生成模型 -- GAN
文章目录
- 1. 生成模型与判别模型
-
- 1.1 生成模型
- 2. VAE
- 3. GAN
-
- 3.1 GAN-生成对抗网络
- 3.2 GAN-生成对抗网络的训练
-
- 3.2.1 判别模型的训练:
- 3.2.2 生成网络的训练:
- 4. LeakyReLU
- 5. GAN代码实例
1. 生成模型与判别模型
生成模型与判别模型
我们前面几章主要介绍了机器学习中的判别式模型,这种模型的形式主要是根据原始图像推测图像具备的一些性质,例如根据数字图像推测数字的名称,根据自然场景图像推测物体的边界;
而生成模型恰恰相反,通常给出的输入是图像具备的性质,而输出是性质对应的图像。这种生成模型相当于构建了图像的分布,因此利用这类模型,我们可以完成图像自动生成(采样)、图像信息补全等工作。
在深度学习之前已经有很多生成模型,但苦于生成模型难以描述难以建模,科研人员遇到了很多挑战,而深度学习的出现帮助他们解决了不少问题。
基于深度学习思想的生成模型——GAN和VAE,以及GAN的变种模型。
1.1 生成模型
- 生成图片
- 人脸生成
- 照片生成
- 生成卡通人物
- 图像转换
- 文本到图片的转换
- 语义图片到照片的转换
- 正脸图片生成
- 生成新的人体姿势
- 照片到表情的转换
- 照片编辑
- 图片混合
- 超分辨率
- 图片修复
- 衣服转换
- 视频预测
- 3D 物体生成
2. VAE
VAE-Variational Autoencoder
变分自动编码器
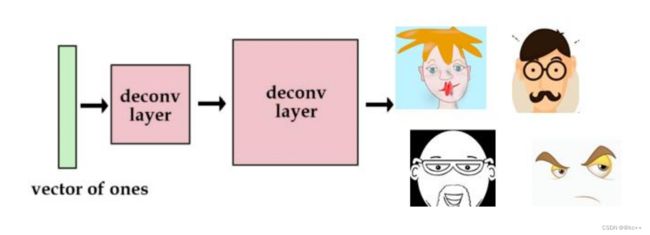
想象这样一个网络,输入是一组全部为1的向量,目标是一张猫脸,经过好多好多轮的训练。 我们只要输入这个全部为1的向量就可以得到这张猫的脸。
其实这是因为在训练的过程中,我们通过不断地训练,网络已经将这张猫的图片的参数保存起来了。
这个工作其实已经可以看出他的意义所在了,通过一个网络,将一个高维空间的脸映射为低维空间的一个向量。
那么如果,我们尝试使用更多的图片。这次我们用one-hot向量而不是全1向量。我们用[1, 0, 0, 0]代表猫,用[0, 1, 0, 0]代表狗。虽然这也没什么问题,但是我们最多只能储存4张图片。
于是,我们可以增加向量的长度和网络的参数,那么我们可以获得更多的图片。
例如,将这个向量定义为四维,采用one-hot的表达方式表达四张不同的脸,那么这个网络就可以表达四个脸。输入不同的数据,他就会输出不同的脸来。
但是,这样的向量很稀疏。为了解决这个问题,我们想使用实数值向量而不是0,1向量。我们可认为这种实数值向量是原图片的一种编码,这也就引出了编码/解码的概念。
举个例子,[3.3, 4.5, 2.1, 9.8]代表猫,[3.4, 2.1, 6.7, 4.2] 代表狗。
这个已知的初始向量可以作为我们的潜在变量。
如果像我上面一样,随机初始化一些向量去代表图片的编码,这不是一个很好的办法,我们更希望计算机能帮我们自动编码。在auto encoder模型中,我们加入一个编码器,它能帮我们把图片编码成向量。然后解码器能够把这些向量恢复成图片。
在下面这个图中,我们通过六个因素来描述最终的人脸形状,而这些因素不同的值则代表了不同的特性。
3. GAN
3.1 GAN-生成对抗网络
什么是生成对抗网络,GAN–Generative Adversarial Network,
- 对抗网络有一个生成器(Generator),还有一个判别器 (Discriminator);
- 生成器从随机噪声中生成图片,由于这些图片都是生成器臆想出来的,所以我 们称之为 Fake Image;
- 生成器生成的照片Fake Image和训练集里的Real Image都会传入判别器,判别器判断他们是 Real 还是 Fake。
那么我们如何训练网络呢?要达到什么样的目的?
