数据结构之并查集
并查集
- 1. 并查集原理
- 2. 并查集实现
- 3. 并查集应用
-
- 3.1 省份数量
- 3.2 等式方程的可满足性
- 4. 并查集的优缺点及时间复杂度
1. 并查集原理
并查表原理是一种树型的数据结构,用于处理一些不相交集合的合并及查询问题。并查集的思想是用一个数组表示了整片森林(parent),树的根节点唯一标识了一个集合,我们只要找到了某个元素的树根,就能确定它在哪个集合里。这类问题的抽象数据类型称为并查集(union-find set)。
这个数据结构主要用于解决一些元素分组的问题,比如在开始时让每个元素构成一个单元素的集合,然后按一定顺序将属于同一组的元素所在的集合合并,其间要反复查找一个元素在哪个集合中。
并查集怎样使用?并查集是用一个数组来进行表示,其中数组下标用来表示一个个体的编号, 数组中存的元素表示的是该个体在哪一个组,用组中的某个元素表示该组有多少个体。
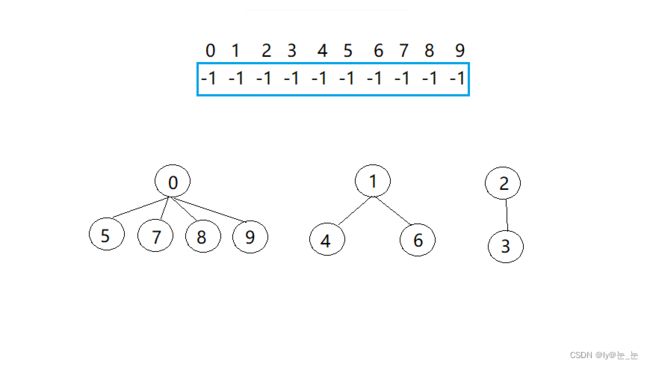
并查集通常用-1进行初始化,为什么不用0/1…呢?这是因为数组中的元素代表的是该个体在哪一个组,如果用0/1进行初始化,那么如果某个个体是自己一个为一组,但并查集中所表示的又是该个体是0/1组的。
接下来举一个并查集的例子
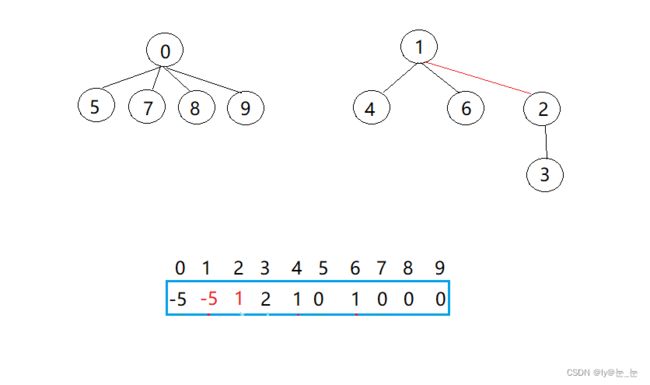
比如:某天有一个班级需要进行分组完成任务,已知该班有10位同学,将其分成3组,每组分别有5、 3、 2位同学。现在给这些学生进行编号:{0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9},其中{0,5,7,8,9},{1,4,6},{2,3}分别是每组同学的编号,0,1,2分别是每组的组长。接下来用一个并查集来表示该结构。
然后每收一个组员,就将该组员的元素加到组长下面,该组员存放的是组长的下边,如下图所示:0,1,2存放的绝对值就是每组成员的个数。
仔细观察数组中内的变化,可以得出以下结论:
- 数组的下标对应集合中元素的编号;
- 数组中如果为负数,负号代表根,数字代表该集合中元素个数;
- 数组中如果为非负数,代表该元素双亲在数组中的下标。
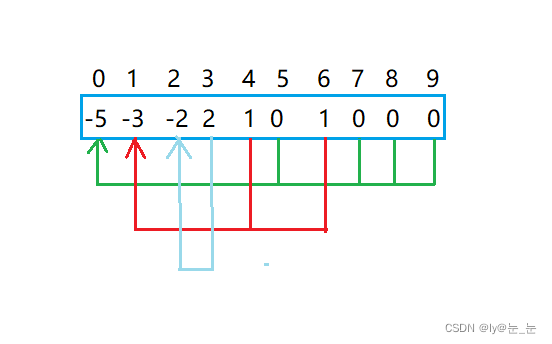
每个小组去做相似的任务,但是发现1组长和2组长所带领的小队进度较慢,时间又有些不够,于是让这两个小组合并,2组长任然是一个组长,这是比昂查表发生如下变化:
- 查找元素属于哪个集合:沿着数组表示树形关系以上一直找到根(即:树中中元素为负数的位置)
- 查看两个元素是否属于同一个集合:沿着数组表示的树形关系往上一直找到树的根,如果根相同表明在同一个集合,否则不在
- 将两个集合归并成一个集合:将两个集合中的元素合并,将一个集合名称改成另一个集合的名称
- 集合的个数:遍历数组,数组中元素为负数的个数即为集合的个数。
2. 并查集实现
接下来用代码来实现如上数据结构。
- 查找元素属于哪个集合
- 查看两个元素是否属于同一个集合
- 将两个集合归并成一个集合
- 集合的个数
#include 测试代码如下:
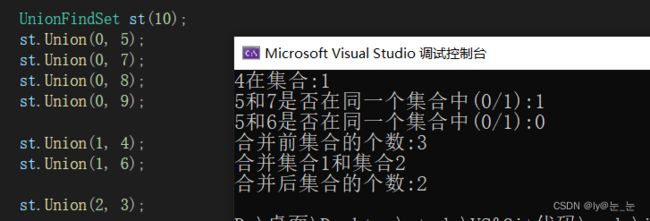
void test()
{
UnionFindSet st(10);
st.Union(0, 5);
st.Union(0, 7);
st.Union(0, 8);
st.Union(0, 9);
st.Union(1, 4);
st.Union(1, 6);
st.Union(2, 3);
cout << "4在集合:" << st.FindRoot(4) << endl;
