scala中json4s 使用详解
预备知识
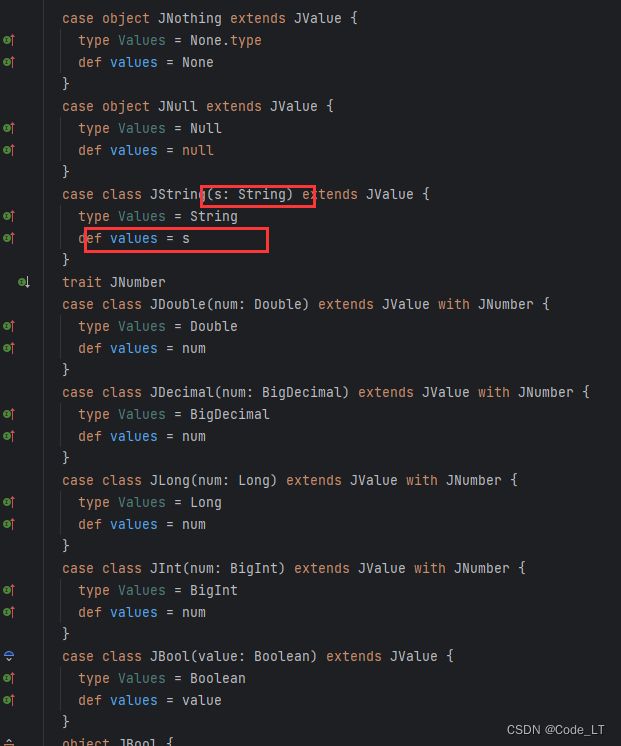
json4s的数据结构AST (Abstract Syntax Tree)。
sealed abstract class JValue
case object JNothing extends JValue // 'zero' for JValue
case object JNull extends JValue
case class JString(s: String) extends JValue
case class JDouble(num: Double) extends JValue
case class JDecimal(num: BigDecimal) extends JValue
case class JInt(num: BigInt) extends JValue
case class JBool(value: Boolean) extends JValue
case class JObject(obj: List[JField]) extends JValue
case class JArray(arr: List[JValue]) extends JValue
type JField = (String, JValue)
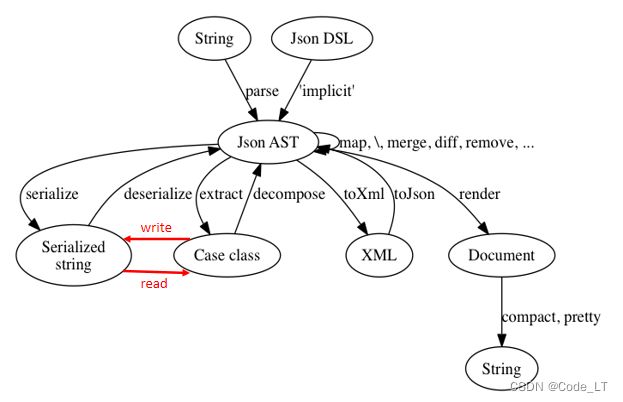
我们可以通过 json4s 对json所做的操作如下图所示,中间为 Json AST (简单理解就是一个用JValue表示的 JSON)。
另外,org.json4s下定义了很多scala原生数据转JValue的隐式转换(即多数操作下可以把原生数据当做JValue直接使用)
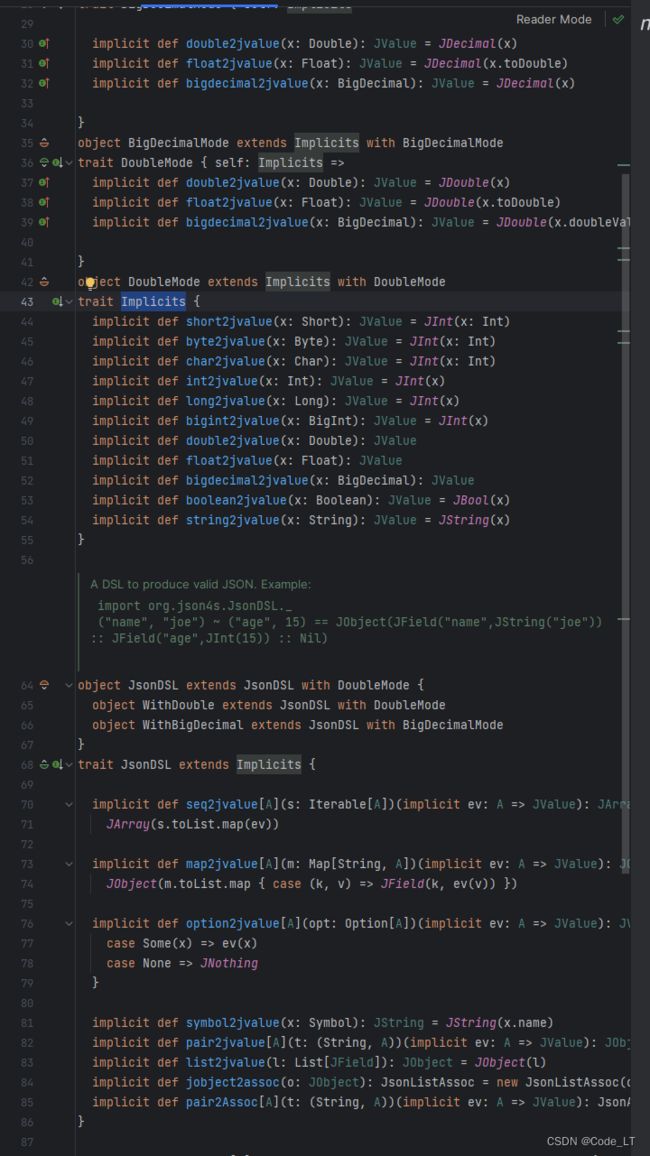
但是注意:Tuple不能自动转为JValue,在需要转换的时候,render先转一下,如:json merge render("height",175)
一、 创建json对象
{"name":"luca", "id": "1q2w3e4r5t", "age": 26, "url":"http://www.nosqlnocry.wordpress.com"}
方式1:parse函数
// parse from string example,得到的是JValue对象
var json = parse("""{"name":"luca", "id": "1q2w3e4r5t", "age": 26, "url":"http://www.nosqlnocry.wordpress.com"}""")
方式2:dsl创建
org.json4s中定义了从tuple到JValue的操作符
// DSL example,是JObject对象
var json = ("name","luca") ~ ("id","1q2w3e4r5t") ~ ("age",26) ~ ("url","http://www.nosqlnocry.wordpress.com")
