文件和IO的核心API
操作文件
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建一个文件对象,并且指向某个路径
File file = new File("C:\\Users\\1162\\Desktop\\1.trx");
//创建文件
System.out.println(file.exists());
boolean newFile = file.createNewFile();
if(newFile){
System.out.println("文件创建成功");
System.out.println(file.exists());
}
//获取文件的各种元素
System.out.println("是否为文件类型"+file.isFile());
System.out.println("文件的长度"+file.length());
System.out.println("文件的可读权限"+file.canRead());
System.out.println("文件名"+file.getName());
System.out.println("文件的绝对路径"+file.getAbsoluteFile());
//
System.out.println("文件最后的修改时间"+file.lastModified());
//时间转换
Date date = new Date(file.lastModified());//初始化时间
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日HH时mm分ss秒");//日期格式化
System.out.println(simpleDateFormat.format(date));
}
操作目录
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建目录
File dir = new File("C:\\Users\\1162\\Desktop\\IOTEST");
if(!dir.exists()){
System.out.println("当前目录不存在,执行创建");
boolean mkdir = dir.mkdir();
if(mkdir){
System.out.println("创建目录成功");
}
}
//获取这个目录的一些元数据
System.out.println(dir.isFile());//是不是文件
System.out.println(dir.getParent());//获取父路径
System.out.println(dir.getParentFile());//获取父路径
//罗列当前目录下的文件内容
String[] list = dir.list();
for (String filename:list) {
System.out.println(filename);
}
File[] files = dir.listFiles();
for (File f : files) {
System.out.println(f.getName());
}
}
过滤符合条件的文件
//实现FilenameFilter接口
public class MyFileNameFilter implements FilenameFilter {
@Override
public boolean accept(File dir, String name) {
if(name.endsWith(".java")){ //是否以.java为结尾
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建目录
File dir = new File("C:\\Users\\1162\\Desktop\\IOTEST\\src\\main\\java");
//只展示".java"结尾的文件
//传个FilenameFilter类型对象
System.out.println("过滤后结果");
String[] filterRes = dir.list(new MyFileNameFilter());
for(String filename: filterRes){
System.out.println(filename);
}
}
动手练习作业
public class LX {
public static void fileRe(File filer){
if(filer.exists()){//文件是否存在
File[] list = filer.listFiles();//获取当前目录下所有内容
for (File f:list) {//遍历内容
if(f.isFile()){//判断是不是文件
System.out.println(f.getName());//打印文件名
}else {
File file1 = new File(f.getParentFile().toString()+"\\"+f.getName());//不是文件就获取文件名全路径,父路径+文件名
fileRe(file1);//递归调用继续判断目录
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
File file = new File("C:\\Users\\1162\\Desktop\\IOTEST\\src\\main\\hello");
fileRe(file);//传递要遍历的文件目录路径
}
}
文件字节流
InputStream 字节为单位读取文件
OutputStream 字节为单位写数据到文件
实现图片的拷贝
InputStream 字节为单位读取文件
public class FileInputStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.创建文件对象
File file = new File("C:\\Users\\1162\\Desktop\\IOTEST\\src\\main\\java\\img\\1.png");
//2.创建一个如此文件的输入流,确定读取哪文件
FileInputStream inputStream=null;
try {
inputStream=new FileInputStream(file);
//3.开始读取内容
//只要没有读到文件末尾,就一直读
int read;
while ((read = inputStream.read())!=-1){//判断是否读完
System.out.println(read);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
//4.关闭文件流
if(inputStream != null){
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
}
OutputStream 结合 字节输出流实现图片复制
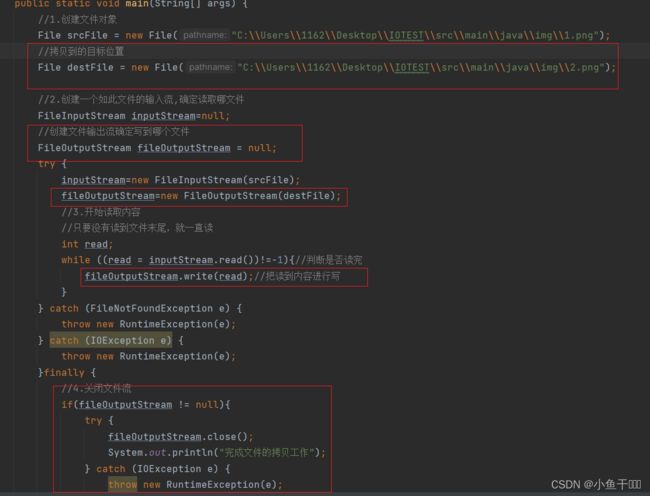
