LeetCode //C - 138. Copy List with Random Pointer
138. Copy List with Random Pointer
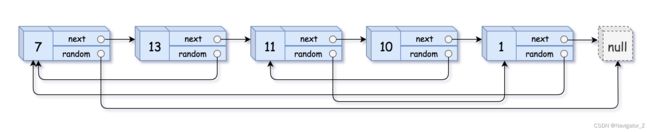
A linked list of length n is given such that each node contains an additional random pointer, which could point to any node in the list, or null.
Construct a deep copy of the list. The deep copy should consist of exactly n brand new nodes, where each new node has its value set to the value of its corresponding original node. Both the next and random pointer of the new nodes should point to new nodes in the copied list such that the pointers in the original list and copied list represent the same list state. None of the pointers in the new list should point to nodes in the original list.
For example, if there are two nodes X and Y in the original list, where X.random --> Y, then for the corresponding two nodes x and y in the copied list, x.random --> y.
Return the head of the copied linked list.
The linked list is represented in the input/output as a list of n nodes. Each node is represented as a pair of [val, random_index] where:
val: an integer representing Node.val
random_index: the index of the node (range from 0 to n-1) that the random pointer points to, or null if it does not point to any node.
Your code will only be given the head of the original linked list.
Example 1:
Input: head = [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
Output: [[7,null],[13,0],[11,4],[10,2],[1,0]]
Example 2:
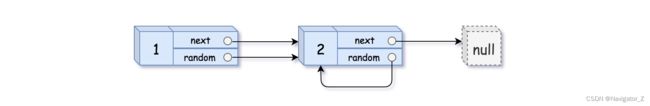
Input: head = [[1,1],[2,1]]
Output: [[1,1],[2,1]]
Example 3:
Input: head = [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
Output: [[3,null],[3,0],[3,null]]
Constraints:
- 0 <= n <= 1000
- − 1 0 4 < = N o d e . v a l < = 1 0 4 -10^4 <= Node.val <= 10^4 −104<=Node.val<=104
- Node.random is null or is pointing to some node in the linked list.
From: LeetCode
Link: 138. Copy List with Random Pointer
Solution:
Ideas:
The main challenge in this problem is to create a deep copy of the linked list while preserving the random pointer relations between nodes. The solution uses a mapping between the original nodes and their copies to ensure that the next and random pointers in the copied list point to the appropriate nodes.
Steps:
1. Count the Nodes:
- Before copying the nodes, we traverse the original list to count the number of nodes. This count helps us allocate memory for our mapping structures.
2. Initialize Mapping Structures:
- We use two arrays: oldNodes and newNodes.
- oldNodes will store pointers to the original nodes.
- newNodes will store pointers to the corresponding copied nodes.
- The relationship between the two arrays is that the index of an original node in oldNodes will match the index of its copy in newNodes.
3. Copy Nodes & Fill Mapping Structures:
- We traverse the original list again and for each node, we create a copy of it.
- We add the original node to the oldNodes array and its copy to the newNodes array, ensuring they are at the same index.
4. Establish next and random Pointers:
- We traverse the original list again.
- For the next pointer of a copied node:
- We find the index of the original node’s next pointer in the oldNodes array.
- We then use this index to set the next pointer of the copied node to point to the appropriate node in the newNodes array.
- Similarly, for the random pointer:
- We find the index of the original node’s random pointer in the oldNodes array.
- We then use this index to set the random pointer of the copied node to point to the appropriate node in the newNodes array.
Code:
/**
* Definition for a Node.
* struct Node {
* int val;
* struct Node *next;
* struct Node *random;
* };
*/
struct Node* copyRandomList(struct Node* head) {
if (head == NULL) return NULL;
struct Node* curr = head;
int count = 0;
// Count nodes
while (curr) {
count++;
curr = curr->next;
}
struct Node* oldNodes[count];
struct Node* newNodes[count];
curr = head;
int index = 0;
// 1. Copy nodes and fill our mapping structure
while (curr) {
struct Node* newNode = (struct Node*)malloc(sizeof(struct Node));
newNode->val = curr->val;
newNode->next = NULL;
newNode->random = NULL;
oldNodes[index] = curr;
newNodes[index] = newNode;
curr = curr->next;
index++;
}
curr = head;
index = 0;
// 2. Copy next and random pointers using our mapping structure
while (curr) {
if (curr->next) {
int nextIndex = 0;
while (oldNodes[nextIndex] != curr->next) {
nextIndex++;
}
newNodes[index]->next = newNodes[nextIndex];
}
if (curr->random) {
int randomIndex = 0;
while (oldNodes[randomIndex] != curr->random) {
randomIndex++;
}
newNodes[index]->random = newNodes[randomIndex];
}
curr = curr->next;
index++;
}
return newNodes[0];
}