LeetCode刷题笔记【13】:二叉树专题-5(找树左下角的值 、路径总和、从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树、从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树)
文章目录
- 前置知识
- 513. 找树左下角的值
-
- 题目描述
- 层序遍历法
- 迭代遍历法
- 递归法
- 112. 路径总和
-
- 题目描述
- 踩的坑
- 反思&修改
- 113. 路径总和 II
-
- 题目描述
- 解题思路
- 代码
- 一些涉及到的八股
- 105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
-
- 题目描述
- 解题思路
- 代码
- 使用unordered_map的改进
- 106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
-
- 题目描述
- 解题思路
- 代码
- 总结
前置知识
参考前文
参考文章:
LeetCode刷题笔记【9】:二叉树专题-1(分别用递归遍历、迭代遍历、标记遍历实现前、中、后序遍历)
LeetCode刷题笔记【10】:二叉树专题-2(二叉树的层序遍历、翻转二叉树、对称二叉树)
LeetCode刷题笔记【10.5】:二叉树专题-2.5(二叉树的层序遍历 - 10道题)
LeetCode刷题笔记【11】:二叉树专题-3(二叉树的最大深度、二叉树的最小深度、完全二叉树的节点个数)
LeetCode刷题笔记【12】:二叉树专题-4(平衡二叉树、二叉树的所有路径、左叶子之和)
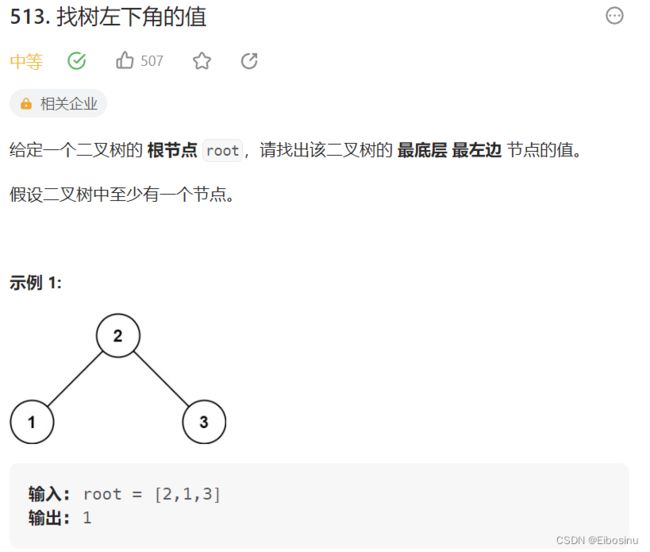
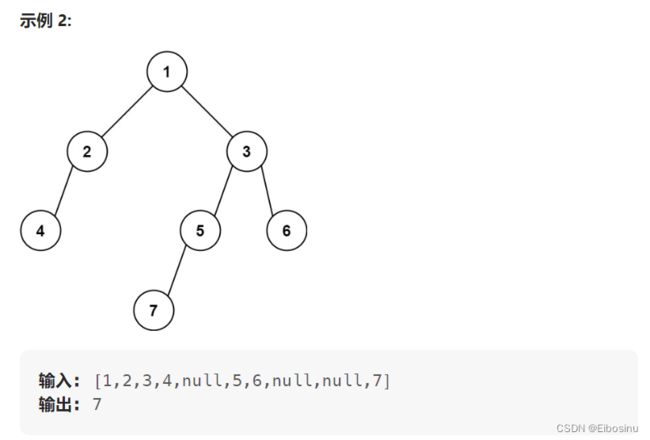
513. 找树左下角的值
题目描述
LeetCode链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/find-bottom-left-tree-value/description/
层序遍历法
思路: 使用层序遍历, 返回最后一层第一个节点的val
具体的做法是每次记录一下队列front元素的val, 最后循环结束的时候记录的就是最后一层最左侧的节点的val
class Solution {
public:
int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> que;
que.push(root);
int ans, size;
while(!que.empty()){
ans = que.front()->val;
size = que.size();
for(int i=0; i<size; ++i){
TreeNode* cur = que.front();
que.pop();
if(cur->left) que.push(cur->left);
if(cur->right) que.push(cur->right);
}
}
return ans;
}
};
迭代遍历法
不使用层序遍历, (使用迭代遍历), 但是保证最底层最左侧的节点是最后一个被遍历到的, 过程中用ans记录当前遍历节点的值
class Solution {
