Fei-Fei Li-Lecture 16:3D Vision 【斯坦福大学李飞飞CV课程第16讲:3D Vision】
目录
P1 2D Detection and Segmentation编辑
P2 Video = 2D + time series
P3 Focus on Two Problems
P4 Many more topics in 3D Vision
P5-10 Multi-View CNN
P11 Experiments – Classification & Retrieval
P12 3D Shape Representations
P13--17 3D Shape Representations: Depth Map
P18--26 3D Shape Representations: Surface Normals 曲面法线
P27--34 3D Shape Representations: Point Cloud
P35--66 3D Shape Representations: Triangle Mesh
P1 2D Detection and Segmentation
Classification分P类:没有空间信息,只是对一张图片进行分类
Semantic Segmentation语义分割: 没有物体,只有像素点,对像素点进行分类
Object Detection目标检测:直接识别出物体并进行分类
Instance Segmentation:实例分割=目标检测+语义分割 (第一次听说这个)
语义分割只需要分出不同类就行,同类的不同个体不需要分,但是Instance Segmentation在语义分割的基础上又把不同的类进行了分割:目标检测后,需要对检测的部分做进一步的语义分割
P2 Video = 2D + time series
视频就是2D的图像加上了时间序列
P3 Focus on Two Problems
今天需要解决的两个问题
①由一张输入图像得到一个3D模型
②识别3D模型进行类别判定
P4 Many more topics in 3D Vision
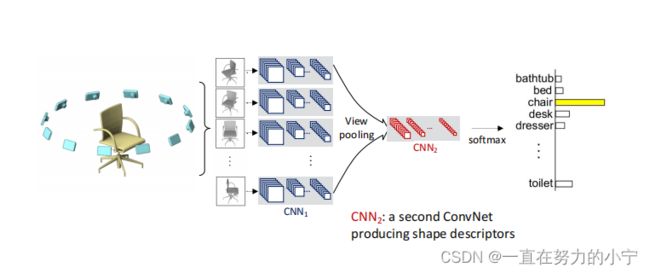
P5-10 Multi-View CNN
CNN1:提取图像特征的卷积神经网络
CNN2:生成描述形状符的卷积神经网络
P11 Experiments – Classification & Retrieval
Q:MVCNN? SPH? LFD? 3D ShapeNets? FV?
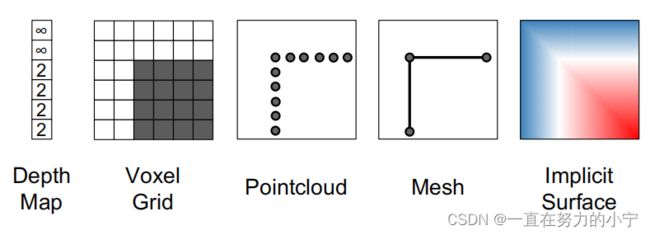
P12 3D Shape Representations
Q: Voxel Grid? Pointcloud? Mesh? Surface?
A:下面详细讲啦
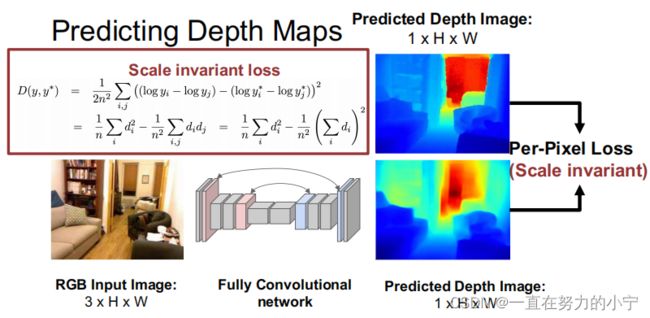
P13--17 3D Shape Representations: Depth Map
Q:H是Height ? W是Width?
可以使用全卷积神经网络进行深度图预测,得到两个估计的深度图,然后还可以得到每像素Loss
Q:L2 距离是什么?
Q:具体是什么意思以及怎么解决?
