VUE笔记(九)vuex
一、vuex的简介
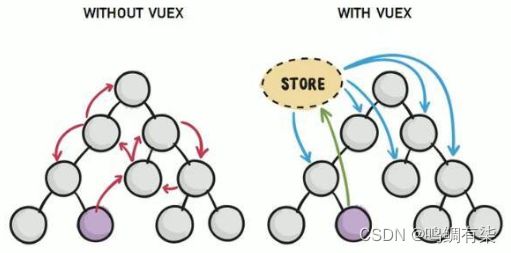
1、回顾组件之间的通讯
父组件向子组件通讯:通过props实现
子组件向父组件通讯:通过自定义事件($emit)方式来实现
兄弟组件之间的通讯:事件总线($eventBus)、订阅与发布方式来实现
跨级组件的通讯:可以通过(provider和inject)方式来实现
2、什么是Vuex
3、使用vuex的好处
-
集中管理共享数据
-
高效实现组件之间数据共享
-
vuex中的数据都是响应式的,能够实施保持数据与页面的同步
4、vuex和localStorage的区别
-
vuex是存储在内存中,localStroage存储数据在浏览器本地存储的
-
vuex的数据是瞬时的,localStroage是持久的,是不容易丢失的
-
vuex的数据是响应式的,localStorage中的数据不是响应式的
-
vuex还能完成异步操作(网络请求的),localStorage仅仅只是一个保存数据和获取数据
-
vuex中数据按照业务进行模块化,localStorage管理数据没有模块化
-
vuex直接操作JS的对象无需转换,localStorage存储数据要转成JSON,取数据要将JSON转成JS对象
-
单页面应用的程序组件数据共享使用使用状态机(vuex),localStorage适合多【页面数据的共享
5、什么情况下我应该使用 Vuex?
Vuex 可以帮助我们管理共享状态,并附带了更多的概念和框架。这需要对短期和长期效益进行权衡。 如果您不打算开发大型单页应用,使用 Vuex 可能是繁项几余的。确实是如此一一如果您的应用够简单,您最好不要使用 Vuex,一个简单的 store 模式就足够您所需了。但是,如果您需要构建一个中大型单页应用,您很可能会考虑如何更好地在组件外部管理状态,Vuex 将会成为自然而然的选择,引用 Redux的作者 Dan Abramov 的话说就是:
Flux 架构就像眼镜: 您自会知道什么时候需要它
6、vuex的安装和基本配置
-
下载vuex的依赖包
npm i [email protected]-
在src目录下创建一个store文件夹
-
在src/store/index.js在此处完成vuex状态机仓库的基本配置
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
//将vuex以插件的方式设置到Vue中
Vue.use(Vuex)
/*
创建仓库
new Vuex.Store(参数)
参数是状态机配置对象,状态机由5大部件组成
state:用来管理vuex仓库(store)中的状态,它是一个对象
mutation:用来操作state的选项,改变数据,它是一个对象
actions:异步操作的
getters:相当于是状态机中的计算属性
modules:模块化
*/
const store=new Vuex.Store({
state:{
num:10
},
mutations:{
}
})
//导出store
export default store-
挂载store到vue中
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import store from '@/store'
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
render: h => h(App),
store
}).$mount('#app')二、vuex的基本使用和原理
1、Store核心概念
-
state:用来存储状态的
-
Mutatations:State的数据只能通过Mutations才能改变
-
Actions:用来完成异步操作,比如从后端获取数据
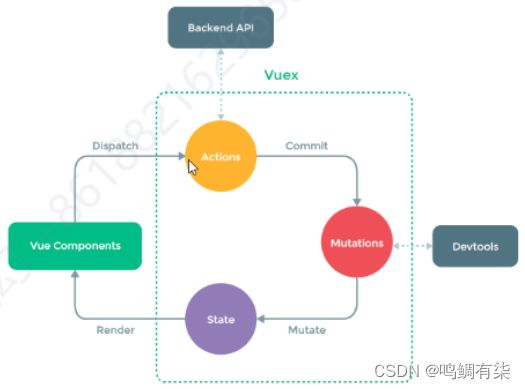
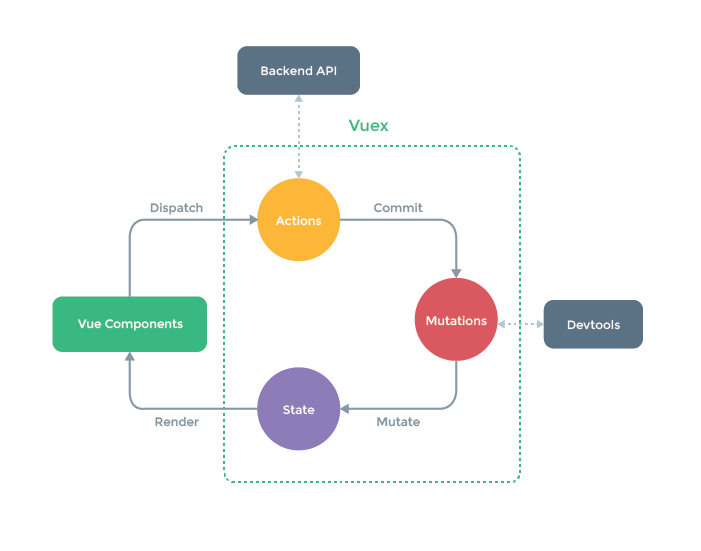
2、vuex的原理
Vuex的执行的流程
-
VueComponents(Vue组件)通过执行dispatch向store对象的Actions发送命令,要求完成异步任务
-
Actions执行异步任务,比如向Backend API(后端)发送请求,从后端获取到结果
-
Actions通过执行commit要求Mutations更改State状态机的数据,Mutatations就开始执行这个操作
-
Vue Componetents(Vue组件)直接从仓库中获取数据
注意点:
-
如果不执行异步任务,组件可以直接操作Mutatation来完成仓库中数据的改变
3、vuex的基本操作
这里以计数器的方式来讲解这个案例
3.1、state
-
首先先在store/index.js的state部分定义状态机状态数据
const store=new Vuex.Store({
state:{
num:10
}
})-
在组件中获取这个状态数据
