可测含多进程的app-- python调用adb命令获取Android App应用的性能数据:CPU、GPU、内存、电池、耗电量(含python源码)
可测含多进程的app–Python–通过adb命令获取Android App应用的性能数据:CPU、GPU、内存、电池、耗电量,并与Perfdog取值对比结果
1、原理
python脚本通过os.popen()方法运行adb命令,获取性能数据,将性能数据保存在csv文件并算出均值、最大值、最小值。
本脚本可测试一个app包含多个进程的场景,可以获取每个进程的性能数据。
2、环境准备:
2.1 软件环境
具备python环境,Android环境
需要python库:os, csv, time, datetime, sys,time,pandas
2.2 手机状态
1、Wi-Fi模式连接手机
2、统一手机环境变量:手机满电,将手机降至常温(每个测试场景取接近的初始温度),屏幕亮度和音量调为50%
3、杀掉其他进程
4、手机温度:脚本获取到的是电池温度(Perfdog也是如此)。温枪测温:可将温枪调整为测物体模式测温,每次选取相同测试温点,测温点可选摄像头附近,不要直对摄像头。温枪测的和电池温度相近。
(手机降温:可以使用冰块、小风扇,或者将手机放入冰箱降温)
3、获取性能指标
统一说明:以下adb命令在Mac电脑上使用的是‘grep’,在windows电脑执行时改为‘findstr’
3.1 同时会用到的其他adb命令
# Wi-Fi模式连接手机,手机与电脑连接同一个Wi-Fi,查看手机IP地址,执行命令:
adb connect 192.168.88.152
# 如果连接失败,可以执行如下命令重启端口5555,再重新连接
adb tcpip 5555
# 获取app应用名
adb shell dumpsys window | grep mCurrentFocus
# 获取进程ID
adb shell ps | grep im.zego.zegoland
# 取出 文件指定行数 区间内容
os.popen("sed -n '{},{}p' {} > {}".format(sed_count['start_count'], sed_count['end_count'], original_path,result_path))
3.2 性能指标相关汇总表
| 性能指标 | 在.csv文件中的名称 | 可测目标 | 与Perfdog对比 | adb命令 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 电池百分比、 电池温度 |
battery_precent、 temperature[°C] |
手机 | 相同 | adb shell dumpsys battery |
| 耗电量:总、 屏幕、CPU、摄像头、Wi-Fi、系统服务、传感器、麦克风 |
‘battery_sum[mAh]’, ‘battery_screen[mAh]’, ‘battery_cpu[mAh]’, ‘battery_camera[mAh]’, ‘battery_wifi[mAh]’, ‘battery_system_services[mAh]’, ‘battery_sensors[mAh]’, ‘battery_audio[mAh]’ |
整个app | Perfdog计算的是功耗 | # 获取耗电量,单位:mAh,一定要WiFi模式连接手机 # 要先清空已有的耗电数据 adb shell dumpsys batterystats --enable full-wake-history # 重置设备耗电数据 adb shell dumpsys batterystats --reset # 执行测试场景后,获取耗电量数据 # 获取应用进ID,去掉下划线,如“u0_a901”,取值“u0a901” # adb shell ps | grep im.zego.zegoland 获取被测应用的耗电量 adb shell dumpsys batterystats > batteryinfo.txt #通过筛选关键字(详细代码中会写)获取耗电量所在开始、结尾行数,再通过sed命令截取区间,最后在这个sed区间内根据uid和耗电项关键字筛选耗电量数据 |
| CPU使用率 | AppCPU[%] | 接近,可替代 | 多进程 | # -n指定刷新次数 adb shell top -n 1 > cpuinfo.txt # 再根据PID筛选被测app的cpu数据 |
| GPU使用率 | GUsage[%] | 与PerfDog误差在0.001位 | 手机 | # 获取GPU数据,使用第2个数除以第1个数 # 部分机型用这个命令,如一加8T,OPPO Reno6 adb shell cat /sys/class/kgsl/kgsl-3d0/gpubusy # 部分机型用这个命令,如红米note7 adb shell su -c ‘cat /sys/class/kgsl/kgsl-3d0/gpubusy’ |
| 内存Pss | PerfDog-Memory-Pss[MB] | 与Perfdog取值相同 | 多进程 | # adb shell dumpsys meminfo > meminfo.txt #通过筛选关键字(详细代码中会写)获取Pss所在开始、结尾行数,再通过sed命令截取区间,最后在这个sed区间内根据PID和内存位置获取内存Pss数据 |
| 内存Uss | Memory-Uss[MB] | 物理专属内存,需要手机root,Perfdog获取的是Pss | / | # 需要手机root #部分手机使用如下命令 adb shell ‘procrank’ # 部分手机使用如下命令 adb shell su -c ‘procrank’ |
关于Android 系统内存耗用:VSS/RSS/PSS/USS 的介绍,可参考:
VSS/RSS/PSS/USS 的介绍【声网】
4、源码
4.1 获取AppCPU使用率,GPU使用率、内存Pss、电池百分比、电池温度、耗电量源码
使用时,根据自己测试信息修改"if main"中的appName、deviceName、性能数据文件名PerfDataFile、收集性能时间runTime(单位秒,可修改为分钟、小时),被测进程(可多个)
