Python测试框架pytest(24)配置文件pytest.ini
目录
1、配置项
1.1、markers
1.2、xfail_strict
1.3、addopts
1.4、log_cli
1.5、minversion
1.6、testpaths
1.7、norecursedirs
1.8、更改测试用例收集规则
2、parser.addini()添加配置信息
pytest 配置文件可以改变 pytest 的运行方式,它是一个固定的文件 pytest.ini 文件,读取配置信息,按指定的方式去运行。
pytest.ini 放在项目的根目录下,名字也不能随意更改。
注意:pytest.ini 不能使用任何中文符号,包括汉字、空格、引号、冒号等等。
pytest 里面有些文件是非 test 文件
-
pytest.ini:pytest 的主配置文件,可以改变 pytest 的默认行为。
-
conftest.py:测试用例的一些 fixture 配置。
-
_init_.py:识别该文件夹为 python 的 package 包。
-
tox.ini 与 pytest.ini 类似,用 tox 工具时候才有用。
-
setup.cfg 也是 ini 格式文件,影响 setup.py 的行为。
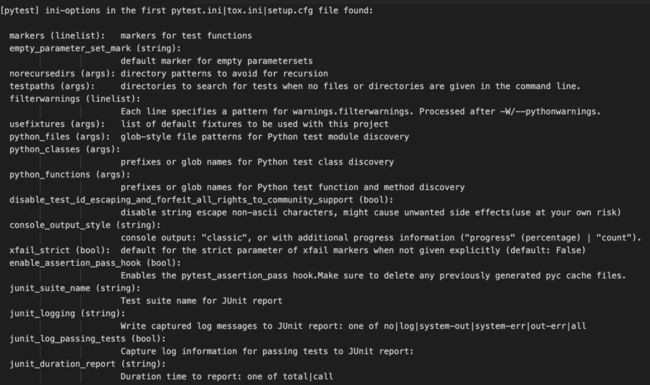
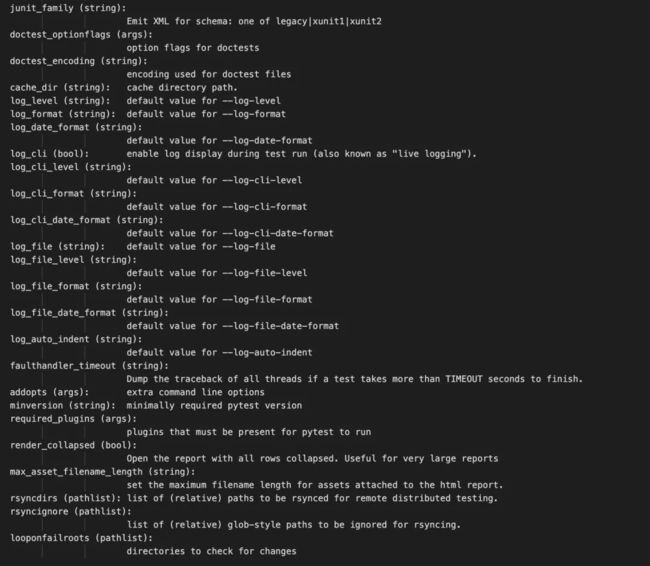
查看 pytest.ini 的配置选项
打开命令行,输入命令
pytest --help关于 pytest.ini 的内容如下:
1、配置项
1.1、markers
1、创建test_markers.py文件
使用两个标签:webtest和apptest,使用mark标记功能对分类测试非常有用。
脚本代码:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
微信公众号:AllTests软件测试
"""
import pytest
@pytest.mark.webtest
def test_send_http():
print("mark web test")
def test_something_quick():
pass
def test_another():
pass
@pytest.mark.apptest
class TestClass:
def test_case1(self):
print("app case1")
def test_case2(self):
print("app case2")
if __name__ == "__main__":
pytest.main(["-v", "test_markers.py"])2、创建pytest.ini文件
有时候标签多了,不容易记住,为了方便后续执行指令的时候能够准确使用mark标签,可以写入到pytest.ini文件。
文件内容:
[pytest]
markers =
webtest: Run the webtest case
apptest: Run the apptest case标记好之后,可以使用 pytest --markers 查看到。
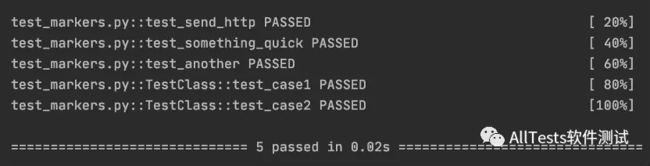
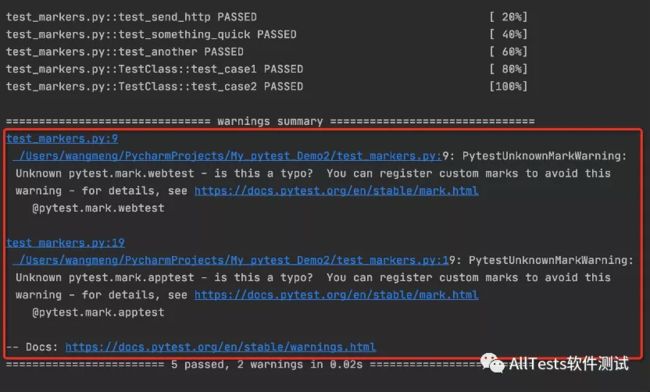
3、运行结果:
注:测试用例中添加了 @pytest.mark.webtest、@pytest.mark.apptest 装饰器,如果不添加 markers 选项的话,执行后就会报 warnings。
如图所示:
1.2、xfail_strict
设置 xfail_strict = True 可以让那些标记为 @pytest.mark.xfail 但实际通过显示 XPASS 的测试用例被报告为失败。
1、创建test_xfail_strict.py文件
脚本代码:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
微信公众号:AllTests软件测试
"""
import pytest
def test_case1():
