Node.js(三、MongoDB数据库)
Node.js(三、MongoDB数据库)
- 1、数据库概述及环境搭建
-
- 1.1、为什么要使用数据库
- 1.2、什么是数据库
- 1.3、MongoDB是什么
- 1.4、MongoDB数据库下载安装
- 1.5、MongoDB数据库相关概念
- 1.6、MongoDB数据库的常用命令
- 1.7、启动MongoDB
-
- 1.7.1、Windows系统:
- 1.7.2、mos系统:
- 2、MongoDB基本操作(命令行)
-
- 2.1、数据库操作
- 2.2、集合操作
- 2.3、文档操作
- 3、MongoDB基本操作(代码)
-
- 3.1、Mongoose第三方包
- 3.2、使用mongoose提供的connect方法即可连接数据库。
- 3.3、MongoDB增删改查操作
-
- 3.3.1、创建集合及向集合中插入文档
- 3.3.2、创建文档
- 3.3.3、MongoDB数据库导入数据
- 3.3.4、查询文档
- 3.3.5、删除文档
- 3.3.6、更新文档
- 3.3.7、集合验证规则
- 3.3.8、集合关联
1、数据库概述及环境搭建
1.1、为什么要使用数据库
- 动态网站中的数据都是存储在数据库中的。
- 数据库可以用来持久存储客户端通过表单收集的用户信息。
- 数据库软件本身可以对数据进行高效的管理。
1.2、什么是数据库
数据库即存储数据的仓库,可以将数据进行有序的分门别类的存储。它是独立于语言之外的软件,可以通过API去操作它。
常见的数据库软件有:mysql、mongoDB、oracle。
1.3、MongoDB是什么
- MongoDB是一个基于分布式文件存储的数据库,由C++语言编写。旨在为WEB应用提供可扩展的高性能数据存储解决方案。
- mongoDB的特点:高性能、易部署、易使用,存储数据非常方便提供的API,采用的是javascript开发;在数据库中存储的数据都是json对象形式。相比其他两个学习起来更加容易。
1.4、MongoDB数据库下载安装
https://www.runoob.com/mongodb/mongodb-osx-install.html
- 附Mac系统下载安装步骤:直接在命令后工具中运行:
(1)、 xcode-select --install
(2)、 brew tap mongodb/brew
(3)、 brew install mongodb-community@5.0
- 附Homebrew下载方法:/bin/zsh -c “$(curl -fsSL https://gitee.com/cunkai/HomebrewCN/raw/master/Homebrew.sh)”
- 附xcode-select安装:
命令执行:xcode-select --install
报错:xcode-select: error: command line tools are already installed, use "Software Update" to install updates
解决方法:$ rm -rf /Library/Developer/CommandLineTools
$ xcode-select --install
还是报错:
$ sudo rm -rf /Library/Developer/CommandLineTools
$ sudo xcode-select --install
1.5、MongoDB数据库相关概念
在一个数据库软件中可以包含多个数据仓库,在每个数据仓库中可以包含多个数据集合,每个数据集合中可以包含多条文档(具体数据)。
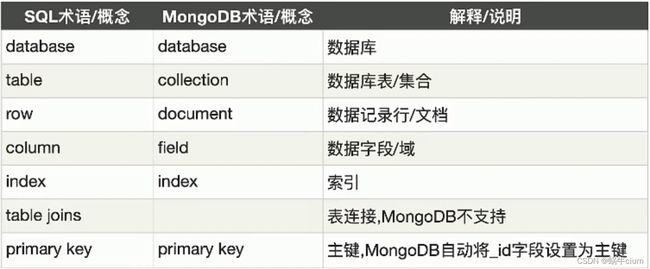
- 一个mongodb中可以建立多个数据库。
- MongoDB的默认数据库为“db”,该数据库存储在data目录中。
- MongoDB的单个实例可以容纳多个独立的数据库,每一个都有自己的集合和权限,不同的数据库也放置在不同的文件夹中。
- 集合就是MongoDB文档组,类似于RDBMS(关系数据库管理系统:Relational Database Management System)中的表格。
- 集合存在于数据库中,集合没有固定的结构,这意味着你在对集合可以插入不同格式和类型的数据,但通常情况下我们插入集合的数据都会有一定的关联性。
- 文档是一个键值(key-value)对(即BSON)。MongoDB的文档不需要设置相同的字段,并且相同的字段不需要相同的数据类型,这与关系型数据库有很大的区别,也是MongoDB非常突出的特点。一个简单的文档例子如下:{“name”: “lgg”, “hobby”: [“sleep”, “running”]}。
- MongoDB的数据类型

1.6、MongoDB数据库的常用命令
1、Help查看命令提示
help
db.help()
db.test.help()
db.test.find().help()
2、创建/切换数据库