#! /usr/bin/env python3
# _*_ coding:utf-8 _*_
"""
@Auth : Dora
@ Time: 2023.5.27
调整为不依赖外部方法的脚本
"""
import os, csv, time, datetime, sys
from time import sleep
import pandas as pd
class Logger(object):
def __init__(self, filename='default.log', stream=sys.stdout):
self.terminal = stream
self.log = open(filename, 'a+')
def write(self, message):
self.terminal.write(message)
self.log.write(message)
def flush(self):
pass
# 将控制台输出到日志文件中,日志是追加模式,记得定时清理
# 便于检验数据获取是否正确。也可将这部分删除
sys.stdout = Logger('../log/stout_log.log', sys.stdout)
sys.stderr = Logger('../log/stout.log_file', sys.stderr)
# 可用
class PertestInfo:
def __init__(self, appName, deviceName, PerfDataFile, runTime, *progress):
self.PerfDataFile = PerfDataFile
# 分割线,便于定位日志
print("{:*^50s}".format("Split Line"))
print("{:+^50s}".format(self.PerfDataFile))
self.appName = appName # 要测试的app
self.progress = progress # 要测试的进程,一个应用可能有多个进程
print("self.progress:", self.progress, type(self.progress))
self.deviceName = deviceName # 设备名称
self.current_time = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d-%H-%M-%S", time.localtime())
# 运行时间
self.run_time = datetime.timedelta(seconds=runTime) # 收集性能数据时长,时间单位可修改为:hours,minutes,seconds
def clear_getsize(self, file_path):
# 可以写成一个装饰器,待优化
with open(file_path,'w'):
pass
start_time = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d-%H-%M-%S", time.localtime())
os.popen('adb -s {} shell top -n 1 > {}'.format(deviceName, file_path))
while not os.path.getsize(file_path):
# os.path.getsize() 返回文件的字节数,如果为 0,则代表空
# 判断执行top命令返回的数据是否存入文件,若文件为0,继续sleep(1)
sleep(1)
end_time = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d-%H-%M-%S", time.localtime())
print('运行top命令开始时间:', start_time)
print('运行top命令数据保存到文件的结束时间:', end_time)
def get_PID(self):
# 获取pid
appPID = {}
# result = os.popen('adb -s {} shell ps | grep {}'.format(self.deviceName, appName))
for app in self.progress:
# print('app:', app)
result = os.popen('adb -s {} shell ps | grep {}'.format(self.deviceName, app))
# print("pid result:", result)
for line in result.readlines():
print('line:', line, type(line))
line = '#'.join(line.split()) + '#'
# print('line#:', line)
appstr = app + '#'
if appstr in line:
print('line#:', line)
pid = line.split('#')[1]
# print("pid:", pid)
appPID[app] = pid
print('appPID:', appPID)
sleep(1)
return appPID
def sed_result(self, original_path, keyword, result_path):
# 获取开始、结束行数
start_time = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d-%H-%M-%S", time.localtime())
print('获取start_index开始时间:', start_time)
sed_index = {'start_index': 0, 'end_index': 0}
while sed_index['start_index'] == 0:
sleep(1)
for index, line in enumerate(open(original_path, 'r')):
if keyword in line:
sed_index['start_index'] = index