public:
int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode* root) {
queue<TreeNode*> que;
que.push(root);
int ans;
while(!que.empty()){
ans = que.front()->val;
TreeNode* cur = que.front();
que.pop();
if(cur->right) que.push(cur->right);
if(cur->left) que.push(cur->left);
}
return ans;
}
};
递归法
使用递归, 深度优先搜索, 优先搜索左节点, 过程中记录当前深度和最大深度, 如果当前深度大于最大深度, 就记录
class Solution {
public:
void dfs(TreeNode* node, int height, int& curMaxHeight, int& ans){
if(node==nullptr)
return;
height++;
if(height > curMaxHeight){
curMaxHeight = height;
ans = node->val;
}
dfs(node->left, height, curMaxHeight, ans);
dfs(node->right, height, curMaxHeight, ans);
return;
}
int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode* root) {
int curMaxHeight = 0, ans = root->val;
dfs(root, 0, curMaxHeight, ans);
return ans;
}
};
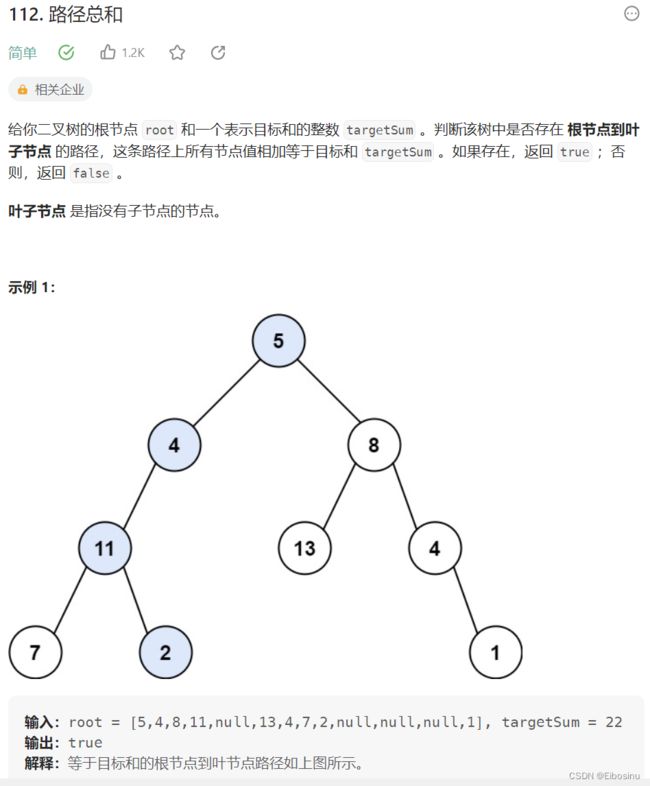
112. 路径总和
题目描述
LeetCode链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/path-sum/description/
踩的坑
思路: 递归实现, 递归过程中维护一个int curVal, 到null节点的时候如果curVal!=targetSum就返回null
class Solution {
public:
bool dfs(TreeNode* node, int curVal, int targetSum){
if(node==nullptr){
if(curVal==targetSum)
return true;
else
return false;
}
return dfs(node->left, curVal+node->val, targetSum) || dfs(node->right, curVal+node->val, targetSum);
}
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
if(root==nullptr)
return false;
return dfs(root, 0, targetSum);
}
};
以上代码看起来很正常,就是很寻常的"遇到null节点就return", 但其实是有问题的.
