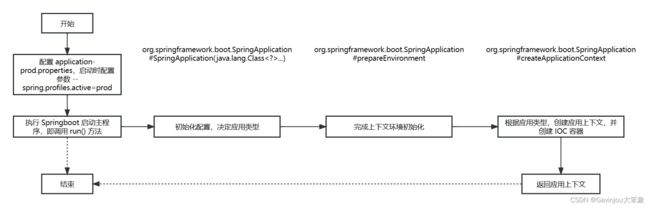
『SpringBoot 源码分析』run() 方法执行流程:(1)初始化 SpringApplication 、上下文环境、应用上下文
『SpringBoot 源码分析』run() 方法执行流程:(1)初始化 SpringApplication 、上下文环境、应用上下文
- 基于 2.2.9.RELEASE
- 问题:当方法进行了注释标记之后,springboot 又是怎么注入到容器中并创建类呢?
- 首先创建测试主程序
package com.lagou;
@SpringBootApplication//标注在类上说明这个类是`SpringBoot`的主配置类
public class SpringBootMytestApplication{
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootMytestApplication.class, args);
}
}
- 创建测试 Controller
package com.lagou.controller;
@RestController
public class TestController {
@RequestMapping("/test")
public String test(){
System.out.println("源码环境构建成功...");
return "源码环境构建成功";
}
}
SpringApplication 初始化过程
- SpringApplication 的初始化过程就是从 run() 开始的
public class SpringBootMytestApplication{
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. 调用 SpringApplication 的 run() 方法
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootMytestApplication.class, args);
}
}
- 在真正执行 run() 方法之前,首先需要初始化 SpringApplication()
public class SpringApplication {
...
public SpringApplication(Class<?>... primarySources) {
//
this(null, primarySources);
}
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) {
// 2. 初始化 SpringApplication()
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
}
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?> primarySource, String... args) {
// 1. 调用重载方法。其中 primarySource = SpringBootMytestApplication.class
return run(new Class<?>[] { primarySource }, args);
}
}
- 执行 SpringApplication() 初始化时,首先设置资源加载器为 null,同时将 primarySources 转换为 List 存到属性中,然后开始推断应用启动的类型
public class SpringApplication {
...
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
// 设置资源加载器为 null
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
// 断言加载资源类不能为 null
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
// 将 primarySources 数组转换为 List,最后放到 LinkedHashSet 集合中
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
// 1. 推断应用类型,后面会根据类型初始化对应的环境。常用的一般都是 servlet 环境
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
...
}
}
- 推断应用启动类型的时候,首先判断 classpath 下面是否存在 org.springframework.web.reactive.DispatcherHandler,如果存在,则把应用设置为 REACTIVE 类型。如果不存在,则继续判断 classpath 下面是否存在 javax.servlet.Servlet 或者 org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext,不存在就设置应用类型为 None,否则默认是 SERVLET
public enum WebApplicationType {
NONE,
SERVLET,
REACTIVE;
private static final String WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS = "org.springframework.web.reactive.DispatcherHandler";
private static final String[] SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES = { "javax.servlet.Servlet",
"org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext" };
...
static WebApplicationType deduceFromClasspath() {
// 1. classpath 下必须存在 org.springframework.web.reactive.DispatcherHandler
if (ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBFLUX_INDICATOR_CLASS, null) && !ClassUtils.isPresent(WEBMVC_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)
&& !ClassUtils.isPresent(JERSEY_INDICATOR_CLASS, null)) {
return WebApplicationType.REACTIVE;
}
for (String className : SERVLET_INDICATOR_CLASSES) {
// 2. classpath 环境下不存在 javax.servlet.Servlet 或者 org.springframework.web.context.ConfigurableWebApplicationContext
if (!ClassUtils.isPresent(className, null)) {
return WebApplicationType.NONE;
}
}
return WebApplicationType.SERVLET;
}
}
- 推断完程序的应用类型之后吗,就开始设置初始化器
public class SpringApplication {
...
