Linux学习之nginx虚拟域名主机,lsof和netstat命令查看端口是否被监听
需要先参考我的博客《Linux学习之Ubuntu 20.04在https://openresty.org下载源码安装Openresty 1.19.3.1,使用systemd管理OpenResty服务》安装好Openresty。
虚拟域名可以使用让不同的域名访问到同一台主机。
cd /usr/local/openresty切换当前访问目录到/usr/local/openresty。
![]()
在/usr/local/openresty/nginx/conf/nginx.conf文件的http配置块末尾添加上以下的内容:
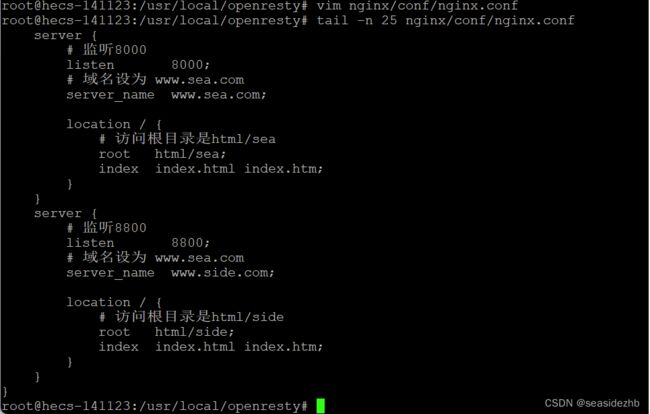
server {
# 监听8000
listen 8000;
# 域名设为 www.sea.com
server_name www.sea.com;
location / {
# 访问根目录是html/sea
root html/sea;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
server {
# 监听8800
listen 8800;
# 域名设为 www.sea.com
server_name www.side.com;
location / {
# 访问根目录是html/side
root html/side;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
/usr/local/openresty/nginx/conf/nginx.conf文件整体内容如下:
worker_processes 1;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}
server {
# 监听8000
listen 8000;
# 域名设为 www.sea.com
server_name www.sea.com;
location / {
# 访问根目录是html/sea
root html/sea;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
server {
# 监听8800
listen 8800;
# 域名设为 www.sea.com
server_name www.side.com;
location / {
# 访问根目录是html/side
root html/side;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
}
我使用的是vim编辑器,要是不知道vim编辑怎么使用,可以看一下我的博客。
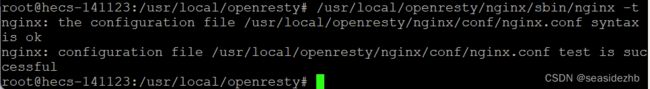
/usr/local/openresty/nginx/sbin/nginx -t可以检查一下格式和测试都是正常的。
/usr/local/openresty/nginx/sbin/nginx进行启动。
![]()
lsof -i:8000可以看到8000端口已经被监听,lsof -i:8800可以看到8800端口也已经被监听,lsof -i:7800没有被监听,因为没有任何输出,注意:7800端口只是测试一下,说明什么叫没有被监听。

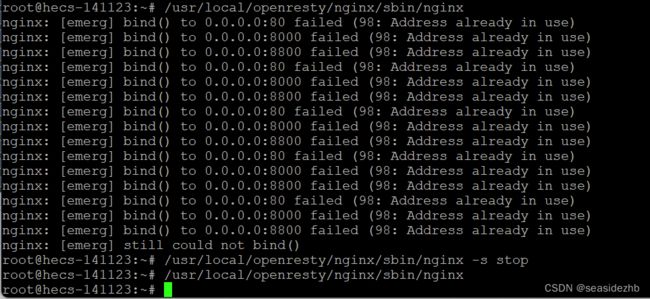
/usr/local/openresty/nginx/sbin/nginx再次进行启动,发现报错如下:
nginx: [emerg] bind() to 0.0.0.0:80 failed (98: Address already in use)
nginx: [emerg] bind() to 0.0.0.0:8000 failed (98: Address already in use)
nginx: [emerg] bind() to 0.0.0.0:8800 failed (98: Address already in use)
/usr/local/openresty/nginx/sbin/nginx -s stop可以停止nginx,/usr/local/openresty/nginx/sbin/nginx再次启动。
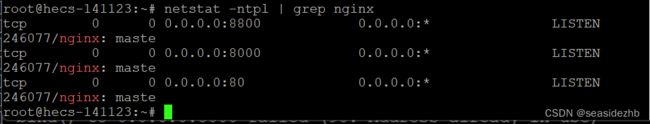
netstat -ntpl | grep nginx查看一下nginx的监听端口。
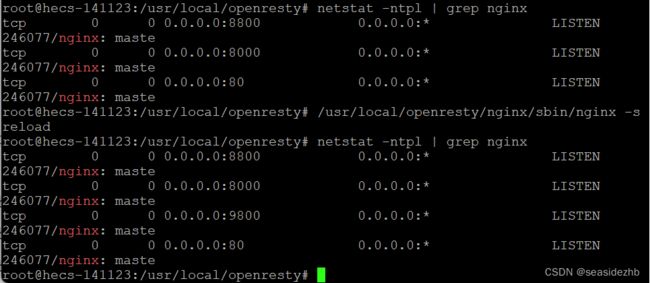
接下来把下边的内容也添加到/usr/local/openresty/nginx/conf/nginx.confhttp配置块里:
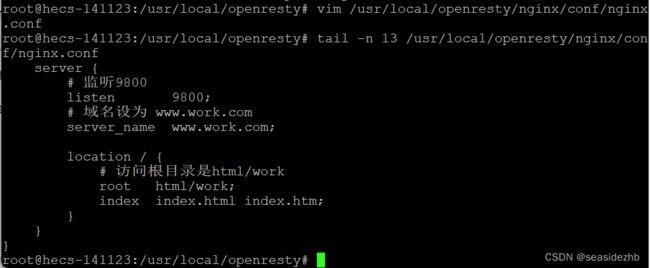
server {
# 监听9800
listen 9800;
# 域名设为 www.work.com
server_name www.work.com;
