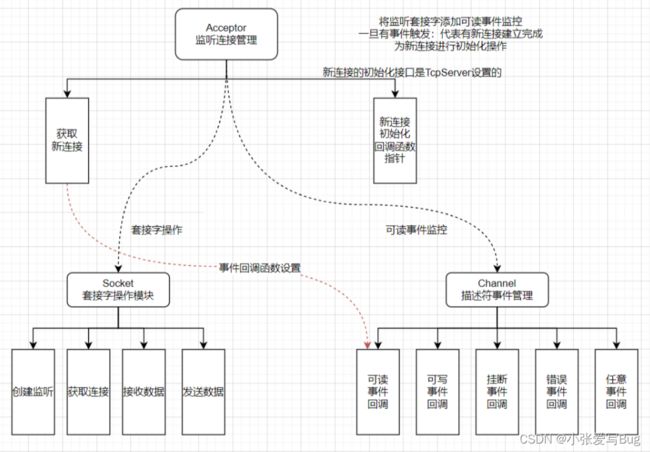
介绍:对Socket和Channel模块的整体封装,实现对一个监听套接字的整体管理。
a.该模块中包含一个Socket对象,实现监听套接字的操作。
b.该模块中包含一个Channel对象,实现监听套接字IO事件就绪的处理。
Accept模块处理流程
1.向Channel提供可读事件的IO事件处理回调函数 --- 获取新连接。
2.为新连接构建一个Connection对象,通过该对象设置各种回调。
class Acceptor
{
private:
Socket _socket; //创建监听套接字
EventLoop *_eloop; //用于对监听套接字进行事件监控
Channel _channel; //用于对监听套接字进行事件管理
using AcceptCallBack = std::function;
AcceptCallBack _accept_ab;
private:
void HandleRead()
{
int newfd = _socket.Accept();
if (newfd < 0)
{
return;
}
if (_accept_ab) _accept_ab(newfd);
}
int CreateServer(uint32_t port)
{
bool ret = _socket.CreateServer(port);
assert(ret == true);
return _socket.GetFd();
}
public:
Acceptor(EventLoop *loop, uint32_t port)
: _socket(CreateServer(port)), _eloop(loop), _channel(loop, _socket.GetFd())
{
_channel.SetReadCallback(std::bind(&Acceptor::HandleRead, this));
}
void SetAcceptCallback(const AcceptCallBack &cb) { _accept_ab = cb; }
void Listen() { _channel.ReadStart(); }
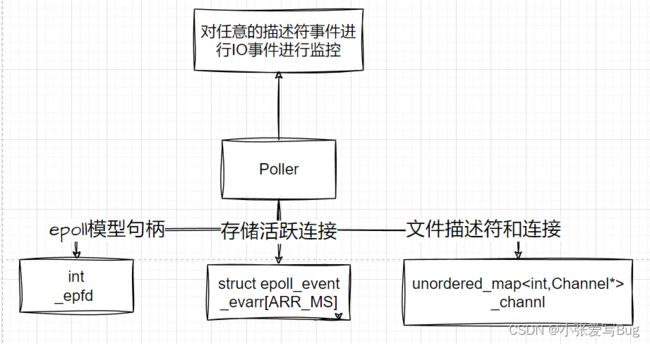
}; Poller模块
介绍:对epoll进行封装,主要实现epoll的IO事件添加,修改,移除,获取活跃连接功能。
//Poller模块
#define ARR_MAX_SIZE 1024
#define EPOLL_CREATE_SIZE 1024
class Poller
{
private:
int _epfd;
struct epoll_event _evarr[ARR_MAX_SIZE];
std::unordered_map _channl;
private:
//通过该接口对epoll直接增删改
void ControlsEpoller(Channel *channl, int op)
{
int fd = channl->GetFd();
struct epoll_event ev;
ev.data.fd = fd;
ev.events = channl->GetEvent();
int ret = epoll_ctl(_epfd, op, fd, &ev);
if (ret < 0)
{
ERROR_LOG("epoll_ctl error");
}
return;
}
//查找chanl在不在
bool FindChannl(Channel *channel)
{
auto it = _channl.find(channel->GetFd());
if (it == _channl.end())
{
//没找到
//ERROR_LOG("Not FIND!!");
return false;
}
//存在
return true;
}
public:
//构造,创建epoll模型
Poller()
{
_epfd = epoll_create(EPOLL_CREATE_SIZE);
if (_epfd < 0)
{
ERROR_LOG("EPOLL_CREATE ERROR");
exit(-1);
}
}
//添加或者修改监控事件
void UpdataEvent(Channel *channel)
{
bool flag = FindChannl(channel);
if (flag == false)
{
//不存在,添加
_channl.insert(std::make_pair(channel->GetFd(), channel));
//_channl[channel->GetFd()] = channel;
ControlsEpoller(channel, EPOLL_CTL_ADD);
return;
}
ControlsEpoller(channel, EPOLL_CTL_MOD);
}
//移除事件监控
void RemoveEvent(Channel *channel)
{
auto it = _channl.find(channel->GetFd());
if (it != _channl.end())
{
_channl.erase(it);
}
ControlsEpoller(channel, EPOLL_CTL_DEL);
}
//从就绪队里中找到活跃连接
void Poll(std::vector &active)
{
int nps = epoll_wait(_epfd, _evarr, EPOLL_CREATE_SIZE, -1);
if (nps < 0)
{
//nps
if (errno == EINTR)
{
return;
}
ERROR_LOG("epoll_wait error");
exit(-1);
}
for (int i = 0; i < nps; ++i)
{
auto it = _channl.find(_evarr[i].data.fd);
assert(it != _channl.end());
it->second->SetReadyEvent(_evarr[i].events);
active.push_back(it->second);
}
return;
}
}; Channel模块
介绍:该模块的主要功能是对每一个描述符上的IO事件进行管理,实现对描述符可读,可写,错误等事件的管理操作。以及,Poller模块对描述符进行IO事件监控 的事件就绪后,根据事件,回调不同的函数。
class EventLoop;
class Poller;
class Channel
{
using EventCallBack = std::function;
private:
int _fd;
EventLoop *_eventloop;
uint32_t _event;
uint32_t _ready_event;
EventCallBack _read_callback;
EventCallBack _write_callback;
EventCallBack _error_callback;
EventCallBack _joinclose_callback;
EventCallBack _atwill_callback;
public:
Channel(EventLoop *eloop, int fd = -1) : _eventloop(eloop), _fd(fd), _event(0), _ready_event(0) {}
//获取fd
int GetFd() { return _fd; }
//获取想要监控的事件
uint32_t GetEvent() { return _event; }
//设置实际就绪的事件
void SetReadyEvent(uint32_t event) { _ready_event = event; }
//设置读、写、错误、连接关闭、任何事件的回调函数
void SetReadCallback(EventCallBack cb) { _read_callback = cb; }
void SetWriteCallback(EventCallBack cb) { _write_callback = cb; }
void SetErrorCallback(EventCallBack cb) { _error_callback = cb; }
void SetJoinCloseCallback(EventCallBack cb) { _joinclose_callback = cb; }
void SetAtwillCallback(EventCallBack cb) { _atwill_callback = cb; }
//当前是否监控了可读
bool ReadFollow() { return (_event & EPOLLIN); }
//当前是否监控了可写
bool WriteFollow() { return (_event & EPOLLOUT); }
//启动读事件监控
void ReadStart(){
(_event |= EPOLLIN);
Update();
}
//启动写事件监控
void WriteStart(){
(_event |= EPOLLOUT);
Update();
}
//关闭读事件监控
void ReadDisable()
{
(_event &= ~EPOLLIN);
Update();
}
//关闭写事件监控
void WriteDisable()
{
(_event &= ~EPOLLOUT);
Update();
}
//关闭所有事件监控
void AllDisable() { (_event = 0); }
void Remove();
void Update();
//事件处理
void EventHand()
{
//DEBUG_LOG("事件处理");
if ((_ready_event & EPOLLIN) || (_ready_event & EPOLLHUP) || (_ready_event & EPOLLPRI))
