- 十.java入门【案例】
JuGeGer
java入门java
day10【练习】减肥计划案例逢七必过案例统计成绩数组求和数组中的元素查找案例数组中的元素反转评委打分案例快捷键:自动分配变量newXxx(...).var或者newXxx(...)alt+回车方法调用(...).var或者方法调用(...)alt+回车生成输出语句表达式.sout方法调用(...).sout第一章基础练习1.1减肥计划if版本需求输入星期数[1,7],显示今天的减肥活动周一:跑步
- 21天学通C++——11多态(引入多态的目的)
不想睡觉_
QT客户端学习路线c++开发语言
多态:利用不同类似的方法处理不同类似的对象笔记原因:既然继承可以进行基类的方法覆盖,为什么还要引入多态呢?解释原因:继承classBase{public:voidfunc(){std::coutfunc();return0;}结果为Base::func()引入多态(Virtual)classBase{public:virtualvoidfunc(){std::coutfunc();return0;
- C++ XML对象序列化与反序列化
zccmid
c++xml算法windowsvisualstudiogithub
一、序列化与反序列化 序列化是将一个对象转换为一种特定的格式或字符串表示,以便可以在不同的系统或程序之间进行传输或存储。序列化通常涉及将一个对象的属性值编码为字节流或字符流,并将其写入文件、网络流或其他媒介中。序列化后的数据可以在需要时进行反序列化,以便重新创建原始的对象。 反序列化是将序列化后的数据还原回原始对象的过程,即将序列化后的数据重新解码为原始对象的属性值。它通常涉及从文件、网络流或
- 第 7 课Python 容器类型与相关操作
嵌入式老牛
Python入门python开发语言
1.容器介绍对象是Python中对数据的抽象,Python程序中的所有数据都是由对象或对象间关系来表示的。Python中,可包含其他对象的引用的对象,称之为“容器”。容器的例子有元组、列表和字典等。这些引用的对象是容器对象值的组成部分。常用的容器主要划分为两种:序列(如:列表、元组等)和映射(如:字典)。序列中,每个元素都有下标,它们是有序的。映射中,每个元素都有名称(又称“键”),它们是无序的。
- C++ macro: Variadic macros (可变参数宏)
Yongqiang Cheng
C++C++macroVariadicmacros可变参数宏
C++macro:Variadicmacros{可变参数宏}1.Variadicmacroextensions(可变参数宏扩展)2.Variadicmacros3.llama.cppReferences1.Variadicmacroextensions(可变参数宏扩展)VariadicmacroextensionsrefertotwoextensionstoC99andStandardC++rel
- 冲刺蓝桥杯之速通vector!!!!!
爱吃生蚝的于勒
备战蓝桥杯蓝桥杯算法数据结构开发语言c语言c++柔性数组
文章目录知识点创建增删查改习题1习题2习题3习题4:习题5:知识点C++的STL提供已经封装好的容器vector,也可叫做可变长的数组,vector底层就是自动扩容的顺序表,其中的增删查改已经封装好创建constintN=30;vectora1;//创建叫a1的空的可变长的数组vectora2(N);//创建大小为30的可变长的数组,里面每个元素为0vectora3(N,2);//创建大小30的可
- Python-基础-字典(dict)
All_Test_Pass
Python-基础python开发语言
目录1、字典2、字典常用操作3、字典的方法1、字典字典(Dictionary)是一种用于存储键值对(key-valuepairs)数据的可变容器类型。每个字典都包含一组键(key)和值(value),通过键可以快速访问对应的值。字典是无序的,也就是说,它们不保证元素的顺序,直到Python3.7之后,字典会保留插入的顺序my_dict={key1:value1,key2:value2,key3:v
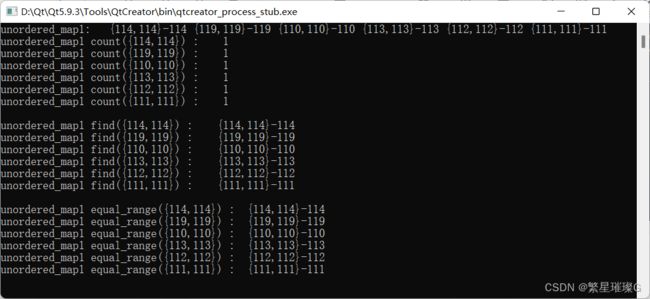
- C++ unordered_map
我要满血复活
c++开发语言
1.unordered系列关联式容器在C++98中,STL提供了底层为红黑树结构的一系列关联式容器,在查询时效率可达到,即最差情况下需要比较红黑树的高度次,当树中的节点非常多时,查询效率也不理想。最好的查询是,进行很少的比较次数就能够将元素找到,因此在C++11中,STL又提供了4个unordered系列的关联式容器,这四个容器与红黑树结构的关联式容器使用方式基本类似,只是其底层结构不同,该系列容