use music
3、查询数据库
show dbs
4、查看当前使用的数据库
db/db.getName()
5、显示当前DB状态
db.stats()
6、查看当前DB版本
db.version()
7、查看当前DB的链接机器地址
db.getMongo()
8、删除数据库
db.dropDatabase()
1.7、启动MongoDB
1.7.1、Windows系统:
- 启动MongoDB服务: $ net start MongoDB或
$ mongod --dbpath d:/data/db
$ mongo - 关闭MongoDB服务: $ net stop MongoDB
- 移除 MongoDB 服务: $ C:\mongodb\bin\mongod.exe --remove
1.7.2、mos系统:
- 启动服务:
$ mongod --config /usr/local/etc/mongod.conf
$ mongo
或mongodb:
mongod --dbpath /usr/local/var/mongodb --logpath /usr/local/var/log/mongodb/mongo.log --fork
(–dbpath 设置数据存放目录;–logpath 设置日志存放目录;–fork 在后台运行) - 如果不想在后端运行,而是在控制台上查看运行过程可以直接设置配置文件启动:mongod --config /usr/local/etc/mongod.conf
- 查看 mongod 服务是否启动:$ ps aux | grep -v grep | grep mongod
- 启动后我们可以使用 mongo 命令打开一个终端:
$ cd /usr/local/mongodb/bin
$ ./mongo
2、MongoDB基本操作(命令行)
2.1、数据库操作
db // 查询当前数据库
show dbs // 查询所有的数据库
use lggFirst // 创建/切换数据库
db.dropDatabase() // 删除数据库
- 附:在MongoDB中不需要显式创建数据库,如果正在使用的数据库不存在,==MongoDB会自动创建。
- 创建:
use 数据库名字; // 如果没有创建集合,则数据库列表中(show dbs)不显示 - 删除:
db.dropDatabase() // 在当前打开的数据库中删除。
2.2、集合操作
创建集合
db.createCollection('名字')
获取当前db所有集合
db.getCollectionNames()
附:在代码中:创建集合分为两步,一是对集合设定规则,二是创建集合,创建mongoose.Schema构造函数的实例即可创建集合。
2.3、文档操作
1、插入数据
// 插入一条数据
db.users.insertOne({})
db.lgg.insert({name: 'lgg'})
// 插入多条数据
db.lgg.insert([{···}, {···}])
db.users.insertMany([{}, {}])
db.lgg.save( ) // 与上面一样
3、修改数据
// 1、如果第二个参数是一个对象,后面两个参数无效。
// 2、如果第二个参数是通过$set设置的话,后两个参数才有效。
db.lgg.update({name: 'lgg'}, {$set: {age: 88}}, true, true)
// 3、第三个参数:true如果查询不到,就创建;false如果查询不到就什么都不做。
// 4、第四个参数:true更新多条;false更新一条。
db.lgg.update({name: 'lgg'}, {$inc: {age: 88}}, true, true)
// 5、如果使用updateMany, 就不需要传递后两个参数第二个了
db.users.updateMany({name: 'lg'}, {$set: {name: 'l'}})
3、删除数据
db.lgg.remove({name: 'lgg'})
4、查询数据
// 1、查询所有记录
db.lgg.find()
// 2、查询去重后数据
db.lgg.distinct('age')
// 3、查询age=10的记录
db.lgg.find({age: 10})
// 4、查询age>10的记录
db.lgg.find({age: {$gt: 10}})
// 5-7、$lt小于;$gte大于等于;$lte小于等于;
// 8、查询大于等于10并且小于等于80
db.lgg.find({age: {$gte: 10, $lte: 80}})
// 9、正则查询
db.lgg.find({name: /l/}) // 查询名字中带有l的
// 10、查询指定列name、age数据
db.lgg.find({}, {_id: 0,age: 1}) // {}表示查找全部,{name: /l/}表示name中带l的;0表示结果不包括此项,1表示包括.