反思&修改
以上内容只考虑了**“到null节点后"的情况, 但是题目中给的要求是"到叶子节点”**;
所以以上解法对于root = [1,2] 的案例就会出错;
以下修改, 增加了对是否是叶子节点的判断;
class Solution {
public:
bool dfs(TreeNode* node, int curVal, int targetSum){
if(node==nullptr)
return false;
curVal += node->val;
if(node->left==nullptr && node->right==nullptr && curVal==targetSum){
return true;
}
return dfs(node->left, curVal, targetSum) || dfs(node->right, curVal, targetSum);
}
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
if(root==nullptr)
return false;
return dfs(root, 0, targetSum);
}
};
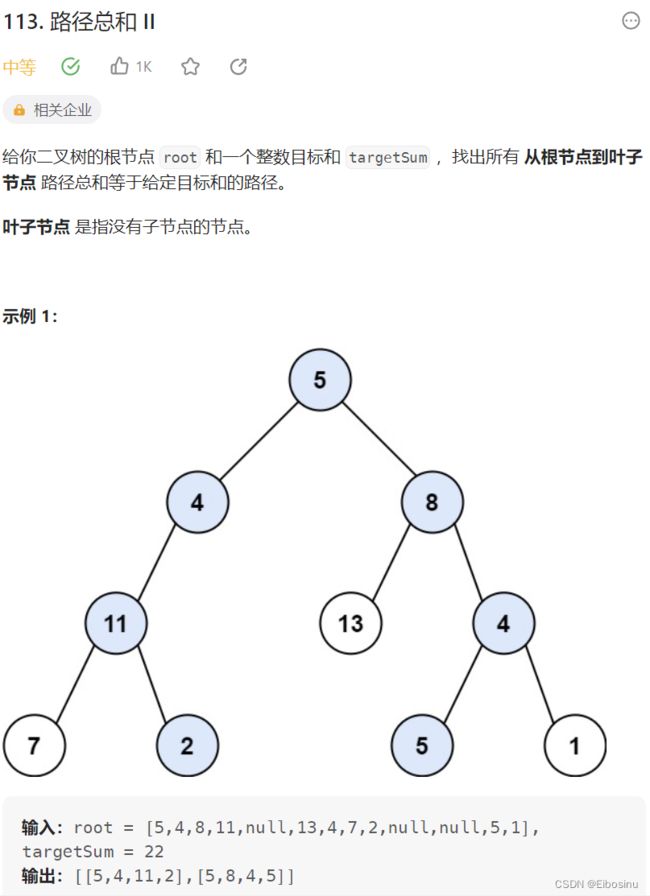
113. 路径总和 II
题目描述
LeetCode链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/path-sum-ii/description/
解题思路
参考上一题的解法, 只要在过程中整一个vector记录路径就行
代码
class Solution {
public:
void dfs(TreeNode* node, int curVal, int targetSum, vector<vector<int>>& ans, vector<int>& curPath){
if(node==nullptr)
return;
curVal += node->val;
curPath.push_back(node->val);
if(node->left==nullptr && node->right==nullptr && curVal==targetSum){
ans.push_back(curPath);// 这里涉及一点C++八股
}
dfs(node->left, curVal, targetSum, ans, curPath);
dfs(node->right, curVal, targetSum, ans, curPath);
curPath.pop_back();
return;
}
vector<vector<int>> pathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
vector<vector<int>> ans;
vector<int> curPath;
int curVal = 0;
dfs(root, curVal, targetSum, ans, curPath);
return ans;
}
};
一些涉及到的八股
C++八股: 当vector 被作为参数传递的时候, 其实生成的是原先curPath的拷贝, 所以这里可以直接push_back进ans;
而对于普通的数组, 其传递的过程中可能涉及到数组退化为指针等问题, 无法这么整;
需要注意的是, 因为传递vector时会生成拷贝, 所以如果不需要生成拷贝, 最好传递vector, 这样就不需要额外的空间存储拷贝.
105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树
题目描述
LeetCode链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/construct-binary-tree-from-preorder-and-inorder-traversal/description/
解题思路
先从preorder的头部找根节点, 然后拿着preorder中找到的根节点, 到inorder中找到其位置(inRoot), 其将inorder划分为左右两部分;
此处从inorder的左右两部分, 得到了左子树序列的长度size=inRoot-inLeft, 就可以用这个从inorder中得到的size, 在preorder中划分出属于左子树的部分;
对于左子树, 递归传入: preLeft+1, preLeft+size, inLeft, inRoot-1
对于右子树, 递归传入: preLeft+size+1, preRight, inRoot+1, inRight
代码
class Solution {// 先不用unordered_map寻址做一遍
public:
TreeNode* build(int preLeft, int preRight, int inLeft, int inRight, vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder){
if(preLeft > preRight)// pre空了以后就return
return nullptr;
int inRoot;
for(inRoot=0; inRoot<inorder.size(); ++inRoot){// 在inorder中找到preorder中第一个元素的下标, 标记为inRoot
if(inorder[inRoot] == preorder[preLeft])
break;
}
int size = inRoot - inLeft;// 用size记录left子数组的长度
TreeNode* node = new TreeNode(preorder[preLeft]);
node->left = build(preLeft+1, preLeft+size, inLeft, inRoot-1, preorder, inorder);
node->right = build(preLeft+size+1, preRight, inRoot+1, inRight, preorder, inorder);
return node;
}
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {
return build(0, preorder.size()-1, 0, inorder.size()-1, preorder, inorder);
}
};
使用unordered_map的改进
使用unordered_map, 在inorder中找到preorder中第一个元素的下标, 速度更快.