location / {
# 访问根目录是html/work
root html/work;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
/usr/local/openresty/nginx/conf/nginx.conf文件整体内容如下:
worker_processes 1;
events {
worker_connections 1024;
}
http {
include mime.types;
default_type application/octet-stream;
sendfile on;
keepalive_timeout 65;
server {
listen 80;
server_name localhost;
location / {
root html;
index index.html index.htm;
}
error_page 500 502 503 504 /50x.html;
location = /50x.html {
root html;
}
}
server {
# 监听8000
listen 8000;
# 域名设为 www.sea.com
server_name www.sea.com;
location / {
# 访问根目录是html/sea
root html/sea;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
server {
# 监听8800
listen 8800;
# 域名设为 www.sea.com
server_name www.side.com;
location / {
# 访问根目录是html/side
root html/side;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
server {
# 监听9800
listen 9800;
# 域名设为 www.work.com
server_name www.work.com;
location / {
# 访问根目录是html/work
root html/work;
index index.html index.htm;
}
}
}
/usr/local/openresty/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload可以在不断开已有连接的基础上重新加载/usr/local/openresty/nginx/conf/nginx.conf。
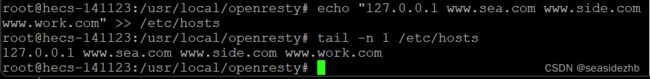
echo "127.0.0.1 www.sea.com www.side.com www.work.com" >> /etc/hosts将127.0.0.1 www.sea.com www.side.com www.work.com写入/etc/hosts里边。
mkdir /usr/local/openresty/nginx/html/sea /usr/local/openresty/nginx/html/side /usr/local/openresty/nginx/html/work在/usr/local/openresty/nginx/html创建三个目录sea、side和work。
![]()
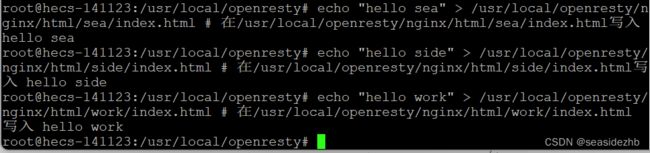
执行下边命令:
echo "hello sea" > /usr/local/openresty/nginx/html/sea/index.html # 在/usr/local/openresty/nginx/html/sea/index.html写入 hello sea
echo "hello side" > /usr/local/openresty/nginx/html/side/index.html # 在/usr/local/openresty/nginx/html/side/index.html写入 hello side
echo "hello work" > /usr/local/openresty/nginx/html/work/index.html # 在/usr/local/openresty/nginx/html/work/index.html 写入 hello work
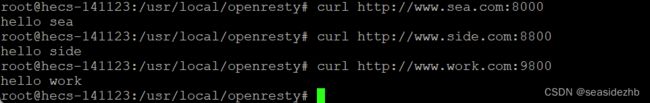
curl http://www.sea.com:8000可以访问虚拟域名www.sea.com的8000端口。
curl http://www.side.com:8800可以访问虚拟域名www.side.com的8800端口。
curl http://www.work.com:9800可以访问虚拟域名www.work.com的9800端口。
此文章为8月Day 26学习笔记,内容来源于极客时间《Linux 实战技能 100 讲》。