- 华为OD机试E卷 --热点网站统计--24年OD统一考试(Java & JS & Python & C & C++)
飞码创造者
最新华为OD机试题库2024华为odjavajavascriptpythonc++c语言
文章目录题目描述输入描述输出描述用例题目解析JS算法源码Java算法源码python算法源码c算法源码c++算法源码题目描述企业路由器的统计页面,有一个功能需要动态统计公司访问最多的网页URLtopN。请设计一个算法,可以高效动态统计TopN的页面。输入描述每一行都是一个URL或一个数字•如果是URL,代表一段时间内的网页访问•如果是一个数字N,代表本次需要输出的TopN个URL输入约束:总访问网
- Rust实现内网穿透工具:从原理到实现
余识-
Rust从入门到精通rust开发语言
目录1.前言2.内网穿透原理3.丐版实现3.1share3.2server3.3client3.4测试4.项目优化4.1工作空间4.2代码合并4.3无锁优化4.4数据分离4.5错误处理4.6测试代码4.7参数解析本篇原文为:Rust实现内网穿透工具:从原理到实现更多C++进阶、rust、python、逆向等等教程,可点击此链接查看:酷程网1.前言rust是一门非常适合写命令行工具的语言,本文将结合
- 华为OD机试2024年E卷-喊7的次数重排[100分]( Java | Python3 | C++ | C语言 | JsNode | Go)实现100%通过率
梅花C
华为OD题库华为od
题目描述喊7是一个传统的聚会游戏,N个人围成一圈,按顺时针从1到N编号。编号为1的人从1开始喊数,下一个人喊的数字为上一个人的数字加1,但是当将要喊出来的数字是7的倍数或者数字本身含有7的话,不能把这个数字直接喊出来,而是要喊"过"。假定玩这个游戏的N个人都没有失误地在正确的时机喊了"过",当喊到数字K时,可以统计每个人喊"过"的次数。现给定一个长度为N的数组,存储了打乱顺序的每个人喊"过"的次数
- C/C++中的strcmp函数的源代码
凌龍墨
C语言c语言中strcm的源代码strcmp函数
附上源代码,不懂得地方可以提问共同提高`#includeintmy_strcmp(constchar*string1,constchar*string2){intret=0;while(!(ret=*(unsignedchar*)string1-*(unsignedchar*)sting2)&&*string2){//从两个字符串的首字母开始比较,相等则进入循环,继续后面字符的比较++string
- 蓝桥杯备赛 Day10.4移动路线
丘大梨
蓝桥杯职场和发展
信息学奥赛一本通(C++版)在线评测系统【题目描述】X桌子上有一个m行n列的方格矩阵,将每个方格用坐标表示,行坐标从下到上依次递增,列坐标从左至右依次递增,左下角方格的坐标为(1,1),则右上角方格的坐标为(m,n)。小明是个调皮的孩子,一天他捉来一只蚂蚁,不小心把蚂蚁的右脚弄伤了,于是蚂蚁只能向上或向右移动。小明把这只蚂蚁放在左下角的方格中,蚂蚁从左下角的方格中移动到右上角的方格中,每步移动一个
- C++auto和decltype的用法
programming expert
算法数据结构
在C++中,auto和decltype是两个非常有用的关键字,它们帮助程序员更方便地处理类型推导和类型声明。以下是它们的具体用法:autoauto关键字用于自动类型推导,即让编译器根据初始化表达式来推断变量的类型。这在处理复杂类型或模板编程时特别有用,因为它可以简化代码并减少类型错误。用法示例:#include#includeintmain(){//自动推导整数类型autox=42;//x的类
- 【LGR-196-Div.4】洛谷入门赛 #26 题A - H 详细题解--优化思路简洁代码(C++,Python语言描述)
多思考少编码
洛谷入门赛题解算法c++python开发语言
前言:觉得这个比赛很有意思的,都是暴力题,涉及一些细节,难度比较适合刚学编程语言的,可以很好的锻炼基础还有手速,最后两题也是比较有意思,之后也准备更新atc的比赛题解和洛谷的一些高质量比赛题解(算法网瘾就是想参加各种比赛)如果觉得有帮助,或者觉得我写的好,可以点个赞或关注,也可以看看我的一些其他文章,我之后也会更新一些基础算法详细解释比赛链接:【LGR-196-Div.4】洛谷入门赛#26-洛谷|