{
if (_read_callback)
_read_callback();
}
if (_ready_event & EPOLLOUT)
{
if (_write_callback)
_write_callback();
}
else if (_ready_event & EPOLLERR)
{
if (_error_callback)
_error_callback();
}
else if (_ready_event & EPOLLHUP)
{
//DEBUG_LOG("执行定时任务");
if (_joinclose_callback)
_joinclose_callback();
}
if (_atwill_callback)
_atwill_callback();
}
};
void Channel::Remove() { _eventloop->RemoveEvent(this); }
void Channel::Update() { _eventloop->UpDataEvent(this); } Connection模块
介绍:该模块是一个对Buffer/Socket/Channel模块的整体封装,实现了对套接字的整体管理。每一个进行数据通信的套接字(accept获取到的新连接)都会构造一个Connetction对象进行管理。
分析:
1.该模块内部包含由组件使用者提供的回调函数:连接建立完成回调,事件回调,新数据回调,关闭回调。
2.该模块包含两个组件使用者提供的接口,数据发送接口和连接关闭接口。
3.该模块中包含两个用户态缓冲区:用户态接收缓冲区和用户态发送缓冲区。
4.该模块中包含一个Socket对象,完成描述符面向系统的IO操作。
5.该模块中包含一个Channel对象,完成描述符IO事件就绪的处理。
该模块的处理流程:
a.向Channel提供可读,可写,错误等不同事件的IO事件回调函数,将Channel和对应的描述符添加到Poller事件监控中。
b.当描述符在Poller模块中就绪了IO可读事件后,调用该描述符对应Channel中保存的读事件处理函数,进行数据读取,读取的过程本质上是将socket接收缓冲区中的数据 读到Connection管理的用户态接收数据中。
c.业务处理完毕后,通过Connection提供的数据发送接口,将数据写入到Connection的发送缓冲区中。
d.启动描述符在Poll模块中的IO事件监控,事件就绪后,调用Channel中保存的写事件处理函数,将发送缓冲区中的数据通过Sockert进行数据的真正发送。
class Connection;
//DISCONECTED -- 连接关闭状态; CONNECTING -- 连接建立成功-待处理状态
//CONNECTED -- 连接建立完成,各种设置已完成,可以通信的状态; DISCONNECTING -- 待关闭状态
typedef enum { DISCONNECTED, CONNECTING, CONNECTED, DISCONNECTING}ConnStatu;
using ptrConnection = std::shared_ptr;
class Connection : public std::enable_shared_from_this {
private:
uint64_t _conn_id; // 连接的唯一ID
//uint64_t _timer_id; //定时器ID
int _sockfd; // 连接关联的文件描述符
bool _enable_inactive_release; // 连接是否启动非活跃销毁的判断标志,默认为false
EventLoop *_loop; // 连接关联的EventLoop
ConnStatu _statu; // 连接状态
Socket _socket; // 套接字操作管理
Channel _channel; // 连接的事件管理
Buffer _in_buffer; // 输入缓冲区---存放从socket中读取到的数据
Buffer _out_buffer; // 输出缓冲区---存放要发送给对端的数据
Any _context; // 接收处理上下文
using ConnectedCallback = std::function;
using MessageCallback = std::function;
using ClosedCallback = std::function;
using AnyEventCallback = std::function;
ConnectedCallback _connected_callback;
MessageCallback _message_callback;
ClosedCallback _closed_callback;
AnyEventCallback _event_callback;
ClosedCallback _server_closed_callback;
private:
void HandleRead() {
//接收socket的数据
char buf[65536];
ssize_t ret = _socket.NonBlockRecv(buf, 65535);
if (ret < 0) {
//出错了
return ShutdownInLoop();
}
_in_buffer.WritePush(buf, ret);
//调用message_callback进行业务处理
if (_in_buffer.MayReadSize() > 0) {
return _message_callback(shared_from_this(), &_in_buffer);
}
}
//描述符可写事件触发后调用的函数,将发送缓冲区中的数据进行发送
void HandleWrite() {
//_out_buffer中保存的数据就是要发送的数据
ssize_t ret = _socket.NonBlockSend(_out_buffer.ReadAddres(), _out_buffer.MayReadSize());
if (ret < 0) {
//发送错误就该关闭连接了,
if (_in_buffer.MayReadSize() > 0) {
_message_callback(shared_from_this(), &_in_buffer);
}
return Release();//这时候就是实际的关闭释放操作了。
}
_out_buffer.ReadMovesBack(ret);//千万不要忘了,将读偏移向后移动
if (_out_buffer.MayReadSize() == 0) {
_channel.WriteDisable();// 没有数据待发送了,关闭写事件监控
//如果当前是连接待关闭状态,则有数据,发送完数据释放连接,没有数据则直接释放
if (_statu == DISCONNECTING) {
return Release();
}
}
return;
}
//描述符触发挂断事件
void HandleClose() {
if (_in_buffer.MayReadSize() > 0) {
_message_callback(shared_from_this(), &_in_buffer);
}
return Release();
}
//描述符触发出错事件
void HandleError() {
return HandleClose();
}
void HandleEvent() {
if (_enable_inactive_release == true) { _loop->TimerRefresh(_conn_id); }
if (_event_callback) { _event_callback(shared_from_this()); }
}
void EstablishedInLoop() {
assert(_statu == CONNECTING);//当前的状态必须一定是上层的半连接状态
_statu = CONNECTED;//当前函数执行完毕,则连接进入已完成连接状态
_channel.ReadStart();
if (_connected_callback) _connected_callback(shared_from_this());
}
//实际的释放接口
void ReleaseInLoop() {
//1. 修改连接状态,将其置为DISCONNECTED
_statu = DISCONNECTED;
//2. 移除连接的事件监控
_channel.Remove();
//3. 关闭描述符
_socket.Close();
//4. 如果当前定时器队列中还有定时销毁任务,则取消任务
if (_loop->HasTimer(_conn_id)) CancelInactiveReleaseInLoop();
//5. 调用关闭回调函数
if (_closed_callback) _closed_callback(shared_from_this());
//移除服务器内部管理的连接信息
if (_server_closed_callback) _server_closed_callback(shared_from_this());
}
//这个接口并不是实际的发送接口,而只是把数据放到了发送缓冲区,启动了可写事件监控
void SendInLoop(Buffer &buf) {
if (_statu == DISCONNECTED) return ;
_out_buffer.WriteBufferPush(buf);
if (_channel.WriteFollow() == false) {
_channel.WriteStart();
}
}
//这个关闭操作并非实际的连接释放操作,需要判断还有没有数据待处理,待发送
void ShutdownInLoop() {
_statu = DISCONNECTING;// 设置连接为半关闭状态
if (_in_buffer.MayReadSize() > 0) {
if (_message_callback) _message_callback(shared_from_this(), &_in_buffer);
