Asp.Net Mvc 运行机制原理分析
最近一段时间接手过的项目都是基于Asp.Net的,以前对aspnet运行机制有一个大概的了解,总觉得不够透彻,按自己的理解来分析一下。
Asp.Net 运行机制
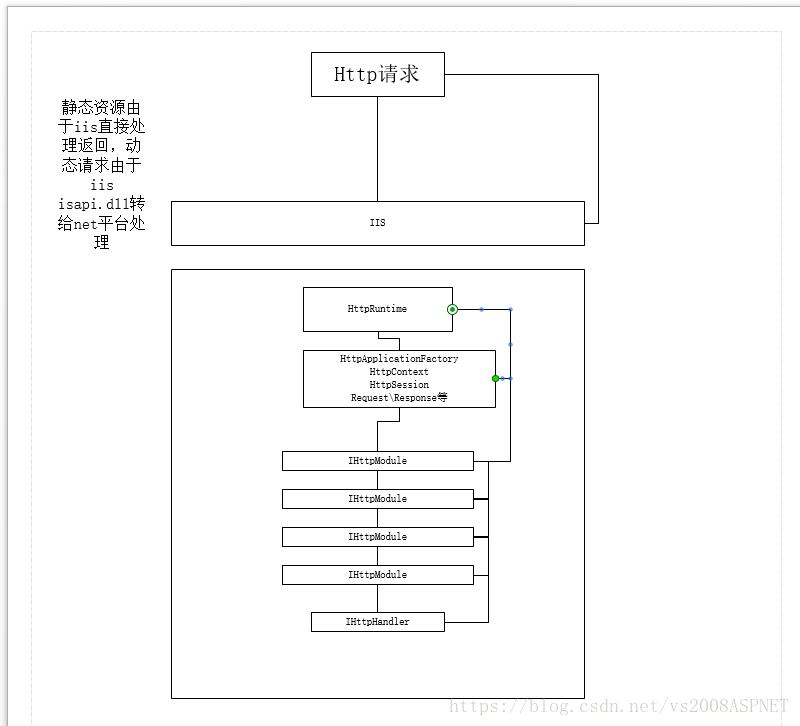
理解mvc运行原理的前提是要了解aspnet运行原理,这方面网上资料多如牛毛,我这里就大致说一下aspnet生命周期
Http请求到IIS后,如果是静态资源则IIS读取后返回客户端,动态请求被isap.dll 转发自net托管平台处理,首先HttpRuntime中创建Application,它是整个请求生命周期的开始,运行在单独的Appdomain中,在Application 中顺序调用所有已注册的Ihttpmodule,在IHttpModule中可以 "短路"(终止后续IHttpModule的执行),很多Web框架都是在这里做了文章,包括大名鼎鼎的Asp.Net Mvc, IHttpModule执行完后 最终请求被交给IHttpHandler, 在Handler中执行完毕后 再一层层返回到客户端。
ASP.NET MVC5 运行原理
这是来自微软官方的运行原理图
![]()
当前请求到达 IIS服务器后,同样动态请求被转发到net平台,在管道执行过程中(IHttpModule),有一个特殊的IHttpModule
它就是 UrlRoutingModule ,MVC从这里就开始了。
它 根据当前的HttpContext封装HttpContextWrapper,从Route路由表中取出和当前URL匹配的路由数据(RouteData),接着生成RequestContext对象,然后创建IHttpHandler这里是MvcHandler在MvcHandler中完成了图中处理管线的所有操作。
下面从源码级分析一次请求处理流程
当请求到达路由Module时,创建MvcHandler并将封装好的RequestContext请求上下文传递给它
public MvcHandler(RequestContext requestContext)
{
if (requestContext == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("requestContext");
}
RequestContext = requestContext;
}执行MvcHandler的BeginProcessRequest方法,创建HttpContextWrapper
protected virtual IAsyncResult BeginProcessRequest(HttpContext httpContext, AsyncCallback callback, object state)
{
HttpContextBase httpContextBase = new HttpContextWrapper(httpContext);
return BeginProcessRequest(httpContextBase, callback, state);
}在BeginProcess中实例化了Controller并执行对应的Action等,做了很多工作,一步步来分析
protected internal virtual IAsyncResult BeginProcessRequest(HttpContextBase httpContext, AsyncCallback callback, object state)
{
IController controller;
IControllerFactory factory;
ProcessRequestInit(httpContext, out controller, out factory);
IAsyncController asyncController = controller as IAsyncController;
if (asyncController != null)
{
// asynchronous controller
// Ensure delegates continue to use the C# Compiler static delegate caching optimization.