public class FileOutputStreamTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.创建文件对象
File srcFile = new File("C:\\Users\\1162\\Desktop\\IOTEST\\src\\main\\java\\img\\1.png");
//拷贝到的目标位置
File destFile = new File("C:\\Users\\1162\\Desktop\\IOTEST\\src\\main\\java\\img\\2.png");
//2.创建一个如此文件的输入流,确定读取哪文件
FileInputStream inputStream=null;
//创建文件输出流确定写到哪个文件
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
try {
inputStream=new FileInputStream(srcFile);
fileOutputStream=new FileOutputStream(destFile);
//3.开始读取内容
//只要没有读到文件末尾,就一直读
int read;
while ((read = inputStream.read())!=-1){//判断是否读完
fileOutputStream.write(read);//把读到内容进行写
}
System.out.println("完成文件的拷贝工作");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
//4.关闭文件流
if(fileOutputStream != null){
try {
fileOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if(inputStream != null){
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
}
增加缓存区提高读写内容
package bb;
import java.io.*;
public class FileOutputStreamWithBufferTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.创建文件对象
File srcFile = new File("C:\\Users\\1162\\Desktop\\IOTEST\\src\\main\\java\\img\\1.png");
//拷贝到的目标位置
File destFile = new File("C:\\Users\\1162\\Desktop\\IOTEST\\src\\main\\java\\img\\3.png");
//2.创建一个如此文件的输入流,确定读取哪文件
FileInputStream inputStream=null;
//创建文件输出流确定写到哪个文件
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
try {
inputStream=new FileInputStream(srcFile);
fileOutputStream=new FileOutputStream(destFile);
//3.开始读取内容
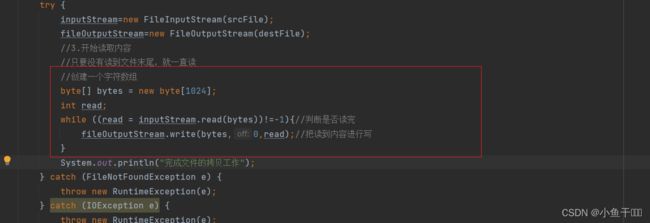
//只要没有读到文件末尾,就一直读
//创建一个字符数组
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];//inputStream.available()获取文件的总字节大小
int read;
while ((read=inputStream.read(bytes))!=-1){
inputStream.read(bytes);
System.out.println(read);
fileOutputStream.write(bytes,0,read);//从0写到1024,放到bytes
}
System.out.println("完成文件的拷贝工作");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
//4.关闭文件流
if(fileOutputStream != null){
try {
fileOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if(inputStream != null){
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
}
public class FileOutputStreamWithBufferTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.创建文件对象
File srcFile = new File("C:\\Users\\1162\\Desktop\\IOTEST\\src\\main\\java\\img\\1.png");
//拷贝到的目标位置
File destFile = new File("C:\\Users\\1162\\Desktop\\IOTEST\\src\\main\\java\\img\\3.png");
//2.创建一个如此文件的输入流,确定读取哪文件
FileInputStream inputStream=null;
//创建文件输出流确定写到哪个文件
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
try {
inputStream=new FileInputStream(srcFile);
fileOutputStream=new FileOutputStream(destFile);
//3.开始读取内容
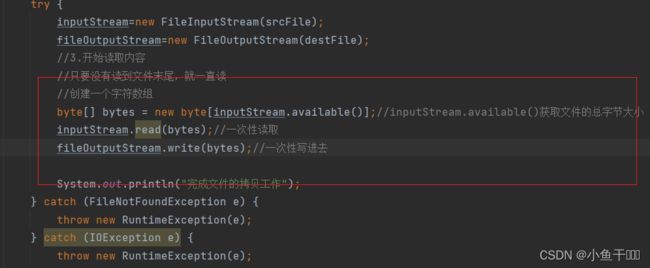
//只要没有读到文件末尾,就一直读
//创建一个字符数组
byte[] bytes = new byte[inputStream.available()];//inputStream.available()获取文件的总字节大小
inputStream.read(bytes);//一次性读取
fileOutputStream.write(bytes);//一次性写进去
System.out.println("完成文件的拷贝工作");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
//4.关闭文件流
if(fileOutputStream != null){
try {
fileOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if(inputStream != null){
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
}
使用自带缓冲区的处理流完成文件的读写
public class bufferedStream {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.创建文件对象