- 黑客常备十大编程语言,每一个都不容易学,但每一个又很有用
一秋的编程笔记
Python编程计算机科技数据库sql爬虫python自动化编程语言
文章目录1、C语言2、Python3、SQL4、Javascript5、PHP6、C++编程7、JAVA8、Ruby9、Perl10、BashPython学习资源分享1、Python所有方向的学习路线2、学习软件3、精品书籍4、入门学习视频5、实战案例6、清华编程大佬出品《漫画看学Python》7、Python副业兼职与全职路线一定要注意,您选择的编程将在很大程度上取决于您要定位的系统类型和计划使
- 【c++】【算法】【动态规划】最长公共子序列
钟离墨笺
算法算法c++动态规划
【c++】【算法】【动态规划】最长公共子序列//递归方式//最长公共子序//直接递归求最长公共子序长度intFindValue(conststring&X,conststring&Y,inti,intj){if(i==0||j==0)return0;if(X[i]==Y[j])returnFindValue(X,Y,i-1,j-1)+1;elsereturnstd::max(FindValue(X
- C++迭代器失效
倒地不起的土豆
C++语言算法c++开发语言
目录什么是迭代器迭代器失效顺序容器迭代器失效添加操作删除操作关联容器迭代器失效swap()操作迭代器为什么不失效注意事项参考什么是迭代器迭代器不是指针,是类模板,表现的像指针。他只是模拟了指针的一些功能,通过重载了指针的一些操作符,->,*,++--等封装了指针,是一个“可遍历STL(StandardTemplateLibrary)容器内全部或部分元素”的对象,本质是封装了原生指针,他可以根据不同
- 工作中常用 CMD 命令
书生-w
windowscmd
文章目录1.网络排障与端口检查1.1检测网络连通性1.2路由追踪1.3查看端口占用与连接状态2.进程管理2.1查看进程列表2.2结束指定进程3.文件与目录操作3.1快速查找并筛选日志3.2批量复制或镜像目录4.环境变量与系统信息4.1设置临时环境变量4.2设置系统环境变量4.3查看系统信息5.批处理脚本与自动化5.1将命令封装成`.bat`脚本5.2重定向和管道组合6.远程管理与故障排查6.1Te
- C++的构造函数、默认构造函数和=default
青草地溪水旁
C++学习记录c++linux
目录1.基本概念2.为什么要加=default?3.参考资料1.基本概念构造函数(contructor)是特殊的成员函数,其作用是控制对象的初始化,初始化类的数据成员。默认构造函数的必要充分条件是构造函数无参默认构造函数分两种:一种是按照C++定义类的规则由编译器自动生成的,即:如果没有显示(隐式的)的定义默认的构造函数,则编译器会为类合成一个默认构造函数。在定义一个类的时候,如果没有定义任何一个
- JVM加载
影࿐ེ
jvm
JVM(Java虚拟机)并不是在工程启动时就将所有类都加载到内存中,而是采用按需加载的方式,即在需要使用某个类时才会加载该类。JVM的类加载机制包括了加载、验证、准备、解析和初始化五个阶段。当Java程序运行时,JVM会根据需要,通过类加载器查找并加载类的字节码数据。这些数据可以来源于本地文件系统、网络、jar包等多种途径。加载完成后,JVM会将类的二进制数据转换成方法区内部的数据结构,并生成一个
- GESP认证C++编程真题解析 | B4004 寻找倍数
热爱编程的通信人
c++开发语言
学习C++从娃娃抓起!记录下CCF-GESP备考学习过程中的题目,记录每一个瞬间。附上汇总帖:GESP认证C++编程真题解析|汇总【题目描述】小杨有一个包含n个正整数的序列A=[a1,a2,…,an]A=[a_1,a_2,\dots,a_n]A=[a1,a2,…,an],他想知道是否存在i(1≤i≤n)i(1\lei\len)i(1≤i≤n)使得aia_iai是序列A中所有数的倍数。【输入】第一行
- Centos7挂载LVM卷
centoslvm
1.背景给单位的云主机上安装一块云硬盘,容量是1T,由于该云主机需要存放大量数据,为了保证将来硬盘具有可扩展性,决定使用LVM来管理硬盘。2.硬盘分区查找到硬盘,然后添加分区fdisk/dev/vdbn--添加新分区p--查看分区t--修改分区的type为lvm15--15表示的是lvm,如果是16禁止的,则为8ew--保存分区结果3.查看分区结果lsblk可以看到产生了/dev/vdb1这个分区
- 解决tsconfig.json配置paths, 却依然报错can't find module?