// 11、排序(1升序;-1降序)
db.lgg.find().sort({age: 1})
// 12、查询前2条数据
db.lgg.find().limit(2)
// 13、查询2条之后的数据
db.lgg.find().skip(2)
// 14、查询3-4条之间的数据
db.lgg.find().limit(2).skip(2)
// 14、查询3-4条之间的数据且排序
db.lgg.find().limit(2).skip(2).sort({age: 1}) // 排序与.sort({age: 1})的位置无关。
// 15、or查询。查询age等于10或80的数据
db.lgg.find({$or: [{age: 10}, {age: 80}]})
// 16、查询第一条数据
db.lgg.findOne()
16、查询某个结果集的记录条数
db.lgg.find().count()
3、MongoDB基本操作(代码)
3.1、Mongoose第三方包
- 使用Node.js操作MongoDB数据库需要依赖Node.js第三方包mongoose.
- 使用npm install mongoose 命令下载。
3.2、使用mongoose提供的connect方法即可连接数据库。
// 必须先启动MongoDB,否则MongoDB将无法连接。
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
// // 在MongoDB中不需要显式创建数据库,如果正在使用的数据库不存在,MongoDB会自动创建。
// 返回的是promise对象
mongoose.connect('mongodb://localhost:27017/lggFirst', { useNewUrlParser: true, useUnifiedTopology: true })
.then(() => console.log('数据库连接成功。'))
.catch(err => console.log(err, '数据库连接失败。'))
3.3、MongoDB增删改查操作
3.3.1、创建集合及向集合中插入文档
// 在MongoDB中不需要显式创建数据库,如果正在使用的数据库不存在,MongoDB会自动创建。
const mongoose = require('mongoose');
// 数据库连接 27017是MongoDB数据库的默认端口
mongoose.connect('mongodb://localhost:27017/lggSecond', {
useNewUrlParser: true,
useUnifiedTopology: true
})
.then(() => console.log('数据库连接成功'))
.catch((err) => console.log(err, '数据库连接失败'))
// 创建集合规则:创建Schema构造函数就是在创建集合规则
const courseSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
name: String,
total: Number,
isOpen: Boolean
})
// 使用规则创建集合:参数一集合名称,参数二集合规则
const Course = mongoose.model('Course', courseSchema) // 在数据库中是courses
// 创建文档
const course = new Course({
name: 'lgg',
total: 3,
isOpen: true
})
// 将文档插入到数据库中
course.save()
3.3.2、创建文档
创建文档实际上就是向集合中插入数据。
- 方法一:
1.创建集合实例。
2.调用实例对象下的save方法将数据保存到数据库中。
// 创建集合实例
const course = new Course({
name: 'Node',
total: 11,
isOpen: true
});
// 将数据保存到数据库中
course.save();
- 方法二:
// 通过回调函数方式
Course.create({name: 'Node基础', total: 9, isOpen: true}, (err, doc) => {
// 错误对象
console.log(err)
// 当前插入的文档
console.log(doc)
});
// 或者通过promise方式
Course.create({name: 'Node基础', total: 9, isOpen: true})
.then(doc => console.log(doc))
.catch(err => console.log(err))
3.3.3、MongoDB数据库导入数据
- mongoimport -d 数据库名字 -c 集合名字 --file 要导入的数据文件
例如:mongoimport -d lggSecond -c users --file ./user.json
在执行命令前,需要找到mongodb数据库的安装目录,将安装目录下的bin目录放置在系统环境变量中
3.3.4、查询文档
// 使用规则创建集合:参数一集合名称,参数二集合规则
const User = mongoose.model('User', usersSchema) // 在数据库中是users
// 1、条件为空则查询全部
User.find()
.then(result => console.log(result)) // 返回文档集合
// 2、查询_id为5c09f267aeb04b22f8460968的文档
User.find({
_id: '5c09f267aeb04b22f8460968'
})
.then(result => console.log(result)) // 虽然只有一条数据但是返回的也是一个数组(find方法返回的都是数组)
// 3、findOne方法返回一条文档,默认返回当前集合中的第一条文档
User.findOne({_id: '5c09f267aeb04b22f8460968'})
.then(result => console.log(result)) // 返回的是一个对象
// 4、查询年龄大于20且小于40的文档
User.find({age: { $gt: 20, $lt: 40 }})
.then(result => console.log(result))
// 5、查询hoppies数组中包含足球的字段(应用:关键字搜索)
User.find({ hobbies: { $in: ['足球']}})
.then(result => console.log(result))
// 6、选择要查询的字段(如果不想包含前面加-)
User.find().select('name -_id')