print("AllTests")
assert 1
@pytest.mark.xfail()
def test_case2():
a = "All"
b = "AllTests"
assert a == b
@pytest.mark.xfail()
def test_case3():
a = "All"
b = "AllTests"
assert a != b
if __name__ == "__main__":
pytest.main(["-v", "test_xfail_strict.py"])2、未设置 xfail_strict = True
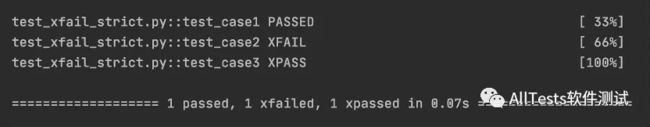
执行test_xfail_strict.py文件,运行结果:
标记为@pytest.mark.xfail()的test_case2和test_case3测试用例,两个都标记失败,我们希望两个用例全部显示xfail,但实际上test_case3显示XPASS(因为test_case3的断言是正确的)。
3、设置 xfail_strict = True
如果想让两个用例都显示xfail,那就在pytest.ini文件加此配置(xfail_strict = True)。
例如:pytest.ini文件内容:
[pytest]
markers =
webtest: Run the webtest case
apptest: Run the apptest case
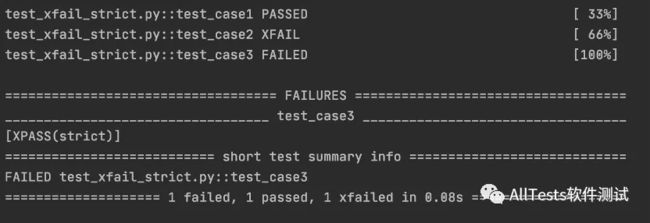
xfail_strict = True执行test_xfail_strict.py文件,运行结果:
test_case3测试用例结果显示为failed。
1.3、addopts
addopts 参数可以更改默认命令行选项,当我们在命令行输入一堆指令去执行用例的时候,就可以用该参数代替,省去重复敲命令的工作。
1、创建test_addopts.py文件
脚本代码:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
微信公众号:AllTests软件测试
"""
def test_case1():
print("AllTests")
assert 1
def test_case2():
a = "All"
b = "AllTests"
assert a == b
def test_case3():
a = "All"
b = "AllTests"
assert a != b2、未设置 addopts 参数
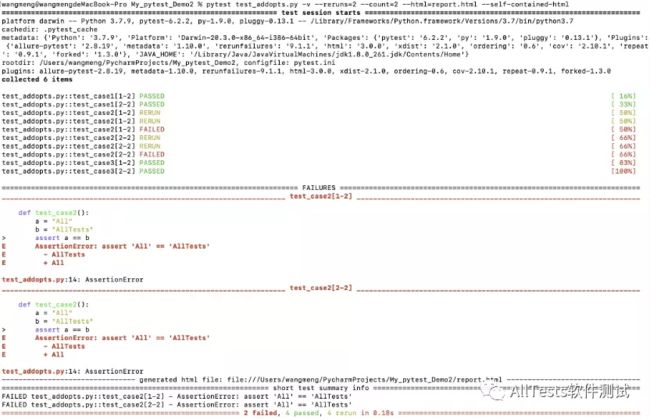
输入执行命令(失败重跑两次,一共运行两次,测试完成后生成测试报告)
pytest test_addopts.py -v --reruns=2 --count=2 --html=report.html --self-contained-html运行结果:
3、设置 addopts 参数
每次测试敲上面的执行命令有些繁琐,则可以将参数写到pytest.ini文件里
addopts = -v --reruns=2 --count=2 --html=report.html --self-contained-html例如:pytest.ini文件内容:
[pytest]
markers =
webtest: Run the webtest case
apptest: Run the apptest case
xfail_strict = True
addopts = -v --reruns=2 --count=2 --html=report.html --self-contained-html命令行输入执行命令pytest test_addopts.py即可
运行结果:
1.4、log_cli
控制台实时输出日志
格式:log_cli = True 或 False(默认),或者 log_cli = 1 或 0
例如:pytest.ini文件内容:
[pytest]
markers =
webtest: Run the webtest case
apptest: Run the apptest case
