k8s基本概念、k8s对象、三个命令玩转所有的yaml写法、给vscode安装插件、kubectl和kubelet及自动补全
文章目录
-
- 1、K8S基本概念
- 2、kubernetes Objects(k8s对象)
-
- 2.1、定义
- 2.2、对象的spec和status
- 2.3、如何写任意资源的yaml(以Pod为例)
- 2.4、pod的yaml文件
- 2.5、k8s对象yaml的结构
- 2.6、管理k8s对象
- 2.7、对象名称
- 2.8、名称空间
- 2.9、标签和选择器
-
- 2.9.1、标签
- 2.9.2、标签选择器
- 2.10、注解annotation
- 3、三个命令玩转所有的yaml写法
- 4、给vscode安装插件
- 5、kubectl和kubelet
- 6、自动补全
1、K8S基本概念
- 集群
- master
- worker
- Node
- Pod
- 应用最终以Pod为一个基本单位部署
- Label
- 很多资源都可以打标签
- Deployment
- 应用部署用它,deployment最终会产生Pod
- Service
- 负载均衡机制
2、kubernetes Objects(k8s对象)
2.1、定义
- k8s里面操作的资源实体,就是k8s的对象,可以使用yaml来声明对象。然后让k8s根据yaml的声明创建出这个对象;kubectl create/run /expose…
- 操作 Kubernetes 对象 —— 无论是创建、修改,或者删除 —— 需要使用 Kubernetes API。比如,当使用 kubectl 命令行接口时,CLI 会执行必要的 Kubernetes API 调用
- Kubernetes对象指的是Kubernetes系统的持久化实体,所有这些对象合起来,代表了你集群的实际情况。常规的应用里,我们把应用程序的数据存储在数据库中,Kubernetes将其数据以Kubernetes对象的形式通过 api server存储在 etcd 中,具体来说,这些数据(Kubernetes对象)描述了:
- 集群中运行了哪些容器化应用程序(以及在哪个节点上运行)
- 集群中对应用程序可用的资源(网络,存储等)
- 应用程序相关的策略定义,例如,重启策略、升级策略、容错策略
- 其他Kubernetes管理应用程序时所需要的
- scheduler先计算应该去哪个节点部署
2.2、对象的spec和status
每一个 Kubernetes 对象都包含了两个重要的字段:
- spec 必须由您来提供,描述了您对该对象所期望的 目标状态
- status 只能由 Kubernetes 系统来修改,描述了该对象在 Kubernetes 系统中的 实际状态
Kubernetes通过对应的 控制器,不断地使实际状态趋向于您期望的目标状态
### 最终一致。
## etcd保存的创建资源期望的状态和最终这个资源的状态要是一致的;spec和status要最终一致
## 1、kubectl create deployment my-nginx --image=nginx
## 2、api-server保存etcd,controller-manager最终解析数据,知道集群要my-nginx一份,保
## 存到etcd
## 3、kubelet就做一件事情,spec状态和最终状态一致
## 类似于一下代码
while(true) {
if(my-nginx.replicas != spec.replicas) {
kubelet.startPod();
}
}
2.3、如何写任意资源的yaml(以Pod为例)
方式一:
kubectl run my-nginx --image=nginx # 1. 先启动一个pod
kubectl get pod my-nginx666 -oyaml # 2. 然后在集群中挑一个同类资源,获取出他的yaml文件
方式二:
kubectl run my-nginx --image=nginx --dry-run=client -oyaml # 只是干跑一遍,并不会创建pod
2.4、pod的yaml文件
kind: Pod # 资源类型 kubectl api-resources: 可以获取到所有资源
apiVersion: v1 # 同一个资源有可能有多个版本, 看 kubectl api-resources提示的
metadata: # 每一个资源定义一些元数据信息
labels:
run: my-tomcat
name: my-tomcat
