Springboot Druid配置可执行sql配置
目录
- 前言
- 项目环境
- 项目配置
- 总结
前言
在实际开发中,所有的sql语句参数都是带占位符的,但在本地开发时,为了方便测试追踪问题,经常需要查看具体执行的SQL语句内容,因此每次只能靠自己进行二次处理,耗时耗力,尤其是访问量大的情况下,很容易混淆,所以需要一个方法能够直接输出可以直接使用的SQL语句(将占位符替换成实际的参数),而Druid就支持此功能(Druid的主要功能可不是这个),所以此文主要讲如何在项目中使用Druid输出可执行SQL。
项目环境
因为是自己写的测试项目所以用到的版本都比较高,低版本的可能略有不同。
本项目使用的环境是:
Spring Boot 3.1
JDK17
Druid 1.2.18
Postgresql 42.6.0
pom.xml文件如下:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starterartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>druid-spring-boot-starterartifactId>
<version>1.2.18version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombokgroupId>
<artifactId>lombokartifactId>
<scope>providedscope>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.postgresqlgroupId>
<artifactId>postgresqlartifactId>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependenciesartifactId>
<version>3.1.1version>
<type>pomtype>
<scope>importscope>
dependency>
项目配置
- 使用
Spring Boot默认的日志logback,可以在classpath下新建application.yml、application.properties或自定义logback.xml文件告诉Spring Boot我们哪些地方需要打印日志;
yml配置如下:
logging:
level:
druid.sql.Statement: debug
spring:
datasource:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
druid:
url: jdbc:postgresql://127.0.0.1:5432/数据库名称
username: 用户名
password: 密码
driver-class-name: org.postgresql.Driver
filter:
slf4j:
enabled: true
# 只有当 isStatementExecutableSqlLogEnable() isStatementLogEnabled() 都为ture的情况才打印 可执行sql
# 在{# LogFilter#logExecutableSql }使用
statement-executable-sql-log-enable: true
# 在{# LogFilter#logExecutableSql }使用
statement-log-enabled: true
statement-create-after-log-enabled: false
statement-log-error-enabled: true
result-set-log-enabled: false
#statementPrepareAfterLogEnable
# 准备好的sql语句打印(此时为执行前)未进行参数拼接
statement-prepare-after-log-enabled: false
#isStatementParameterSetLogEnabled
#打印参数
statement-parameter-set-log-enabled: false
#statementExecuteAfterLogEnable
#sql语句执行完成后打印(执行后)未进行参数拼接
statement-execute-after-log-enabled: false
#statementCloseAfterLogEnable
statement-close-after-log-enabled: false
properties配置如下:
logging.level.druid.sql.Statement=debug
spring.datasource.druid.filter.slf4j.enabled=true
#配置可执行sql语句日志打印
#只有当 isStatementExecutableSqlLogEnable() isStatementLogEnabled() 都为ture的情况才打印 可执行sql
#在{# LogFilter#logExecutableSql }使用
spring.datasource.druid.filter.slf4j.statement-executable-sql-log-enable=true
spring.datasource.druid.filter.slf4j.statement-log-enabled=true
spring.datasource.druid.filter.slf4j.statement-log-error-enabled=true
spring.datasource.druid.filter.slf4j.statement-create-after-log-enabled=false
spring.datasource.druid.filter.slf4j.result-set-log-enabled=false
spring.datasource.druid.filter.slf4j.statement-prepare-after-log-enabled=false
spring.datasource.druid.filter.slf4j.statement-parameter-set-log-enabled=false
spring.datasource.druid.filter.slf4j.statement-execute-after-log-enabled=false
spring.datasource.druid.filter.slf4j.statement-close-after-log-enabled=false
xml配置如下:
其它配置需要配置在yml、properties文件中
<logger name="druid.sql.Statement" level="DEBUG" additivity="false">
<-换成自己的appender引用->
<appender-ref ref="STDOUT" />
logger>
以上配置则可以输出可执行SQL,因为Spring Boot默认使用的是Logback,druid中没有logback的过滤器,slf4j是所有日志的门面,所以使用slf4j输出日志,如果需要使用用log4j只需要吧slf4j替换成log4j即可,不过还是推荐使用slf4j,至于为什么使用slf4j,百度很多人都已经说的很好了,另外druid的其他配置说明也请移步专业的druid文章,他们写的更加详细,另外还需要指定druid的日志登记为debug才能显示