.then(result => console.log(result))
// 7、根据年龄字段进行排序(前面加-表示降序)
User.find().sort('-age')
.then(result => console.log(result))
// 8、skip跳过多少条数据;limit限制多少条数据
User.find().skip(5).limit(2)
.then(result => console.log(result))
3.3.5、删除文档
// 使用规则创建集合:参数一集合名称,参数二集合规则
const User = mongoose.model('User', usersSchema) // 在数据库中是users
// // 查找到一条文档并且删除,返回的是删除的文档。如果查询到了多个那么只会删除第一个匹配的文档。
User.findOneAndDelete({_id: '123'})
.then(result => console.log(result))
// 删除多个文档(如果传入的为空或{}则删除全部),返回一个对象
User.deleteMany({})
.then(result => console.log(result)) // { n: 2, ok: 1, deletedCount: 2 }
3.3.6、更新文档
// 使用规则创建集合:参数一集合名称,参数二集合规则
const User = mongoose.model('User', usersSchema) // 在数据库中是users
// 更新单个
User.updateOne({ name: '狗蛋'}, { name: 'lgg' })
.then(result => console.log(result)) // { n: 1, nModified: 1, ok: 1 }
// 更新多个
User.updateMany({age: 20}, {age: 18})
.then(result => console.log(result)) // { n: 0, nModified: 0, ok: 1 } { n: 1, nModified: 1, ok: 1 }
3.3.7、集合验证规则
在创建集合规则时,可以设置当前字段的验证规则,验证失败就则输入插入失败。
- 获取错误信息:error.errors[‘字段名称’].message
// 创建集合规则:创建Schema构造函数就是在创建集合规则
const informationSchema = new mongoose.Schema({
name: {
type: String,
require: true,
minlength: [4, '长度不能小于4'],
maxlength: [20, '长度不能大于20'],
trim: true, // 去除两边字符串
},
total: {
type: Number,
min: [0, '最小值为0'],
max: [999, '最大值为999'],
default: 0, // 默认值
},
isOpen: Boolean,
publishDate: {
type: Date,
default: Date.now, // 默认值
},
author: {
type: String,
validator: v => { // 返回布尔值true验证成功;false验证失败
return v && v.length > 4 // v就是传入的值。
},
message: '自定义错误信息'
}
})
// 使用规则创建集合:参数一集合名称,参数二集合规则
const Information = mongoose.model('Information', informationSchema)
Information.create({
name: 'lgggg',
total: 99,
isOpen: true,
})
.then(result => console.log(result))
// 获取错误信息:error.errors['字段名称'].message
.catch(err => {
// 获取错误信息对象
const errs = err.errors
// 循环错误信息对象
for(var val in errs) {
// 将错误信息打印到控制台
console.log(errs[val].message);
}
})
/*
required: true 必传字段
minlength:3 字符串最小长度
maxlength: 20 字符串最大长度
min: 2 数值最小为2
max: 100 数值最大为100
enum: ['html', 'css', 'javascript', 'node.js'] // 枚举,只能传这几个值
// 或者
enum: {
// values: ['html', 'css', 'javascript', 'node.js'],
// message: '自定义错误信息'
// }
trim: true 去除字符串两边的空格
validate: 自定义验证器
default: 默认值
*/
3.3.8、集合关联
通常不同集合的数据之间是有关系的,例如文章信息集合和用户信息存储在不同集合中,但文章是某个用户发表的,要查询文章的所有信息包括发表用户,就需要用到集合关联。
- 使用id对集合进行关联
- 使用populate方法进行关联集合查询
const Author = mongoose.model('Author', new mongoose.Schema({name: String}))
// 文章集合
const Post = mongoose.model('Post', new mongoose.Schema({
title: {
type: String
},
// 使用ID将文章集合和作者集合进行关联
author: {
type: mongoose.Schema.Types.ObjectId,
ref: 'Author'
}
}))
// Author.create({
// name: 'lgg'
// })
// Post.create({
// author: '6212657009f6a1023efebce8',
// title: 'lz'
// })
// 联合查询
Post.find()
.populate('author') // 没有这行代码的话author存放的是6212657009f6a1023efebce8,而不是对象
.then((result) => console.log(result))/*[
{
_id: 621265df07646d033be1ea14,
author: { _id: 6212657009f6a1023efebce8, name: 'lgg', __v: 0 },
title: 'lz',
__v: 0
}
]*/