python+TensorFlow实现人脸识别智能小程序的项目(包含TensorFlow版本与Pytorch版本)(一)
python+TensorFlow实现人脸识别智能小程序的项目(包含TensorFlow版本与Pytorch版本)(一)
- 一:TensorFlow基础知识内容部分(简明扼要,快速适应)
- 1、下载Cifar10数据集,并进行解压缩处理
- 2、将Cifar10数据集利用OpenCV转换成数据图像保存在对应类别的目录下
- 3、将本地Cifar10图像数据打包成TF-Record的格式
- 4、将本地Cifar10图像数据打包成TF-Record的格式并写入宽、高数据
- 5、TensorFlow有关的数据加载读取方式
-
- 1、读取文件地址列表以及对应的标签列表数据
- 2、读取csv格式类的文件名列表数据形式如下:
- 3、读取本地图像路径列表数据
- 4、读取本地TF-Record格式的数据
- 1、TF-Record数据格式讲述
- 6、Graph的概念
-
- 1、声明Graph以及Graph的获取
- 2、保存pb文件以及利用pb文件恢复Graph
- 3、使用tensorboard可视化计算图结构
- 7、Session的概念
-
- 1、Session的几种创建方式
- 2、Session的注入机制
- 3、制定资源设备
- 4、资源分配
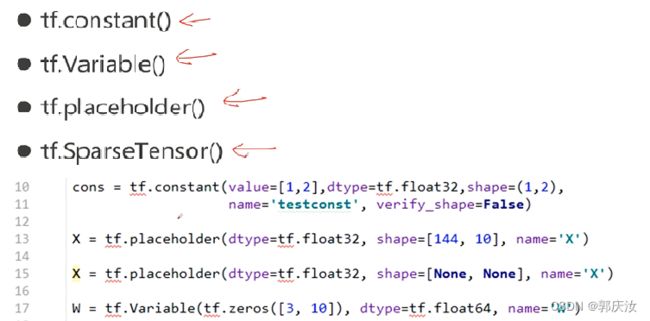
- 8、Tensor
-
- 1、Tensor的定义
- 9、Operation
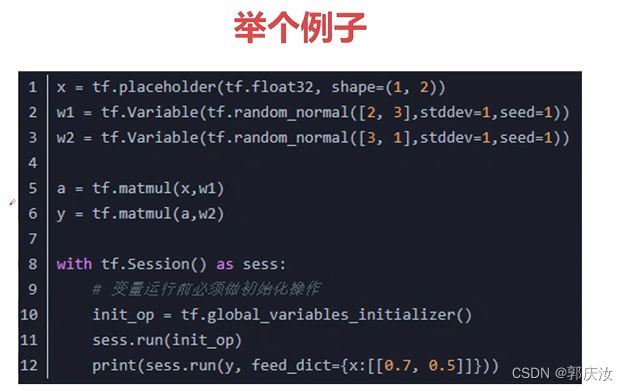
- 10、feed数据的喂入
- 11、TensorFlow中常用的API
-
- 1、tf.nn库
- 2、tf.train库
- 12、TensorFlow中数据的处理方式
-
- 1、数据的写入相关API
- 2、数据读取相关API
- 13、TensorFlow中的高级API接口------TF-slim
-
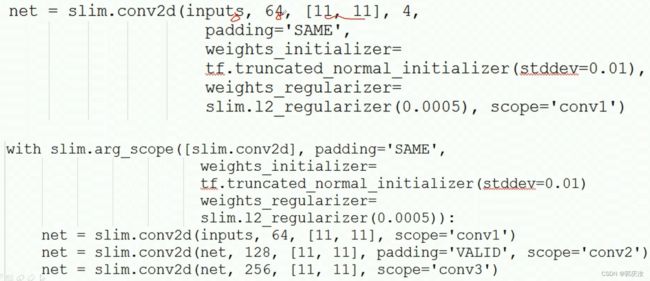
- 1、slim包参数作用域相关
- 2、slim包的BatchNorm层相关
- 3、slim包的net模型
- 4、slim包的loss损失
- 5、slim包的学习率
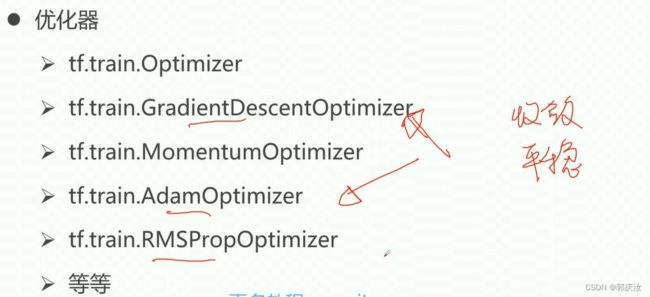
- 6、slim包的优化器
- 7、slim包的模型度量
- 8、slim包的评估
- 9、slim包的数据操作方法
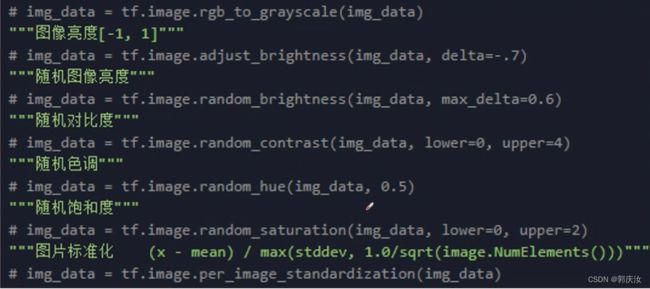
- 9、slim数据增强的方法
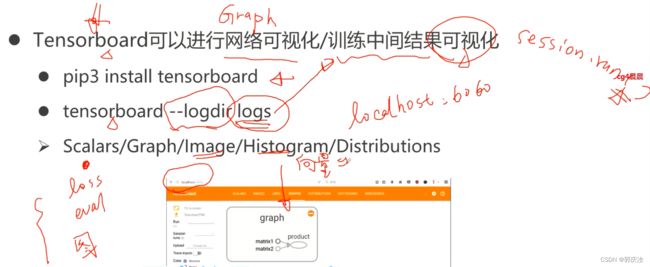
- 15、Tensorbord使用
-
- 1、tf.summary写入数据方式
- 16、TensorFlow实战Cifar10图像分类项目代码实现