组件中如果要获取store中的state数据的语法
如果要在js代码部分获取
this.$store.state.数据名如果要在template部分获取
{{$store.state.数据名}}
或者
3.2、mutations
组件中操作状态机的数据
如果组件内要更改状态机的数据,如果是通过的话,直接通过Mutations的方式去操作
-
在store对象配置对象中添加mutations选项,并定义要操作的方法
const store=new Vuex.Store({
state:{
num:10
},
mutations:{
INCREMENT(state,payload){
state.num++
}
}
})参数说明
1) 参数1:state对象
2) 参数2:载荷数据,此数据来源于组件或者actions
-
组件中操作state的数据
this.$store.commit(方法名,传递的参数)
export default {
methods:{
increment(){
this.$store.commit('INCREMENT')
}
}
}-
如果组件需要给仓库中传递数据,可以通过载荷传值
const store=new Vuex.Store({
state:{
num:10
},
mutations:{
INCREMENT_N(state,payload){
state.num+=payload
}
}
})
export default {
methods:{
incrementN(n){
this.$store.commit('INCREMENT_N',3)
}
}
}3.3、actions
组件中要调用store仓库中的actions的语法
this.$store.dispatch('actions的相关方法名',参数)购物车案例
-
组件
购物车列表
{{$store.state.shopcartList}}
ID
名称
数量
价格
小计
{{index+1}}
{{item.name}}
{{item.num}}
{{item.price}}
{{item.num*item.price}}
-
store
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const store=new Vuex.Store({
state:{
shopcartList:[]
},
mutations:{
getShopcartList_Sync(state,payload){
console.log('------2、store中的mutations的getShopcartList_Sync--------------');
console.log('payload',payload);
state.shopcartList=payload
}
},
//完成异步操作
actions:{
async getShopcartList_Async(context){
console.log('------1、store中的actions的getShopcartListAsync--------------');
let result=await Vue.prototype.$api.shopcart.getShopcartData()
console.log(result.data);
console.log('context',context);
context.commit('getShopcartList_Sync',result.data)
}
}
})
//导出store
export default store3.4、getters
getters选项中专门是依赖于state数据,产生新的数据,就相当于组件中计算属性
语法
const store=new Vuex.Store({
getters:{
getter方法名称(state){
return 处理后的数据
}
}
})在组件中调用的语法
this.$store.getters.getter方法名称案例:使用getters完成总价计算
const store=new Vuex.Store({
getters:{
totalPrice:state=>state.shopcartList.filter(item=>item.checked).reduce((prev,cur)=>prev+cur.price*cur.num,0)
}
})组件中方法问
总价:{{$store.getters.totalPrice}}三、辅助函数
之前我们如果要在组件中访问状态机仓库中的数据,或者操作状态机仓库的数据,必须通过this.$store这个对象来完成,除了这种方式之外,vuex为我们提供了另外一种组件中访问或者操作store的方式,这种方式就是辅助函数
辅助函数最重要的思想是将状态机中的数据或者方法映射成组件内方法
vuex中提供了以下四种常用方法
-
mapState():这个方法就是将状态机仓库中的state数据映射成组件内数据
-
