c#对c++动态库的调用全流程以及详解
如果对pcl里的函数导出为动态库,分为以下几部分:
- 对c++动态库的导出;
- c#对c++动态库的加载;
- c#对第2步的调用
一、对c++动态库的导出
定义导出的宏定义:
#ifndef EXPORT
# define EXPORT(rettype) __declspec( dllexport ) rettype __cdecl
#endif
这里的rettype是占位符,用来表示函数的返回值
比如下面的代码就是将DBSCANKdtreeCluster替代了占位符,其实就是在使用的时候用实际的类型进行了替代。
EXPORT(DBSCANKdtreeCluster<pcl::PointXYZ>*)
segment_dbscankdtreecluster_xyz_ctor(){
return new DBSCANKdtreeCluster<pcl::PointXYZ>();
}
二、c#对c++动态库的加载
在c#中调用c++导出的动态库,一般是采用c#中的P/Invoke 技术来实现。P/Invoke 是指通过 Platform Invocation Services(平台调用服务)在托管代码中调用非托管函数或动态库的技术。通过Dllimport导入函数:
//导入对应的动态库以及对应的函数
[DllImport("dbscan_pcl_lib.dll", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl)]
public static extern IntPtr segment_dbscankdtreecluster_xyz_ctor();
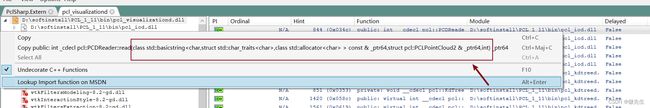
可以通过DependenciesGui去查看动态库的调用约定方式,如下图所示:
可以看到其对应的调用方式都是__cdecl的方式,所以在导入的时候也是指定 CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl,另外再指定函数名字的时候有两种方式,一种是通过EntryPoint ="函数名"的方式,另一种是将底下的函数命名为同名函数,因为这样就会默认导出的函数名是定义的函数名字。并且参数也要是一一对应的。
所以为了方便就可以对导入的函数进行封装调用,比如把它放进一个类的静态函数中,然后在同一命名空间里的另外一个类就可以封装对其的调用,如下所示:
//做一个命名空间,防止调用冲突
namespace PclSharp
{
//导入c++动态库的函数,使用静态函数的方式进行调用
public static class DLLInvoke
{
[DllImport("dbscan_pcl_lib.dll", CallingConvention = CallingConvention.Cdecl)]
public static extern IntPtr segment_dbscankdtreecluster_xyz_ctor();
}
//通过另一个类去封装对前面导入的函数的调用
class DBSCANCluster
{
public IntPtr _ptr;
public DBSCANCluster()
{
_ptr = DLLInvoke.segment_dbscankdtreecluster_xyz_ctor();
}
}
}
三、在要调用的方法实现调用即可
- 主要注意参数那些要对应上。
在main函数中使用如下:
DBSCANCluster ec = new DBSCANCluster();
ec.setMinPts(20);
//构建kd-tree
var tree = new PclSharp.Search.KdTreeOfXYZ();
tree.SetInputCloud(cloud);
ec.setTolerance(0.1);
ec.setMinClusterSize(10);
ec.setMaxClusterSize(200);
ec.setSearchMethod(tree);
ec.setInputCloud(cloud);
var clusterIndices = new VectorOfPointIndices();
ec.extract(clusterIndices);
四、从c#调用c++动态库整体总结
参考文章:c#实现隐式的用户自定义类型转换(关键字implicit operator)
隐式转换可以理解为对象A=要被隐式转换的对象,当这样的公式就会调用隐式转换这个函数,如下所示:
public static implicit operator float(MyType m)
{
return m.A +m.B/10F;
}
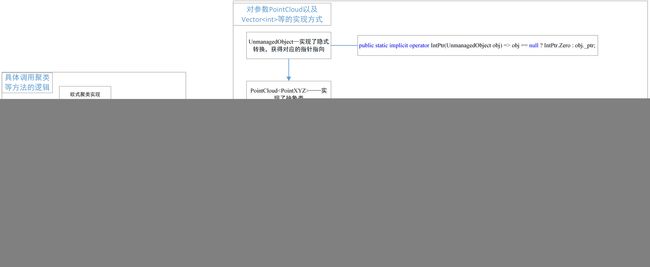