// tuples can be defined also like this: ("id" -> "1q2w3e4r5t")
println(json)
JObject(List((name,JString(luca)), (id,JString(1q2w3e4r5t)), (age,JInt(26)), (url,JString(http://www.nosqlnocry.wordpress.com))))
二、常用操作
2.1 新增一个field
注意,以下两个方法都不会覆盖,若原json中已有height,则新json中会有两个height.
//法1:使用dsl,JObject才有~方法
json = json ~ ("height" -> 175)
//法2: 使用merge,要求类型和左边一致,所以json为parse出来的JValue时,要用render生成JValue再merge
json = json merge render("height",175)
2.2 更新一个field
使用 transformField
json = json transformField {
case JField("name", _) => ("NAME", JString("Luca")) //还可重命名
case JField("age", JInt(age)) => ("age", JInt(age+1))//更新值
}
json = json merge render("age",26) //若json 中已有"age"
2.3 删除一个field
json = json removeField {
case JField("NAME", _) => true //被删除
case _ => false
}
// 或等价的
json = json filterField {
case JField("NAME", _) => false
case _ => true //被保留
}
2.4 获取一个field
println(compact(json \\ "age")) // 27 嵌套获取-见下
println(compact(json \ "age")) // 27
println(compact(json.children(1))) // 27
三、高阶操作
{
"name": "luca",
"id": "1q2w3e4r5t",
"age": 26,
"url": "http://www.nosqlnocry.wordpress.com",
"url": "https://nosqlnocry.wordpress.com",
"loginTimeStamps": [
1434904257,
1400689856,
1396629056
],
"messages": [
{
"id": 1,
"content": "Please like this post!"
},
{
"id": 2,
"content": "Forza Roma!"
