网络套接字
网络套接字
文章目录
- 网络套接字
-
-
- 认识端口号
- 初识TCP协议
- 初识UDP协议
- 网络字节序
- socket编程接口
-
-
- socket创建socket文件描述符
- bind绑定端口号
- sockaddr结构体
-
- netstat -nuap:查看服务器网络信息
- 代码编译运行展示
-
- 实现简单UDP服务器开发
-
认识端口号
端口号(port)是传输层协议的内容
- 端口号是一个2字节16位的整数。在Linux系统下其类型为
uint16_t - 端口号用来标识一个进程, 告诉操作系统, 当前的这个数据要交给哪一个进程来处理
- IP地址 + 端口号能够标识网络上的某一台主机的某一个进程
- 一个端口号只能被一个进程占用
初识TCP协议
先对TCP((Transmission Control Protocol)有一个直观的认识,它有以下性质
- 传输层协议
- 有连接
- 可靠传输
- 面向字节流
初识UDP协议
先对对UDP(User Datagram Protocol)有一个直观的认识,它有以下性质
- 传输层协议
- 无连接
- 不可靠传输
- 面向数据报
网络字节序
内存中的多字节数据相对于内存地址有大端和小端之分, 磁盘文件中的多字节数据相对于文件中的偏 移地址也有大端小端之分, 网络数据流同样有大端小端之分. 那么如何定义网络数据流的地址呢?
首先先回顾一下大小端
- 发送主机通常将发送缓冲区中的数据按内存地址从低到高的顺序发出
- 接收主机把从网络上接到的字节依次保存在接收缓冲区中,也是按内存地址从低到高的顺序保存
- 因此,网络数据流的地址应这样规定:先发出的数据是低地址,后发出的数据是高地址
- TCP/IP协议规定,网络数据流应采用大端字节序,即低地址存放高字节,高地址存放低字节
- 不管这台主机是大端机还是小端机, 都会按照这个TCP/IP规定的网络字节序来发送/接收数据,如果当前发送主机是小端, 就需要先将数据转成大端; 否则就忽略, 直接发送即可
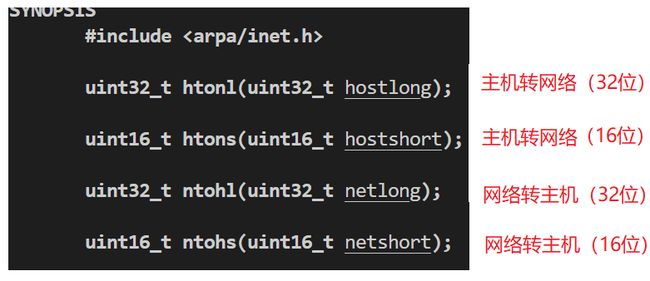
为了使得网络程序具备可移植性,使得同样的代码在大端和小端计算机上编译后都能运行,可以调用以下库函数,使得网络字节序和主机字节序的相互转换。
#include - h表示host,n表示network,l表示32位长整数,s表示16位短整数。
- 例如
htonl(uint16_t hostshort)意思是将16位的短整形主机字节序转换成网络字节序,例如端口号的发送 - 如果主机是小端字节序,这些函数将参数做相应的大小端转换然后返回,如果主机是大端字节序,这些函数不做转换,将参数原封不动地返回
socket编程接口
socket创建socket文件描述符
函数原型
#include -
domain指协议域,常见的协议有AF_INET(ipv4) AF_INET6(ipv6) AF_LOCAL(本地协议)。协议决定了socket的地址类型,在通信中必须采用相应的地址。例如使用的是ipv4的协议,那么参数需要传AF_INET
-
type为socket的类型,主要分为流格式套接字(SOCK_STREAM)即使用TCP协议和数据报格式,也因此称之为面向连接的套接字,是一种可靠的、双向的通信数据流.它的数据可以准确无误的到达另一台里算计,如果损坏或者丢失会重新发送套接字;(SOCK_DGRAM)即使用UDP协议,也因此称之为无连接的套接字,计算机只负责传输数据,不进行数据校验
-
protocol默认输入0
-
若创建成功,返回值是一个socket文件描述符,若创建失败,返回-1,错误信息保存在错误码
bind绑定端口号
函数原型
#include - socket指需要绑定的socket文件描述符
- address指一个指向特定协议的地址结构的指针
- address_len指该地址结构的长度。
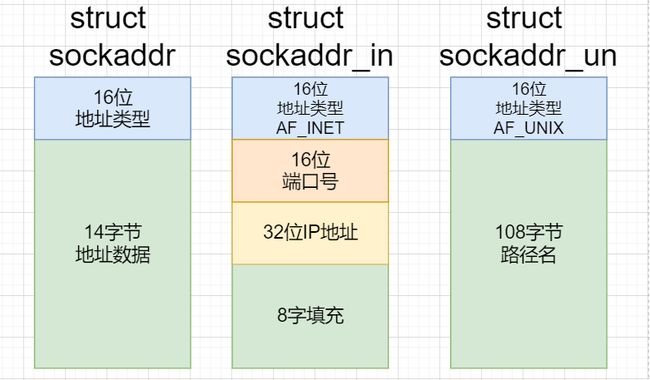
sockaddr结构体
很多网络编程函数诞生早于IPv4协议,那时候都使用的是sockaddr结构体,为了向前兼容,现在sockaddr退化成了(void *)的作用,传递一个地址给函数,至于这个函数是sockaddr_in还是其他的,由地址族确定,然后函数内部再强制类型转化为所需的地址类型。
sackaddr_in结构源码
struct sockaddr_in
{
__SOCKADDR_COMMON(sin_);
int_port_t sin_port; /*Port number. */
struct in_addr sin_addr; /*Internet address. */
/*Pad to size of 'struct sockaddr'. */
unsigned char sin_zero[sizeof(struct sockaddr)-
__SOCKADDR_COMMON_SIZE-
sizeof(in_port_t)-