-
- 1、将Cifar10数据打包成TF-record格式
- 2、读取Cifar10格式数据与数据增强部分
- 3、网络结构定义、tensorbord具体使用以及模型训练部分
- 4、更换另一个骨干网络——ResNet网络模型骨干网络定义
- 5、保存的文件详解
- 17、TensorFlow-slim包进行图像数据集分类---具体流程
一:TensorFlow基础知识内容部分(简明扼要,快速适应)
1、下载Cifar10数据集,并进行解压缩处理
import urllib.request as ur
import os
import sys
import tarfile
import glob
import pickle
import numpy as np
import cv2
# gqr:下载Cifair10数据集,并进行解压缩处理
def download_and_uncompress_tarball(tarball_url, dataset_dir):
"""Downloads the `tarball_url` and uncompresses it locally.
Args:
tarball_url: The URL of a tarball file.
dataset_dir: The directory where the temporary files are stored.
"""
filename = tarball_url.split('/')[-1] # gqr:获取文件名
filepath = os.path.join(dataset_dir, filename) # gqr:拼接数据集存放路径
# gqr:_progress为下载数据集时的回调函数,显示当前的下载进度
def _progress(count, block_size, total_size):
print("-------------------",count, block_size, total_size)
sys.stdout.write('\r>> Downloading %s %.1f%%' % (
filename, float(count * block_size) / float(total_size) * 100.0))
sys.stdout.flush()
filepath, _ = ur.urlretrieve(tarball_url, filepath, _progress) # gqr:_progress为下载数据集时的回调函数,显示当前的下载进度
print()
statinfo = os.stat(filepath) # gqr: 是用来获取指定路径的状态信息,这里的指定路径可以是文件,也可以是文件夹
print('Successfully downloaded', filename, statinfo.st_size, 'bytes.')