print("start_index:", sed_index['start_index'])
break
end_time = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d-%H-%M-%S", time.localtime())
print('获取start_index结束时间:', end_time)
with open(original_path, 'r') as f:
result = f.readlines()[sed_index['start_index']:]
index = sed_index['start_index']
for line in result:
index = index + 1
if line in ['\n', '\r\n']:
sed_index['end_index'] = index
print("end_index:", sed_index['end_index'])
break
# 从开始、结束行数截取内容
os.popen("sed -n '{},{}p' {} > {}".format(sed_index['start_index'], sed_index['end_index'], original_path,
result_path))
# 案例:取出 / etc / passwd的第2行到第5行
# sed - n '2,5p' / etc / passwd
# result = os.popen('sed -n {}p {}'.format(500, filename)).read()
def get_batteryPercent_temperature(self):
# 获取电量半分比和电池温度
result = os.popen("adb -s {} shell dumpsys battery".format(self.deviceName)) # .read()
# print(result)
battery_percent = {'battery_percent': '', 'temperature': ''}
for line in result:
# print("line:{}-----", line)
if "level" in line:
battery_percent['battery_percent'] = int(line.split(":")[1])
# print("battery_percent:{},type(battery_percent):{}".format(battery_percent, type(battery_percent)))
if "temperature" in line:
battery_percent['temperature'] = int(line.split(":")[1]) / 10
# print("battery_percent:{},type(battery_percent):{}".format(battery_percent, type(battery_percent)))
print("battery_percent:", battery_percent)
return battery_percent
def reset_battery(self):
# 执行业务场景前,清空耗电数据,并重置设备耗电数据
os.popen("adb -s {} shell dumpsys batterystats --enable full-wake-history".format(self.deviceName)) # 清空已有的耗电数据
sleep(2)
os.popen("adb -s {} shell dumpsys batterystats --reset".format(self.deviceName)) # 重置设备耗电数据
def get_battery(self):
# 获取耗电量,单位:mAh
# 一定要WiFi模式连接手机
battery = {'battery_sum': '', 'battery_screen': '', 'battery_cpu': '', 'battery_camera': '', 'battery_wifi': '',
'battery_system_services': '', 'battery_sensors': '', 'battery_audio': ''}
# 获取进程ID:uid
cmd1 = "adb -s {} shell ps | grep {}".format(self.deviceName, self.appName)
uid_data = os.popen(cmd1).read()
uid_original = uid_data.split()[0]
uid = uid_original.replace('_', '')
print('uid:', uid)
original_path = '../log/original_data.txt'
result_path = '../log/sed_result.txt'
# 先清空之前的内容
with open(original_path,'w'):
pass
with open(result_path,'w'):
pass
start_time = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d-%H-%M-%S", time.localtime())
str1 = ' Estimated power use (mAh):'
cmd2 = 'adb -s {} shell dumpsys batterystats > {}'.format(self.deviceName, original_path)
os.popen(cmd2)
while not os.path.getsize(original_path):
# os.path.getsize() 返回文件的字节数,如果为 0,则代表空
# 耗电量数据存储需要时间,判断执行top命令返回的数据是否存入文件
sleep(1)
end_time = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d-%H-%M-%S", time.localtime())