}
],
"profile": {
"id": "my-nickname",
"score": 123,
"avatar": "path.jpg"
}
}
3.1 选取field
println(JSON)
//JObject(List((name,JString(luca)), (id,JString(1q2w3e4r5t)), (age,JInt(26)), (url,JString(http://www.nosqlnocry.wordpress.com)), (url,JString(https://nosqlnocry.wordpress.com)), (loginTimeStamps,JArray(List(JInt(1434904257), JInt(1400689856), JInt(1396629056)))), (messages,JArray(List(JObject(List((id,JInt(1)), (content,JString(Please like this post!)))), JObject(List((id,JInt(2)), (content,JString(Forza Roma!))))))), (profile,JObject(List((id,JString(my-nickname)), (score,JInt(123)), (avatar,JString(path.jpg)))))))
println(JSON\\"id") //获取所有嵌套的id数据
// prints: JObject(List((id,JString(1q2w3e4r5t)), (id,JInt(1)), (id,JInt(2)), ...
println(JSON\"id")//获取第一层的id数据
// prints: JString(1q2w3e4r5t)
println(JSON\"url") //如果第一层有多个,则返回JArray
// prints: JArray(List(JString(http://www...), JString(https://nosqlnocry...
val messagesIds = (JSON \ "messages") \ "id" //获取JAray中的id数据
println(messagesIds)
// prints: JArray(List(JInt(1), JInt(2)))
println(messagesIds.values)
// prints: List(1,2)
//或用for语句
val messagesIds2= for {
JObject(child) <- JSON
JField("id", JInt(id)) <- child
} yield id
println(messagesIds2)
// prints: List(1,2)
for语句的<-在JValue中做了特殊处理,会返回所有匹配项。
for {
JObject(child) <- JSON //这回匹配所有JObject,不管是不是嵌套
}{
println(child)
}
//List((name,JString(luca)), (id,JString(1q2w3e4r5t)), (age,JInt(26)), (url,JString(http://www.nosqlnocry.wordpress.com)), (url,JString(https://nosqlnocry.wordpress.com)), (loginTimeStamps,JArray(List(JInt(1434904257), JInt(1400689856), JInt(1396629056)))), (messages,JArray(List(JObject(List((id,JInt(1)), (content,JString(Please like this post!)))), JObject(List((id,JInt(2)), (content,JString(Forza Roma!))))))), (profile,JObject(List((id,JString(my-nickname)), (score,JInt(123)), (avatar,JString(path.jpg))))))
//List((id,JInt(1)), (content,JString(Please like this post!)))
//List((id,JInt(2)), (content,JString(Forza Roma!)))
//List((id,JString(my-nickname)), (score,JInt(123)), (avatar,JString(path.jpg)))
JValue的<-调用的是
def foreach(f: JValue => Unit): Unit =
self.filter(p).foreach(f)
Array的<-调用的是
def foreach[U](f: A => U): Unit = {
var i = 0
val len = length
while (i < len) { f(this(i)); i += 1 }
}
3.2 取出field
println(compact(render(JSON \ "messages")))
// prints: [{"id":1,"content":"Please like this post!"},{"id":2,"content":"Forza Roma!"}]
println(pretty(render((JSON \ "messages")\"content")))
// prints: [ "Please like this post!", "Forza Roma!" ] // note it is not compacted anymore
println(pretty(render(JSON \ "age")))
// prints: 26
println(compact(render(JSON \ "name")))
// prints: "luca" // note the apostrophes
var name = for { JString(x) <- (JSON \\ "name") } yield x //或用for表达式去掉双引号
println(name(0))
// prints: luca
var name = (JSON \ "name") //或用values去掉双引号,保留对应基本类型时,推荐这种方法
println(name.values)
// prints: luca
implicit val formats = DefaultFormats
val name = (JSON \ "name").extract[String]//或直接extract,已知需要的类型时推荐这种方法
println(name)
// prints: luca
3.3 查找和过滤filed
//返回第一个遇到的元素
val URL = JSON findField {
case JField("url", _) => true
case _ => false
}
println(URL)
// prints: Some((url,JString(http://www.nosqlnocry.wordpress.com)))
// 返回所有符合条件的元素
val URLs = JSON filterField {
case JField("url", _) => true
case _ => false
}
println(URLs)
// prints: List((url,JString(http://www.nosqlnocry...)), (url,JString(https://nosqlnocry...)
3.4 合并与差异另一个Json2:merge和diff
{
"messages": [
{
"id": 3,
"content": "how to merge?"