spec: #资源的规格(镜像名、镜像的环境变量信息等等)
containers:
- image: tomcat
name: my-tomcat
resources: {}
dnsPolicy: ClusterFirst
restartPolicy: Always
当您在 Kubernetes 中创建一个对象时,您必须提供
- 该对象的 spec 字段,通过该字段描述您期望的 目标状态
- 该对象的一些基本信息,例如名字
可以使用 kubectl 命令行创建对象,业可以编写 .yaml 格式的文件进行创建
以deployment为例子 (deployment.yaml)
apiVersion: apps/v1
kind: Deployment
metadata:
name: nginx-deployment
spec:
selector:
matchLabels:
app: nginx
replicas: 2 # 运行 2 个容器化应用程序副本
template:
metadata:
labels:
app: nginx
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx
image: nginx:1.7.9
ports:
- containerPort: 80
1、部署: kubectl apply -f deployment.yaml
2、移除: kubectl delete -f deployment.yaml
集群中所有的资源, k8s只依赖一个存储就是etcd
2.5、k8s对象yaml的结构
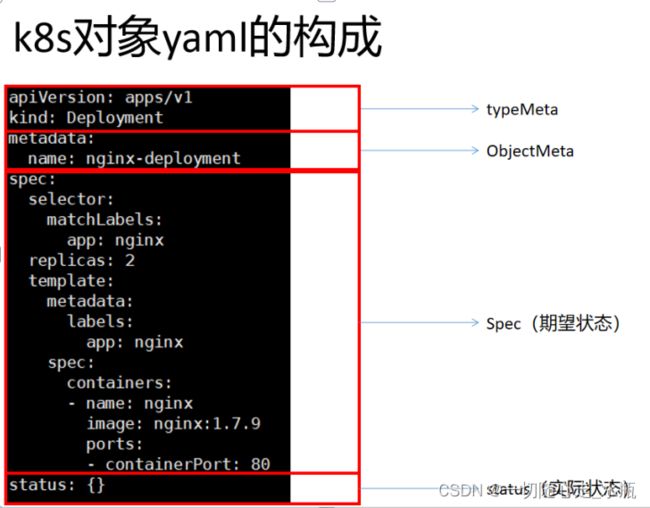
必填字段
在上述的 .yaml 文件中,如下字段是必须填写的:
- apiVersion 用来创建对象时所使用的Kubernetes API版本
- kind 被创建对象的类型
- metadata 用于唯一确定该对象的元数据:包括 name 和 namespace ,如果 namespace 为空,则默认值为 default
- spec 描述您对该对象的期望状态
不同类型的 Kubernetes,其 spec 对象的格式不同(含有不同的内嵌字段),通过 API 手册 可以查看 Kubernetes 对象的字段和描述。例如,假设您想了解 Pod 的 spec 定义,可以在 这里找到,Deployment 的 spec 定义可以在 这里 找到
https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/generated/kubernetes-api/v1.23/ 这就是我们以后要完全参照的文档
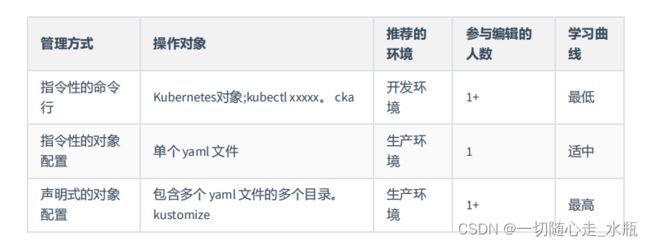
2.6、管理k8s对象
同一个Kubernetes对象应该只使用一种方式管理,否则可能会出现不可预期的结果
# 1、命令式
kubectl run nginx --image nginx
kubectl create deployment nginx --image nginx
apply -f : 没有就创建,有就修改
# 2、指令性
- 使用指令性的对象配置(imperative object configuration)时,需要向 kubectl 命令指定具体
的操作(create,replace,apply,delete等),可选参数以及至少一个配置文件的名字。配置文件中必须
包括一个完整的对象的定义,可以是 yaml 格式,也可以是 json 格式。
# 创建对象
kubectl create -f nginx.yaml
# 删除对象
kubectl delete -f nginx.yaml -f redis.yaml
# 替换对象
kubectl replace -f nginx.yaml
# 3、声明式
# 处理 configs 目录中所有配置文件中的Kubernetes对象,根据情况创建对象、或更新Kubernetes中已
经存在的对象。可以先执行 diff 指令查看具体的变更,然后执行 apply 指令执行变更;
kubectl diff -f configs/
kubectl apply -f configs/
# 递归处理目录中的内容:
kubectl diff -R -f configs/
kubectl apply -R -f configs/
# 移除
kubectl delete -f configs/
2.7、对象名称