NodeJs程序中若使用typescript经常会遇到一个问题,即明明在tsconfig.json里配置了paths映射,为啥import使用路径别名,例如@test/a.ts时,会报错can'tfindmodule'@test/a.ts'?其实根本原因在于typescript只负责编译期检查,而执行模块时,tsconfig.json配置的paths自然无法影响js的模块查找机制,故报错分享:要解
- 【拒绝算法PUA】3065. 超过阈值的最少操作数 I
BigDark的笔记
#LEETCODE#每日一题算法
系列文章目录【拒绝算法PUA】0x00-位运算【拒绝算法PUA】0x01-区间比较技巧【拒绝算法PUA】0x02-区间合并技巧【拒绝算法PUA】0x03-LeetCode排序类型刷题【拒绝算法PUA】LeetCode每日一题系列刷题汇总-2025年持续刷新中C++刷题技巧总结:[温习C/C++]0x04刷题基础编码技巧文章目录系列文章目录LeetCode3065.超过阈值的最少操作数I链接题目解题
- 职工管理系统c++
LE715
c++开发语言
职工管理系统一.头文件部分职工抽象类worker.h老板类boss.h普通员工类employee.h经理类manager.h职工管理类workerManager.h二.源文件部分老板类boss.cpp普通员工类employee.cpp经理类manager.cpp职工管理类workerManager.cpp职工管理系统.cpp三.系统运行界面职工管理系统职工管理系统可以用来管理公司内所有员工的信息本
- idea中的tomcat vm_IntelliJ IDEA Tomcat配置详解(图文)
涟雪沧
idea中的tomcatvm
查找该问题的童鞋我相信IntelliJIDEA,Tomcat的下载,JDK等其他的配置都应该完成了,那我直接进入正题了。1>进入EditConfigurations2>点击+,选择Tomcat服务器,如果是本地Tomcat选择Local3>TomcatServer->Unnamed->Server->Applicationserver的Configuration,找到本地Tomcat服务器,再点击
- idea的tomcat改端口号_IntelliJ IDEA Tomcat配置详解(图文)
weixin_39630880
idea的tomcat改端口号
查找该问题的童鞋我相信IntelliJIDEA,Tomcat的下载,JDK等其他的配置都应该完成了,那我直接进入正题了。1>进入EditConfigurations2>点击+,选择Tomcat服务器,如果是本地Tomcat选择Local3>TomcatServer->Unnamed->Server->Applicationserver的Configuration,找到本地Tomcat服务器,再点击
- 3.C++中的判断语句
赵鑫亿
C++基础入门c++开发语言
C++中的判断语句一、if语句if语句是最基本的判断结构,用于根据条件执行不同的代码块。基本形式:if(condition){//当condition为真时执行的代码块}例如:#includeintmain(){intnum=10;if(num>5){std::coutintmain(){intnum=3;if(num>5){std::coutintmain(){intnum=7;if(num>1
- 华为OD机试E卷 - 数大雁(Java & Python& JS & C++ & C )
算法大师
最新华为OD机试华为odpythonjavac语言javascriptc++华为od机考e卷
最新华为OD机试真题目录:点击查看目录华为OD面试真题精选:点击立即查看题目描述一群大雁往南飞,给定一个字符串记录地面上的游客听到的大雁叫声,请给出叫声最少由几只大雁发出。具体的:1.大雁发出的完整叫声为”quack“,因为有多只大雁同一时间嘎嘎作响,所以字符串中可能会混合多个”quack”。2.大雁会依次完整发出”quack”,即字符串中’q’,‘u’,‘a’,‘c’,‘k’这5个字母按顺序完整
- C/C++Win32编程基础详解视频下载
择善Zach
编程C++Win32
课题视频:C/C++Win32编程基础详解
视频知识:win32窗口的创建
windows事件机制
主讲:择善Uncle老师
学习交流群:386620625
验证码:625
--
- Guava Cache使用笔记
bylijinnan
javaguavacache
1.Guava Cache的get/getIfPresent方法当参数为null时会抛空指针异常