}
//要么就是写入数据的时候出错关闭,要么就是没有待发送数据,直接关闭
if (_out_buffer.MayReadSize() > 0) {
if (_channel.WriteFollow() == false) {
_channel.WriteStart();
}
}
if (_out_buffer.MayReadSize() == 0) {
Release();
}
}
//启动非活跃连接超时释放规则
void EnableInactiveReleaseInLoop(int sec) {
//1. 将判断标志 _enable_inactive_release 置为true
_enable_inactive_release = true;
//2. 如果当前定时销毁任务已经存在,那就刷新延迟一下即可
if (_loop->HasTimer(_conn_id)) {
return _loop->TimerRefresh(_conn_id);
}
//3. 如果不存在定时销毁任务,则新增
_loop->TimerAdd(_conn_id, sec, std::bind(&Connection::Release, this));
}
void CancelInactiveReleaseInLoop() {
_enable_inactive_release = false;
if (_loop->HasTimer(_conn_id)) {
_loop->TimerCancel(_conn_id);
}
}
void UpgradeInLoop(const Any &context,
const ConnectedCallback &conn,
const MessageCallback &msg,
const ClosedCallback &closed,
const AnyEventCallback &event) {
_context = context;
_connected_callback = conn;
_message_callback = msg;
_closed_callback = closed;
_event_callback = event;
}
public:
Connection(EventLoop *loop, uint64_t conn_id, int sockfd):_conn_id(conn_id), _sockfd(sockfd),
_enable_inactive_release(false), _loop(loop), _statu(CONNECTING), _socket(_sockfd),
_channel(loop, _sockfd) {
_channel.SetJoinCloseCallback(std::bind(&Connection::HandleClose, this));
_channel.SetAtwillCallback(std::bind(&Connection::HandleEvent, this));
_channel.SetReadCallback(std::bind(&Connection::HandleRead, this));
_channel.SetWriteCallback(std::bind(&Connection::HandleWrite, this));
_channel.SetErrorCallback(std::bind(&Connection::HandleError, this));
}
~Connection() { DEBUG_LOG("RELEASE CONNECTION:%p", this); }
//获取管理的文件描述符
int GetFd() { return _sockfd; }
//获取连接ID
int GetConId() { return _conn_id; }
//是否处于CONNECTED状态
bool IsCommunication() { return (_statu == CONNECTED); }
//设置上下文--连接建立完成时进行调用
void SetContext(const Any &context) { _context = context; }
//获取上下文,返回的是指针
Any *GetContext() { return &_context; }
void SetConnectCallBack(const ConnectedCallback&cb) { _connected_callback = cb; }
void SetMessageCallBack(const MessageCallback&cb) { _message_callback = cb; }
void SetCloseCallBack(const ClosedCallback&cb) { _closed_callback = cb; }
void SetAnyEventtCallBack(const AnyEventCallback&cb) { _event_callback = cb; }
void SetServerCloseCallBack(const ClosedCallback&cb) { _server_closed_callback = cb; }
//连接建立就绪后,进行channel回调设置,启动读监控,调用_connected_callback
void Established() {
_loop->RunInLoop(std::bind(&Connection::EstablishedInLoop, this));
}
//发送数据,将数据放到发送缓冲区,启动写事件监控
void Send(const char *data, size_t len) {
Buffer buf;
buf.WritePush(data, len);
_loop->RunInLoop(std::bind(&Connection::SendInLoop, this, std::move(buf)));
}
//提供给组件使用者的关闭接口--并不实际关闭,需要判断有没有数据待处理
void Shutdown() {
_loop->RunInLoop(std::bind(&Connection::ShutdownInLoop, this));
}
void Release() {
_loop->QueueInLoop(std::bind(&Connection::ReleaseInLoop, this));
}
//启动非活跃销毁,并定义多长时间无通信就是非活跃,添加定时任务
void EnableInactiveRelease(int sec) {
_loop->RunInLoop(std::bind(&Connection::EnableInactiveReleaseInLoop, this, sec));
}
//取消非活跃销毁
void CancelInactiveRelease() {
_loop->RunInLoop(std::bind(&Connection::CancelInactiveReleaseInLoop, this));
}
void Upgrade(const Any &context, const ConnectedCallback &conn, const MessageCallback &msg,
const ClosedCallback &closed, const AnyEventCallback &event) {
_loop->AssertInLoop();
_loop->RunInLoop(std::bind(&Connection::UpgradeInLoop, this, context, conn, msg, closed, event));
}
}; LoopThreadPool模块
LoopThread模块的功能就是将EventLoop模块与thread整合到一起。EventLoop模块实例化的对象,在构造的时候会初始化_thread_id。在后续的操作中,通过当前线程ID和EventLoop模块中的_thread_id进行一个比较,相同就表示在同一个线程,不同就表示当前运行的线程并不是EventLoop线程。因此,我们必须先创建线程,然后在线程的入口函数中,去实例化EventLoop对象。
LoopThreadPool模块的功能主要是对所有的LoopThread进行管理及分配。
在服务器中,主Reactor负责新连接的获取,从属线程负责新连接的事件监控及处理,因此当前的线程池,游有可能从属线程数量为0。也就是实现单Reactor服务器,一个线程既负责获取连接,也负责连接的处理。该模块就是对0个或者多个LoopThread对象进行管理。
关于线程分配,当主线程获取了一个新连接,需要将新连接挂到从属线程上进行事件监控及处理。假设有0个从属线程,则直接分配给主线程的EventLoop,进行处理。假设有多个从属线程,采用轮转的思想,进行线程的分配(将对应线程的EventLoop获取到,设置给对应的Connection)。
EventLoop模块
介绍:EventLoop模块对Poller,TimerQueue,Socket模块进行了封装。也是Reactor模型模块。
●EventLoop模块必须是一个对象对应一个线程,线程内部运行EventLoop的启动函数。
●EventLoop模块为了保证整个服务器的线程安全问题,因此要求使用者对于Connection的所有操作一定要在其对应的EventLoop线程内完成。
●EventLoop模块保证自己内部所监控的所有描述符 都要是活跃连接,非活跃连接就要及时的释放 避免资源浪费。
●EventLoop模块内部包含一个eventfd:内核提供的事件fd,专门用于事件通知。
●EventLoop模块内部含有一个Poller对象,用于进行描述符的IO事件管理。
●EventLoop模块内部包含有一个TimeQueue对象,用于进行定时任务的管理。