sizeof(struct in_addr)];
}
__SOCKADDR_COMMON的宏定义
#define __SOCKADDR_COMMON_(sa_prefix)
sa_family_t sa_prefix##fimily
- 第一个成员传sin_进去,##具有将左右两个符号合并成一个符号的作用,因此返回sin_family,参数类型是sa_family_t ,该参数称为协议家族,对应sackaddr_in结构的16位地址类型
- sin_port成员指对应的端口号,其类型是uint16_t
- sin_addr成员指对应的IP地址,其类型是uint32_t。实际上这个类型用于网络通信,而常见的192.155.172.83这样风格的IP地址类型是string,又被称为点分十进制,这个类型唯一的用处是可读性好,专门用于在用户机上供用户读取。实际上OS提供有相应接口供类型uint32_t和string类型的相互转换
- 剩余部分用于填充结构体剩余部分
in_addr结构源码
/* Internet address. */
typedef uint32_t in_addr_t;
struct in_addr
{
in_addr_t s_addr;
};
- in_addr结构体内有一个in_addr_t类型的s_addr变量,实际上是用的这个变量接收的IP地址
需要注意的是:
- 对于虚拟机用户来说,填入sackaddr_in结构体中的ip地址不能填入公网ip即连接上虚拟机使用的公网ip。但可以填入内网ip
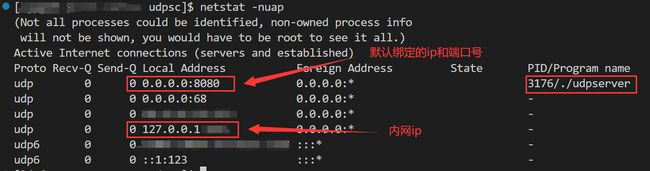
netstat -nuap:查看服务器网络信息
根据上面的接口可以写出server端的部分代码
netstat -nupa
server.c
1 #include"server.hpp"
2 #include<memory>
3
4 using namespace std;
5 using namespace udpServer ;
6 static void Usage(string proc)
7 {
8 cerr<<"Usage: \n\t"<<proc<<" serverport"<<endl;
9 }
10 int main(int argc,char* argv[])
11 {
12 if(argc!=2)
13 {
14 Usage(argv[0]);
15 exit(USAGE_ERR);
16 }
17
18 uint16_t port=atoi(argv[1]);//atoi作用:把port的str类型转化成int类型。而uin16_t本质类型是int
19
20 unique_ptr<udpserver> uspr(new udpserver(port));
21 uspr->initudpserver();//初始化服务端
22 uspr->start();//启动服务端
23 return 0;
24 }
server.hpp
1 #pragma once
2 #include<iostream>
3 #include <sys/types.h>
4 #include <sys/socket.h>
5 #include <netinet/in.h>
6 #include <arpa/inet.h>
7 #include <errno.h>
8 #include <strings.h>
9 #include <stdlib.h>
10 #include <string.h>
11 #include<unistd.h>
12 using namespace std;
13
14 namespace udpServer
15 {
16 static const string defaultIP="0.0.0.0";//默认IP地址
17 static int SIZE=1024;
18 enum {USAGE_ERR=1,SOCKET_ERR,BIND_ERR,OPEN_ERR};//用枚举函数定义各自错误的返回值
19 class udpserver
20 {
21 public:
22
23 udpserver(const uint16_t& port,const string& ip=defaultIP)
24 :_port(port)
25 ,_ip(ip)
26 ,_sockfd(-1)
27 {}
28
29 void initudpserver()
30 {
31 //1.创建套接字
32 _sockfd=socket(AF_INET,SOCK_DGRAM,0);//创建套接字文件描述符
33 if(_sockfd==-1)
34 {
35 cerr<<"socket err"<<errno<<" : "<<strerror(errno)<<endl;
36 exit(SOCKET_ERR);
37 }
38 cout<<"socket success"<<": "<< _sockfd<<endl;