}
],
"url": "anotherURL",
"loginTimeStamps": 1400689856,
"profile": {
"avatar": "new.jpg"
},
"new": "new value"
}
Json1 merge Json2
- 如果字段法Json1/f1与Json2/f1结构不同,或者仅具有简单结构,则Json2会替换Json1的f1
- 若结构相同且为复杂结构,则会合并
- 若Json2/f1在Json1中不存在,则新增

diff 获取两个JSon间的不同(用得少):
val newUserJSON = """
{
"name":"luca",
"id": "anotherID",
"age": 26,
"url":"http://www.nosqlnocry.wordpress.com",
"profile":{"id":"another-nickname", "score":99999, "avatar":"path.jpg"}
}
"""
val Diff(changed, added, deleted) = JSON diff parse(newUserJSON)
println(compact(render(changed)))
println(added)
println(pretty(render(deleted)))
/* print:
{"id":"anotherID","profile":{"id":"another-nickname","score":99999}}
JNothing
{
"url" : "https://nosqlnocry.wordpress.com",
"loginTimeStamps" : [ 1434904257, 1400689856, 1396629056 ],
"messages" : [ {
"id" : 1,
"content" : "Please like this post!"
}, {
"id" : 2,
"content" : "Forza Roma!"
} ]
}*/
3.5 类和JSon间的转换:decompose, extract, write和read
case class Item(info: String, rank: Int)
case class Item2(info: String, rank: Int, name:String)
implicit val formats: Formats = DefaultFormats
val vMap=Map("info" -> "abcd", "rank" -> 123, "other" -> "dsf")
val jsonStr = write(vMap)
println(jsonStr)
//{"info":"abcd","rank":123,"other":"dsf"}
val json = parse(jsonStr)
println(json)
val json2 = Extraction.decompose(vMap)//可以理解为等价于parse(write(vMap))
println(json2)
val json=parse(jsonStr)
//val json2=
println(json.extract[Map[String,Any]])
//Map(info -> abcd, rank -> 123, other -> dsf)
println(read[Map[String,Any]](jsonStr))//可理解为和json.extract效果一样,但是跳过了将str转为JValue对象的过程
//Map(info -> abcd, rank -> 123, other -> dsf)
println(json.extract[Item])//case class 的字段名要和json的field一致,可少不可多与json有的field
//Item(abcd,123)
println(read[Item](jsonStr))
//Item(abcd,123)
println(json.extract[Item2])//不可多于json有的field
//报错,org.json4s.MappingException: No usable value for name
println(read[Item2](jsonStr))
//报错,org.json4s.MappingException: No usable value for name
不用默认格式:(非scala基类作为父类的话,默认格式解析会出错)
trait Animal
case class Dog(name: String) extends Animal
case class Fish(weight: Double) extends Animal
case class Animals(animals: List[Animal])
implicit val formats1: Formats = DefaultFormats
val formats2: Formats = Serialization.formats(ShortTypeHints(List(classOf[Dog], classOf[Fish])))
implicit val mf = manifest[Animals]
val ser1 = write(Animals(Dog("pluto") :: Fish(1.2) :: Nil))(formats1)
val ser2 = write(Animals(Dog("pluto") :: Fish(1.2) :: Nil))(formats2)
println(ser1)
//{"animals":[{"name":"pluto"},{"weight":1.2}]}
println(ser2)
//{"animals":[{"jsonClass":"BasicTest$Dog","name":"pluto"},{"jsonClass":"BasicTest$Fish","weight":1.2}]}
println(read[Animals](ser2)(formats2, mf))
//Animals(List(Dog(pluto), Fish(1.2)))
println(parse(ser2).extract[Animals](formats2,mf))
//Animals(List(Dog(pluto), Fish(1.2)))
println( read[Animals](ser2)(formats1,mf))// 报错
//org.json4s.MappingException: No usable value for animals,No constructor for type Animal, JObject(List((jsonClass,JString(BasicTest$Dog)), (name,JString(pluto))))
println( read[Animals](ser1))//等价于println( read[Animals](ser1)(formats1,mf)) ,报错
//org.json4s.MappingException: No usable value for animals No constructor for type Animal, JObject(List((name,JString(pluto))))
println(parse(ser1).extract[Animals])//报错
//org.json4s.MappingException: No usable value for animals No constructor for type Animal, JObject(List((name,JString(pluto))))
println(parse(ser2).extract[Animals])//报错
//org.json4s.MappingException: No constructor for type Animal, JObject(List((jsonClass,JString(BasicTest$Dog)), (name,JString(pluto))))
参考
官方教程
WORKING WITH JSON IN SCALA USING THE JSON4S LIBRARY (PART ONE)
WORKING WITH JSON IN SCALA USING THE JSON4S LIBRARY (PART TWO)
Purpose of render in json4s