JavaWeb-Listener监听器
目录
监听器Listener
1.功能
2.监听器分类
3.监听器的配置
4.ServletContext监听
5.HttpSession监听
6.ServletRequest监听
监听器Listener
1.功能
- 用于监听域对象ServletContext、HttpSession和ServletRequest的创建,与销毁事件
- 监听一个对象的事件,如果发生了某事件则可以执行相应的代码
默认的优先级别:Listener>Filter>Servlet
2.监听器分类
由于事件的复杂性,监听器也有许多对应的监听器。总体上按照作用域可以分为以下三类
- Servlet上下文相关监听接口,包括ServletContextListener、ServletAttributeListener
- HTTP会话监听接口,包括HttpSessionListener、HttpActivationListener等
- Servlet请求监听接口,包括ServletRequestListener、ServletRequestAttributeListener
3.监听器的配置
1.通过xml配置
com.company.Listener.ListenerDemo1
2.通过注解类配置
@WebListener只需要填写@WebListener即可
4.ServletContext监听
通过实现ServletContext接口实现监听器功能
1.生命周期监听
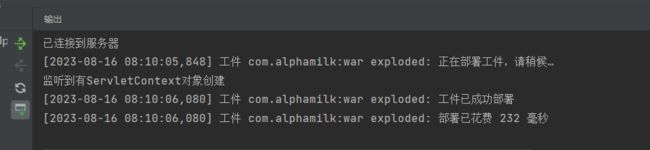
ServletContext的生命周期监听,监听ServletContext对象的创建与销毁方法如下
| 方法名 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| contextInitialized() | 当ServletContext对象被创建时,容器会自动调用该方法。在这个方法中,你可以执行一些初始化操作,比如加载配置文件、建立数据库连接等。 |
| contextDestroyed() | 当ServletContext对象被销毁时,容器会自动调用该方法。在这个方法中,你可以执行一些清理操作,比如释放资源、关闭数据库连接等。 |
package com.company.Listener;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextEvent;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextListener;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener;
//使用注解类配置
@WebListener
public class ListenerDemo1 implements ServletContextListener {
// 在创建出ServletContext对象时候自动调用函数
@Override
public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent servletContextEvent) {
System.out.println("监听到有ServletContext对象创建");
}
// 检测到ServletContext对象被销毁
@Override
public void contextDestroyed(ServletContextEvent servletContextEvent) {
System.out.println("监听到有ServletContext对象被销毁");
}
}
具体案例代码:
创建ServletContext对象代码:
package com.company;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebServlet("/ServletContextDemo1")
public class ServletContextDemo1 extends HttpServlet{
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 创建ServletContext对象
ServletContext context = req.getServletContext();
System.out.println("ServletContextDemo1被调用");
}
// 实现方法统一
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doPost(req, resp);
}
}
2.属性监听
通过实现ServletContextAttributeListener接口实现监听属性的添加、替换、修改的功能,方法如下
| 方法名 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| attributeAdded() | 当向ServletContext、HttpSession或ServletRequest添加属性时,容器会自动调用该方法。在这个方法中,你可以对添加的属性进行处理。 |
| attributeReplaced() | 当ServletContext、HttpSession或ServletRequest中的属性被替换时,容器会自动调用该方法。在这个方法中,你可以对替换后的属性进行处理。 |
| attributeRemoved() | 当ServletContext、HttpSession或ServletRequest中的属性被移除时,容器会自动调用该方法。在这个方法中,你可以对移除的属性进行处理 |
案例代码:
监听器类代码
package com.company.Listener;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextAttributeEvent;
import javax.servlet.ServletContextAttributeListener;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener;
@WebListener
public class ListenerDemo2 implements ServletContextAttributeListener {
// 当新创建一个ServletContext对象时候调用
@Override
public void attributeAdded(ServletContextAttributeEvent servletContextAttributeEvent) {
// 获取域对象
ServletContext context = servletContextAttributeEvent.getServletContext();
// 获取新增的域 名和值
String name = servletContextAttributeEvent.getName();
Object value = servletContextAttributeEvent.getValue();
// 输出修改对象
System.out.println("域对象"+context+"范围内增加了"+name+"值为"+value);
}
// 当ServletContext对象被移除的时候执行
@Override
public void attributeRemoved(ServletContextAttributeEvent servletContextAttributeEvent) {
ServletContext context = servletContextAttributeEvent.getServletContext();
String name = servletContextAttributeEvent.getName();
Object value = servletContextAttributeEvent.getValue();
System.out.println("域对象"+context+"范围内删除了"+name+"值为"+value);
}
@Override
public void attributeReplaced(ServletContextAttributeEvent servletContextAttributeEvent) {
ServletContext context = servletContextAttributeEvent.getServletContext();
String name = servletContextAttributeEvent.getName();
Object value = servletContextAttributeEvent.getValue();
System.out.println("域对象"+context+"范围内替换了"+name+"值为"+value);
}
}
Servlet属性类代码
package com.company;
import javax.servlet.ServletContext;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebServlet("/ServletContextDemo3")
public class ServletContextDemo3 extends HttpServlet{