从哪里看?——pclsharp可以看看通过隐式转换获得new Vector这样的结果。所以在pclsharp中VectorOfInt、PointCloud都是通过这样实现的
示例——隐式转换的示例如下:
首先定义了一个自定义的类型MyType,关键是隐式转换那里的写法,放在这里其实就是float f=mt。
class MyType//定义自己的类型,相当于int类型
{
private int A,B;
public MyType(int a,int b)
{
this.A =a;
this.B =b;
}
public static implicit operator float(MyType m)
{
return m.A +m.B/10F;
}
}
//在这里调用隐式转换
class test
{
static void Main()
{
MyType mt=new MyType (12,6);//相当于int mt=12
float f=mt;//这里进行的是一个隐式转换,相当于float f=mt
Console.WriteLine (f);//输出12.6
}
}
所以这里输出的最后结果就是12.6。
用于控制是否自动释放,在PointCloud
public unsafe class PointCloudOfXYZ : PointCloud<PointXYZ>
{
private bool _suppressDispose;//属性声明
internal PointCloudOfXYZ(IntPtr ptr, bool suppressDispose)//带有_suppressDispose的构造函数
:this(ptr)
{
_suppressDispose = suppressDispose;
}
//在释放资源的时候会进行释放,判断是否释放非托管资源
protected override void DisposeObject()
{
if (_suppressDispose)
return;
Invoke.pointcloud_xyz_delete(ref _ptr);
}
}
单独看欧式聚类的实现看PointCloud是在c++和c#之间如何调用的:
//在c#中
//在c#中导入动态库
public static extern void segmentation_euclideanclusterextraction_xyz_setInputCloud(IntPtr ptr, IntPtr cloud);
[DllImport(Native.DllName, CallingConvention=Native.CallingConvention)]
//调用动态库导入的函数,从这里传入的参数是PointCloud cloud,而实际传入的是IntPtr,由于c#中实际调用的PointCloudOfXYZ,这个PointCloudOfXYZ继承了抽象类PointCloud cloud,它实现构造方法,最终指针指向了PointCloud*(并且这里对应也是c++的PointCloud*),同时实现了隐式转换,所以最终对象其实就是指针了,也就是PointCloud*
public override void SetInputCloud(PointCloud<PointXYZ> cloud)
{
Invoke.segmentation_euclideanclusterextraction_xyz_setInputCloud(_ptr, cloud);
}
//在实际使用的进行调用
var cloudFiltered = new PointCloudOfXYZ();
using (var ec = new EuclideanClusterExtractionOfXYZ
{
ClusterTolerance = 0.02,
MinClusterSize = 100,
MaxClusterSize = 25000
})
{
ec.SetSearchMethod(tree);
ec.SetInputCloud(cloudFiltered);
ec.Extract(clusterIndices);
}
//在c++中
EXPORT(void) segmentation_euclideanclusterextraction_xyz_setInputCloud(EuclideanClusterExtraction<PointXYZ>* ptr, PointCloud<PointXYZ>* cloud)
{
ptr->setInputCloud(std_cloud(std_cloud(), cloud));
}
为什么参数要用指针EuclideanClusterExtraction,而不是直接对象,同时参数PointCloud也是指针。这是因为结构体的接收比较麻烦,需要按照c++的结构1:1进行接收,对应的函数就不用管了,但是这里如果是字符串传输就会出现问题,因为字符串有编码的问题,而换成指针进行导出就可以直接用IntPtr去接收,所以这就是所带来的最大的好处。