39 //2.绑定port端口号
40 //2.1将port和ip填入结构体中,该结构体可以理解成用户定义的数据或用户栈
41 struct sockaddr_in local;//创建结构
42 bzero(&local,sizeof(local));//将结构清零
43 local.sin_family=AF_INET;//填充协议家族
44 local.sin_port=htons(_port);//填充端口号。htons将port主机序列转化为网络序列
45 //local.sin_addr.s_addr=inet_addr(_ip.c_str());
46 //填充ip地址。inet_addr函数作用:将ip地址的string类型转化为uint32_t,其次ip地址的将主机序列转化为网络序> 列
47 local.sin_addr.s_addr=htons(INADDR_ANY);//不绑定指定ip,可以接收任何传达到指定端口号的ip主机发的数据
48 //2.2将sockaddr_in与套接字进行绑定
49 int n=bind(_sockfd,(struct sockaddr*)&local,sizeof(local));
50 if(n==-1)
51 {
52 cerr<<"bind err"<<errno<<" : "<<strerror(errno)<<endl;
53 exit(BIND_ERR);
54 }
55 }
56
57 void start()
58 {
59 for(;;)
60 {
61 char buffer[SIZE];//缓冲区
62 struct sockaddr_in out;
63 socklen_t len=sizeof(out);
64 ssize_t s=recvfrom(_sockfd,buffer,sizeof(buffer)-1,0,(sockaddr*)&out,&len);
65 if(s>0)
66 {
67 buffer[s]=0;
68 string clientip=inet_ntoa(out.sin_addr);//网络序列转换为主机序列;uin32t_t->string
69 uint16_t clientport=ntohs(out.sin_port);//网络序列转化为主机序列
70 string message=buffer;
71 cout<<clientip<<"["<<clientport<<"]# "<<message<<endl;
72 }
73 }
74 }
75
76 ~udpserver()
77 {}
78
79 private:
80 uint16_t _port;//端口号
81 string _ip;//ip地址
82 int _sockfd;//套接字文件描述符
83 };
84 }
-
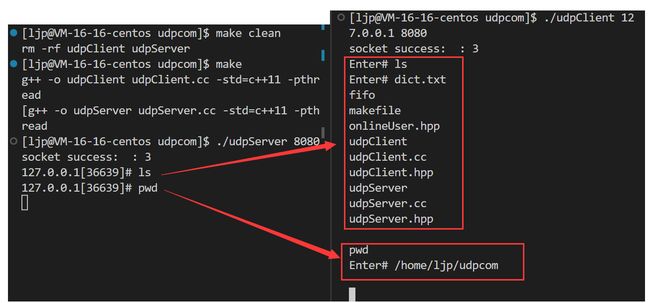
根据server.hpp的47行可知:server端(服务端)不能绑定指定ip地址,绑定ip地址意味着只接收指定ip地址和端口号的主机发来的报文;而不绑定ip地址可以接收任意ip地址的主机只需绑定指定端口号即发送报文給服务端。因此在server.cc只需要传参端口号port
-
server.hpp中start启动函数内是个死循环,即服务器本质是一个死循环,这个进程被称为常驻内存进程sockaddr_in类型的结构的ip地址INADDR_ANY就是全0,即接收任意绑定了对应端口的进程发送来的数据。
-
server.hpp的42行的bzero函数用于将local结构体清零
bzero函数原型
#include 将参数s 所指的内存区域前n 个字节全部设为零
- 第64行recvfrom用于从一个已连接的套接字接收数据的函数。它的作用是从指定的套接字接收数据,并将接收到的数据保存到指定的缓冲区中。
recvfrom函数原型
#include - sockfd是接收数据的套接字文件描述符
- buf是接收数据存放缓冲区
- len是缓冲区的大小
- flags是标志位默认为0表示阻塞式读取
- src_addr是输入输出型参数,用于接收发送端发来的数据信息如ip和port。这里要传参结构体的地址
- addrlen是src_addr结构体大小,这里要传参地址
- 第68行inet_ntoa函数用于将网络字节序的IP地址转换为点分十进制的字符串形式。一是将uint32_t类型转化为string类型,二是将网络序列转化为主机序列
函数原型
#include - in_addr表示网络字节序的IPv4地址的结构体
需要注意的是:
- 云服务器的公网ip不能绑定,由于该服务器是虚拟服务器,因此公网ip也是虚拟ip,但内网ip:127.0.0.1可以绑定。而服务端绑定127.0.0.1,客户端接收数据,即数据完成了本地环回。在这个过程代码数据的传输不会到达物理层。

- netstat -nuap:查看服务器网络信息