File srcFile = new File("C:\\Users\\1162\\Desktop\\IOTEST\\src\\main\\java\\img\\1.png");
//拷贝到的目标位置
File destFile = new File("C:\\Users\\1162\\Desktop\\IOTEST\\src\\main\\java\\img\\4.png");
//2.创建一个如此文件的输入流,确定读取哪文件
FileInputStream inputStream=null;
//创建文件输出流确定写到哪个文件
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream = null;
try {
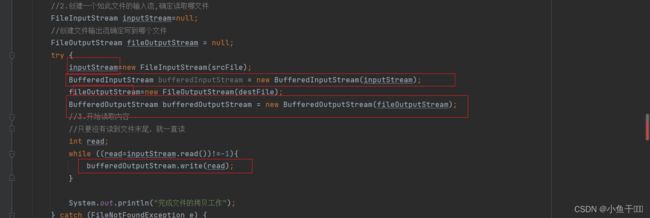
inputStream=new FileInputStream(srcFile);
BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(inputStream);
fileOutputStream=new FileOutputStream(destFile);
BufferedOutputStream bufferedOutputStream = new BufferedOutputStream(fileOutputStream);
//3.开始读取内容
//只要没有读到文件末尾,就一直读
int read;
while ((read=inputStream.read())!=-1){
bufferedOutputStream.write(read);
}
System.out.println("完成文件的拷贝工作");
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
//4.关闭文件流
if(fileOutputStream != null){
try {
fileOutputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
//4.关闭文件流
if(inputStream != null){
try {
inputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
}
字符流
字节流可以处理所有的文件,包括文本文件,但如果我们想获取其中的文本信息那么需要自己将读取到的字节再转换为字符,就相当麻烦,所以采用字符流可以简化开发;
FileReader读取到文本的内容
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建字符读取刘
FileReader reader = null;
try {
reader=new FileReader("C:\\Users\\1162\\Desktop\\IOTEST\\src\\main\\java\\img\\1.txt");
//开始读文件内容
int temp;
while ((temp = reader.read())!=-1){
System.out.print((char)temp);//输出读取到的内容,转换成字符类型
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
if(reader!=null){
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
FileWriter实现写文件
public class FileWriterTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建一个字符输出流对象确认要写的文件
FileWriter writer =null;
try {
//不加true进行写东西源文件字符会被覆盖,想向文件追加写字符加个true即可
writer= new FileWriter("C:\\Users\\1162\\Desktop\\IOTEST\\src\\main\\java\\img\\1.txt",true);
//向文件写内容
writer.write(97);//写个字符a到文件里
writer.write("中华");//写字符中华到文件里
//刷新
writer.flush();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
if(writer!=null){
try {
writer.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
强化练习
实现字符的拷贝
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileReader reader=null;
FileWriter writer=null;
try {
reader=new FileReader("C:\\Users\\1162\\Desktop\\IOTEST\\src\\main\\java\\img\\1.txt");
writer=new FileWriter("C:\\Users\\1162\\Desktop\\IOTEST\\src\\main\\java\\img\\2.txt");
int temp;
while ((temp=reader.read())!=-1){ //读取1.txt内容
System.out.println((char)temp);
writer.write(temp);//读到的内容写到2.tex里
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
if(writer!=null) {
try {
writer.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if(reader!=null){
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
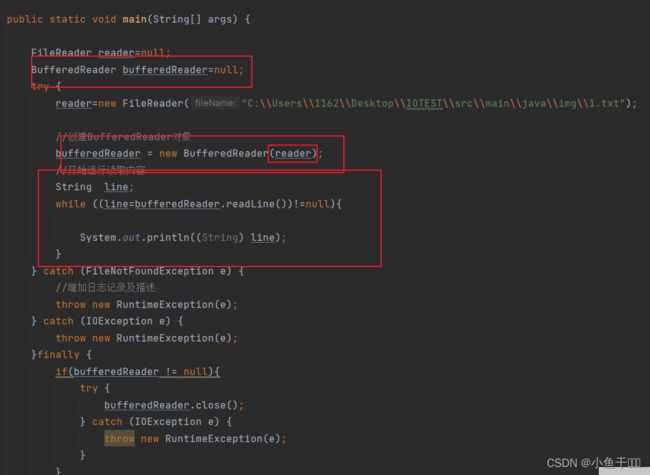
BufferedReader实现逐行读文件
public static void main(String[] args) {
FileReader reader=null;
BufferedReader bufferedReader=null;
try {
reader=new FileReader("C:\\Users\\1162\\Desktop\\IOTEST\\src\\main\\java\\img\\1.txt");
//创建BufferedReader对象
bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(reader);
//开始逐行读取内容
String line;
while ((line=bufferedReader.readLine())!=null){