cout << "5和7是否在同一个集合中(0/1):" << st.IsSameRoot(5, 7) << endl;
cout << "5和6是否在同一个集合中(0/1):" << st.IsSameRoot(5, 6) << endl;
cout << "合并前集合的个数:" << st.SetCount() << endl;
cout << "合并集合1和集合2" << endl;
st.Union(1, 2);
cout << "合并后集合的个数:" << st.SetCount() << endl;
}
3. 并查集应用
3.1 省份数量
1.题目描述:有 n 个城市,其中一些彼此相连,另一些没有相连。如果城市 a 与城市 b 直接相连,且城市 b 与城市 c 直接相连,那么城市 a 与城市 c 间接相连。
省份 是一组直接或间接相连的城市,组内不含其他没有相连的城市。
给你一个 n x n 的矩阵 isConnected ,其中 isConnected[i][j] = 1 表示第 i 个城市和第 j 个城市直接相连,而 isConnected[i][j] = 0 表示二者不直接相连。
返回矩阵中 省份 的数量。
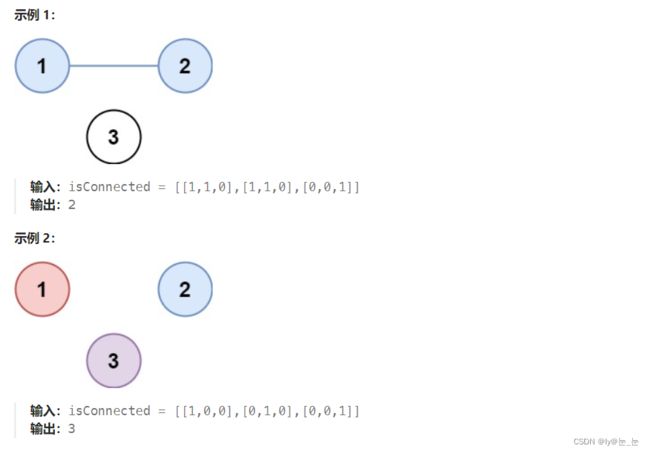
2.题目分析:可以用并查集来实现,对题目进行分析可以知道,要求集合的数量,所以需要上述3集合的合并函数和4集合的数量函数,其中3中又需要1函数,可以简单实现这几个函数,然后遍历题目中isConnected数组,只需要遍历一半即可。
3.代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
size_t FindRoot(vector<int>& ufs, int x)
{
while (ufs[x] >= 0)
x = ufs[x];
return x;
}
void Union(vector<int>& ufs, int x1, int x2)
{
int root1 = FindRoot(ufs, x1);
int root2 = FindRoot(ufs, x2);
if (root1 != root2)
{
ufs[root1] += ufs[root2];
ufs[root2] = root1;
}
}
size_t UfsCount(vector<int>& ufs)
{
int count = 0;
for (auto& x : ufs)
if (x < 0)
++count;
return count;
}
int findCircleNum(vector<vector<int>>& isConnected)
{
int n = isConnected.size();
vector<int> ufs(n, -1);
//合并相连的城市
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
{
for (int j = i + 1; j < n; ++j)
{
if (isConnected[i][j] == 1)
Union(ufs, i, j);
}
}
//寻找不相连省份的数量
size_t count = UfsCount(ufs);
return count;
}
};
3.2 等式方程的可满足性
1.题目描述:给定一个由表示变量之间关系的字符串方程组成的数组,每个字符串方程 equations[i] 的长度为 4,并采用两种不同的形式之一:“a==b” 或 “a!=b”。在这里,a 和 b 是小写字母(不一定不同),表示单字母变量名。
只有当可以将整数分配给变量名,以便满足所有给定的方程时才返回 true,否则返回 false。