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
...
// 1. 初始化 classpath 下 META-INF/spring.factories 中已配置的 ApplicationContextInitializer
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
...
}
public void setInitializers(Collection<? extends ApplicationContextInitializer<?>> initializers) {
// 2. 设置参数
this.initializers = new ArrayList<>(initializers);
}
}
- 其中,初始化器的设置主要思路是从 META-INF/spring.factories 找到所有 key 为 org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer 的实现类,然后逐一初始化,并按照 org.springframework.core.annotation.Order 注解排序
public class SpringApplication {
...
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type) {
return getSpringFactoriesInstances(type, new Class<?>[] {});
}
/**
* 通过指定的 classloader 从 META-INF/spring.factories 获取指定的 Spring 的工厂实例
*/
private <T> Collection<T> getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
ClassLoader classLoader = getClassLoader();
// 1. 通过指定的 classLoader 从 META-INF/spring.factories 的资源文件中,
// 读取 key 为 type.getName() 的 value
Set<String> names = new LinkedHashSet<>(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
// 2. 创建工厂实例
List<T> instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes, classLoader, args, names);
// 4. 对 Spring 工厂实例排序(org.springframework.core.annotation.Order 注解指定的顺序)
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);
return instances;
}
private <T> List<T> createSpringFactoriesInstances(Class<T> type, Class<?>[] parameterTypes,
ClassLoader classLoader, Object[] args, Set<String> names) {// 反射创建对象
List<T> instances = new ArrayList<>(names.size());
for (String name : names) {
try {
Class<?> instanceClass = ClassUtils.forName(name, classLoader);
Assert.isAssignable(type, instanceClass);
Constructor<?> constructor = instanceClass.getDeclaredConstructor(parameterTypes);
// 3. 对象实例化
T instance = (T) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(constructor, args);
instances.add(instance);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot instantiate " + type + " : " + name, ex);
}
}
return instances;
}
}
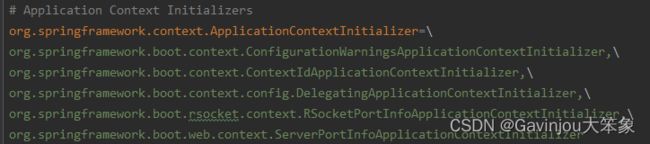
5. 设置完初始化器之后,开始设置监听器。同样是调用 getSpringFactoriesInstances() 的工作流程,首先去 META-INF/spring.factories 找到所有 key 为 org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener 的实现类,逐一初始化,并按照 org.springframework.core.annotation.Order 注解排序
public class SpringApplication {
...
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
...
// 1. 初始化 classpath 下 META-INF/spring.factories 中已配置的 ApplicationListener
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
...
}
public void setListeners(Collection<? extends ApplicationListener<?>> listeners) {
// 2. 设置参数
this.listeners = new ArrayList<>(listeners);
}
}
6. 然后根据调用栈,找到 main 入口,获取到主程序类,设置到 mainApplicationClass 属性中,并返回
public class SpringApplication {
...
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
...
// 1. 根据调用栈,推断出 main 方法的类名
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
...