- 默认情况下
Druid是关闭输出可执行SQL的,需要将statement-executable-sql-log-enable设置为true,详细配置文件在:
public abstract class LogFilter extends FilterEventAdapter implements LogFilterMBean {
//druid准备了四种类型的日志输出
//这些logger分别对应打印 datasource相关、connection相关、statement相关、resultSet相关的日志
//这里我们只关注statementLoggerName是打印可执行sql的关键
protected String dataSourceLoggerName = "druid.sql.DataSource";
protected String connectionLoggerName = "druid.sql.Connection";
protected String statementLoggerName = "druid.sql.Statement";
protected String resultSetLoggerName = "druid.sql.ResultSet";
//需设置为true
private boolean statementExecutableSqlLogEnable;
}
总结
踩坑点:
- 一开始参考其它文章说是将
statement-log-enabled设置为false导致半天没有看到打印的日志最后查看源码在LogFilter#logExecutableSql有如下代码片段:
//此方法就是打印可执行SQL的方法
private void logExecutableSql(StatementProxy statement, String sql) {
//这里判断 StatementExecutableSqlLogEnable 和 StatementLogEnabled字段必须为ture
if ((!isStatementExecutableSqlLogEnable()) || !isStatementLogEnabled()) {
return;
}
int parametersSize = statement.getParametersSize();
if (parametersSize == 0) {
statementLog("{conn-" + statement.getConnectionProxy().getId() + ", " + stmtId(statement) + "} executed. "
+ sql);
return;
}
List<Object> parameters = new ArrayList<Object>(parametersSize);
for (int i = 0; i < parametersSize; ++i) {
JdbcParameter jdbcParam = statement.getParameter(i);
parameters.add(jdbcParam != null
? jdbcParam.getValue()
: null);
}
DbType dbType = DbType.of(statement.getConnectionProxy().getDirectDataSource().getDbType());
String formattedSql = SQLUtils.format(sql, dbType, parameters, this.statementSqlFormatOption);
//最终调用 statementLog 方法 打印可执行SQL语句
statementLog("{conn-" + statement.getConnectionProxy().getId() + ", " + stmtId(statement) + "} executed. "
+ formattedSql);
}
Spring Boot默认的日志框架为logback,笔者在配置的时候一直没有找到logback相关的配置信息,最后知道slf4j是日志统一接口,logback是slf4j的实现,所以druid的官方文档中没有logback的配置。只有slf4j的配置。
测试结果:

源码分析:
Druid的Filter提供了强大的扩展功能,如连接池监控(连接池配置信息、SQL执行、并发、慢查询、执行时间区间分布等,由StatFilter实现)、防止SQL注入(WallFilter)、连接池信息日志输出(LogFilter)等,这里我们只关注日志输出的Filter,其在Druid内置的实现如下:
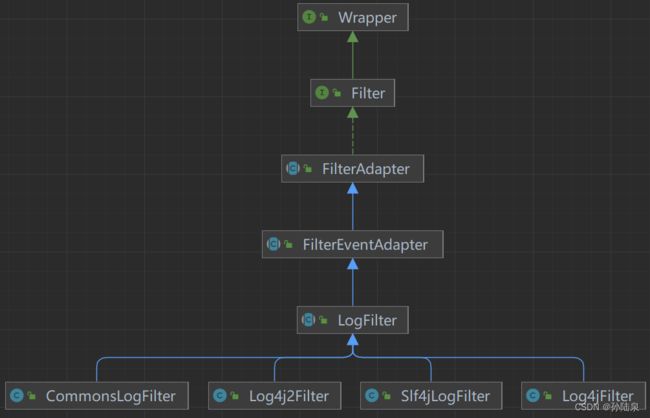
可以看到在LogFilter的实现类有CommonsLogFilter、Log4j2Filter、Slf4jLogFilter、Log4jFilter。
介绍上面几个过滤器前需要说明:slf4j、log4j、log4j2、logback的区别,这不是本文的重点,请参考:带你深入Java Log框架,彻底搞懂Log4J、Log4J2、LogBack,SLF4J
CommonsLogFilter:由于本项目使用的是Logback,Log4j2相关jar包没有引全所以爆红,实际项目中如果需要使用这个过滤器,需要引入Log4j2相关依赖。
Log4j2Filter:如果项目使用的是Log4j2请引入相关依赖并修改配置文件为log4j2

Slf4jLogFilter:注意Druid中并没有类似LogbackFilter相关类,但Logback是Slf4j的实现所以后面追踪源码我们以这个进行展开说明。

Log4jFilter:由于2015年9月,Apache软件基金业宣布,Log4j不在维护,建议所有相关项目升级到Log4j2,因此这里不做太多说明。
-
过滤器初始化注册
-
dataSource:这里可以看到实例的dataSource实现类为
DruidDataSourceWrapper,其中filters属性就是存储我们所注册的过滤器,这里是上面配置的Slf4jLogFilter
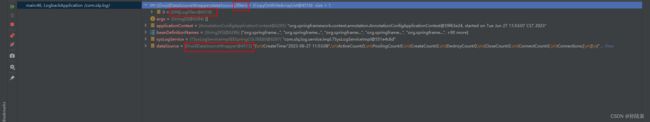
DruidDataSourceWrapper的主要初始化代码如下,仅粘出核心代码
@ConfigurationProperties("spring.datasource.druid")
public class DruidDataSourceWrapper extends DruidDataSource implements InitializingBean {
@Autowired
private DataSourceProperties basicProperties;
/**
* 这里可以看出
* spring.datasource.druid.username == spring.datasource.username
* password、url、deiverClassName等这两种方式都可以
**/
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
//if not found prefix 'spring.datasource.druid' jdbc properties ,'spring.datasource' prefix jdbc properties will be used.