BeginInvokeDelegate beginDelegate = delegate(AsyncCallback asyncCallback, object asyncState, ProcessRequestState innerState)
{
try
{
return innerState.AsyncController.BeginExecute(innerState.RequestContext, asyncCallback, asyncState);
}
catch
{
innerState.ReleaseController();
throw;
}
};
EndInvokeVoidDelegate endDelegate = delegate(IAsyncResult asyncResult, ProcessRequestState innerState)
{
try
{
innerState.AsyncController.EndExecute(asyncResult);
}
finally
{
innerState.ReleaseController();
}
};
ProcessRequestState outerState = new ProcessRequestState()
{
AsyncController = asyncController, Factory = factory, RequestContext = RequestContext
};
SynchronizationContext callbackSyncContext = SynchronizationContextUtil.GetSynchronizationContext();
return AsyncResultWrapper.Begin(callback, state, beginDelegate, endDelegate, outerState, _processRequestTag, callbackSyncContext: callbackSyncContext);
}
else
{
// synchronous controller
Action action = delegate
{
try
{
controller.Execute(RequestContext);
}
finally
{
factory.ReleaseController(controller);
}
};
return AsyncResultWrapper.BeginSynchronous(callback, state, action, _processRequestTag);
}
} 在ProcessRequestInit 中,
首先在http响应报文中添加mvc版本信息
AddVersionHeader(httpContext);从本次请求的路由数据中得到Controller(控制器)名称
//得到控制器名称
string controllerName = RequestContext.RouteData.GetRequiredString("controller");
//从默认的控制器工厂创建控制器实例
factory = ControllerBuilder.GetControllerFactory();
controller = factory.CreateController(RequestContext, controllerName);
if (controller == null)
{
throw new InvalidOperationException(
String.Format(
CultureInfo.CurrentCulture,
MvcResources.ControllerBuilder_FactoryReturnedNull,
factory.GetType(),
controllerName));
}实例化后的Controller
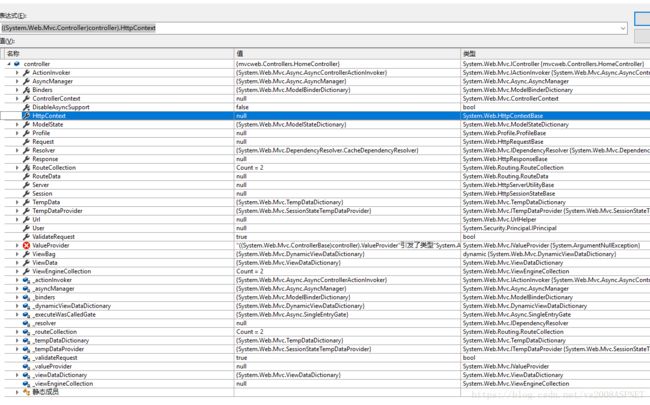
在这个实例化的控制器中,可以拿到很多相关的请求对象 Request Respone Model 等等,
接着如果Controller是异步则异步执行BeginExecute,否则直接执行Execute
Execute方法中执行注册的过滤器(Filter),然后通过反射调用我们的Action,执行完后返回IActionResult,这个IActionResult就是返回给客户端数据包装对象(可能不太贴切)。
处理完成后会执行factory.ReleaseController(controller); 以释放Controller
至此一次http请求在mvc中处理完毕。
有错误的地方望指正。