freemarker
目录
简介
快速入门
测试
freemarker基础
基础语法种类
集合指令(List和Map)
if指令
运算符
比较运算符
空值处理
内建函数
静态化测试
简介
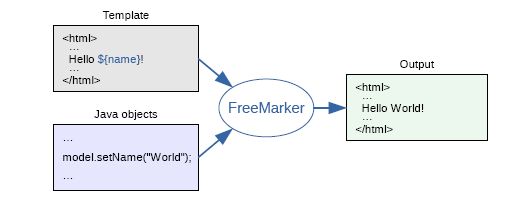
FreeMarker 是一款 模板引擎: 即一种基于模板和要改变的数据, 并用来生成输出文本(HTML网页,电子邮件,配置文件,源代码等)的通用工具。 它不是面向最终用户的,而是一个Java类库,是一款程序员可以嵌入他们所开发产品的组件。
模板编写为FreeMarker Template Language (FTL)。它是简单的,专用的语言, 不是 像PHP那样成熟的编程语言。 那就意味着要准备数据在真实编程语言中来显示,比如数据库查询和业务运算, 之后模板显示已经准备好的数据。在模板中,你可以专注于如何展现数据, 而在模板之外可以专注于要展示什么数据。
快速入门
freemarker作为springmvc一种视图格式,默认情况下SpringMVC支持freemarker视图格式。
创建一个freemarker-demo 的测试工程专门用于freemarker的功能测试与模板的测试。
heima-leadnews-test
com.heima
1.0-SNAPSHOT
4.0.0
freemarker-demo
8
8
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-web
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-freemarker
org.springframework.boot
spring-boot-starter-test
org.projectlombok
lombok
org.apache.commons
commons-io
1.3.2
配置application.yml
server:
port: 8881 #服务端口
spring:
application:
name: freemarker-demo #指定服务名
freemarker:
cache: false #关闭模板缓存,方便测试
settings:
template_update_delay: 0 #检查模板更新延迟时间,设置为0表示立即检查,如果时间大于0会有缓存不方便进行模板测试
suffix: .ftl #指定Freemarker模板文件的后缀名 :html ftlh jsp 等等创建模板
在resources下创建templates,此目录为freemarker的默认模板存放目录。
在templates下创建模板文件 01-basic.ftl ,模板中的插值表达式最终会被freemarker替换成具体的数据。
Hello World!
普通文本 String 展示:
Hello ${name}
对象Student中的数据展示:
姓名:${stu.name}
年龄:${stu.age}
在freemarker的测试工程下创建模型类型用于测试
package com.freemarker.entity;
import lombok.Data;
import java.util.Date;
@Data
public class Student {
private String name;//姓名
private int age;//年龄
private Date birthday;//生日
private Float money;//钱包
}创建controller,向Map中添加name,最后返回模板文件。
package com.freemarker.controller;
import com.freemarker.entity.Student;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.ui.Model;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
@Controller
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("/basic")
public String test(Model model) {
//1.纯文本形式的参数
model.addAttribute("name", "freemarker");
//2.实体类相关的参数
Student student = new Student();
student.setName("小明");
student.setAge(18);
model.addAttribute("stu", student);
return "01-basic";
}
}创建启动类
package com.heima.freemarker;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class FreemarkerDemotApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(FreemarkerDemotApplication.class,args);
}
}测试
请求:http://localhost:8881/basic
freemarker基础
基础语法种类
- 注释,即<#-- -->,介于其之间的内容会被freemarker忽略
<#--我是一个freemarker注释-->- 插值(Interpolation):即
${..}部分,freemarker会用真实的值代替${..}
Hello ${name}- FTL指令:和HTML标记类似,名字前加#予以区分,Freemarker会解析标签中的表达式或逻辑。
<# >FTL指令 - 文本,仅文本信息,这些不是freemarker的注释、插值、FTL指令的内容会被freemarker忽略解析,直接输出内容。
<#--freemarker中的普通文本-->
我是一个普通的文本集合指令(List和Map)
1、数据模型:
在HelloController中新增如下方法:
@GetMapping("/list")
public String list(Model model){
//------------------------------------
Student stu1 = new Student();
stu1.setName("小强");
stu1.setAge(18);
stu1.setMoney(1000.86f);
stu1.setBirthday(new Date());
//小红对象模型数据
Student stu2 = new Student();
stu2.setName("小红");
stu2.setMoney(200.1f);
stu2.setAge(19);
//将两个对象模型数据存放到List集合中
List stus = new ArrayList<>();
stus.add(stu1);
stus.add(stu2);
//向model中存放List集合数据
model.addAttribute("stus",stus);
//------------------------------------
//创建Map数据
HashMap stuMap = new HashMap<>();
stuMap.put("stu1",stu1);
stuMap.put("stu2",stu2);
// 3.1 向model中存放Map数据
model.addAttribute("stuMap", stuMap);
return "02-list";
} 2、模板:
在templates中新增02-list.ftl文件
Hello World!