tarfile.open(filepath, 'r:gz').extractall(dataset_dir) # gqr:解压压缩包数据
DATA_URL = 'http://www.cs.toronto.edu/~kriz/cifar-10-python.tar.gz'
DATA_DIR = 'data'
download_and_uncompress_tarball(DATA_URL, DATA_DIR) # gqr:下载数据集代码
2、将Cifar10数据集利用OpenCV转换成数据图像保存在对应类别的目录下
import urllib.request as ur
import os
import sys
import tarfile
import glob
import numpy as np
import cv2
# gqr:官方解析cifair10的脚本函数 对数据集进行解码
def unpickle(file):
import pickle
with open(file, 'rb') as fo:
dict = pickle.load(fo, encoding='bytes')
return dict
folders = './data/cifar-10-batches-py'
# trfiles = glob.glob(folders + "/data_batch*") # gqr:训练集存放
trfiles = glob.glob(folders + "/test_batch*") # gqr:测试集存放
print("--------------------")
data = []
labels = []
for file in trfiles:
dt = unpickle(file) # gqr:对数据进行解码,得到解码后的数据
data += list(dt[b"data"]) # gqr:读取字典中的数据
labels += list(dt[b"labels"]) # gqr:解析labels
print(labels)
imgs = np.reshape(data, [-1, 3, 32, 32]) # gqr:将数据进行转化,得到四维度的数据 通道优先
classification = ['airplane',
'automobile',
'bird',
'cat',
'deer',
'dog',
'frog',
'horse',
'ship',
'truck']
for i in range(imgs.shape[0]):
im_data = imgs[i, ...]
im_data = np.transpose(im_data, [1, 2, 0]) # gqr:交换数据的通道,RGB排列
im_data = cv2.cvtColor(im_data, cv2.COLOR_RGB2BGR)
# f = "{}/{}".format("data/image/train", classification[labels[i]]) # gqr:存放训练集
f = "{}/{}".format("data/image/test", classification[labels[i]]) # gqr:存放测试集
if not os.path.exists(f): # gqr:判断对应类别的目录是否存在
os.makedirs(f)
cv2.imwrite("{}/{}.jpg".format(f, str(i)), im_data)
3、将本地Cifar10图像数据打包成TF-Record的格式
import tensorflow as tf
import cv2
import numpy as np
classification = ['airplane',
'automobile',
'bird',
'cat',
'deer',
'dog',
'frog',
'horse',
'ship',
'truck']
import glob
idx = 0
im_data = [] # gqr:总的图像数据路径list
im_labels = [] # 类别标签对对应的id list
for path in classification:
# path = "data/image/train/" + path # gqr:训练数据路径地址
path = "data/image/test/" + path # gqr:测试数据路径地址
im_list = glob.glob(path + "/*")
im_label = [idx for i in range(im_list.__len__())] # gqr:表示对应图片的id标签
idx += 1
im_data += im_list
im_labels += im_label
# print(im_labels)
# print(im_data)
# tfrecord_file = "data/train.tfrecord" # gqr:生成的Tf-record文件存放路径
tfrecord_file = "data/test.tfrecord" # gqr:生成的Tf-record文件存放路径
writer = tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter(tfrecord_file) # gqr:定义Tf-record的写入的实例
index = [i for i in range(im_data.__len__())]
np.random.shuffle(index) # gqr:对打包的数据进行shuffle处理
for i in range(im_data.__len__()):
im_d = im_data[index[i]]
im_l = im_labels[index[i]]
data = cv2.imread(im_d)
#data = tf.gfile.FastGFile(im_d, "rb").read() # gqr:也可以使用该方法读取数据图像,读取到的数据为byte形式,所以以下进行数据封装时不需要再转换成byte形式
# gqr:对一组图片的数据与标签进行封装
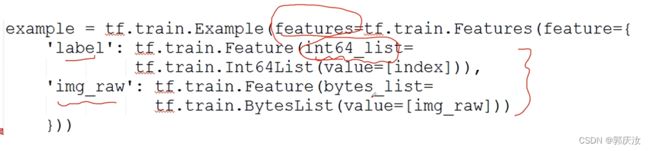
ex = tf.train.Example(
features = tf.train.Features(
feature = {
"image":tf.train.Feature(
bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(
value=[data.tobytes()])), # gqr:图像采用byte格式的形式进行存储
"label": tf.train.Feature(
int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(