●EventLoop模块中包含一个任务队列,组件使用者要对Connection进行的所有操作,都加入到任务队列中并由EventLoop模块进行管理,并在EventLoop对应的线程中进行执行。
●每一个Connection对象都会绑定到一个EventLoop上,这样一来 对连接的所有操作就能保证在一个线程中进行。
●通过Poller模块对当前 模块管理内的所有描述符进行IO事件监控,当有描述符事件就绪后,通过描述符对应的Channel进行事件的处理。
●所有就绪的描述符IO事件处理完毕后,对任务队列中的所有操作 进行顺序执行。
●epoll的事件监控,有可能会因为没有事件到来而持续阻塞。导致任务队列中的任务不能得到及时的处理。对此的处理方式是创建一个eventfd,添加到Poller的事件监控中,每当向任务队列添加任务的时候,通过向eventdf写入数据来唤醒epoll的阻塞。
class EventLoop
{
using Functor = std::function;
private:
std::thread::id _thread_id;
int _event_fd;
std::unique_ptr _event_channal;
Poller _poller;
std::vector _tasks_pool;
std::mutex _mutex;
TimeWheel _timewheel;
public:
//创建Eventfd
static int CreateEventId()
{
int efd = eventfd(0, EFD_CLOEXEC | EFD_NONBLOCK);
if (efd < 0)
{
ERROR_LOG("EVENTFD_ERROR");
exit(-1);
}
return efd;
}
//读取
int ReadEventfd()
{
uint64_t res = 0;
int ret = read(_event_fd, &res, 8);
if (ret < 0)
{
if (errno == EINTR || errno == EAGAIN)
{
return 0;
}
ERROR_LOG("READ_ERROR!!");
return -1;
}
return ret;
}
void WeakUpEventfd()
{
uint64_t val = 1;
int res = write(_event_fd, &val, 8);
if (res < 0)
{
if (errno == EINTR)
{
return;
}
ERROR_LOG("WRITE_ERROR");
exit(-1);
}
return;
}
public:
EventLoop()
: _thread_id(std::this_thread::get_id()),
_event_fd(CreateEventId()),
_event_channal(new Channel(this, _event_fd)),
_timewheel(this)
{
_event_channal->SetReadCallback(std::bind(&EventLoop::ReadEventfd, this));
_event_channal->ReadStart();
}
//执行任务中的所有任务
void PerformTask()
{
//DEBUG_LOG("我在执行任务");
std::vector functor;
{
std::unique_lock _lock(_mutex);
_tasks_pool.swap(functor);
}
for (auto &fun : functor)
{
fun();
}
return;
}
void Start()
{
while (true)
{
//事件监控
std::vector actives;
_poller.Poll(actives);
//事件处理
for (auto &channal : actives)
{
channal->EventHand();
}
//执行任务
PerformTask();
}
}
bool IsInLoop()
{
//std::cout<<_thread_id< lock(_mutex);
_tasks_pool.push_back(cb);
}
//给eventfd写入一个数据,eventfd会触发读事件
WeakUpEventfd();
}
//添加或修改描述符的事件监控
void UpDataEvent(Channel *channal) { return _poller.UpdataEvent(channal); }
//移除描述符的事件监控
void RemoveEvent(Channel *channal) { return _poller.RemoveEvent(channal); }
void TimerAdd(uint64_t id, uint32_t timeout, const TaskFun &co)
{
_timewheel.TimerAdd(id, timeout, co);
}
void TimerRefresh(uint64_t id)
{
_timewheel.TimerRefresh(id);
}
void TimerCancel(uint16_t id)
{
_timewheel.TimerCancel(id);
}
bool HasTimer(uint16_t id)
{
return _timewheel.HasTimer(id);
}
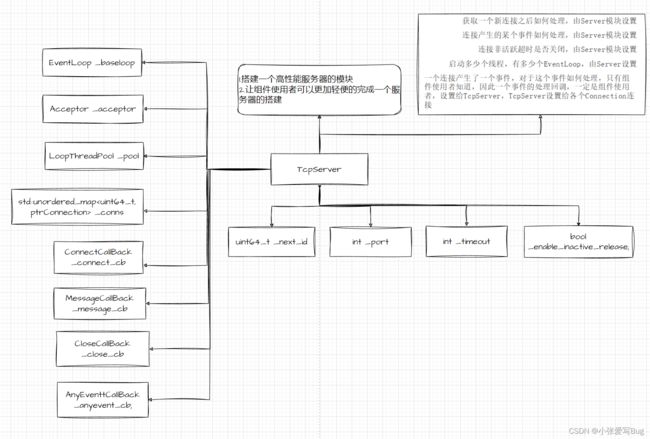
}; TcpServer模块
1.在该模块中,包含有一个EventLoop对象 -- baseloop,以备在超轻量使用场景中不需要EventLoop线程池,只需要在主线程中完成所有操作的情况。
2.TcpServer模块内部包含一个EventLoop Pool (从属Rector线程池)对象。
3.该模块中包含一个Accepts对象,用来获取客户端新连接,并处理任务。
4.TcpServer模块内部包含有⼀个std::shared_ptr
操作流程:
1. 在实例化TcpServer对象过程中,完成BaseLoop的设置,Acceptor对象的实例化,以及EventLoop 线程池的实例化,以及std::shared_ptr
2. 为Acceptor对象设置回调函数:获取到新连接后,为新连接构建Connection对象,设置Connection的各项回调,并使⽤shared_ptr进⾏管理,并添加到hash表中进⾏管理,并Connection选择⼀个EventLoop线程,为Connection添加⼀个定时销毁任务,为Connection添加事件监控。
3. 启动BaseLoop。
class TcpServer
{
private:
uint64_t _next_id; //自动增长的id
int _port; //服务端端口号
int _timeout; //非活跃连接的统计时间
bool _enable_inactive_release; //是否启动了非活跃连接超时销毁的判断标志
EventLoop _baseloop; //这是主线程的EventLoop,负责监听事件的处理
Acceptor _acceptor; //管理监听套接字的对象
LoopThreadPool _pool; //从属EventLoop线程池
std::unordered_map _conns; //保存管理所有连接对应的shared_ptr对象
using ConnectCallBack = std::function;
using MessageCallBack = std::function;
using CloseCallBack = std::function;
using AnyEventtCallBack = std::function;
using Functor = std::function;
ConnectCallBack _connect_cb;
MessageCallBack _message_cb;
CloseCallBack _close_cb;
AnyEventtCallBack _anyevent_cb;
private:
void RunAfterInLoop(const Functor &task, int delay)
{
_next_id++;
_baseloop.TimerAdd(_next_id, delay, task);
}
void NewConnection(int fd)
{
_next_id++;
ptrConnection conn(new Connection(_next_id, fd, _pool.NextLoop()));
conn->SetMessageCallBack(_message_cb);
conn->SetCloseCallBack(_close_cb);
conn->SetConnectCallBack(_connect_cb);
conn->SetAnyEventtCallBack(_anyevent_cb);
conn->SetServerCloseCallBack(std::bind(&TcpServer::RemoveConnection, this, std::placeholders::_1));
if (_enable_inactive_release)
conn->EnableInactiveRelease(_timeout);
conn->Established(); //就绪初始化
_conns.insert(std::make_pair(_next_id, conn));
}
void RemoveConnectionInLoop(const ptrConnection &conn)
{
auto it = _conns.find(conn->GetConID());
if (it != _conns.end())
{
_conns.erase(conn->GetConID());
}
}
void RemoveConnection(const ptrConnection &conn)
{