System.out.println((String) line);
}
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
//增加日志记录及描述
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
if(bufferedReader != null){
try {
bufferedReader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
if(reader != null){
try {
reader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
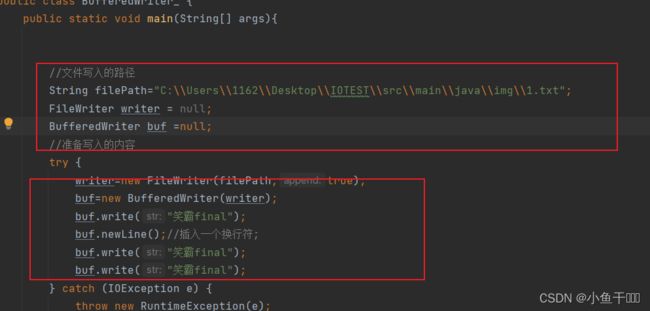
BufferedWriter实现写文件
逐行写
public class BufferedWriter_ {
public static void main(String[] args){
//文件写入的路径
String filePath="C:\\Users\\1162\\Desktop\\IOTEST\\src\\main\\java\\img\\1.txt";
FileWriter writer = null;
BufferedWriter buf =null;
//准备写入的内容
try {
writer=new FileWriter(filePath,true);
buf=new BufferedWriter(writer);
buf.write("笑霸final");
buf.newLine();//插入一个换行符;
buf.write("笑霸final");
buf.write("笑霸final");
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
try {
buf.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
转换流
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1.将字节流-----转换-----为字符输入流
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
//读取用户键盘录入的内容
System.out.println("请说说今天的心情");
String s = bufferedReader.readLine();
System.out.println(s);
while (true){
System.out.println("有什么事吗");
s=bufferedReader.readLine();
if("88".equals(s)){
break;
}
System.out.println(s);
}
System.out.println("聊天结束");
}
对象流

我们在网络上传输数据时,都会以二进制流的形式进行传输,所以如果我们希望传输的是一个Java对象,则需要经历以下两个步骤:
1,将该对象转换为二进制流
2,接收方再把这个二进制流恢复为Java对象将Java对象转换二进制流称为对象的序列化;将二进制流恢复为Java对象称为对象的反序列化;
操作基本数据类型
0bjectoutputStream 对象—文件/网络 序列化动作
ObjectInputStream 文件/网络—对象 反序列号动作
public class Book implements Serializable {//进行序列化
public String name;
public Integer price;
public Book(){
}
public Book(String name,Integer price){
this.name=name;
this.price=price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Book{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
}
进行写到磁盘
//1.创建对象
Book book = new Book("小黄书",99);
//创建对象流对象
ObjectOutputStream outputStream = null;
//对象写到磁盘
try {
outputStream=new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("C:\\Users\\1162\\Desktop\\IOTEST\\src\\main\\java\\img\\1.txt"));
outputStream.writeObject(book);
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
try {
outputStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
磁盘里读取对象
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
//创建对象的输入流
ObjectInputStream inputStream=null;
inputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("C:\\Users\\1162\\Desktop\\IOTEST\\src\\main\\java\\img\\1.txt"));
//读取文件中的数据并转换为对象
Object o = inputStream.readObject();
if(o instanceof Book){//是不是Book类型
System.out.println((Book)o);
}else {
System.out.println("不是Book类型");
}
inputStream.close();
}
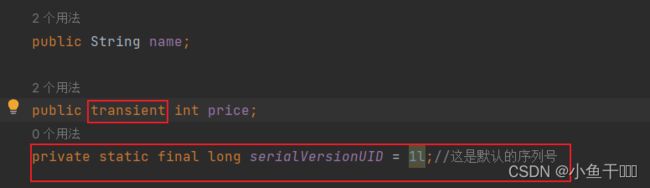
序列化隐私设置和序列化ID的作用
public class Book implements Serializable {
public String name;
public transient int price;
private static final long serialVersionUID = 1l;//这是默认的序列号
注意设置一个自己的序列化ID需要先清空对象磁盘文件内容,重新输出到磁盘文件里,读取磁盘文件对象就发现Book的价格属性就为0了;
序列化ID的作用
这个序列化ID起着关键的作用,它决定着是否能够成功反序列化!简单来说,java的序列化机制是通过在运行时判断类的serialVersionUID来验证版本一致性的。在进行反序列化时,JVM会把传来的字节流中的serialVersionUID与本地实体类中的serialVersionUID进行比较,如果相同则认为是一致的,便可以进行反序列化,否则就会报序列化版本不一致的异常。