<#-- list 数据的展示 -->
展示list中的stu数据:
序号
姓名
年龄
钱包
<#list stus as stu>
${stu_index+1}
${stu.name}
${stu.age}
${stu.money}
<#-- Map 数据的展示 -->
map数据的展示:
方式一:通过map['keyname'].property
输出stu1的学生信息:
姓名:${stuMap['stu1'].name}
年龄:${stuMap['stu1'].age}
方式二:通过map.keyname.property
输出stu2的学生信息:
姓名:${stuMap.stu2.name}
年龄:${stuMap.stu2.age}
遍历map中两个学生信息:
序号
姓名
年龄
钱包
<#list stuMap?keys as key >
${key_index}
${stuMap[key].name}
${stuMap[key].age}
${stuMap[key].money}
${k_index}: index:得到循环的下标,使用方法是在stu后边加"_index",它的值是从0开始
if指令
if 指令即判断指令,是常用的FTL指令,freemarker在解析时遇到if会进行判断,条件为真则输出if中间的内容,否则跳过内容不再输出。
<#if >1、数据模型:
使用list指令中测试数据模型,判断名称为小红的数据字体显示为红色。
2、模板:
姓名
年龄
钱包
<#list stus as stu >
<#if stu.name='小红'>
${stu_index}
${stu.name}
${stu.age}
${stu.money}
<#else >
${stu_index}
${stu.name}
${stu.age}
${stu.money}
3、输出:
姓名为“小强”则字体颜色显示为红色。
运算符
1、算数运算符
FreeMarker表达式中完全支持算术运算,FreeMarker支持的算术运算符包括:
-
加法:
+ -
减法:
- -
乘法:
* -
除法:
/ -
求模 (求余):
%
模板代码
算数运算符
100+5 运算: ${100 + 5 }
100 - 5 * 5运算:${100 - 5 * 5}
5 / 2运算:${5 / 2}
12 % 10运算:${12 % 10}
除了 + 运算以外,其他的运算只能和 number 数字类型的计算。
比较运算符
-
=或者==:判断两个值是否相等. -
!=:判断两个值是否不等. -
>或者gt:判断左边值是否大于右边值 -
>=或者gte:判断左边值是否大于等于右边值 -
<或者lt:判断左边值是否小于右边值 -
<=或者lte:判断左边值是否小于等于右边值
= 和 == 模板代码
Hello World!
比较运算符
- =/== 和 != 比较:
-
<#if "xiaoming" == "xiaoming">
字符串的比较 "xiaoming" == "xiaoming"
-
<#if 10 != 100>
数值的比较 10 != 100
- 其他比较
-
<#if 10 gt 5 >
形式一:使用特殊字符比较数值 10 gt 5
-
<#-- 日期的比较需要通过?date将属性转为data类型才能进行比较 -->
<#if (date1?date >= date2?date)>
形式二:使用括号形式比较时间 date1?date >= date2?date
Controller 的 数据模型代码
@GetMapping("operation")
public String testOperation(Model model) {
//构建 Date 数据
Date now = new Date();
model.addAttribute("date1", now);
model.addAttribute("date2", now);
return "03-operation";
}比较运算符注意
-
=和!=可以用于字符串、数值和日期来比较是否相等 -
=和!=两边必须是相同类型的值,否则会产生错误 -
字符串
"x"、"x "、"X"比较是不等的.因为FreeMarker是精确比较 -
其它的运行符可以作用于数字和日期,但不能作用于字符串
-
使用
gt等字母运算符代替>会有更好的效果,因为 FreeMarker会把>解释成FTL标签的结束字符 -
可以使用括号来避免这种情况,如:
<#if (x>y)>
3、逻辑运算符
-
逻辑与:&&
-
逻辑或:||
-
逻辑非:!
逻辑运算符只能作用于布尔值,否则将产生错误 。
模板代码
逻辑运算符
<#if (10 lt 12 )&&( 10 gt 5 ) >
(10 lt 12 )&&( 10 gt 5 ) 显示为 true
<#if !false>
false 取反为true
空值处理
1、判断某变量是否存在使用 “??”
用法为:variable??,如果该变量存在,返回true,否则返回false
例:为防止stus为空报错可以加上判断如下:
<#if stus??>
<#list stus as stu>
......
缺失变量默认值使用 “!”