print('运行获取耗电量开始时间:', start_time)
print('运行耗电量数据保存到文件的结束时间:', end_time)
self.sed_result(original_path=original_path, keyword=str1, result_path=result_path)
while not os.path.getsize(result_path):
sleep(1)
with open(result_path, 'r') as f:
for line in f.readlines():
if uid in line:
print('battery_line:', line)
line = '#'.join(line.split())
battery['battery_sum'] = line.split('#')[2]
if 'screen=' in line:
battery['battery_screen'] = line.split('screen=')[1].split('#')[0]
if 'cpu=' in line:
battery['battery_cpu'] = line.split('cpu=')[1].split('#')[0]
if 'camera=' in line:
battery['battery_camera'] = line.split('camera=')[1].split('#')[0]
if 'wifi=' in line:
battery['battery_wifi'] = line.split('wifi=')[1].split('#')[0]
if 'system_services=' in line:
battery['battery_system_services'] = line.split('system_services=')[1].split('#')[0]
if 'sensors=' in line:
battery['battery_sensors'] = line.split('sensors=')[1].split('#')[0]
if 'audio=' in line:
battery['battery_audio'] = line.split('audio=')[1].split('#')[0]
print('battery:\n', battery)
return battery
def get_cpuinfo(self):
# 获取PID
appPID = self.get_PID()
# print("appPID:", appPID)
appCPU = {}
file_path = '../log/cpuinfo.txt'
# 先清空之前的内容
with open(file_path,'w'):
pass
start_time = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d-%H-%M-%S", time.localtime())
os.popen('adb -s {} shell top -n 1 > {}'.format(deviceName, file_path))
while not os.path.getsize(file_path):
# os.path.getsize() 返回文件的字节数,如果为 0,则代表空
# 判断执行top命令返回的数据是否存入文件
sleep(1)
end_time = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d-%H-%M-%S", time.localtime())
print('运行top命令开始时间:', start_time)
print('运行top命令数据保存到文件的结束时间:', end_time)
with open(file_path, 'r') as f:
for line in f.readlines():
for app in self.progress:
if app in appPID.keys():
if appPID[app] in line:
# print('app:', app)
# print('appPID line:', line)
# appCPU['time'] = int(time.time()) # 当前时间)
cpu = round(float(line.split()[-4]) / 8, 2)
appCPU[app] = cpu
print("appCPU:", appCPU)
return appCPU
def get_GUsage(self):
# 获取GPU使用率,与PerfDog误差在0.001以内
result1 = os.popen(
'adb -s {} shell "cat /sys/class/kgsl/kgsl-3d0/gpubusy"'.format(deviceName)).read() # 获取GPU占用率,一加8T
# print("result:", result1)
result2 = os.popen('adb -s {} shell su -c "cat /sys/class/kgsl/kgsl-3d0/gpubusy"'.format(
deviceName)).read() # 获取GPU占用率,红米note7
# print("result:", result2)
GUsage = 0
if result1:
data1 = result1.split()
GUsage = round(int(data1[0]) / int(data1[1]) * 100, 3) # round(i,j)给i取j位小数,X100,转化为百分比
print('GUsage1:', GUsage)
elif result2:
data2 = result2.split()
GUsage = round(int(data2[0]) / int(data2[1]) * 100, 3) # round(i,j)给i取j位小数,X100,转化为百分比
print('GUsage2:', GUsage)
else:
print("GUsage获取失败,可能获取GPU命令不适用于被测机型")
return GUsage
def get_memory_Pss(self):
# 获取pid
appPID = self.get_PID()
# 获取内存数据
original_path = '../log/original_data.txt'
result_path = '../log/sed_result.txt'
# 先清空之前的内容
with open(original_path,'w'):
pass
with open(result_path,'w'):
pass
start_time = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d-%H-%M-%S", time.localtime())
str1 = 'Total PSS by process:'
cmd2 = 'adb -s {} shell dumpsys meminfo > {}'.format(self.deviceName, original_path)
print('cmd2:', cmd2)
os.popen(cmd2)
while not os.path.getsize(original_path):
# os.path.getsize() 返回文件的字节数,如果为 0,则代表空
# 判断执行top命令返回的数据是否存入文件
sleep(1)
end_time = time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d-%H-%M-%S", time.localtime())
print('运行获取内存开始时间:', start_time)
print('运行内存数据保存到文件的结束时间:', end_time)
self.sed_result(original_path=original_path, keyword=str1, result_path=result_path)
while not os.path.getsize(result_path):
sleep(1)
# appPSS = {'im.zego.zegoland:zegoland_avatar': 0, 'im.zego.zegoland:zegoland_unity': 0,'im.zego.zegoland:zegoland': 0}
appPss = {}
with open(result_path, 'r') as f:
for line in f.readlines():
for app in self.progress:
if app in appPID.keys():
if appPID[app] in line:
# print('app:', app)
print('app_mem_line:', line, app, appPID[app])
Pss = round((int(line.strip().split('K: ')[0].replace(',', ''))) / 1024, 2)
# print("Pss:", Pss)
appPss[app] = Pss
print("appPss", appPss)
return appPss
def analyse_dumpsys_Csv(self, fileName):
# 对性能数据文件进行计算,获取均值、最大值、最小值
analyse_data = []
info = pd.read_csv(fileName, encoding='gbk')
rowsName = info.columns # 列名
print('列名:', rowsName)
lines = info.shape[0] # 行数
rows = info.shape[1] # 列数
print("行:{},type{},列:{}".format(lines, type(lines), rows))
# result = {}
avg_data = ['', '', '', 'avg'] # 存放均值
max_data = ['', '', '', 'max'] # 存放最大值
min_data = ['', '', '', 'min'] # 存放最小值
for row_name in rowsName:
if row_name not in ['id', 'hour', 'minute', 'second']:
avg_value = round(info[row_name].mean(), 2)
max_value = info[row_name].max()
min_value = info[row_name].min()
avg_data.append(avg_value)
max_data.append(max_value)
min_data.append(min_value)
# 将均值、最大值、最小值存入analyse_data以便输入csv文件
analyse_data.append(avg_data)
analyse_data.append(max_data)
analyse_data.append(min_data)
print('analyse_data:', analyse_data)
# 在数据表中插入平均值、最大值、最小值
with open(fileName, 'a+', newline='') as file:
# a+ 追加方式写+读
writer = csv.writer(file)
writer.writerows(analyse_data)
sleep(1)
file.close()
def perf_run(self):
# 执行获取数据函数
GPU_battery_data = [
['id', 'hour', 'minute', 'second', 'GUsage[%]', 'battery_percent[%]', 'temperature', 'battery_sum[mAh]',
'battery_screen[mAh]', 'battery_cpu[mAh]', 'battery_camera[mAh]', 'battery_wifi[mAh]',
'battery_system_services[mAh]', 'battery_sensors[mAh]', 'battery_audio[mAh]']]