client.cc
#includeclient.hpp
1 #pragma once
2 #include <iostream>
3 #include <string>
4 #include <strings.h>
5 #include <cerrno>
6 #include <cstring>
7 #include <cstdlib>
8 #include <unistd.h>
9 #include <sys/types.h>
10 #include <sys/socket.h>
11 #include <arpa/inet.h>
12 #include <netinet/in.h>
13 #include <pthread.h>
14 using namespace std;
15 namespace udpClient
16 {
17 class udpclient
18 {
19 public:
20 udpclient(const string& ip,const uint16_t port)
21 :_serverip(ip)
22 ,_serverport(port)
23 ,_sockfd(-1)
24 ,flag(false)
25 {}
26 void initclient()
27 {
28 //1.创建套接字
29 _sockfd=socket(AF_INET,SOCK_DGRAM,0);
30 if(_sockfd==-1)
31 {
32 cout<<"socket error"<<errno<<":"<<strerror(errno)<<endl;
33 exit(2);
34 }
35 cout<<"socket success: "<<_sockfd<<endl;
36 //2.绑定,但不用显示绑定,OS会自动绑定指定ip和端口
37 }
38 void run()
39 {
40 // pthread_create(&_pt,nullptr,readmessage,(void*)&_sockfd);
41
42 struct sockaddr_in server;
43 server.sin_family=AF_INET;
44 server.sin_addr.s_addr=inet_addr(_serverip.c_str());//主机序列转换为网络序列;string->uin32t_t
45 server.sin_port=htons(_serverport);//主机序列转换为网络序列
46
47 string message;
48 char cmdbuffer[1024];
49 while(!flag)
50 {
51 fprintf(stderr,"enter# ");
52 fflush(stderr);
53 fgets(cmdbuffer,sizeof(cmdbuffer),stdin);//键盘上的内容写入缓冲区cmdbuffer
54 cmdbuffer[strlen(cmdbuffer)-1]=0;
55 message=cmdbuffer;
56 sendto(_sockfd,message.c_str(),message.size(),0,(struct sockaddr*)&server,sizeof(server));
57 //将缓冲区的内容发送到套接字里通常用于UDP
58 }
59 }
60 ~udpclient(){}
61 private:
62 int _sockfd;
63 string _serverip;
64 uint16_t _serverport;
65 bool flag;
66 };
67 }
- client.cc中atoi函数用于将我们命令行输入的端口号string类型转化成int类型,而uin16_t本质类型是int
- client.hpp56行sendto函数是在Linux系统下用于发送数据报的函数。它可以向指定的socket文件描述符中发送数据报,适用于面向无连接的UDP套接字或以connectionless模式工作的AF_INET套接字。
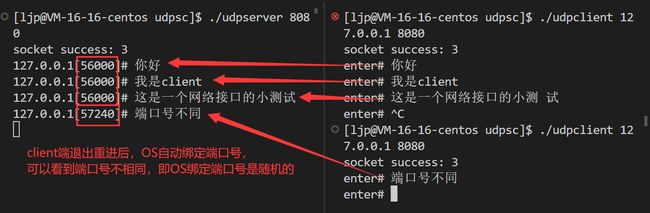
- 可以看到在client端无需bind指定端口号和ip地址。一个端口只能被一个进程绑定,若客户端绑定指定端口,其他客户端就不能往该端口中发数据了。因此客户端不需要自主绑定,OS会自动绑定。在第一次发送数据时OS会帮我们绑定ip和端口即使用sendto函数时。而OS帮我们绑定端口是随机的。
sendto函数原型
#include - sockfd是传入数据报指定的socket文件描述符
- buf是需要传输数据的缓冲区
- len是缓冲区的大小
- flags是标志位默认为0表示阻塞式读取
- dest_addr是输入型参数,用于发送数据信息如ip和port。这里要传参结构体的地址
- addrlen是dest_addr结构体的大小
代码编译运行展示