}
private Class<?> deduceMainApplicationClass() {
try {
StackTraceElement[] stackTrace = new RuntimeException().getStackTrace();
for (StackTraceElement stackTraceElement : stackTrace) {
if ("main".equals(stackTraceElement.getMethodName())) {
return Class.forName(stackTraceElement.getClassName());
}
}
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
// Swallow and continue
}
return null;
}
}
获取启动监听器
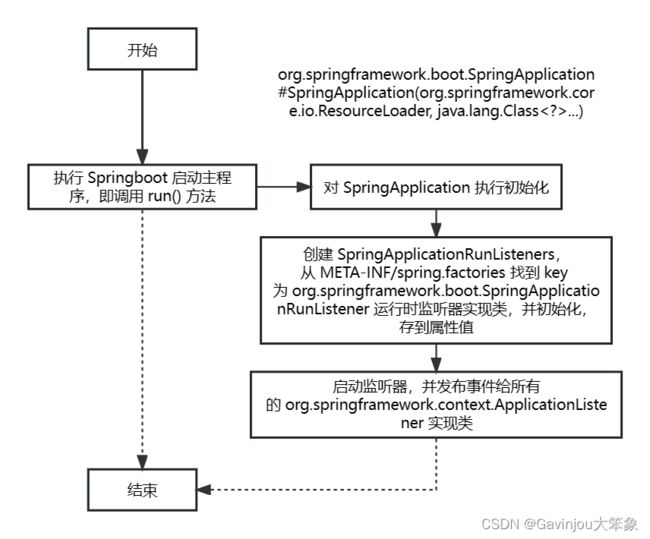
- 当完成初始化 SpringApplication 后,开始真正执行 run() 方法
public class SpringApplication {
...
public static ConfigurableApplicationContext run(Class<?>[] primarySources, String[] args) {
// 两件事:
// 初始化 SpringApplication
// 1. 执行 run() 方法
return new SpringApplication(primarySources).run(args);
}
}
- 首先初始化 StopWatch 监控程序运行时间,然后开始获取运行时监听器
public class SpringApplication {
...
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
// 记录程序运行时间
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
// ConfigurableApplicationContext Spring 的上下文
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
configureHeadlessProperty();
// 1. 获取并动监听器
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
...
}
}
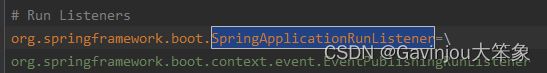
- 在执行 getRunListeners() 时,首先同样需要先从 META-INF/spring.factories 获取 key 为 org.springframework.boot.SpringApplicationRunListener 的实现类,然后存到属性中。其中 getSpringFactoriesInstances() 已经说明过了,就不再叙述,同时 SpringApplicationRunListener.class 和 org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener 不一样,这个是个发布器,主要是将在 SpringBoot 不同阶段广播出来的消息传递给 ApplicationListener 实现类
public class SpringApplication {
private final Log log;
private final List<SpringApplicationRunListener> listeners;
...
private SpringApplicationRunListeners getRunListeners(String[] args) {
Class<?>[] types = new Class<?>[] { SpringApplication.class, String[].class };
// 1. SpringApplicationRunListeners 负责在 SpringBoot 启动的不同阶段,
// 广播出不同的消息,传递给 ApplicationListener 监听器实现类
return new SpringApplicationRunListeners(logger,
getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringApplicationRunListener.class, types, this, args));
}
}
- 其中,SpringApplicationRunListeners 对所有 SpringApplicationRunListener.class 的实现类进行了封装
class SpringApplicationRunListeners {
private final Log log;
private final List<SpringApplicationRunListener> listeners;
...
SpringApplicationRunListeners(Log log, Collection<? extends SpringApplicationRunListener> listeners) {
this.log = log;
this.listeners = new ArrayList<>(listeners);
}
}
- 其实实现了 SpringApplicationRunListener.class 接口的,也就只有 org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener,它初始化的时候,会把所有 org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener 存入到属性中,用于后面的广播事件给这些监听器
public class EventPublishingRunListener implements SpringApplicationRunListener, Ordered {
private final SpringApplication application;
private final String[] args;
private final SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster initialMulticaster;
public EventPublishingRunListener(SpringApplication application, String[] args) {
this.application = application;
this.args = args;
this.initialMulticaster = new SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster();
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : application.getListeners()) {
this.initialMulticaster.addApplicationListener(listener);
}
}
...
}
- 当拿到运行时监听器之后,就开始对每个运行时监听器执行监听
public class SpringApplication {
...
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
...
// 获取并启动监听器
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
// 1. 给 listener 发送 starting 事件回调
listeners.starting();
...
}
}
- 其中,所有的运行时监听器都封装在 SpringApplicationRunListeners,实际也就只有一个运行时监听器 org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener
class SpringApplicationRunListeners {
private final Log log;
private final List<SpringApplicationRunListener> listeners;
...