我刚开始使用时还以为Guava Cache跟HashMap一样,get(null)返回null。
实际上Guava整体设计思想就是拒绝null的,很多地方都会执行com.google.common.base.Preconditions.checkNotNull的检查。
2.Guava
- 解决ora-01652无法通过128(在temp表空间中)
0624chenhong
oracle
解决ora-01652无法通过128(在temp表空间中)扩展temp段的过程
一个sql语句后,大约花了10分钟,好不容易有一个结果,但是报了一个ora-01652错误,查阅了oracle的错误代码说明:意思是指temp表空间无法自动扩展temp段。这种问题一般有两种原因:一是临时表空间空间太小,二是不能自动扩展。
分析过程:
既然是temp表空间有问题,那当
- Struct在jsp标签
不懂事的小屁孩
struct
非UI标签介绍:
控制类标签:
1:程序流程控制标签 if elseif else
<s:if test="isUsed">
<span class="label label-success">True</span>
</
- 按对象属性排序
换个号韩国红果果
JavaScript对象排序
利用JavaScript进行对象排序,根据用户的年龄排序展示
<script>
var bob={
name;bob,
age:30
}
var peter={
name;peter,
age:30
}
var amy={
name;amy,
age:24
}
var mike={
name;mike,
age:29
}
var john={
- 大数据分析让个性化的客户体验不再遥远
蓝儿唯美
数据分析
顾客通过多种渠道制造大量数据,企业则热衷于利用这些信息来实现更为个性化的体验。
分析公司Gartner表示,高级分析会成为客户服务的关键,但是大数据分析的采用目前仅局限于不到一成的企业。 挑战在于企业还在努力适应结构化数据,疲于根据自身的客户关系管理(CRM)系统部署有效的分析框架,以及集成不同的内外部信息源。
然而,面对顾客通过数字技术参与而产生的快速变化的信息,企业需要及时作出反应。要想实
- java笔记4
a-john
java
操作符
1,使用java操作符
操作符接受一个或多个参数,并生成一个新值。参数的形式与普通的方法调用不用,但是效果是相同的。加号和一元的正号(+)、减号和一元的负号(-)、乘号(*)、除号(/)以及赋值号(=)的用法与其他编程语言类似。
操作符作用于操作数,生成一个新值。另外,有些操作符可能会改变操作数自身的
- 从裸机编程到嵌入式Linux编程思想的转变------分而治之:驱动和应用程序
aijuans
嵌入式学习
笔者学习嵌入式Linux也有一段时间了,很奇怪的是很多书讲驱动编程方面的知识,也有很多书将ARM9方面的知识,但是从以前51形式的(对寄存器直接操作,初始化芯片的功能模块)编程方法,和思维模式,变换为基于Linux操作系统编程,讲这个思想转变的书几乎没有,让初学者走了很多弯路,撞了很多难墙。
笔者因此写上自己的学习心得,希望能给和我一样转变
- 在springmvc中解决FastJson循环引用的问题
asialee
循环引用fastjson
我们先来看一个例子:
package com.elong.bms;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import co
- ArrayAdapter和SimpleAdapter技术总结
百合不是茶
androidSimpleAdapterArrayAdapter高级组件基础
ArrayAdapter比较简单,但它只能用于显示文字。而SimpleAdapter则有很强的扩展性,可以自定义出各种效果
ArrayAdapter;的数据可以是数组或者是队列
// 获得下拉框对象
AutoCompleteTextView textview = (AutoCompleteTextView) this
- 九封信
bijian1013
人生励志
有时候,莫名的心情不好,不想和任何人说话,只想一个人静静的发呆。有时候,想一个人躲起来脆弱,不愿别人看到自己的伤口。有时候,走过熟悉的街角,看到熟悉的背影,突然想起一个人的脸。有时候,发现自己一夜之间就长大了。 2014,写给人
- Linux下安装MySQL Web 管理工具phpMyAdmin
sunjing
PHPInstallphpMyAdmin
PHP http://php.net/