A: 意思大概是单目图像中信息有限
Scale invariant 尺度不变性
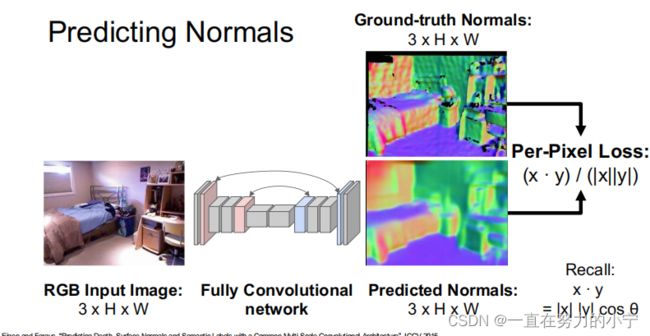
P18--26 3D Shape Representations: Surface Normals 曲面法线
对于每个像素,表面法线给出一个向量,表示该像素的世界上的对象的法向向量
假设 RGB Image为 3 x H x W,那么法线图 Normals: 3 x H x W
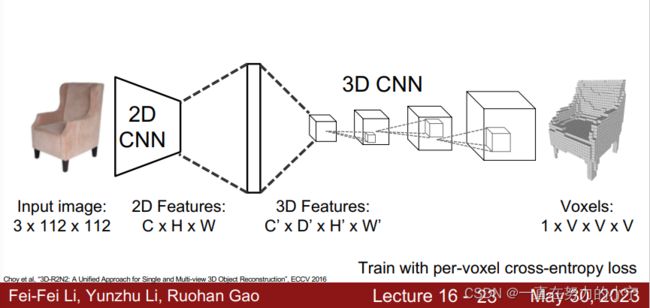
3D Shape Representations: Voxels
• Represent a shape with a V x V x V grid of occupancies 网格表示形状
• Just like segmentation masks in Mask R-CNN, but in 3D! 分割掩码
• (+) Conceptually simple: just a 3D grid! 只是一个3D网格
• (-) Need high spatial resolution to capture fine structures 需要高空间分辨率捕捉精细结构
• (-) Scaling to high resolutions is nontrivial ! 缩放到高分辨率并不容易
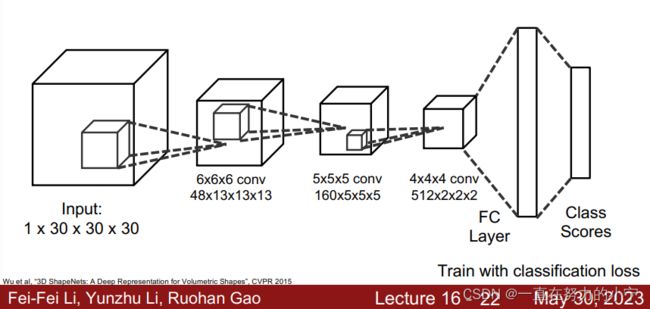
Processing Voxel Inputs: 3D Convolution
Generating Voxel Shapes: 3D Convolution
Voxel Problems: Memory Usage
Storing 1024(3次方) voxel grid takes 4GB of memory
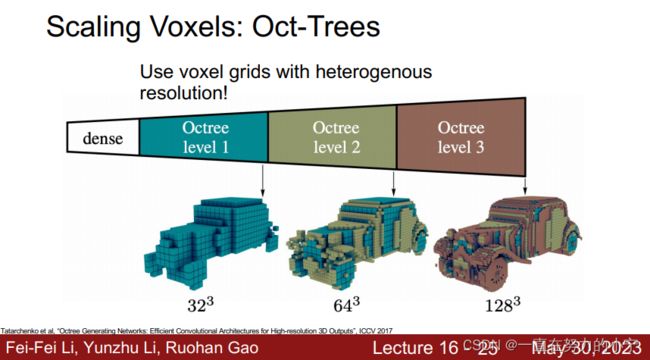
Scaling Voxels: Oct-Trees 八叉树
Q: 没太看懂这个Oct-Trees
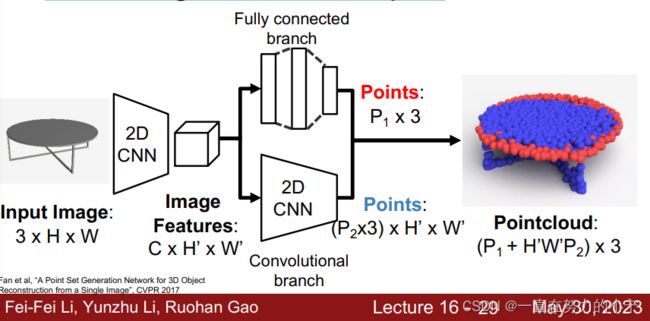
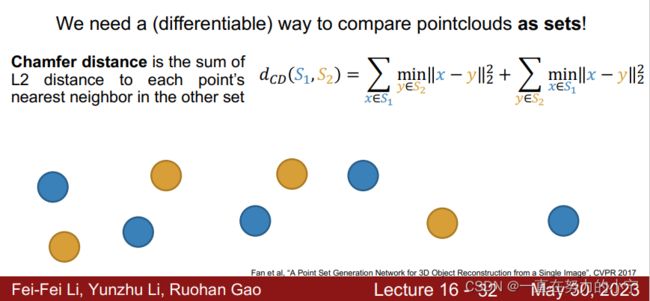
P27--34 3D Shape Representations: Point Cloud
• Represent shape as a set of P points in 3D space
• (+) Can represent fine structures without huge numbers of points
• ( ) Requires new architecture, losses, etc
• (-) Doesn’t explicitly represent the surface of the shape: extracting a mesh for rendering or other applications requires post-processing
提取网格为渲染或其他应用提取网格需要进行后处理
Proessing Pointcloud Inputs: PointNet
MLP ?
Max-Pool?