_baseloop.RunInLoop(std::bind(&TcpServer::RemoveConnectionInLoop, this, conn));
}
public:
TcpServer(int port)
: _port(port), _next_id(0), _timeout(0), _enable_inactive_release(false), _acceptor(&_baseloop, port), _pool(&_baseloop)
{
_acceptor.SetAcceptCallback(std::bind(&TcpServer::NewConnection, this, std::placeholders::_1));
_acceptor.Listen();
}
void SetThreadCount(int count) { _pool.SetThreadCount(count); }
//设置回调函数
void SetConnectCallBack(const ConnectCallBack &cb) { _connect_cb = cb; }
void SetMessageCallBack(const MessageCallBack &cb) { _message_cb = cb; }
void SetCloseCallBack(const CloseCallBack &cb) { _close_cb = cb; }
void SetAnyEventtCallBack(const AnyEventtCallBack &cb) { _anyevent_cb = cb; }
void EnableInactiveRelease(int timeout)
{
_timeout = timeout;
_enable_inactive_release = true;
}
void RunAfter(const Functor &task, int delay)
{
_baseloop.RunInLoop(std::bind(&TcpServer::RunAfterInLoop, this, task, delay));
}
void Start()
{
_pool.Create();
_baseloop.Start();
}
}; Http协议模块
Util模块
该模块为工具模块,主要提供Http协议模块所用到的一些工具函数,比如Url编码解码,文件读写。
class Util
{
public:
//根据分割字符串,对字符串进行分割,将分割后的字符串存放到容器中
static size_t Split(const std::string &str, const std::string &seq, std::vector &arr)
{
int offset = 0;
while (offset < str.size())
{
auto it = str.find(seq, offset);
if (it == std::string::npos)
{
//没有找到,但是还有字符串,将剩余的字符串存到容器中
if (it == str.size())
break;
arr.push_back(str.substr(offset));
return arr.size();
}
//走到这里,说明找到了分割字符串,但是为空串
if (it == offset)
{
offset = it + seq.size();
continue;
}
//找到且后面不是空串
arr.push_back(str.substr(offset, it - offset));
offset = it + seq.size();
}
return arr.size();
}
//读取一个文件的所有内容
static bool ReadFile(const std::string &filename, std::string &buf)
{
std::ifstream ifs(filename, std::ios::binary);
if (ifs.is_open() == false)
{
printf("OPEN %s FILE FAILED!!", filename.c_str());
return false;
}
//将读写偏移跳转到末尾
ifs.seekg(0, ifs.end);
size_t fsize = ifs.tellg();
ifs.seekg(0, ifs.beg);
buf.resize(fsize);
ifs.read(&buf[0], fsize);
if (ifs.good() == false)
{
printf("read %s FILE FAILED!!", filename.c_str());
ifs.close();
return false;
}
ifs.close();
return true;
}
//向一个文件中截断式的写入内容
static bool WriteFile(const std::string &filename, const std::string &buf)
{
std::ofstream ofs(filename, std::ios::binary | std::ios::trunc);
if (ofs.is_open() == false)
{
printf("OPEN %s FILE FAILED!!", filename.c_str());
return false;
}
ofs.write(buf.c_str(), buf.size());
if (ofs.good() == false)
{
printf("write %s FILE FAILED!!", filename.c_str());
ofs.close();
return false;
}
ofs.close();
return true;
}
static std::string UrlEncode(const std::string url, bool convert_space_to_plus)
{
std::string res;
for (auto &c : url)
{
if (c == '.' || c == '-' || c == '_' || c == '~' || isalnum(c))
{
res += c;
continue;
}
if (c == ' ' && convert_space_to_plus)
{
res += '+';
continue;
}
//需要进行转换的字符,%HH的格式
char tmp[4] = {0};
snprintf(tmp, 4, "%%%02X", c);
res += tmp;
}
return res;
}
static char HexToI(char c)
{
if (c >= '0' && c <= '9')
{
return c - '0';
}
else if (c >= 'a' && c <= 'z')
{
return c - 'a' + 10;
}
else if (c >= 'A' && c <= 'Z')
{
return c - 'A' + 10;
}
return -1;
}
static std::string UrlDecode(const std::string &url, bool convert_plus_to_space)
{
//解码规则:如果遇到了%,则将紧跟在后面的2个字符,转换为数字。第一个数字左移4位,然后加上第二个数字
std::string res;
for (int i = 0; i < url.size(); ++i)
{
if (url[i] == '+' && convert_plus_to_space)
{
res += ' ';
continue;
}
if (url[i] == '%' && (i + 2) < url.size())
{
char v1 = HexToI(url[i + 1]);
char v2 = HexToI(url[i + 2]);
char v = v1 * 16 + v2;
res += v;
i += 2;
continue;
}
res += url[i];
}
return res;
}
//状态码的获取
static std::string StatuDesc(int statu)
{
auto it = _statu_msg.find(statu);
if (it == _statu_msg.end())
{
//没找到
return "UnKnow";
}
return it->second;
}
//根据文件名的后缀,获取文件的扩展名
static std::string ExtMime(const std::string &filename)
{
//a.html => 获取后缀 .html
size_t pos = filename.find_last_of('.');
if (pos == std::string::npos)
{
return "application/octet-stream";
}
//获取到了后缀,通过后缀获取扩展名
std::string str = filename.substr(pos);
auto it = _mime_msg.find(str);
if (it == _mime_msg.end())
{
//没找到
return "application/octet-stream";
}
return it->second;
}
//判断一个文件是否是一个目录
static bool IsDirectory(const std::string &filename)
{
struct stat st;
int ret = stat(filename.c_str(), &st);
if (ret < 0)
{
return false;
}
return S_ISDIR(st.st_mode);
}
//判断一个文件是否为一个普通文件
static bool IsRegular(const std::string &filename)
{
struct stat st;