phpMyAdmin http://www.phpmyadmin.net
Error compiling PHP on CentOS x64
一、安装Apache
请参阅http://billben.iteye.com/admin/blogs/1985244
二、安装依赖包
sudo yum install gd
- 分布式系统理论
bit1129
分布式
FLP
One famous theory in distributed computing, known as FLP after the authors Fischer, Lynch, and Patterson, proved that in a distributed system with asynchronous communication and process crashes,
- ssh2整合(spring+struts2+hibernate)-附源码
白糖_
eclipsespringHibernatemysql项目管理
最近抽空又整理了一套ssh2框架,主要使用的技术如下:
spring做容器,管理了三层(dao,service,actioin)的对象
struts2实现与页面交互(MVC),自己做了一个异常拦截器,能拦截Action层抛出的异常
hibernate与数据库交互
BoneCp数据库连接池,据说比其它数据库连接池快20倍,仅仅是据说
MySql数据库
项目用eclipse
- treetable bug记录
braveCS
table
// 插入子节点删除再插入时不能正常显示。修改:
//不知改后有没有错,先做个备忘
Tree.prototype.removeNode = function(node) {
// Recursively remove all descendants of +node+
this.unloadBranch(node);
// Remove
- 编程之美-电话号码对应英语单词
bylijinnan
java算法编程之美
import java.util.Arrays;
public class NumberToWord {
/**
* 编程之美 电话号码对应英语单词
* 题目:
* 手机上的拨号盘,每个数字都对应一些字母,比如2对应ABC,3对应DEF.........,8对应TUV,9对应WXYZ,
* 要求对一段数字,输出其代表的所有可能的字母组合
- jquery ajax读书笔记
chengxuyuancsdn
jQuery ajax
1、jsp页面
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="GBK"%>
<%
String path = request.getContextPath();
String basePath = request.getScheme()
- JWFD工作流拓扑结构解析伪码描述算法
comsci
数据结构算法工作活动J#
对工作流拓扑结构解析感兴趣的朋友可以下载附件,或者下载JWFD的全部代码进行分析
/* 流程图拓扑结构解析伪码描述算法
public java.util.ArrayList DFS(String graphid, String stepid, int j)
- oracle I/O 从属进程
daizj
oracle
I/O 从属进程
I/O从属进程用于为不支持异步I/O的系统或设备模拟异步I/O.例如,磁带设备(相当慢)就不支持异步I/O.通过使用I/O 从属进程,可以让磁带机模仿通常只为磁盘驱动器提供的功能。就好像支持真正的异步I/O 一样,写设备的进程(调用者)会收集大量数据,并交由写入器写出。数据成功地写出时,写入器(此时写入器是I/O 从属进程,而不是操作系统)会通知原来的调用者,调用者则会
- 高级排序:希尔排序
dieslrae
希尔排序
public void shellSort(int[] array){
int limit = 1;
int temp;
int index;
while(limit <= array.length/3){
limit = limit * 3 + 1;
- 初二下学期难记忆单词
dcj3sjt126com
englishword
kitchen 厨房
cupboard 厨柜
salt 盐
sugar 糖
oil 油
fork 叉;餐叉
spoon 匙;调羹
chopsticks 筷子
cabbage 卷心菜;洋白菜
soup 汤
Italian 意大利的
Indian 印度的
workplace 工作场所