Generating Pointcloud Outputs
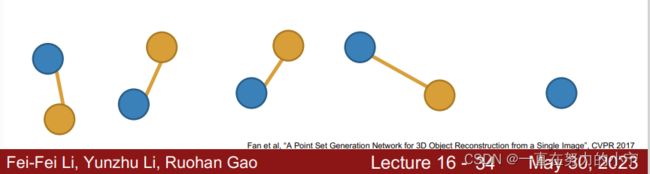
Predicting Point Clouds: Loss Function
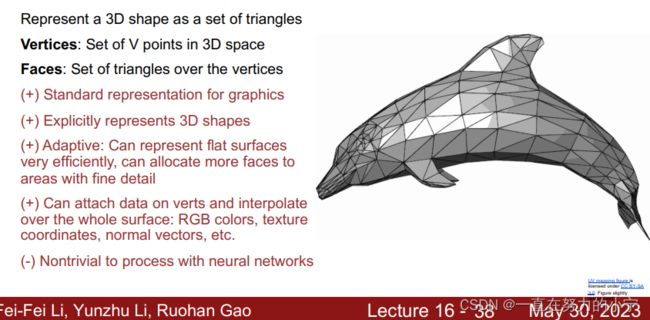
P35--66 3D Shape Representations: Triangle Mesh
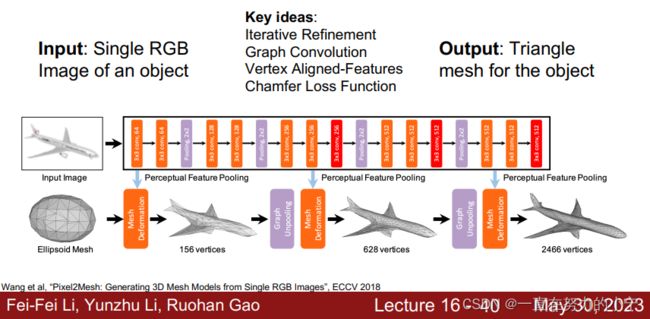
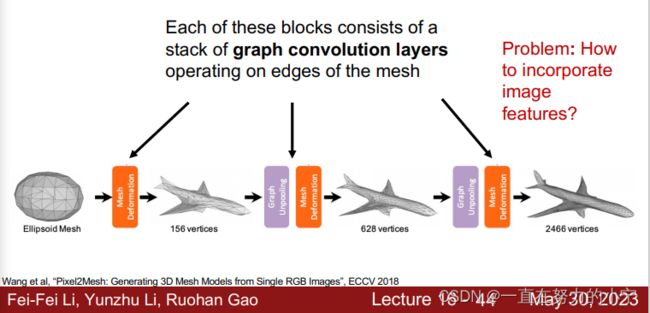
Predicting Meshes: Pixel2Mesh
Idea #1: Iterative mesh refinement
Start from initial ellipsoid mesh Network predicts offsets for each vertex Repeat.
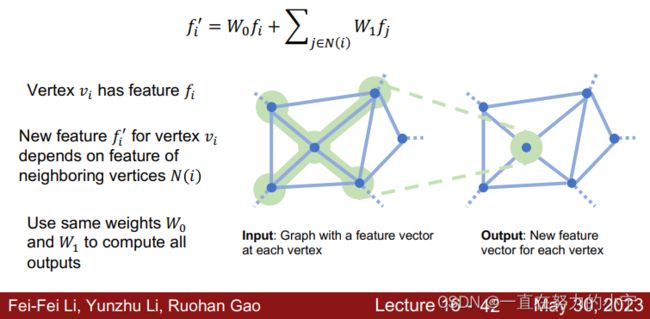
Predicting Triangle Meshes: Graph Convolution
Problem: How to incorporate image features?
Predicting Triangle Meshes: Vertex-Aligned Features
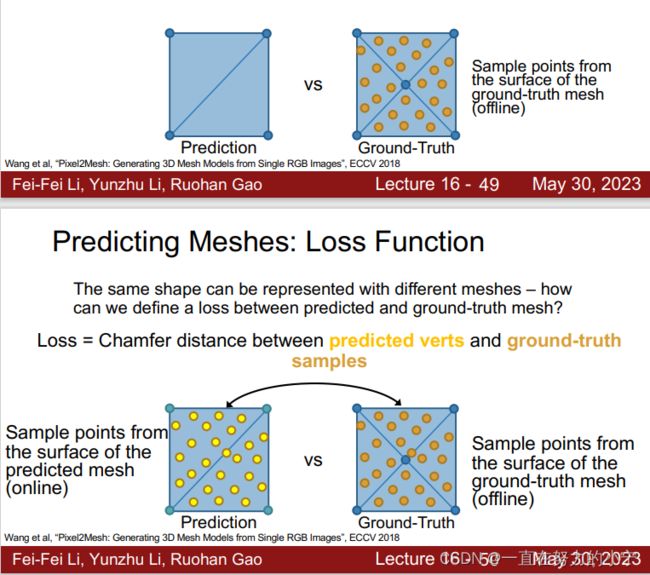
Predicting Meshes: Loss Function
The same shape can be represented with different meshes – how can we define a loss between predicted and ground-truth mesh?
Idea: Convert meshes to pointclouds, then compute loss
3D Shape Prediction: Mesh R-CNN
Mesh R-CNN: Hybrid 3D shape representation
未完待续