- 我们希望生成器生成的图片足够真实,可以骗过判别器;
- 我们也希望判别器足够“精明”,可以很好的分别出真图还是生成图;
- 最后在训练中,生成器和判别器达到一种“对抗”中的平衡,结束训练。
- 这时,我们分离出生成器,它便可以帮助我们“生成”想要的图片。
我们要明白在使用GAN的时候的2个问题
- 我们有什么?
比如上图,我们有的只是真实采集而来的人脸样本数据集,仅此而已,而且很关键的一点是我们连人脸数据集的类标签都没有,也就是我们不知道那个人脸对应的是谁。 - 我们要得到什么?
至于要得到什么,不同的任务得到的东西不一样,我们只说最原始的GAN目的,那就是我们想通过输入一个噪声,模拟得到一个人脸图像,这个图像可以非常逼真以至于以假乱真。
首先判别模型,就是图中右半部分的网络,直观来看就是一个简单的神经网络结构,输入就是一副图像,输出就是一个概率值,用于判断真假使用(概率值大于0.5那就是真,小于0.5那就是假),真假也不过是人们定义的概率而已。
其次是生成模型,同样也可以看成是一个神经网络模型,输入是一组随机数Z,输出是一个图像,不再是一个数值。
从图中可以看到,会存在两个数据集,一个是真实数据集,另一个是假的数据集.
GAN的目标:
- 判别网络的目的:就是能判别出来输入的一张图它是来自真实样本集还是假样本集。假如输入的是真样本,网络输出就接近1,输入的是假样本,网络输出接近0,达到了很好的判别的目的。
- 生成网络的目的:生成网络是造样本的,它的目的就是使得自己造样本的能力尽可能强,尽可能的使判别网络没法判断是真样本还是假样本。
生成网络与判别网络的目的正好是相反的,一个说我能判别的好,一个说我让你判别不好。
所以叫做对抗,叫做博弈。
那么最后的结果到底是谁赢呢?
这就要归结到设计者,也就是我们希望谁赢了。
作为设计者的我们,我们的目的是要得到以假乱真的样本,那么很自然的我们希望生成样本赢了,也就是希望生成样本很真,判别网络的能力不足以区分真假样本为止。
3.2 GAN-生成对抗网络的训练
单独交替迭代训练
3.2.1 判别模型的训练:
假设现在生成网络模型已经有了(当然可能不是最好的生成网络),那么给一堆随机数组,就会得到一堆假的样本集(因为不是最终的生成模型,那么现在生成网络可能就处于劣势,导致生成的样本就不咋地,可能很容易就被判别网络判别出来了说这货是假冒的)。
假设我们现在有了这样的假样本集,而真样本集一直都有,现在我们人为地定义真假样本集的标签,因为我们希望真样本集的输出尽可能为1,假样本集为0,很明显这里我们就已经默认真样本集所有的类标签都为1,而假样本集的所有类标签都为0.。
所以,我们现在有了真样本集以及它们的label(都是1)、假样本集以及它们的label(都是0)
这样单就判别网络来说,此时问题就变成了一个再简单不过的有监督的二分类问题了,直接送到神经网络模型中训练就可以了。
3.2.2 生成网络的训练:
想想我们的目的,是生成尽可能逼真的样本。
那么原始的生成网络生成的样本,怎么知道它真不真呢?
就是送到判别网络中,所以在训练生成网络的时候,我们需要联合判别网络一起才能达到训练的目的。
把刚才的判别网络串接在生成网络的后面,这样我们就知道真假了,也就有了误差了。
所以对于生成网络的训练其实是对生成-判别网络串接的训练。
对于样本,我们要把生成的假样本的标签都设置为1,也就是认为这些假样本在生成网络训练的时候是真样本。
那么为什么要这样呢?我们想想,是不是这样才能起到迷惑判别器的目的,也才能使得生成的假样本逐渐逼近为真样本。
现在对于生成网络的训练,我们有了样本集(只有假样本集,没有真样本集),有了对应的label(全为1)。
注意,在训练这个串接的网络的时候,一个很重要的操作就是不要更新判别网络的参数,只是把误差一直传, 传到生成网络后更新生成网络的参数。
在完成生成网络训练后,我们就可以根据目前新的生成网络再对先前的那些噪声Z生成新的假样本了。
并且训练后的假样本应该是更真了才对。
所有这样我们又有了新的真假样本集,这样又可以重复上述过程了。
我们把这个过程称作为单独交替训练。
4. LeakyReLU
Relu的输入值为负的时候,输出始终为0,其一阶导数也始终为0,这样会导致神经元不能更新参数,也就是神经元不学习了,这种现象叫做“Dead Neuron”。
为了解决Relu函数这个缺点,在Relu函数的负半区间引入一个泄露(Leaky)值,所以称为Leaky Relu函数。即ReLU在取值小于零部分没有梯度,LeakyReLU在取值小于0部分给一个很小的梯度。

5. GAN代码实例
from __future__ import print_function, division
from keras.datasets import mnist
from keras.layers import Input, Dense, Reshape, Flatten, Dropout
from keras.layers import BatchNormalization, Activation, ZeroPadding2D
from keras.layers.advanced_activations import LeakyReLU
from keras.layers.convolutional import UpSampling2D, Conv2D
from keras.models import Sequential, Model
from keras.optimizers import Adam
import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2'
import tensorflow as tf
gpu_options = tf.GPUOptions(per_process_gpu_memory_fraction=0.5)
sess = tf.Session(config=tf.ConfigProto(gpu_options=gpu_options))
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import sys
import numpy as np
class GAN():
def __init__(self):
self.img_rows = 28
self.img_cols = 28
self.channels = 1
self.img_shape = (self.img_rows, self.img_cols, self.channels)
self.latent_dim = 100
optimizer = Adam(0.0002, 0.5)
# Build and compile the discriminator
self.discriminator = self.build_discriminator()
self.discriminator.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy',
optimizer=optimizer,
metrics=['accuracy'])
# Build the generator
self.generator = self.build_generator()
# The generator takes noise as input and generates imgs
z = Input(shape=(self.latent_dim,))