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException{
ServletContext context = req.getServletContext();
// 创建context域对象值
context.setAttribute("msg","Hello");
// 替换对象内容
context.setAttribute("msg","你好");
// 销毁对象
context.removeAttribute("msg");
}
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doPost(req, resp);
}
}
5.HttpSession监听
通过实现接口HttpSessionListener实现HttpSession。HttpSession对象监听有三种方式,1.生命周期监听、2.属性监听、3.session监听
1.生命周期监听
| 方法名 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| sessionCreated() | 当一个新的HttpSession对象被创建时,容器会自动调用该方法。在这个方法中,你可以对新创建的HttpSession对象进行处理。 |
| sessionDestroyed() | 当一个HttpSession对象被销毁时,容器会自动调用该方法。在这个方法中,你可以对销毁的HttpSession对象进行处理。 |
监听类代码
package com.company.Listener;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionEvent;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionListener;
@WebListener
public class ListenerDemo3 implements HttpSessionListener {
// 当session被创建时候调用
@Override
public void sessionCreated(HttpSessionEvent httpSessionEvent) {
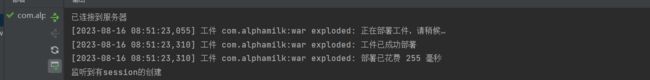
System.out.println("监听到有session的创建");
}
// 当session被销毁时候调用
@Override
public void sessionDestroyed(HttpSessionEvent httpSessionEvent) {
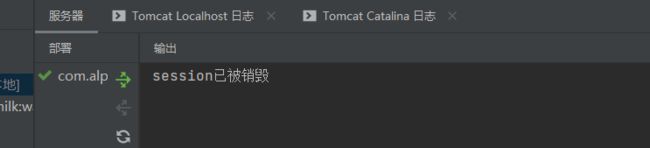
System.out.println("session已被销毁");
}
}
Servlet实现代码
package com.company;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebServlet("/SessionListenerDemo1")
public class SessionListenerDemo1 extends HttpServlet{
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
// 创建session
HttpSession session = req.getSession();
session.setAttribute("name","AlphaMilk");
// 销毁session
session.invalidate();
}
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doPost(req, resp);
}
}
2.属性监听
| 方法名 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| attributeAdded() | 当一个属性被添加到HttpSession对象中时,容器会自动调用该方法。在这个方法中,你可以对新添加的属性进行处理。 |
| attributeReplaced() | 当一个属性在HttpSession对象中被替换时,容器会自动调用该方法。在这个方法中,你可以对替换的属性进行处理。 |
| attributeRemoved() | 当一个属性从HttpSession对象中被移除时,容器会自动调用该方法。在这个方法中,你可以对被移除的属性进行处理 |
案例代码:
监听类
package com.company.Listener;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebListener;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionAttributeListener;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSessionBindingEvent;
@WebListener
public class ListenerDemo4 implements HttpSessionAttributeListener {
// 当session属性增加时候调用
@Override
public void attributeAdded(HttpSessionBindingEvent httpSessionBindingEvent) {
System.out.println("Session添加了一个新的属性");
}
// 当session属性销毁时候调用
@Override
public void attributeRemoved(HttpSessionBindingEvent httpSessionBindingEvent) {
System.out.println("Session销毁了一个属性");
}
// 当session属性替换时候调用
@Override
public void attributeReplaced(HttpSessionBindingEvent httpSessionBindingEvent) {
System.out.println("Session替换了一个属性");
}
}
Servlet实现类
package com.company;
import javax.servlet.ServletException;
import javax.servlet.annotation.WebServlet;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpSession;
import java.io.IOException;
@WebServlet("/SessionDemo5")
public class SessionDemo5 extends HttpServlet{
@Override
protected void doPost(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
HttpSession session = req.getSession();
// 增加属性
session.setAttribute("userName","AlphaMilk");
// 属性覆盖
session.setAttribute("userName","alpha");
// 属性删除
session.removeAttribute("userName");
}
@Override
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest req, HttpServletResponse resp) throws ServletException, IOException {
this.doPost(req, resp);
}
}
6.ServletRequest监听
与上述几个接口类似,分别由生命周期监听与属性监听
1.生命周期监听
| 方法名 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| requestInitialized() | 当一个ServletRequest对象被创建并初始化时,容器会自动调用该方法。在这个方法中,你可以对新创建的ServletRequest对象进行处理。 |
| requestDestroyed() | 当一个ServletRequest对象被销毁时,容器会自动调用该方法。在这个方法中,你可以对销毁的ServletRequest对象进行处理。 |
2.属性监听
| 方法名 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| attributeAdded() | 当一个属性被添加到ServletRequest对象中时,容器会自动调用该方法。在这个方法中,你可以对新添加的属性进行处理。 |
| attributeReplaced() | 当一个属性在ServletRequest对象中被替换时,容器会自动调用该方法。在这个方法中,你可以对替换的属性进行处理。 |
| attributeRemoved() | 当一个属性从ServletRequest对象中被移除时,容器会自动调用该方法。在这个方法中,你可以对被移除的属性进行处理 |