-
使用!要以指定一个默认值,当变量为空时显示默认值
例: ${name!''}表示如果name为空显示空字符串。
-
如果是嵌套对象则建议使用()括起来
例: ${(stu.bestFriend.name)!''}表示,如果stu或bestFriend或name为空默认显示空字符串。
内建函数
内建函数语法格式: 变量+?+函数名称
1、和到某个集合的大小
${集合名?size}
2、日期格式化
显示年月日: ${today?date} 显示时分秒:${today?time} 显示日期+时间:${today?datetime} 自定义格式化: ${today?string("yyyy年MM月")}
3、内建函数c
model.addAttribute("point", 102920122);
point是数字型,使用${point}会显示这个数字的值,每三位使用逗号分隔。
如果不想显示为每三位分隔的数字,可以使用c函数将数字型转成字符串输出
${point?c}
4、将json字符串转成对象
一个例子:
其中用到了 assign标签,assign的作用是定义一个变量。
<#assign text="{'bank':'工商银行','account':'10101920201920212'}" />
<#assign data=text?eval />
开户行:${data.bank} 账号:${data.account}模板代码:
inner Function
获得集合大小
集合大小:${stus?size}
获得日期
显示年月日: ${today?date}
显示时分秒:${today?time}
显示日期+时间:${today?datetime}
自定义格式化: ${today?string("yyyy年MM月")}
内建函数C
没有C函数显示的数值:${point}
有C函数显示的数值:${point?c}
声明变量assign
<#assign text="{'bank':'工商银行','account':'10101920201920212'}" />
<#assign data=text?eval />
开户行:${data.bank} 账号:${data.account}
内建函数Controller数据模型:
@GetMapping("innerFunc")
public String testInnerFunc(Model model) {
//1.1 小强对象模型数据
Student stu1 = new Student();
stu1.setName("小强");
stu1.setAge(18);
stu1.setMoney(1000.86f);
stu1.setBirthday(new Date());
//1.2 小红对象模型数据
Student stu2 = new Student();
stu2.setName("小红");
stu2.setMoney(200.1f);
stu2.setAge(19);
//1.3 将两个对象模型数据存放到List集合中
List stus = new ArrayList<>();
stus.add(stu1);
stus.add(stu2);
model.addAttribute("stus", stus);
// 2.1 添加日期
Date date = new Date();
model.addAttribute("today", date);
// 3.1 添加数值
model.addAttribute("point", 102920122);
return "04-innerFunc";
} 静态化测试
之前的测试都是SpringMVC将Freemarker作为视图解析器(ViewReporter)来集成到项目中,工作中,有的时候需要使用Freemarker原生Api来生成静态内容,下面一起来学习下原生Api生成文本文件。
需求分析
使用freemarker原生Api将页面生成html文件,测试html文件生成的方法:
静态化测试
根据模板文件生成html文件
1.修改application.yml文件,添加以下模板存放位置的配置信息,完整配置如下:
server:
port: 8881 #服务端口
spring:
application:
name: freemarker-demo #指定服务名
freemarker:
cache: false #关闭模板缓存,方便测试
settings:
template_update_delay: 0 #检查模板更新延迟时间,设置为0表示立即检查,如果时间大于0会有缓存不方便进行模板测试
suffix: .ftl #指定Freemarker模板文件的后缀名
template-loader-path: classpath:/templates #模板存放位置2.在test下创建测试类
package com.freemarker.test;
import com.freemarker.FreemarkerDemotApplication;
import com.freemarker.entity.Student;
import freemarker.template.Configuration;
import freemarker.template.Template;
import freemarker.template.TemplateException;
import org.junit.Test;
import org.junit.runner.RunWith;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.test.context.junit4.SpringRunner;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.*;
@SpringBootTest(classes = FreemarkerDemotApplication.class)
@RunWith(SpringRunner.class)
public class FreemarkerTest {
@Autowired
private Configuration configuration;
@Test
public void test() throws IOException, TemplateException {
//freemarker的模板对象,获取模板
Template template = configuration.getTemplate("02-list.ftl");
Map params = getData();
//合成
//第一个参数 数据模型
//第二个参数 输出流
template.process(params, new FileWriter("d:/list.html"));
}
private Map getData() {
Map map = new HashMap<>();
//小强对象模型数据
Student stu1 = new Student();
stu1.setName("小强");
stu1.setAge(18);
stu1.setMoney(1000.86f);
stu1.setBirthday(new Date());
//小红对象模型数据
Student stu2 = new Student();
stu2.setName("小红");
stu2.setMoney(200.1f);
stu2.setAge(19);
//将两个对象模型数据存放到List集合中
List stus = new ArrayList<>();
stus.add(stu1);
stus.add(stu2);
//向map中存放List集合数据
map.put("stus", stus);
//创建Map数据
HashMap stuMap = new HashMap<>();
stuMap.put("stu1", stu1);
stuMap.put("stu2", stu2);
//向map中存放Map数据
map.put("stuMap", stuMap);
//返回Map
return map;
}
}