Kubernetes REST API 中,所有的对象都是通过 name 和 UID 唯一性确定
可以通过 namespace + name 唯一性地确定一个 RESTFUL 对象,例如:
/api/v1/namespaces/{namespace}/pods/{name}
同一个名称空间下,同一个类型的对象,可以通过 name 唯一性确定。如果删除该对象之后,可以再
重新创建一个同名对象。
依据命名规则,Kubernetes对象的名字应该:
- 最长不超过 253个字符
- 必须由小写字母、数字、减号 - 、小数点 . 组成
- 某些资源类型有更具体的要求
下面的配置文件定义了一个 name 为 nginx-demo 的 Pod,该 Pod 包含一个 name 为 nginx 的
容器:
apiVersion: v1
kind: Pod
metadata:
name: nginx-demo ##pod的名字
spec:
containers:
- name: nginx ##容器的名字
image: nginx:1.7.9
ports:
- containerPort: 80 UIDs
2.8、名称空间
Kubernetes 安装成功后,默认有初始化了三个名称空间:
- default 默认名称空间,如果 Kubernetes 对象中不定义 metadata.namespace 字段,该对象将放在此名称空间下
- kube-system Kubernetes系统创建的对象放在此名称空间下
- kube-public 此名称空间自动在安装集群是自动创建,并且所有用户都是可以读取的(即使是那些未登录的用户)。主要是为集群预留的,例如,某些情况下,某些Kubernetes对象应该被所有集群用户看到。
kubectl get namespaces
kubectl describe namespaces
2.9、标签和选择器
2.9.1、标签
标签(Label)是附加在Kubernetes对象上的一组名值对,其意图是按照对用户有意义的方式来标识
Kubernetes对象,同时,又不对Kubernetes的核心逻辑产生影响。标签可以用来组织和选择一组
Kubernetes对象。您可以在创建Kubernetes对象时为其添加标签,也可以在创建以后再为其添加标签。
每个Kubernetes对象可以有多个标签,同一个对象的标签的 Key 必须唯一,例如
metadata:
labels:
key1: value1
key2: value2
2.9.2、标签选择器
通常来讲,会有多个Kubernetes对象包含相同的标签。通过使用标签选择器(label selector),用户/客户端可以选择一组对象。标签选择器(label selector)是 Kubernetes 中最主要的分类和筛选手段
#Job、Deployment、ReplicaSet 和 DaemonSet 同时支持基于等式的选择方式和基于集合的选择方式。
例如:
selector:
matchLabels:
component: redis
matchExpressions:
- {key: tier, operator: In, values: [cache]}
- {key: environment, operator: NotIn, values: [dev]}
matchLabels 是一个 {key,value} 组成的 map。map 中的一个 {key,value} 条目相当于
matchExpressions 中的一个元素,其 key 为 map 的 key,operator 为 In, values 数组则只包含 value 一个元素。matchExpression 等价于基于集合的选择方式,支持的 operator 有 In、NotIn、Exists 和 DoesNotExist。当 operator 为 In 或 NotIn 时,values 数组不能为空。所有的选择条件都以 AND 的形式合并计算,即所有的条件都满足才可以算是匹配
#添加或者修改标签
kubectl label --help
# Update pod 'foo' with the label 'unhealthy' and the value 'true'.
kubectl label pods foo unhealthy=true
# Update pod 'foo' with the label 'status' and the value 'unhealthy',
overwriting any existing value.