print('GPU_battery_data:', GPU_battery_data)
print("now:", datetime.datetime.now())
print('run_time:', self.run_time)
self.reset_battery() # 清空耗电数据,并重置耗电数据
sleep(1)
id = 1 # id:可以运行的次数
end_time = datetime.datetime.now() + self.run_time
mem_Pss_data = []
cpu_data = []
while end_time > datetime.datetime.now():
# 在指定时间内运行
battery_percent = self.get_batteryPercent_temperature() # 获取电量百分数和电池温度
print('battery_percent:', battery_percent)
# sleep(1)
GUsage = self.get_GUsage() # 获取GPU占用率
# sleep(1)
GPU_battery_data.append((
str(id), str(datetime.datetime.now().hour), str(datetime.datetime.now().minute),
str(datetime.datetime.now().second), str(GUsage),
battery_percent['battery_percent'], battery_percent['temperature'], '', '', '', '', ''))
cpu_info = self.get_cpuinfo() # 获取cpu
cpu_info['id'] = id
cpu_info['hour'] = datetime.datetime.now().hour
cpu_info['minute'] = datetime.datetime.now().minute
cpu_info['second'] = datetime.datetime.now().second
# cpu_info['time'] = str(datetime.datetime.now().hour)+':'+str(datetime.datetime.now().minute)+':'+str(datetime.datetime.now().second)
cpu_data.append(cpu_info)
# sleep(1)
mem_Pss = self.get_memory_Pss() # 获取内存
mem_Pss['id'] = id
mem_Pss['hour'] = datetime.datetime.now().hour
mem_Pss['minute'] = datetime.datetime.now().minute
mem_Pss['second'] = datetime.datetime.now().second
mem_Pss_data.append(mem_Pss)
# print("多组Pss数据:", mem_Pss_data)
id = id + 1
sleep(1)
# 最后一组数据展示耗电量 mAh
battery_percent = self.get_batteryPercent_temperature() # 获取电量和电池温度
# sleep(1)
cpu_info = self.get_cpuinfo() # 获取cpu
print('cpu_info:', cpu_info)
cpu_info['id'] = id
cpu_info['hour'] = datetime.datetime.now().hour
cpu_info['minute'] = datetime.datetime.now().minute
cpu_info['second'] = datetime.datetime.now().second
cpu_data.append(cpu_info)
# sleep(1)
GUsage = self.get_GUsage() # 获取GPU占用率
# sleep(1)
mem_Pss = self.get_memory_Pss() # 获取内存
id = id + 1
mem_Pss['id'] = id
mem_Pss['hour'] = datetime.datetime.now().hour
mem_Pss['minute'] = datetime.datetime.now().minute
mem_Pss['second'] = datetime.datetime.now().second
# print("一组Pss数据:", mem_Pss)
mem_Pss_data.append(mem_Pss)
# print("多组Pss数据:", mem_Pss_data)
# sleep(1)
battery = self.get_battery() # 耗电量数据,单位:mAh
print("")
GPU_battery_data.append((
str(id), str(datetime.datetime.now().hour), str(datetime.datetime.now().minute),
str(datetime.datetime.now().second), str(GUsage),
battery_percent['battery_percent'], battery_percent['temperature'], battery['battery_sum'],
battery['battery_screen'], battery['battery_cpu'], battery['battery_camera'], battery['battery_wifi'],
battery['battery_system_services'], battery['battery_sensors'], battery['battery_audio']))
print("收集性能数据结束时间:", datetime.datetime.now())