xfail_strict = True
log_cli = True1、创建logtest包,在包下分别创建test_log1.py、test_log2.py文件
test_log1.py脚本代码:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
微信公众号:AllTests软件测试
"""
def test_case1():
print("AllTests")
def test_case2():
a = "All"
b = "AllTests"
assert a != btest_log2.py脚本代码:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
微信公众号:AllTests软件测试
"""
def test_case1():
print("test_case1")
class TestClass:
def test_case2(self):
print("test_case2")
def test_case3(self):
print("test_case3")2、log_cli 参数为 False 或 0
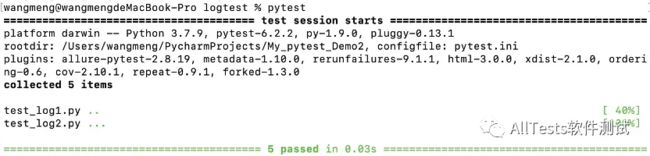
命令行输入pytest运行logtest包下的所有用例,运行结果:
3、log_cli 参数为 True 或 1
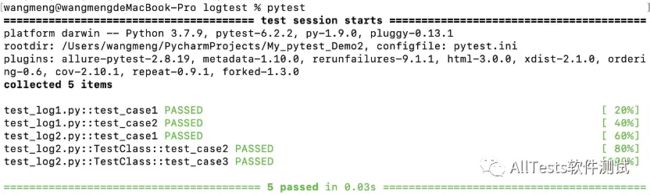
命令行输入pytest运行logtest包下的所有用例,运行结果:
可以清楚的看到哪个用例执行的结果
1.5、minversion
指定最低要求的 pytest 版本
例如:
[pytest]
minversion = 3.01.6、testpaths
testpaths 限定测试用例的搜索范围,只有在 pytest 范围指定文件目录参数或测试用例标识符时,该选项才会启用。
testpaths 指定的路径是以 testpaths 所在的目录为基准的相对路径。
例如:
[pytest]
testpaths = testing doc这会告诉pytest只在testing和doc从根目录执行时的目录。
1.7、norecursedirs
递归要避免的目录模式。
pytest 收集测试用例时,会递归遍历所有子目录,包括某些你明知道没必要遍历的目录,遇到这种情况,可以使用 norecursedirs 参数简化 pytest 的搜索工作。
默认模式为 '*.egg' , '.*' , '_darcs' , 'build' , 'CVS' , 'dist' , 'node_modules' , 'venv' , '{{arch}}'
norecursedirs = *.egg .* _darcs build CVS dist node_modules venv {{arch}}注:多个路径用空格隔开
例如:修改pytest.ini文件
[pytest]
norecursedirs = .svn _build tmp*这会告诉pytest不查看典型的Subversion或Sphinx构建目录或tmp前缀目录。
1.8、更改测试用例收集规则
pytest 默认的测试用例收集规则:
1、文件名以 test_*.py 文件和 *_test.py 文件。
2、以 test_ 开头的函数。
3、以 Test 开头的类,不能包含 __init__ 方法。
4、以 test_ 开头的类里面的方法。
1.8.1、python_classes
一个或多个名称前缀或全局样式模式,用于确定要为测试集合考虑哪些类。通过在模式之间添加空格来搜索多个全局模式。默认情况下,pytest 将考虑以 Test 作为测试集合。
python_classes = Test*
例如:修改pytest.ini文件
python_classes = Test* test* *Suite搜索模式是:前缀Test开头和前缀test开头和后缀Suite结尾的测试集合
1.8.2、python_files
一个或多个全局样式的文件模式,用于确定哪些 python 文件被视为测试模块。通过在模式之间添加空格来搜索多个全局模式。