even 甚至;更
Italy 意大利
laugh 笑
m
- Go语言使用MySQL数据库进行增删改查
dcj3sjt126com
mysql
目前Internet上流行的网站构架方式是LAMP,其中的M即MySQL, 作为数据库,MySQL以免费、开源、使用方便为优势成为了很多Web开发的后端数据库存储引擎。MySQL驱动Go中支持MySQL的驱动目前比较多,有如下几种,有些是支持database/sql标准,而有些是采用了自己的实现接口,常用的有如下几种:
http://code.google.c...o-mysql-dri
- git命令
shuizhaosi888
git
---------------设置全局用户名:
git config --global user.name "HanShuliang" //设置用户名
git config --global user.email "
[email protected]" //设置邮箱
---------------查看环境配置
git config --li
- qemu-kvm 网络 nat模式 (四)
haoningabc
kvmqemu
qemu-ifup-NAT
#!/bin/bash
BRIDGE=virbr0
NETWORK=192.168.122.0
GATEWAY=192.168.122.1
NETMASK=255.255.255.0
DHCPRANGE=192.168.122.2,192.168.122.254
TFTPROOT=
BOOTP=
function check_bridge()
- 不要让未来的你,讨厌现在的自己
jingjing0907
生活 奋斗 工作 梦想
故事one
23岁,他大学毕业,放弃了父母安排的稳定工作,独闯京城,在家小公司混个小职位,工作还算顺手,月薪三千,混了混,混走了一年的光阴。 24岁,有了女朋友,从二环12人的集体宿舍搬到香山民居,一间平房,二人世界,爱爱爱。偶然约三朋四友,打扑克搓麻将,日子快乐似神仙; 25岁,出了几次差,调了两次岗,薪水涨了不过百,生猛狂飙的物价让现实血淋淋,无力为心爱银儿购件大牌
- 枚举类型详解
一路欢笑一路走
enum枚举详解enumsetenumMap
枚举类型详解
一.Enum详解
1.1枚举类型的介绍
JDK1.5加入了一个全新的类型的”类”—枚举类型,为此JDK1.5引入了一个新的关键字enum,我们可以这样定义一个枚举类型。
Demo:一个最简单的枚举类
public enum ColorType {
RED
- 第11章 动画效果(上)
onestopweb
动画
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/xhtml1/DTD/xhtml1-transitional.dtd">
<html xmlns="http://www.w3.org/
- Eclipse中jsp、js文件编辑时,卡死现象解决汇总
ljf_home
eclipsejsp卡死js卡死
使用Eclipse编辑jsp、js文件时,经常出现卡死现象,在网上百度了N次,经过N次优化调整后,卡死现象逐步好转,具体那个方法起到作用,不太好讲。将所有用过的方法罗列如下:
1、取消验证
windows–>perferences–>validation
把 除了manual 下面的全部点掉,build下只留 classpath dependency Valida
- MySQL编程中的6个重要的实用技巧
tomcat_oracle
mysql
每一行命令都是用分号(;)作为结束
对于MySQL,第一件你必须牢记的是它的每一行命令都是用分号(;)作为结束的,但当一行MySQL被插入在PHP代码中时,最好把后面的分号省略掉,例如:
mysql_query("INSERT INTO tablename(first_name,last_name)VALUES('$first_name',$last_name')");
- zoj 3820 Building Fire Stations(二分+bfs)
阿尔萨斯
Build
题目链接:zoj 3820 Building Fire Stations
题目大意:给定一棵树,选取两个建立加油站,问说所有点距离加油站距离的最大值的最小值是多少,并且任意输出一种建立加油站的方式。
解题思路:二分距离判断,判断函数的复杂度是o(n),这样的复杂度应该是o(nlogn),即使常数系数偏大,但是居然跑了4.5s,也是醉了。 判断函数里面做了3次bfs,但是每次bfs节点最多