int ret = stat(filename.c_str(), &st);
if (ret < 0)
{
return false;
}
return S_ISREG(st.st_mode);
}
//想要访问的资源路径是否合法
static bool ValidPath(const std::string &path)
{
std::vector v_str;
Split(path, "/", v_str);
int leve = 0;
for (auto &ss : v_str)
{
if (ss == "..")
{
//在访问上层路径
leve--;
if (leve < 0)
return false;
continue;
}
leve++;
}
return true;
}
}; HttpRequest模块
这个模块是Http请求数据模块,用于保存Http请求数据被解析后的各项请求元素信息。
class HttpRequest
{
public:
std::string _method; //请求方法
std::string _path; //资源路径
std::string _version; //协议版本
std::string _body; //请求正文
std::smatch _matches; //资源路径的正则提取数据
std::unordered_map _headers; //头部字段
std::unordered_map _params; //查询字符串
public:
HttpRequest() : _version("HTTP/1.1") {}
void ReSet()
{
_method.clear();
_path.clear();
_version = "HTTP/1.1";
_body.clear();
std::smatch match;
_matches.swap(match);
_headers.clear();
_params.clear();
}
//插入头部字段
void SetHeader(const std::string &key, const std::string &val)
{
//_headers[key] = val;
_headers.insert(std::make_pair(key, val));
}
//判断是否有头部字段
bool HasHeader(const std::string &key) const
{
auto it = _headers.find(key);
if (it == _headers.end())
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
//获取指定头部字段的值
std::string GetHeader(const std::string &key) const
{
auto it = _headers.find(key);
if (it == _headers.end())
{
return "";
}
return it->second;
}
//插入查询字符串
void SetParam(const std::string &key, const std::string &val)
{
_params.insert(std::make_pair(key, val));
}
//判断是否有某个查询字符串
bool HasParam(const std::string &key) const
{
auto it = _params.find(key);
if (it == _params.end())
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
//获取指定的查询字符串
std::string GetParam(const std::string &key) const
{
auto it = _params.find(key);
if (it == _params.end())
{
return "";
}
return it->second;
}
//获取正文长度
size_t ContentLength() const
{
bool ret = HasHeader("Content-Length");
if (ret == false)
{
return 0;
}
std::string clen = GetHeader("Content-Length");
return std::stol(clen);
}
//判断是否为短连接
bool Close() const
{
//DEBUG_LOG("[%s] ",GetHeader("Connection").c_str());
if (HasHeader("Content-Length") == true && GetHeader("Connection") == "keep-alive")
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
}; HttpResponse模块
这个模块是Http响应数据块,用于业务处理后设置并保存Http响应数据的各项元素信息,最终会被按照Http协议响应格式组织成为响应信息发送给客户端。
class HttpResponse
{
public:
int _statu;
bool _redirect_flag;
std::string _body;
std::string _redirect_url;
std::unordered_map _headers;
public:
HttpResponse() : _statu(200), _redirect_flag(false) {}
HttpResponse(int statu) : _statu(statu), _redirect_flag(false) {}
void ReSet()
{
_statu = 200;
_redirect_flag = false;
_body.clear();
_redirect_url.clear();
_headers.clear();
}
//插入头部字段
void SetHeader(const std::string &key, const std::string &val)
{
//_headers[key] = val;
_headers.insert(std::make_pair(key, val));
}
//判断是否有头部字段
bool HasHeader(const std::string &key) const
{
auto it = _headers.find(key);
if (it == _headers.end())
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
//获取指定头部字段的值
std::string GetHeader(const std::string &key) const
{
auto it = _headers.find(key);
if (it == _headers.end())
{
return "";
}
return it->second;
}
void SetContent(const std::string &body, const std::string &type = "text/html")
{
_body = body;
SetHeader("Content-Type", type);
}
void SetRedirect(const std::string &url, int statu = 302)
{
_statu = statu;
_redirect_flag = true;
_redirect_url = url;
}
bool Close() const
{
//DEBUG_LOG("[%s] ",GetHeader("Connection").c_str());
if (HasHeader("Connection") == true && GetHeader("Connection") == "keep-alive")
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
}; HttpContext 模块
该模块是一个Http请求接收的上下文模块,主要是为了防止在一次接收的数据中,不是一个完整的Http请求,需要在下次接收到新数据后继续根据上下文进行解析,最终得到一个HttpRequest请求信息对象,因此在请求数据的接收以及解析部分需要一个上下文来进行控制接收和处理节奏。
typedef enum
{
RECV_HTTP_ERROR,
RECV_HTTP_LINE,
RECV_HTTP_HEAD,
RECV_HTTP_BODY,
RECV_HTTP_OVER
} HttpRecvStatu;
#define MAX_LINE 8192
class HttpContext
{
private:
int _resp_statu; //响应状态码
HttpRecvStatu _recv_statu; //当前解析的状态
HttpRequest _request; //已经解析得到的请求信息
private:
bool ParseHttpLine(const std::string &line)
{
boost::smatch matches;
boost::regex e("(GET|HEAD|POST|PUT|DELETE) ([^?]*)(?:\\?(.*))? (HTTP/1\\.[01])(?:\n|\r\n)?", boost::regex::icase);
bool ret = boost::regex_match(line, matches, e);
if (ret == false)
{
_recv_statu = RECV_HTTP_ERROR;
_resp_statu = 400;
return false;
}
_request._method = matches[1];