默认情况下,文件匹配 test_*.py 和 *_test.py 将被视为测试模块。
python_files = test_*.py *_test.py或每行一个
python_files =
test_*.py
*_test.py
例如:修改pytest.ini文件
python_files = test_*.py *_test.py check_*.py或者
python_files =
test_*.py
*_test.py
check_*.py
除了默认的匹配文件模式,新添加了check_*.py匹配模式
1.8.3、python_functions
一个或多个名称前缀或全局模式决定哪些测试函数和方法被视为测试。通过在模式之间添加空格来搜索多个全局模式。默认情况下,pytest 将考虑前缀为 test 作为一个测试。
python_functions = test_*
例如:修改pytest.ini文件
python_functions = test_* *_test除了默认的以前缀为test作为一个测试,新增了以后缀为test作为一个测试。
2、parser.addini()添加配置信息
parser.addini() 添加 pytest.ini 文件配置信息
参数:
-
name 参数名称。
-
help 设置帮助文档。
-
type 类型,默认 None,可选:string(字符串)、pathlist(多个路径)、args(多个参数)、linelist(多个命令行参数)、bool(bool值)。
-
default 设置默认值,默认 None。
创建项目,项目目录结构:
创建conftest.py文件
parser.addini()方法将参数添加到pytest.ini配置文件里。
使用pytestconfig.getini()、request.config.getini()来获取pytest.ini配置参数。
脚本代码:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
微信公众号:AllTests软件测试
"""
import pytest
def pytest_addoption(parser):
parser.addini("url", help="添加url参数到pytest.ini配置文件里", type=None, default="https://www.baidu.com/")
@pytest.fixture(scope="session")
def get_url(pytestconfig):
url = pytestconfig.getini("url")
print("\n获取pytest.ini配置文件url参数信息:%s" % url)
return url
@pytest.fixture(scope="session")
def get_url2(request):
url2 = request.config.getini("url")
print("\n获取pytest.ini配置文件url参数信息:%s" % url2)
return url2创建test_demo.py文件,编写2条用例。
脚本代码:
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
"""
微信公众号:AllTests软件测试
"""
def test_case1(get_url):
print("执行用例,url地址:%s" % get_url)
def test_case2(get_url2):
print("执行用例,url地址:%s" % get_url2)打开命令行,输入执行命令:
pytest -s test_demo.py运行结果:
获取parser.addini()方法添加的配置信息。
使用pytest.ini配置文件添加配置信息
之后项目的根目录创建pytest.ini配置文件
文件内容:
[pytest]
url = https://www.cnblogs.com/alltests/命令行再次执行命令:
pytest -s test_demo.py运行结果:
获取到pytest.ini文件里的配置信息