if (super.getUsername() == null) {
super.setUsername(basicProperties.determineUsername());
}
if (super.getPassword() == null) {
super.setPassword(basicProperties.determinePassword());
}
if (super.getUrl() == null) {
super.setUrl(basicProperties.determineUrl());
}
if (super.getDriverClassName() == null) {
super.setDriverClassName(basicProperties.getDriverClassName());
}
}
//这里就是注册我们在配置文件中配置的过滤器了
@Autowired(required = false)
public void autoAddFilters(List<Filter> filters) {
super.filters.addAll(filters);
}
}
这里先贴出完整的调用过程:这里我们只关注Filter打印可执行SQL语句的出发时机(其它类似),我们以上图的查询为例,其它方法类似
com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource#getConnection
com.alibaba.druid.filter.FilterChainImpl#dataSource_connect
com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidPooledPreparedStatement#execute
com.alibaba.druid.proxy.jdbc.PreparedStatementProxyImpl#execute
com.alibaba.druid.filter.FilterChainImpl#preparedStatement_execute
com.alibaba.druid.filter.FilterEventAdapter#preparedStatement_execute
com.alibaba.druid.filter.logging.LogFilter#statementExecuteAfter
com.alibaba.druid.filter.logging.LogFilter#logExecutableSql
com.alibaba.druid.filter.logging.Slf4jLogFilter#statementLog
以上便是可执行SQL日志的调用链,我们debug进入DruidDataSource#getConnection
protected List<Filter> filters = new CopyOnWriteArrayList<Filter>();
public DruidPooledConnection getConnection(long maxWaitMillis) throws SQLException {
//防止connection对象为空,一般不会出现这种情况
init();
//我们注册的所有filter都在 filters
final int filtersSize = filters.size();
if (filtersSize > 0) {
//创建或者直接从缓存中获取 由druid提供了唯一实现的FilterChain过滤器链对象
FilterChainImpl filterChain = createChain();
try {
//获取连接对象
return filterChain.dataSource_connect(this, maxWaitMillis);
} finally {
recycleFilterChain(filterChain);
}
} else {
return getConnectionDirect(maxWaitMillis);
}
}
- druid首先判断是否初始化过connection对象,如果没有则进行初始化;
- 创建FilterChain对象,由FilterChain对象返回连接实际的连接对象。
接下来我们进入到filterChain.dataSource_connect
public DruidPooledConnection dataSource_connect(DruidDataSource dataSource,
long maxWaitMillis) throws SQLException {
if (this.pos < filterSize) {
//这里执行了获取连接的调用链(注意这里是迭代执行,有先后顺序) 如果connectionConnectAfterLogEnable为true且connectionLogEnabled为ture则会打印相关日志信息
DruidPooledConnection conn = nextFilter().dataSource_getConnection(this, dataSource, maxWaitMillis);
return conn;
}
return dataSource.getConnectionDirect(maxWaitMillis);
}
上面就是在获取连接之前执行了一遍调用链,并不是我们关注的重点,接下来我们看DruidPooledPreparedStatement#execute
public boolean execute() throws SQLException {
//检测Statement是否打开
checkOpen();
//执行次数增量统计
incrementExecuteCount();
//事务相关处理
transactionRecord(sql);
//oracle特殊处理
oracleSetRowPrefetch();
conn.beforeExecute();
try {
//真正的执行逻辑交给stmt对象
return stmt.execute();
} catch (Throwable t) {
errorCheck(t);
throw checkException(t);
} finally {
conn.afterExecute();
}
}
接下来我们主要看stmt的实例PreparedStatementProxyImpl#execute做了什么
public boolean execute() throws SQLException {
updateCount = null;
//最终的执行sql语句 带占位符的
lastExecuteSql = sql;
//获取语句的执行类型 这里是:Execute
// Execute, ExecuteBatch, ExecuteQuery, ExecuteUpdate
lastExecuteType = StatementExecuteType.Execute;
lastExecuteStartNano = -1L;
lastExecuteTimeNano = -1L;
//前面已经创建过调用链了,这个直接从缓存中获取
FilterChainImpl chain = createChain();
//获取执行结果 我们重点分析
firstResultSet = chain.preparedStatement_execute(this);
recycleFilterChain(chain);
return firstResultSet;
}