// 1. 在 run() 方法开始执行时,该方法就立即被调用,可用于在初始化最早期时做一些工作
void starting() {
for (SpringApplicationRunListener listener : this.listeners) {
listener.starting();
}
}
}
- 在执行 starting() 的时候,实际上就是给所有 org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener 发布一个 ApplicationStartingEvent 事件
public class EventPublishingRunListener implements SpringApplicationRunListener, Ordered {
...
@Override
public void starting() {
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(new ApplicationStartingEvent(this.application, this.args));
}
}
构建应用上下文环境(上)
- 首先在程序启动前配置两个文件,并且启动时添加运行时参数
- 设置 application.properties
server.port=8080
- 设置 application-prod.properties
server.port=2222
- 运行时参数设置
--spring.profiles.active=prod
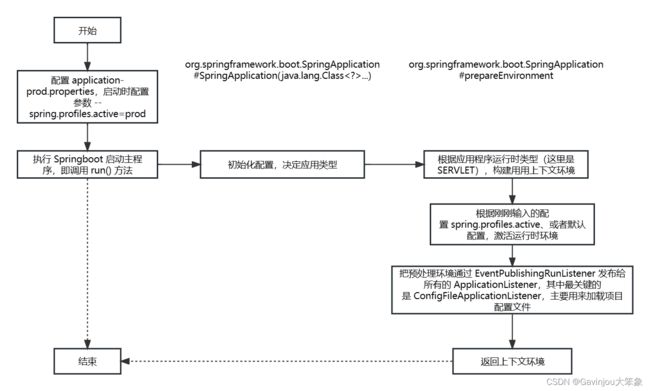
- 当完成监听器配置,并启动监听后,就需要设置应用环境上下文,从而为其他配置提供一个统一配置环境
public class SpringApplication {
...
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
...
try {
// 将运行时参数封装
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
// 1. 构造应用上下文环境
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
// 2. 处理需要忽略的 Bean
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
// 3. 打印 banner
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
...
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
...
}
...
}
}
- 首先执行 prepareEnvironment(),调用 getOrCreateEnvironment() 配置相应的运行时环境
public class SpringApplication {
...
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {// 构建整个环境上下文(用户配置,profile)
// 1. 创建并配置相应的环境
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
...
}
}
- 其中 getOrCreateEnvironment() 是根据之前创建 SpringApplication 时推断出来的 webApplicationType 来决定创建哪个环境,这里肯定创建的是 StandardServletEnvironment
public class SpringApplication {
private WebApplicationType webApplicationType;
...
private Class<? extends StandardEnvironment> deduceEnvironmentClass() {
switch (this.webApplicationType) {
case SERVLET:
return StandardServletEnvironment.class;
case REACTIVE:
return StandardReactiveWebEnvironment.class;
default:
return StandardEnvironment.class;
}
}
}
- 完成创建 StandardServletEnvironment 之后,需要根据用户配置配置 environment 系统环境
public class SpringApplication {
...
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {// 构建整个环境上下文(用户配置,profile)
// 创建并配置相应的环境
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
// 1. 根据用户配置,配置 environment 系统环境
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
...
}
}
- 配置 environment 系统环境时,首先把刚刚加的
--spring.profiles.active=prod运行时参数封装成 SimpleCommandLinePropertySource 加入环境中
public class SpringApplication {
...
protected void configureEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) {
if (this.addConversionService) {
ConversionService conversionService = ApplicationConversionService.getSharedInstance();
environment.setConversionService((ConfigurableConversionService) conversionService);
}
// 1. 将 main() 的 args(即 --spring.profiles.active=prod)封装成 SimpleCommandLinePropertySource 加入环境中
configurePropertySources(environment, args);
...