class Solution {// 尝试加入unordered_map辅助寻址
private:
unordered_map<int,int> index;
public:
TreeNode* build(int preLeft, int preRight, int inLeft, int inRight, vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder){
if(preLeft > preRight)
return nullptr;
int inRoot = index[preorder[preLeft]];// 这样可以加快速度
int size = inRoot - inLeft;
TreeNode* node = new TreeNode(preorder[preLeft]);
node->left = build(preLeft+1, preLeft+size, inLeft, inRoot-1, preorder, inorder);
node->right = build(preLeft+size+1, preRight, inRoot+1, inRight, preorder, inorder);
return node;
}
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& preorder, vector<int>& inorder) {
for(int i=0; i<inorder.size(); ++i){
index[inorder[i]] = i;
}
return build(0, preorder.size()-1, 0, inorder.size()-1, preorder, inorder);
}
};
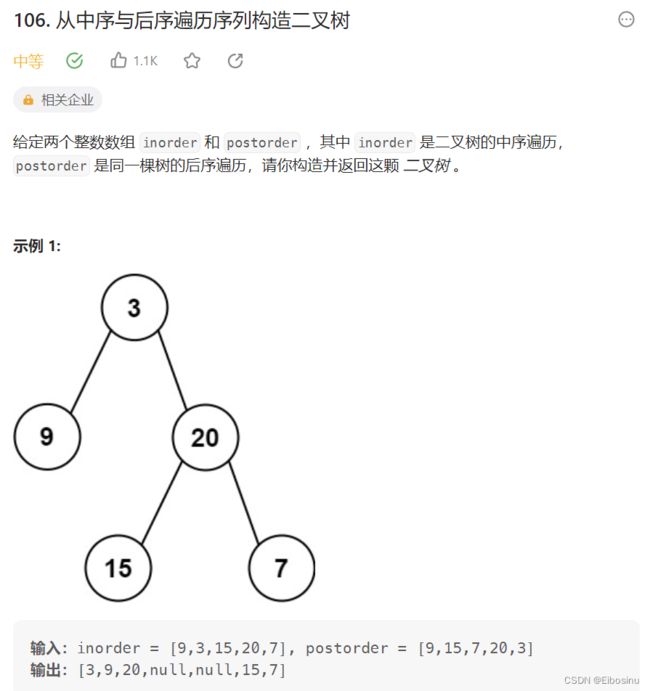
106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树
题目描述
LeetCode链接:https://leetcode.cn/problems/construct-binary-tree-from-inorder-and-postorder-traversal/description/
解题思路
参考上一题, 原理是一样的
代码
class Solution {
private:
unordered_map<int,int> index;
public:
TreeNode* build(int inLeft, int inRight, int postLeft, int postRight, vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder){
if(postLeft>postRight){
return nullptr;
}
int inRoot = index[postorder[postRight]];
int size = inRight - inRoot;
TreeNode* node = new TreeNode(postorder[postRight]);
node->left = build(inLeft, inRoot-1, postLeft, postRight-size-1, inorder, postorder);
node->right = build(inRoot+1, inRight, postRight-size, postRight-1, inorder, postorder);
return node;
}
TreeNode* buildTree(vector<int>& inorder, vector<int>& postorder) {
for(int i=0; i<inorder.size(); ++i){
index[inorder[i]] = i;
}
return build(0, inorder.size()-1, 0, postorder.size()-1, inorder, postorder);
}
};
总结
几天前3题难度不高, 后两题难度很高. 综合起来, 在做二叉树题目的时候, 需要注意以下部分:
注意:
① 把思路尽量细致地理清楚, 理地越清楚, 写起来越顺畅, 越复杂的题目越是如此;
② 注意是否用vector, 还是要用vector, 不然次次复制, 空间占用大;
③ 很多时候用纸笔记录, 思路清晰很多.
(以上三条主要针对后两题)
④ 注意递归结束的条件, 是到cur==NULL还是叶节点, 如果需要到叶节点的话需要后者.(针对第一题)
本文参考:
513. 找树左下角的值
112. 路径总和 I&II
105. 从前序与中序遍历序列构造二叉树 & 106. 从中序与后序遍历序列构造二叉树