提示:
- <= equations.length <= 500
- equations[i].length == 4
- equations[i][0] 和 equations[i][3] 是小写字母
- equations[i][1] 要么是 ‘=’,要么是 ‘!’
- equations[i][2] 是 ‘=’

2.题目分析:这道题需要合并相等的字母,所以需要函数3和1,由题知equations[i][0] 和 equations[i][3] 是小写字母,所以开辟一个大小为26的数组,把相等的字母合并为一组,再寻找不相等的,如果不相等得两个字母有相同的根,则返回false。
3.代码如下:
class Solution {
public:
size_t FindRoot(vector<int>& ufs, int x)
{
while (ufs[x] >= 0)
x = ufs[x];
return x;
}
void Union(vector<int>& ufs, int x1, int x2)
{
int root1 = FindRoot(ufs, x1);
int root2 = FindRoot(ufs, x2);
if (root1 != root2)
{
ufs[root1] += ufs[root2];
ufs[root2] = root1;
}
}
bool equationsPossible(vector<string>& equations)
{
vector<int> ufs(26, -1);
// 把相等的值加到一个集合中
for (auto& str : equations)
{
if (str[1] == '=')
{
Union(ufs, str[0] - 'a', str[3] - 'a');
}
}
// 在遍历一遍,找不相等的,不相等的根一定在一个集合
for (auto& str : equations)
{
if (str[1] == '!')
{
int root1 = FindRoot(ufs, str[0] - 'a');
int root2 = FindRoot(ufs, str[3] - 'a');
if (root1 == root2)
{
return false;
}
}
}
return true;
}
};
4. 并查集的优缺点及时间复杂度
并查集这个数据结构的优缺点是
优点:
- 简单:并查集只需要一个一维数组来存储每个元素的父节点,操作也很简单,一般只需要两个基本函数:find和union。
- 高效:并查集的时间复杂度主要取决于树的高度,通过一些优化策略,如路径压缩和按秩合并,可以将树的高度控制在对数级别,从而实现近乎常数的查询和合并操作。
- 灵活:并查集可以用来解决各种涉及到元素分组、连通性、最小生成树等问题,可以根据具体问题进行扩展和修改。
缺点:
- 动态:并查集只能支持动态添加和合并元素,不能支持删除和分割元素,这限制了它的应用范围。
- 无序:并查集不能保证每个集合内部的元素是有序的,也不能提供遍历每个集合内部元素的方法,这使得它难以处理一些需要排序或遍历的问题。
- 单向:并查集只能判断两个元素是否属于同一个集合,不能判断两个元素之间的具体关系,如距离、方向、层次等,这使得它难以处理一些需要细节信息的问题。
时间复杂度
并查集的时间复杂度主要取决于树的高度,通过一些优化策略,如路径压缩和按秩合并,可以将树的高度控制在对数级别,从而实现近乎常数的查询和合并操作。具体来说:
初始化:O(n),其中n为元素个数。
查找:O(log n),其中n为元素个数。
合并:O(log n),其中n为元素个数。