从上面可以看出,执行逻辑和前面获取连接类似,首先将当前实例交给FilterChain对象,FilterChain对象执行完调用链后再执行查询结果的逻辑,具体我们看chain.preparedStatement_execute
public boolean preparedStatement_execute(PreparedStatementProxy statement) throws SQLException {
if (this.pos < filterSize) {
//这里执行了获取连接的调用链(注意这里是迭代执行,有先后顺序)
return nextFilter().preparedStatement_execute(this, statement);
}
return statement.getRawObject().execute();
}
上面执行逻辑和前面获取连接时候的逻辑基本一致,下面我们主要关注nextFilter().preparedStatement_execute,这个时候进去到Slf4jLogFilter的祖父类FilterEventAdapter对象的preparedStatement_execute方法
public boolean preparedStatement_execute(FilterChain chain, PreparedStatementProxy statement) throws SQLException {
try {
//statement 执行前操作
statementExecuteBefore(statement, statement.getSql());
//调用其它filter的preparedStatement_execute方法
boolean firstResult = chain.preparedStatement_execute(statement);
//statement 执行后操作 这里是打印可执行sql的方法
this.statementExecuteAfter(statement, statement.getSql(), firstResult);
return firstResult;
} catch (SQLException error) {
statement_executeErrorAfter(statement, statement.getSql(), error);
throw error;
} catch (RuntimeException error) {
statement_executeErrorAfter(statement, statement.getSql(), error);
throw error;
} catch (Error error) {
statement_executeErrorAfter(statement, statement.getSql(), error);
throw error;
}
}
接下来我们进入FilterEventAdapter对象的子类LogFilter#statementExecuteAfter,然后进入logExecutableSql方法
protected void statementExecuteAfter(StatementProxy statement, String sql, boolean firstResult) {
//这里是调用打印可执行sql
logExecutableSql(statement, sql);
// 是否打印执行后的日志
if (statementExecuteAfterLogEnable && isStatementLogEnabled()) {
statement.setLastExecuteTimeNano();
double nanos = statement.getLastExecuteTimeNano();
double millis = nanos / (1000 * 1000);
statementLog("{conn-" + statement.getConnectionProxy().getId() + ", " + stmtId(statement) + "} executed. "
+ millis + " millis. " + sql);
}
}
private void logExecutableSql(StatementProxy statement, String sql) {
//只有当 StatementExecutableSqlLogEnable 和 StatementLogEnabled 都为true才进行打印
//这也就是前面的配置
if ((!isStatementExecutableSqlLogEnable()) || !isStatementLogEnabled()) {
return;
}
int parametersSize = statement.getParametersSize();
if (parametersSize == 0) {
statementLog("{conn-" + statement.getConnectionProxy().getId() + ", " + stmtId(statement) + "} executed. "
+ sql);
return;
}
List<Object> parameters = new ArrayList<Object>(parametersSize);
// 获取参数
for (int i = 0; i < parametersSize; ++i) {
JdbcParameter jdbcParam = statement.getParameter(i);
parameters.add(jdbcParam != null
? jdbcParam.getValue()
: null);
}
DbType dbType = DbType.of(statement.getConnectionProxy().getDirectDataSource().getDbType());
// 参数拼接
String formattedSql = SQLUtils.format(sql, dbType, parameters, this.statementSqlFormatOption);
// 真正的打印输出交给子类
statementLog("{conn-" + statement.getConnectionProxy().getId() + ", " + stmtId(statement) + "} executed. "
+ formattedSql);
}
最后会调用子类Slf4jLogFilter#statementLog的方法
protected String statementLoggerName = "druid.sql.Statement";
private Logger statementLogger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(statementLoggerName);
protected void statementLog(String message) {
//注意这里是debug 且日志打印地址是 “druid.sql.Statement”
statementLogger.debug(message);
}
至此可执行SQL的执行流程就全部完毕了。
最后打印的sql语句如下
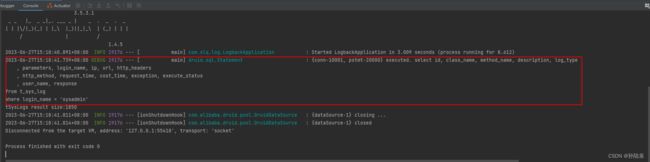
有什么不对的地方请大家指正,谢谢。
附上druid相关链接:
常见问题解决(官方)
Spring boot 整合 druid 配置链接(官方)