}
}
- 其中加入参数时,先从 environment 中获取 MutablePropertySources 源,然后判断是否包含名为 commandLineArgs 的属性,不包含的话,就把运行时参数封装成 SimpleCommandLinePropertySource 添加到源中
public class SpringApplication {
...
protected void configurePropertySources(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) {
// 1. 先获取 MutablePropertySources
MutablePropertySources sources = environment.getPropertySources();
if (this.defaultProperties != null && !this.defaultProperties.isEmpty()) {
sources.addLast(new MapPropertySource("defaultProperties", this.defaultProperties));
}
if (this.addCommandLineProperties && args.length > 0) {
// 2. 判断是否包含名为 commandLineArgs 的属性
String name = CommandLinePropertySource.COMMAND_LINE_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME;
if (sources.contains(name)) {
...
}
else {
// 3. 把运行时参数(即 --spring.profiles.active=prod)封装成 SimpleCommandLinePropertySource 添加到源中
sources.addFirst(new SimpleCommandLinePropertySource(args));
}
}
}
}
- 配置完 environment 系统环境后,就开始激活环境
public class SpringApplication {
...
protected void configureEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) {
if (this.addConversionService) {
ConversionService conversionService = ApplicationConversionService.getSharedInstance();
environment.setConversionService((ConfigurableConversionService) conversionService);
}
// 将 main() 的 args(即 --spring.profiles.active=prod)封装成 SimpleCommandLinePropertySource 加入环境中
configurePropertySources(environment, args);
// 1. 激活相应的配置文件
configureProfiles(environment, args);
}
}
- 激活的时候,就是把 environment 的属性开启为对应激活的配置,这里就是 prod
public class SpringApplication {
private Set<String> additionalProfiles = new HashSet<>();
...
protected void configureProfiles(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) {// 设置激活的profile信息
Set<String> profiles = new LinkedHashSet<>(this.additionalProfiles);
// 1. 获取到的 activeProfiles 就是 prod
profiles.addAll(Arrays.asList(environment.getActiveProfiles()));
// 2. 把对应属性设置为 prod
environment.setActiveProfiles(StringUtils.toStringArray(profiles));
}
}
- 配置环境并激活后,就需要使用监听器发布对应的环境给对应的监听器
public class SpringApplication {
...
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {// 构建整个环境上下文(用户配置,profile)
// 创建并配置相应的环境
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
// 根据用户配置,配置 environment系统环境
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
// 1. 启动相应的监听器,其中一个重要的监听器 ConfigFileApplicationListener 就是加载项目配置文件的监听器。
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
...
}
}
- 其中,监听器的发布,交由 org.springframework.boot.context.event.EventPublishingRunListener 广播给所有的 org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener,其中,EventPublishingRunListener 会把 environment 封装成 ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent,然后调用广播器广播
public class EventPublishingRunListener implements SpringApplicationRunListener, Ordered {
private final SpringApplication application;
private final String[] args;
private final SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster initialMulticaster;
...
@Override
public void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
// 1. 通过广播器进行广播发布
this.initialMulticaster
.multicastEvent(new ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(this.application, this.args, environment));
}
}
- 广播器实际上就是先解析 ApplicationEvent 的类型,然后获取对应的 ApplicationListener 来执行监听任务
public class SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster extends AbstractApplicationEventMulticaster {
@Nullable
private Executor taskExecutor;
...
@Override
public void multicastEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
multicastEvent(event, resolveDefaultEventType(event));
}
...
@Override
public void multicastEvent(final ApplicationEvent event, @Nullable ResolvableType eventType) {
// 1. 解析 ApplicationEvent 类型,这里是 org.springframework.boot.context.event.ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent
ResolvableType type = (eventType != null ? eventType : resolveDefaultEventType(event));
// 2. 线程池为空,所以不会调用线程池来执行
Executor executor = getTaskExecutor();
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : getApplicationListeners(event, type)) {
if (executor != null) {
executor.execute(() -> invokeListener(listener, event));
}
else {
// 3. 对 ApplicationListener 执行监听任务
invokeListener(listener, event);
}
}
}
}
- 其中,最重要的是 ConfigFileApplicationListener 监听器,主要是用来加载项目配置文件
public class ConfigFileApplicationListener implements EnvironmentPostProcessor, SmartApplicationListener, Ordered {
...