img = self.generator(z)
# For the combined model we will only train the generator
self.discriminator.trainable = False
# The discriminator takes generated images as input and determines validity
validity = self.discriminator(img)
# The combined model (stacked generator and discriminator)
# Trains the generator to fool the discriminator
self.combined = Model(z, validity)
self.combined.compile(loss='binary_crossentropy', optimizer=optimizer)
def build_generator(self):
model = Sequential()
model.add(Dense(256, input_dim=self.latent_dim))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Dense(512))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Dense(1024))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(BatchNormalization(momentum=0.8))
model.add(Dense(np.prod(self.img_shape), activation='tanh'))
model.add(Reshape(self.img_shape))
model.summary()
noise = Input(shape=(self.latent_dim,))
img = model(noise)
return Model(noise, img)
def build_discriminator(self):
model = Sequential()
model.add(Flatten(input_shape=self.img_shape))
model.add(Dense(512))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dense(256))
model.add(LeakyReLU(alpha=0.2))
model.add(Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))
model.summary()
img = Input(shape=self.img_shape)
validity = model(img)
return Model(img, validity)
def train(self, epochs, batch_size=128, sample_interval=50):
# Load the dataset
(X_train, _), (_, _) = mnist.load_data()
# Rescale -1 to 1
X_train = X_train / 127.5 - 1.
X_train = np.expand_dims(X_train, axis=3)
# Adversarial ground truths
valid = np.ones((batch_size, 1))
fake = np.zeros((batch_size, 1))
for epoch in range(epochs):
# ---------------------
# Train Discriminator
# ---------------------
# Select a random batch of images
idx = np.random.randint(0, X_train.shape[0], batch_size)
imgs = X_train[idx]
noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (batch_size, self.latent_dim))
# Generate a batch of new images
gen_imgs = self.generator.predict(noise)
# Train the discriminator
d_loss_real = self.discriminator.train_on_batch(imgs, valid)
d_loss_fake = self.discriminator.train_on_batch(gen_imgs, fake)
d_loss = 0.5 * np.add(d_loss_real, d_loss_fake)
# ---------------------
# Train Generator
# ---------------------
noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (batch_size, self.latent_dim))
# Train the generator (to have the discriminator label samples as valid)
g_loss = self.combined.train_on_batch(noise, valid)
# Plot the progress
print ("%d [D loss: %f, acc.: %.2f%%] [G loss: %f]" % (epoch, d_loss[0], 100*d_loss[1], g_loss))
# If at save interval => save generated image samples
if epoch % sample_interval == 0:
self.sample_images(epoch)
def sample_images(self, epoch):
r, c = 5, 5
noise = np.random.normal(0, 1, (r * c, self.latent_dim))
gen_imgs = self.generator.predict(noise)
# Rescale images 0 - 1
gen_imgs = 0.5 * gen_imgs + 0.5
fig, axs = plt.subplots(r, c)
cnt = 0
for i in range(r):
for j in range(c):
axs[i,j].imshow(gen_imgs[cnt, :,:,0], cmap='gray')
axs[i,j].axis('off')
cnt += 1
fig.savefig("./images/mnist_%d.png" % epoch)
plt.close()
if __name__ == '__main__':
gan = GAN()
gan.train(epochs=2000, batch_size=32, sample_interval=200)