- udpclient发送一条信息,udpserver接收一条信息。另外可以将udpserver打包发送到另一台服务器,该台服务器运行后输入8080端口号,本主机发送的信息在该台服务器也能接收到!
若绑定了IP地址,那么服务器只能接收改绑定的IP地址的数据,其他IP地址发送来的不能接收
INADDR_ANY:任意地址绑定,任何绑定了8080ip的地址都能发数据来并接收(全0)
socket函数原型
#include -
domain:协议域,常见的协议组用AF_INET(ipv4) AF_INET6(ipv6) AF_LOCAL AF_ROUTE . 协议族决定了socket的地址类型,在通信中必须采用相应的地址
-
type为socket的类型,主要分为流格式套接字(SOCK_STREAM)即使用TCP协议和数据报格式套接字(SOCK_DGRAM)即使用UDP协议
-
默认输入0
bind
#include - 套接字
- sockaddr结构体地址
- 结构体大小
recvfrom
recvfrom函数是用于从一个已连接的套接字接收数据的函数。它的作用是从指定的套接字接收数据,并将接收到的数据保存到指定的缓冲区中。
#include - socket文件描述符
- 缓冲区
- 缓冲区大小
- 标志位默认为0表示阻塞式读取
- 存储的结构体地址
- 结构体大小
- src_addr是输入输出型参数,用于接收发送端发来的数据信息如ip和port
- 读取成功返回读取到的字节数,读取失败返回-1
inet_ntoa()将网络序列转化为主机序列,将整数转化为字符串类型
课里讲的主要是代码和接口
inet_addr
inet_addr是一个用于将点分十进制表示的IP地址转换成网络字节序的32位二进制IP地址的函数。该函数定义在C语言的头文件
中。一是将string类型转化为uint32_t类型,二是将主机序列转化为网络序列
#include - cp指主机序列string类型的ip
sendto
用于通过指定的套接字向目标地址发送数据。该函数通常用于面向无连接的协议(如UDP)中发送数据报。
#include - sockfd是套接字描述符,指定要发送数据的套接字
- buf是指向要发送的数据的缓冲区的指针
- len是要发送的数据的长度
- flags是发送操作的标志位,通常设置为 0,即为阻塞式发送
- dest_addr是指向目标地址的结构体指针,包括目标 IP 地址和端口号
- addrlen是目标地址结构体的长度
实现简单UDP服务器开发
makefile
.PHONY:all
all:udpClient udpServer
udpClient:udpClient.cc
g++ -o $@ $^ -std=c++11 -pthread
udpServer:udpServer.cc
g++ -o $@ $^ -std=c++11 -pthread
.PHONY:clean
clean:
rm -rf udpClient udpServer
udpClient.cc
#include "udpClient.hpp"
#include - 先创建一个udpClient对象,然后调用对象的initClient和run函数
udpClient.hpp
#pragma once
#include - Client端的父进程进行sendto操作,子进程进行recvfrom操作。在客户端的命令行解析器输入数据后,客户端将数据sendto給服务器。服务器进行数据处理后,sendto回来給客户端,客户端的子进程进行recvfrom接收数据并打印
udpServer.hpp
#pragma once
#include udpServer.cc
#include "udpServer.hpp"
#include "onlineUser.hpp"
#include usvr(new udpServer(handlerMessage, port));
// std::unique_ptr usvr(new udpServer(execCommand, port));
std::unique_ptr<udpServer> usvr(new udpServer(routeMessage, port));
usvr->initServer();
usvr->start();
return 0;
}
demo1:实现一个英译中服务
static bool cutString(const string &target, string *s1, string *s2, const string &sep)
{
auto pos = target.find(sep);
if(pos == string::npos) return false;
*s1 = target.substr(0, pos);
*s2 = target.substr(pos + sep.size());
return true;
}
static void initDict()
{