std::transform(_request._method.begin(), _request._method.end(), _request._method.begin(), ::toupper);
//std::transform()
_request._path = Util::UrlDecode(matches[2], false);
_request._version = matches[4];
std::vector query_string_arry;
std::string query_string = matches[3];
Util::Split(query_string, "&", query_string_arry);
for (auto &str : query_string_arry)
{
size_t pos = str.find("=");
if (pos == std::string::npos)
{
_recv_statu = RECV_HTTP_ERROR;
_resp_statu = 400;
return false;
}
std::string key = Util::UrlDecode(str.substr(0, pos), true);
std::string val = Util::UrlDecode(str.substr(pos + 1), true);
_request.SetParam(key, val);
}
return true;
}
bool RecvHttpLine(Buffer *buf)
{
if (_recv_statu != RECV_HTTP_LINE)
return false;
//获取一行数据
std::string s_line = buf->GetLinePop();
if (s_line.size() == 0)
{
//一行都没获取上来
if (buf->MayReadSize() > MAX_LINE)
{
_recv_statu = RECV_HTTP_ERROR;
_resp_statu = 414;
return false;
}
//缓冲区中的数据不足一行
return true;
}
if (s_line.size() > MAX_LINE)
{
_recv_statu = RECV_HTTP_ERROR;
_resp_statu = 414;
return false;
}
bool ret = ParseHttpLine(s_line);
if (ret == false)
return false;
_recv_statu = RECV_HTTP_HEAD;
return true;
}
bool RecvHttpHead(Buffer *buf)
{
if (_recv_statu != RECV_HTTP_HEAD)
return false;
while (1)
{
std::string line = buf->GetLinePop();
if (line.size() == 0)
{
if (buf->MayReadSize() > MAX_LINE)
{
_recv_statu = RECV_HTTP_ERROR;
_resp_statu = 414;
return false;
}
return true;
}
if (line.size() > MAX_LINE)
{
_recv_statu = RECV_HTTP_ERROR;
_resp_statu = 414;
return false;
}
if (line == "\n" || line == "\r\n")
break;
bool ret = ParseHttpHead(line);
if (ret == false)
{
return false;
}
}
_recv_statu = RECV_HTTP_BODY;
return true;
}
bool ParseHttpHead(std::string &line)
{
if (line.back() == '\n')line.pop_back();
if (line.back() == '\r')line.pop_back();
size_t pos = line.find(": ");
if (pos == std::string::npos)
{
_recv_statu = RECV_HTTP_ERROR;
_resp_statu = 400;
return false;
}
std::string key = line.substr(0, pos);
std::string val = line.substr(pos + 2);
_request.SetHeader(key, val);
return true;
}
bool RecvHttpBody(Buffer *buf)
{
if (_recv_statu != RECV_HTTP_BODY)
return false;
//获取正文长度
size_t content_length = _request.ContentLength();
if (content_length == 0)
{
_recv_statu = RECV_HTTP_OVER;
return true;
}
size_t real_len = content_length - _request._body.size();
if (buf->MayReadSize() >= real_len)
{
_request._body.append(buf->ReadAddres(), real_len);
buf->ReadMovesBack(real_len);
_recv_statu = RECV_HTTP_OVER;
return true;
}
_request._body.append(buf->ReadAddres(), buf->MayReadSize());
buf->ReadMovesBack(buf->MayReadSize());
return true;
}
public:
HttpContext() : _resp_statu(200), _recv_statu(RECV_HTTP_LINE) {}
void ReSet()
{
_resp_statu = 200;
_recv_statu = RECV_HTTP_LINE;
_request.ReSet();
}
int RespStatu() { return _resp_statu; }
HttpRecvStatu RecvStatu() { return _recv_statu; }
HttpRequest &Request() { return _request; }
void RecvHttpRequest(Buffer *buf)
{
switch (_recv_statu)
{
case RECV_HTTP_LINE:
RecvHttpLine(buf);
case RECV_HTTP_HEAD:
RecvHttpHead(buf);
case RECV_HTTP_BODY:
RecvHttpBody(buf);
}
return;
}
}; HttpServer 模块
主要目标:最终给组件使用者提供的Http服务器模块,用于以简单的接口实现Http服务器的搭建。
a. HttpServer模块内部包含有⼀个TcpServer对象:TcpServer对象实现服务器的搭建 。
b. HttpServer模块内部包含有两个提供给TcpServer对象的接口:连接建⽴成功设置上下⽂接口,数据处理接口。
c. HttpServer模块内部包含有⼀个hash-map表存储请求与处理函数的映射表:组件使⽤者向HttpServer设置哪些请求应该使⽤哪些函数进⾏处理,等TcpServer收到对应的请求就会使⽤对应的函数进⾏处理。
#define DEFALT_TIMEOUT 10
class HttpServer
{
private:
using Handle = std::function;
using Handlers = std::vector>;
Handlers _get_route;
Handlers _put_route;
Handlers _post_route;
Handlers _delete_route;
TcpServer _server;
std::string _basedir;
private:
void ErrorHandler(const HttpRequest &req, HttpResponse *rsp)
{
//1. 组织一个错误展示页面
std::string body;
body += "";
body += "";
body += "";
body += "";
body += "";
body += "";
body += std::to_string(rsp->_statu);
body += " ";
body += Util::StatuDesc(rsp->_statu);
body += "
";
body += "";
body += "";
//2. 将页面数据,当作响应正文,放入rsp中
rsp->SetContent(body, "text/html");
}
void WriteReponse(const ptrConnection &conn, const HttpRequest &req, HttpResponse &rsp)
{
//先完善头部字段
//1. 先完善头部字段
if (req.Close() == true)
{
rsp.SetHeader("Connection", "close");
}
else
{
rsp.SetHeader("Connection", "keep-alive");
}
if (rsp._body.empty() == false && rsp.HasHeader("Content-Length") == false)
{
rsp.SetHeader("Content-Length", std::to_string(rsp._body.size()));
}