mapMutatations():将状态机仓库中mutations选项中方法映射组件的方法
-
mapActions():将状态机仓库中actions选项中的方法映射成组件的方法
-
mapGetters():将状态机仓库中getters选项中的方法映射成组件内的计算属性
1、mapActions的使用
-
导入mapActoins
import {mapActions} from 'vuex'-
在methods选项中使用扩展运算符来映射仓库中的actions选项的方法到组件中
export default{
methods:{
...mapActions(["仓库中actions选项中的对应的方法名"])
}
}-
直接调用
export default{
methods:{
...mapActions(["getShopcartList_Async"]),
getShopcartList(){
this.getShopcartList_Async()
}
}
}2、mapState的使用
-
导入mapState
import {mapState} from 'vuex'-
必须在计算属性中使用扩展运算符来进行映射
语法
computed:{
...mapState(['state中的属性名'])
}案例
export default {
computed:{
...mapState(["shopcartList"])
}
}-
组件中直接使用
{{shopcartList}}3、mapMutations
-
导入mapMutations
import {mapMutations} from 'vuex'-
必须在methods中使用扩展运算符的方式将其映射成组件中相关方法
export default {
methods:{
...mapMutations(["increment_Sync"]),
increment(){
this.increment_Sync()
}
}
}4、mapGetters
-
导入mapGetters
import {mapGetters} from 'vuex'-
在computed选项中使用扩展运算符将其映射
export default {
computed:{
...mapGetters(["totalPrice"])
},
}5、别名
如果你映射仓库中的名字正好和你的组件内的名子冲突了怎么办
export default{
methods:{
...mapMutations({"新名称1":"仓库中名称"}),
...mapActions({"新名称1":"仓库中名称"})
},
compouted:{
...mapState({"新名称1":"仓库中名称"}),
...mapGetters({"新名称1":"仓库中名称"})
}
}总结:actions和mutations是在methods选项中映射的,state和getters是在computed选项中映射的。
四、vuex的模块化
随着项目的规模越来越大,状态机的功能越来越多的时候,我们仅仅将所有的功能写在store/index.js中,这样会带来如下的麻烦
-
业务结构不够清晰
-
可读性很差
-
可维护性很差
1、模块的实现步骤
-
在src/store文件夹下创建modules文件夹
-
在modules文件下创建shopcart.js,内容如下
特别注意:如果要模块化,必须要在该对象中设置
namespaced:true
export default {
namespaced:true,
state: {
shopcartList: []
},
mutations: {
getShopcartList_Sync(state, payload) {
console.log('------2、store中的mutations的getShopcartList_Sync--------------');
console.log('payload', payload);
state.shopcartList = payload
}
},
actions: {
async getShopcartList_Async(context) {
console.log('------1、store中的actions的getShopcartListAsync--------------');
let result = await Vue.prototype.$api.shopcart.getShopcartData()
context.commit('getShopcartList_Sync', result.data)
},
async checkedProduct_Async(context, payload) {
console.log('------1、store中的actions的checkedProduct_Async--------------', payload);
let result = await Vue.prototype.$api.shopcart.checkProducts(payload)