ifstream in(dictTxt, std::ios::binary);
if(!in.is_open())
{
cerr << "open file " << dictTxt << " error" << endl;
exit(OPEN_ERR);
}
string line;
std::string key, value;
while(getline(in, line))
{
if(cutString(line, &key, &value, ":"))
{
dict.insert(make_pair(key, value));
}
}
in.close();
cout << "load dict success" << endl;
}
void reload(int signo)
{
(void)signo;
initDict();
}
// // demo1
void handlerMessage(int sockfd, string clientip, uint16_t clientport, string message)
{
// 就可以对message进行特定的业务处理,而不关心message怎么来的 ---- server通信和业务逻辑解耦!
// 婴儿版的业务逻辑
string response_message;
auto iter = dict.find(message);
if(iter == dict.end()) response_message = "unknown";
else response_message = iter->second;
// 开始返回
struct sockaddr_in client;
bzero(&client, sizeof(client));
client.sin_family = AF_INET;
client.sin_port = htons(clientport);
client.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(clientip.c_str());
sendto(sockfd, response_message.c_str(), response_message.size(), 0, (struct sockaddr*)&client, sizeof(client));
}
// ./udpServer port
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc != 2)
{
Usage(argv[0]);
exit(USAGE_ERR);
}
uint16_t port = atoi(argv[1]);
// string ip = argv[1];
signal(2, reload);
// initDict();
std::unique_ptr<udpServer> usvr(new udpServer(handlerMessage, port));
usvr->initServer();
usvr->start();
return 0;
}
- 在客户端输入后将数据sendto給服务器,服务器对数据进行recvfrom接收,接收后进行解析,若输入的数据在unordermap dict的键值中,就将键值对应的value返回,而键值是英文,value是英文对应的中文。对应关系保存在当前目录的dict.txt文件中
dict.txt文件中数据对应关系
| apple | 苹果 |
|---|---|
| banana | 香蕉 |
| hello | 你好 |
| goodman | 好人 |
- 启动服务器后,需要先发送2号信号加载dict.txt文件,即热加载
demo2:将客户端发送来的代码当作命令行在服务器上做解析,即客户端输入命令对服务器进行命令行操作,操作后的服务器命令行解析器的结果返回給客户端
void execCommand(int sockfd, string clientip, uint16_t clientport, string cmd)
{
//1. cmd解析,ls -a -l
//2. 如果必要,可能需要fork, exec*
if(cmd.find("rm") != string::npos || cmd.find("mv") != string::npos || cmd.find("rmdir") != string::npos)
{
cerr << clientip << ":" << clientport << " 正在做一个非法的操作: " << cmd << endl;
return;
}
string response;
FILE *fp = popen(cmd.c_str(), "r");
if(fp == nullptr) response = cmd + " exec failed";
char line[1024];
while(fgets(line, sizeof(line), fp))