sleep(1)
print("保存数据")
# 保存数据GPU和battery数据
with open('../data/batatery_GPU-%s' % self.PerfDataFile, 'w', newline='') as file:
writer = csv.writer(file, quoting=csv.QUOTE_ALL)
writer.writerows(GPU_battery_data)
sleep(10)
file.flush()
sleep(2)
file.close()
print("分析数据")
# 分析数据
# self.analyse_perf_Csv('../data/batatery_GPU-%s' % self.PerfDataFile)
# 分析GPU和battery数据
self.analyse_dumpsys_Csv('../data/batatery_GPU-%s' % self.PerfDataFile)
# 保存内存数据
fieldName = []
for app in self.progress:
# print('app:', app)
fieldName.append(app)
els = ['id', 'hour', 'minute', 'second']
fieldName = els + fieldName
print('filedName:', fieldName)
with open('../data/mem_Pss-%s' % self.PerfDataFile, 'w', newline='') as csvfile:
writer = csv.DictWriter(csvfile, fieldnames=fieldName)
writer.writeheader()
for row in mem_Pss_data:
writer.writerow(row)
self.analyse_dumpsys_Csv('../data/mem_Pss-%s' % self.PerfDataFile)
# 保存cpu数据
"""
cpu_fieldName = []
for app in self.progress:
# print('app:', app)
cpu_fieldName.append(app)
cpu_els = ['id', 'time']
cpu_fieldName = cpu_els + cpu_fieldName
"""
with open('../data/AppCPU-%s' % self.PerfDataFile, 'w', newline='') as csvfile:
writer = csv.DictWriter(csvfile, fieldnames=fieldName)
writer.writeheader()
for row in cpu_data:
writer.writerow(row)
self.analyse_dumpsys_Csv('../data/AppCPU-%s' % self.PerfDataFile, )
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 一定要Wi-Fi模式连接手机
# deviceName = '192.168.89.48:5555'
# deviceName = '192.168.1.105:5555'
# deviceName = '192.168.88.152:5555' # 一加8T
# deviceName = '192.168.88.145:5555' # 华为P50
deviceName = '192.168.88.210:5555' # oppo reno6
# deviceName = '192.168.1.106:5555'
# deviceName = '192.168.88.192:5555' # 小米11青春版
# deviceName = '192.168.88.198:5555' # 红米note7
# deviceName = '192.168.88.199:5555' # oppo reno3 pro
appName = 'im.zego.zegoland' # ZegoLand
# appName = 'com.zego.goavatar' # avatar
# 运行时常
runTime = 60
PerfDataFile = "OPPOreno6-语聊房-{}.csv".format(
str(time.strftime("%Y-%m-%d-%H-%M-%S", time.localtime())))
# 应用包含多个进程时,存放于*progress
# ZL
phone = PertestInfo(appName, deviceName, PerfDataFile, runTime, 'im.zego.zegoland:zegoland_avatar',
'im.zego.zegoland:zegoland_unity',
'im.zego.zegoland')
# phone = PertestInfo(appName, deviceName, PerfDataFile, runTime,'com.zego.goavatar')
# appPID = phone.get_PID()
# phone.get_battery()
# phone.get_GUsage()
# phone.get_cpuinfo()
# phone.get_memory_Pss()
phone.perf_run()
5、测试数据示例
测试数据输入到csv文件,并算出平均值、最大值、最小值。示例截图如下:
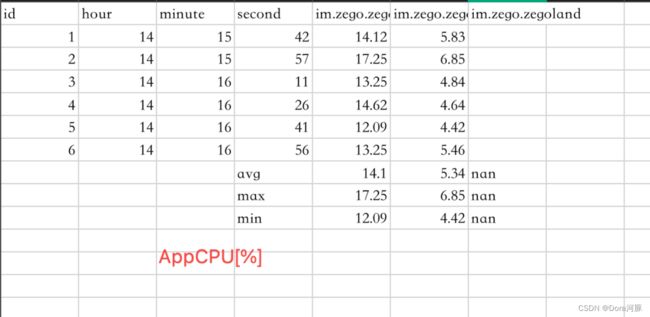
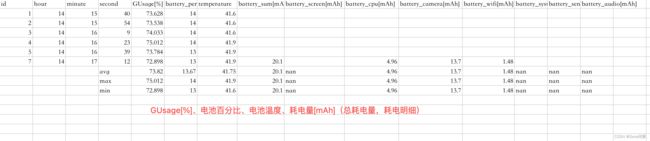

6、使用场景:
1、手动将app设置到测试场景,运行性能测试脚本perftestino.py,收集性能数据;
2、使用多线程,在执行monkey测试的同时收集性能数据和log cat日志,同时检测crash,导出crash日志;
3、使用多线程,在执行UI自动化测试场景的同时收集性能数据
4、手工测试功能时,运行性能测试脚本,捕捉可能存在的内存泄露等问题