if (result.code) {
//在actions中方法调用actions中的方法
context.dispatch('getShopcartList_Async')
}
},
async changeNum_Async(context, payload) {
console.log('------1、store中的actions的changeNum_Async--------------', payload);
let result = await Vue.prototype.$api.shopcart.changeNum(payload)
if (result.code) {
context.dispatch('getShopcartList_Async')
}
}
},
getters: {
totalPrice: state => state.shopcartList.filter(item => item.checked).reduce((prev, cur) => prev + cur.price * cur.num, 0)
}
}-
在store/index文件中引入该模块
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import shopcart from './modules/shopcart'
import counter from './modules/counter'
Vue.use(Vuex)
const store=new Vuex.Store({
state:{},
mutations:{},
actions:{},
getters:{},
modules:{
a:shopcart,
b:counter
}
})
//导出store
export default store-
在组件中引用
-
原生方式引入
调用actions的方法
this.$store.dispatch("模块名/actions的相关方法名")调用getters
{{$store.getters['模块名/getters的相关名称']}}调用state
{{$store.state.模块名.数据名}}调用mutations
this.$store.commit('模块名/mutations的相关方法名')2、辅助函数访问模块化
-
辅助函数访问模块化的vuex的步骤
-
导入createNamespacedHelpers
import {createNamespacedHelpers} from 'vuex'-
通过createNamespacedHelpers()来获取辅助函数
const {mapActions,mapState,mapGetters}=createNamespacedHelpers('模块名')注意:如果在一个组件中要映射多个模块的辅助函数,就需要为每个模块的辅助函数取别名,解决命名冲突
const {mapActions:别名,mapState:别名,mapGetters:别名}=createNamespacedHelpers(模块名)-
在computed或者methods选项中通过扩展运算符实现映射
methods:{
...mapShopcartActions(["getShopcartList_Async"]),
...mapCounterMutations(["increment_Sync"]),
},
computed:{
...mapShopcartState(["shopcartList"]),
...mapShopcartGetters(["totalPrice"]),
...mapCounterState(["num"])
} 五、vuex的持久化
vuex中的数据,一旦页面刷新之后会丢失?怎么处理?【回答】
由于vuex状态机中的数据是瞬时的, 保存在内存中的,所以页面刷新后,数据会丢失,如果要解决这个问题,需要将状态机中的数据进行持久化
不是所有的状态机的数据都需要持久化的
持久化的思路:持久化就是将vuex状态机中的数据保存在localStorage中存一份
1、使用vuex-persistedstate插件来实现vuex持久化
使用的步骤如下所示
-
安装
vuex-persistedstate依赖包
npm i vuex-persistedstate-
在src/store/index.js中导入
vue-persistedstate
import createPersistedstate from 'vuex-persistedstate'-
在src/store/index.js在仓库入口文件中配置插件
const store=new Vuex.Store({
//....省略
plugins:[
createPersistedstate({
//存在localstorage中的名字
key:'store-num-key',
//模块名.数据名
paths:['b.num']
})
]
})