kubectl label --overwrite pods foo status=unhealthy
# Update all pods in the namespace
kubectl label pods --all status=unhealthy
# Update a pod identified by the type and name in "pod.json"
kubectl label -f pod.json status=unhealthy
# Update pod 'foo' only if the resource is unchanged from version 1.
kubectl label pods foo status=unhealthy --resource-version=1
# Update pod 'foo' by removing a label named 'bar' if it exists.
# Does not require the --overwrite flag.
kubectl label pods foo bar-
2.10、注解annotation
字段选择器 (Field selectors )允许您根据一个或多个资源字段的值筛选 Kubernetes 资源。 下面是一些使用字段选择器查询的例子:
- metadata.name=my-service
- metadata.namespace!=default
- status.phase=Pending
kubectl get pods --field-selector status.phase=Running 1
3、三个命令玩转所有的yaml写法
- kubectl get xxx -oyaml
- kubectl create deploy xxxxx --dry-run=client -oyaml
- kubectl explain pod.spec.xx
写完yaml 然后 kubectl apply -f 即可
4、给vscode安装插件
搜索kubernetes , 安装 yaml 和 kubernetes template 插件即可
idea、pycharm等其他编辑器也有kubernetes插件
5、kubectl和kubelet
- kubeadm安装的集群,二进制后来就是 yum install etcd api-server
- 认识核心文件夹 /etc/kubernetes . 以Pod方式安装的核心组件。
- etcd,api-server,scheduler。(安装k8s的时候,yum kubeadm kubelet kubectl)
- 集群安装的时候,为什么只有master节点的kubectl可以操作集群
- kubelet额外参数配置 /etc/sysconfig/kubelet;kubelet配置位置 /var/lib/kubelet/config.yaml
kubectl的所有命令参考:
kubectl controls the Kubernetes cluster manager.
Find more information at: https://kubernetes.io/docs/reference/kubectl/overview/
Basic Commands (Beginner): # 初学者掌握的命令
create Create a resource from a file or from stdin
expose Take a replication controller, service, deployment or pod and expose it as a new Kubernetes service
run 在集群中运行一个指定的镜像
set 为 objects 设置一个指定的特征
Basic Commands (Intermediate): # 基础命令
explain Get documentation for a resource
get 显示一个或更多 resources
edit 在服务器上编辑一个资源
delete Delete resources by file names, stdin, resources and names, or by resources and label selector
Deploy Commands: # 部署用的命令
rollout Manage the rollout of a resource
scale Set a new size for a deployment, replica set, or replication controller
autoscale Auto-scale a deployment, replica set, stateful set, or replication controller
Cluster Management Commands: # 集群管理的命令
certificate 修改 certificate 资源.
cluster-info Display cluster information
top Display resource (CPU/memory) usage
cordon 标记 node 为 unschedulable
uncordon 标记 node 为 schedulable
drain Drain node in preparation for maintenance
taint 更新一个或者多个 node 上的 taints
Troubleshooting and Debugging Commands: # debug调试使用的命令
describe 显示一个指定 resource 或者 group 的 resources 详情
logs 输出容器在 pod 中的日志
attach Attach 到一个运行中的 container
exec 在一个 container 中执行一个命令
port-forward Forward one or more local ports to a pod
proxy 运行一个 proxy 到 Kubernetes API server
cp Copy files and directories to and from containers
auth Inspect authorization
debug Create debugging sessions for troubleshooting workloads and nodes
Advanced Commands: # 高阶命令
diff Diff the live version against a would-be applied version
apply Apply a configuration to a resource by file name or stdin
patch Update fields of a resource
replace Replace a resource by file name or stdin
wait Experimental: Wait for a specific condition on one or many resources
kustomize Build a kustomization target from a directory or URL.
Settings Commands: # 设置
label 更新在这个资源上的 labels
annotate 更新一个资源的注解
completion Output shell completion code for the specified shell (bash, zsh or fish)
Other Commands: #其他
alpha Commands for features in alpha
api-resources Print the supported API resources on the server
api-versions Print the supported API versions on the server, in the form of "group/version"
config 修改 kubeconfig 文件
plugin Provides utilities for interacting with plugins
version 输出 client 和 server 的版本信息
Usage:
kubectl [flags] [options]
Use "kubectl --help" for more information about a given command.
Use "kubectl options" for a list of global command-line options (applies to all commands).
6、自动补全
# 安装
yum install bash-completion
# 自动补全
echo 'source <(kubectl completion bash)' >>~/.bashrc
kubectl completion bash >/etc/bash_completion.d/kubectl
source /usr/share/bash-completion/bash_completion