if (rsp._body.empty() == false && rsp.HasHeader("Content-Type") == false)
{
rsp.SetHeader("Content-Type", "application/octet-stream");
}
if (rsp._redirect_flag == true)
{
rsp.SetHeader("Location", rsp._redirect_url);
}
//2. 将rsp中的要素,按照http协议格式进行组织
//StatuDesc获取状态码
std::stringstream rsp_str;
rsp_str << req._version << " " << std::to_string(rsp._statu) << " " << Util::StatuDesc(rsp._statu) << "\r\n";
for (auto &head : rsp._headers)
{
rsp_str << head.first << ": " << head.second << "\r\n";
}
rsp_str << "\r\n";
rsp_str << rsp._body;
//3. 发送数据
conn->Send(rsp_str.str().c_str(), rsp_str.str().size());
}
//要访问的资源是否合法
bool IsFileHandler(const HttpRequest &req)
{
//必须设置了资源根目录
if (_basedir.empty() == true)
return false;
//必须是Head或者GET
if (req._method != "GET" && req._method != "HEAD")
return false;
//请求的资源路径必须是一个合法的路径
if (Util::ValidPath(req._path) == false)
return false;
//请求的资源存在,且是一个普通文件
std::string req_path = _basedir + req._path;
if (req._path.back() == '/')
{
req_path += "index.html";
}
if (Util::IsRegular(req_path) == false)
{
return false;
}
return true;
}
void FileHandler(const HttpRequest &req, HttpResponse *rsp)
{
//根目录加上静态资源的请求
std::string req_path = _basedir + req._path;
if (req_path.back() == '/')
{
//默认要访问的资源
req_path += "index.html";
}
//读取文件的所有内容
bool ret = Util::ReadFile(req_path, rsp->_body);
if (ret == false)
return;
//获取文件的扩展名
std::string mime = Util::ExtMime(req_path);
rsp->SetHeader("Content-Type", mime);
return;
}
//功能性请求的分类处理
void Dispatcher(HttpRequest &req, HttpResponse *rsp, Handlers &handlers)
{
for (auto &handler : handlers)
{
const std::regex &re = handler.first;
const Handle &functor = handler.second;
bool ret = std::regex_match(req._path, req._matches, re);
if (ret == false)
{
continue;
}
return functor(req, rsp); //传入请求信息,和空的rsp,执行处理函数
}
rsp->_statu = 404;
}
void Route(HttpRequest &req, HttpResponse *rsp)
{
if (IsFileHandler(req) == true)
{
//是一个静态资源请求, 则进行静态资源请求的处理
return FileHandler(req, rsp);
}
if (req._method == "GET" || req._method == "HEAD")
{
return Dispatcher(req, rsp, _get_route);
}
else if (req._method == "POST")
{
return Dispatcher(req, rsp, _post_route);
}
else if (req._method == "PUT")
{
return Dispatcher(req, rsp, _put_route);
}
else if (req._method == "DELETE")
{
return Dispatcher(req, rsp, _delete_route);
}
rsp->_statu = 405; //上述方法都不是,设置状态码
}
//设置上下文
void OnConnected(const ptrConnection &conn)
{
conn->SetContext(HttpContext());
DEBUG_LOG("NEW CONNECTION %p", conn.get());
}
//功能性请求的分类处理
//void Dispatcher(HttpRequest &req, HttpResponse *rsp, Handlers &handlers) {}
void OnMessage(const ptrConnection &conn, Buffer *buf)
{
while (buf->MayReadSize() > 0)
{
//获取上下文
HttpContext *context = conn->GetContext()->get();
//通过上下文对缓冲区数据进行解析,得到HttpRequest对象
context->RecvHttpRequest(buf);
HttpRequest &req = context->Request();
HttpResponse rsp(context->RespStatu());
if (context->RespStatu() >= 400)
{
ErrorHandler(req, &rsp); //填充一个错误显示页面数据到rsp中
WriteReponse(conn, req, rsp); //组织响应发送给客户端
context->ReSet();
buf->ReadMovesBack(buf->MayReadSize());
conn->Shutdown();
return ;
}
if (context->RecvStatu() != RECV_HTTP_OVER)
{
return;
}
//请求路由 + 业务处理
Route(req, &rsp);
//对HttpResponse进行组织发送
WriteReponse(conn, req, rsp);
//重置上下文
context->ReSet();
//根据长短连接判断是否关闭连接或者继续处理
if (rsp.Close() == true)
conn->Shutdown();
}
return;
}
public:
HttpServer(int port, int timeout = DEFALT_TIMEOUT) : _server(port)
{
_server.EnableInactiveRelease(timeout);
_server.SetConnectedCallback(std::bind(&HttpServer::OnConnected, this, std::placeholders::_1));
_server.SetMessageCallback(std::bind(&HttpServer::OnMessage, this, std::placeholders::_1, std::placeholders::_2));
}
void SetBaseDir(const std::string &path)
{
assert(Util::IsDirectory(path) == true);
_basedir = path;
}
/*设置/添加,请求(请求的正则表达)与处理函数的映射关系*/
void Get(const std::string &pattern, const Handle &handler)
{
_get_route.push_back(std::make_pair(std::regex(pattern), handler));
}
void Post(const std::string &pattern, const Handle &handler)
{
_post_route.push_back(std::make_pair(std::regex(pattern), handler));
}
void Put(const std::string &pattern, const Handle &handler)
{
_put_route.push_back(std::make_pair(std::regex(pattern), handler));
}
void Delete(const std::string &pattern, const Handle &handler)
{
_delete_route.push_back(std::make_pair(std::regex(pattern), handler));
}
void SetThreadCount(int count)
{
_server.SetThreadCount(count);
}
void Listen()
{
_server.Start();
}
};