{
response += line;
}
pclose(fp);
// 开始返回
struct sockaddr_in client;
bzero(&client, sizeof(client));
client.sin_family = AF_INET;
client.sin_port = htons(clientport);
client.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(clientip.c_str());
sendto(sockfd, response.c_str(), response.size(), 0, (struct sockaddr*)&client, sizeof(client));
}
// ./udpServer port
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc != 2)
{
Usage(argv[0]);
exit(USAGE_ERR);
}
uint16_t port = atoi(argv[1]);
std::unique_ptr<udpServer> usvr(new udpServer(execCommand, port));
usvr->initServer();
usvr->start();
return 0;
}
- popen函数执行cmd字符串里的命令,然后通过fgets按行读取将执行后的结果写入response字符串中,再通过sendto函数返回給client端
popen函数用于在一个子进程中执行一个 shell 命令,并建立一个与该子进程之间的管道,以便可以通过管道进行输入输出操作。
#include - command是要执行的 shell 命令,以字符串形式传递
- 指定管道的类型,可以是
"r"(读取模式)或"w"(写入模式) popen函数将返回一个文件流指针(FILE *),您可以使用该指针进行读取或写入操作,具体取决于您指定的管道类型。当不再需要时,应使用pclose函数来关闭子进程并释放资源
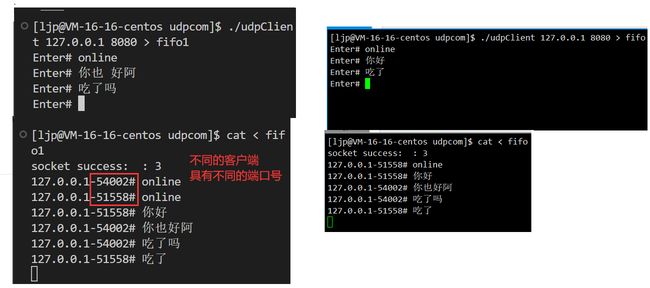
demo3:在客户端输入online上线,在服务器接收客户端发送来消息,当客户端发送online給服务器时,客户端才算上线成功,那么服务器才会将客户端发送来的信息返回給客户端
OnlineUser.hpp
#pragma once
#include OnlineUser onlineuser;
// demo3
void routeMessage(int sockfd, string clientip, uint16_t clientport, string message)
{
if (message == "online") onlineuser.addUser(clientip, clientport);
if (message == "offline") onlineuser.delUser(clientip, clientport);
if (onlineuser.isOnline(clientip, clientport))
{
// 消息的路由
onlineuser.broadcastMessage(sockfd, clientip, clientport, message);
}
else
{
struct sockaddr_in client;
bzero(&client, sizeof(client));
client.sin_family = AF_INET;
client.sin_port = htons(clientport);
client.sin_addr.s_addr = inet_addr(clientip.c_str());
string response = "你还没有上线,请先上线,运行: online";
sendto(sockfd, response.c_str(), response.size(), 0, (struct sockaddr *)&client, sizeof(client));
}
}
// ./udpServer port
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
if (argc != 2)
{
Usage(argv[0]);
exit(USAGE_ERR);
}
uint16_t port = atoi(argv[1]);
std::unique_ptr<udpServer> usvr(new udpServer(routeMessage, port));
usvr->initServer();
usvr->start();
return 0;
}
- 只需要打开一个服务器server端,然后打开两个客户端,但要求各自新建命名管道fifo,将客户端接收到的信息通过命名管道读出来