算法实验作业记录(C++)
1. 藏书问题:
小明藏书真可谓汗牛充栋,现在有一道难题问:小明到底有多少本不一样的书,每样书的名字是什么,因为有的书名是样的,我们把他视为同样的书。

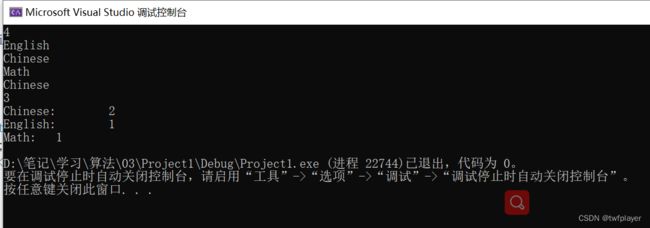
4
English
Math
Chinese
Chinese
样例输出
3
Chinese 2
English 1
Math 1
代码如下:
//map集合
#include2. 破案问题:

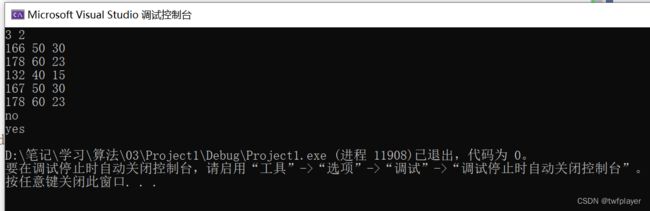
样例输入
3 2
166 50 30
178 60 23
132 40 15
167 50 30
178 60 23
样例输出
no
yes
代码如下:
//set集合,遍历criminal,man.count()
#include3. 重复最大值
给定n个整数,求里面出现次数最多的数,如果有多个重复出现的数,求值最大的那个。
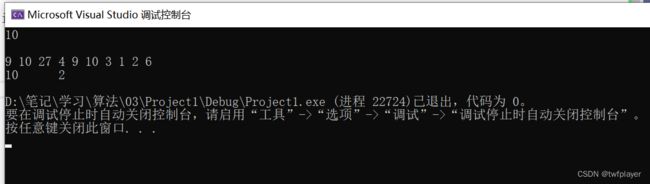
输入样例1
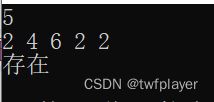
5
1 1 2 3 4
//map集合自动排序,小->大,出现次数
#include4. 水果明细表
告诉你每一笔销售记录的水果名称、产地和销售的数量,请生产明细表。
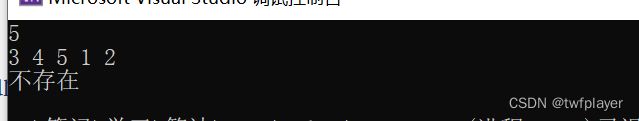
输入样例:
5
apple shandong 3
pineapple guangdong 1
sugarcane guangdong 1
pineapple guangdong 3
pineapple guangdong 1
输出样例
guangdong
|----pineapple(5)
|----sugarcane(1)
shandong
|----apple(3)
//map<产地,map<水果,数量>>
#include有一个含n(n>2)个整数的数组a,判断是否存在出现次数超过所有元素一半的元素;
#include一个字符串采用string对象存储,设计一个算法判断该字符串是否为回文;
//双指针
#include有一个整数序列,设计一个算法判断其中是否存在两个元素的和恰好=给定的整数k;
//双指针
#include有两个整数序列,每个序列中的所有元素均不相同,设计一个算法求它们的公共元素,要求不使用STL的集合算法;
//排序,比较,
#include正整数n(n>1)可以写成质数的乘积,称为整数的因式分解,例如12=223,18=233;11=11;设计一个算法,求n这样分解后各个质因数出现的次数,采用vector向量存放结果;
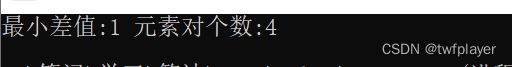
#include有一个整数序列,所有元素均不相同,设计算法求相差最小的元素对的个数.
例如{4,1,2,3}相差最小的元素对的个数为3, 元素对为(1,2), (2,3), (3,4).
//排序,直接遍历计算差值,map存储出现次数
#include有一个map容器,其中已经存放了较多元素,设计一个算法求出其中重复的value并且返回重复value的个数。
#include有两个整数序列,每个序列中的所有元素均不相同,设计一个算法求它们的公共元素,使用Map容器;
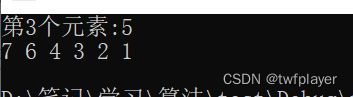
#include假设有一个含n(n>1)个元素的stack栈容器st,设计一个算法出栈从栈顶到栈底的第k(1≤k≤n)个元素,其他栈元素不变。
#include