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (event instanceof ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) {
// 1. 加载项目配置文件
onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent((ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) event);
}
if (event instanceof ApplicationPreparedEvent) {
onApplicationPreparedEvent(event);
}
}
}
- 完成系统环境预处理之后,就将环境配置返回给上文使用
public class SpringApplication {
...
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {// 构建整个环境上下文(用户配置,profile)
// 创建并配置相应的环境
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
// 根据用户配置,配置 environment系统环境
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
// 启动相应的监听器,其中一个重要的监听器 ConfigFileApplicationListener 就是加载项目配置文件的监听器。
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader()).convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment,
deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
// 1. 返回环境
return environment;
}
}
构建应用上下文环境(下)
- 完成上下文环境初始化后,第一步开始构建应用上下文
public class SpringApplication {
...
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
...
try {
// 将运行时参数封装
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
// 构造应用上下文环境
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
// 处理需要忽略的 Bean
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
// 打印 banner
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
// 1. 刷新应用上下文前的准备阶段
context = createApplicationContext();
...
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
...
}
...
}
}
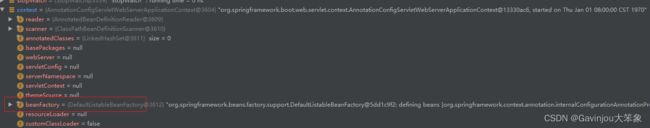
- 创建上下文也是根据 SpringApplication 初始化时的应用类型来初始化对应应用上下文,这次的类型是 SERVLET,所以创建的时候会初始化 org.springframework.boot.web.servlet.context.AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext。创建是交由 BeanUtils.instantiateClass 创建
public class SpringApplication {
private WebApplicationType webApplicationType;
private Class<? extends ConfigurableApplicationContext> applicationContextClass;
public static final String DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS = "org.springframework.context."
+ "annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext";
public static final String DEFAULT_SERVLET_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS = "org.springframework.boot."
+ "web.servlet.context.AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext";
public static final String DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS = "org.springframework."
+ "boot.web.reactive.context.AnnotationConfigReactiveWebServerApplicationContext";
...
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
Class<?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass;
if (contextClass == null) {
try {
switch (this.webApplicationType) {
case SERVLET:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_SERVLET_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
case REACTIVE:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
default:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS);
}
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Unable create a default ApplicationContext, please specify an ApplicationContextClass", ex);
}
}
return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
}
- 其中,AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext 实现了 ConfigurableWebServerApplicationContext 接口,所以返回的时候,能够强转返回。同时,也继承了 GenericWebApplicationContext,后面的代码中会经常看到这个类
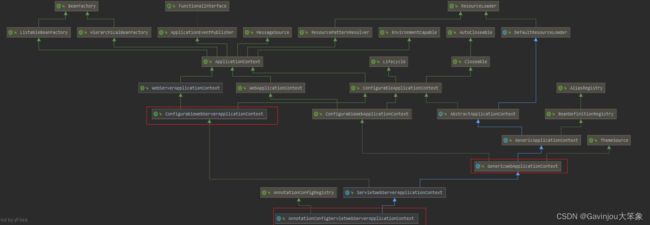
- 创建完 AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext 上下文之后,再从 META-INF/spring.factories 找到所有 key 为 org.springframework.boot.SpringBootExceptionReporter 实现类,用于报告启动的错误
public class SpringApplication {
...
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
...
try {
// 将运行时参数封装
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
// 构造应用上下文环境
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
// 处理需要忽略的 Bean
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
// 打印 banner
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
// 刷新应用上下文前的准备阶段
context = createApplicationContext();
// 1. 实例化 SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,用来支持报告关于启动的错误
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
...
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
...
}
...
}
}