value=[im_l])), # gqr:图片的标签数据是一个int型的数据,所以使用int64_list,value为一个列表的形式
}
)
)
# gqr:将封装好的数据进行序列化,写入到TF-Record中
writer.write(ex.SerializeToString())
writer.close()
4、将本地Cifar10图像数据打包成TF-Record的格式并写入宽、高数据
import tensorflow as tf
import cv2
import numpy as np
"""
tf.train.Example 是 TensorFlow 中用于序列化和反序列化数据的协议缓冲区消息类型之一。它是一种通用的数据表示格式,用于在 TensorFlow 训练和推理过程中存储和传输数据。
tf.train.Example 包含一个或多个 tf.train.Feature 对象,每个 tf.train.Feature 对象都可以是以下三种类型之一:
tf.train.BytesList:用于表示字节字符串的列表。
tf.train.FloatList:用于表示浮点数的列表。
tf.train.Int64List:用于表示整数的列表。
通过将数据转换为这些基本类型之一,并将其包装在 tf.train.Feature 对象中,我们可以将数据转换为可以序列化和存储的格式。然后,可以使用 tf.train.Example 对象将这些特征进行组合,并进行序列化和存储,或者在需要时进行反序列化和解析。
例如,可以使用 tf.train.Example 来表示图像数据,其中图像的原始字节字符串存储在 BytesList 中,标签或类别信息存储在 Int64List 中。
"""
classification = ['airplane',
'automobile',
'bird',
'cat',
'deer',
'dog',
'frog',
'horse',
'ship',
'truck']
import glob
idx = 0
im_data = []
im_labels = []
for path in classification:
path = "data/image/test/" + path # gqr:数据路径地址
im_list = glob.glob(path + "/*")
im_label = [idx for i in range(im_list.__len__())]
idx += 1
im_data += im_list
im_labels += im_label
print(im_labels)
print(im_data)
tfrecord_file = "data/test.tfrecord" # gqr:生成的Tf-record文件存放路径
writer = tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter(tfrecord_file) # gqr:定义Tf-record的写入的实例
index = [i for i in range(im_data.__len__())]
np.random.shuffle(index) # gqr:对打包的数据进行shuffle处理
for i in range(im_data.__len__()):
im_d = im_data[index[i]]
im_l = im_labels[index[i]]
data = cv2.imread(im_d) # gqr:读取数据图像
#data = tf.gfile.FastGFile(im_d, "rb").read() # gqr:也可以使用该方法读取数据图像,读取到的数据为byte形式,所以以下进行数据封装时不需要再转换成byte形式
# gqr:对一组图片的数据与标签进行封装
ex = tf.train.Example(
features = tf.train.Features(
feature = {
"image":tf.train.Feature(
bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(
value=[data.tobytes()])), # gqr:图像采用byte格式的形式进行存储
"label": tf.train.Feature(
int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(
value=[im_l])), # gqr:图片的标签数据是一个int型的数据,所以使用int64_list,value为一个列表的形式
# gqr:也可以将图像的高与宽打包到TF-Record中
"height": tf.train.Feature(
int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(
value=[data.shape[0]])), # gqr:图片的标签数据是一个int型的数据,所以使用int64_list,value为一个列表的形式
"width": tf.train.Feature(
int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(
value=[data.shape[1]])), # gqr:图片的标签数据是一个int型的数据,所以使用int64_list,value为一个列表的形式
}
)
)
# gqr:将封装好的数据进行序列化,写入到TF-Record中
writer.write(ex.SerializeToString())
writer.close()
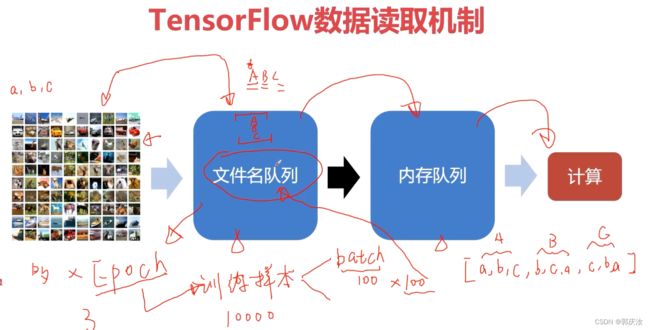
5、TensorFlow有关的数据加载读取方式
tf.train.slice_input_producer()
tf.train.string_input_producer()
1、读取文件地址列表以及对应的标签列表数据
import tensorflow as tf
# 为tensorflow对文件列表中的样本进行读取的方式
images = ['image1.jpg', 'image2.jpg', 'image3.jpg', 'image4.jpg'] # gqr:图片的路径list
labels = [1, 2, 3, 4] # gqr:图片对应的label
[images, labels] = tf.train.slice_input_producer([images, labels],
num_epochs=None, # gqr:所有样本循环的次数
shuffle=True) # gqr:tf.train.slice_input_producer可以对输入的list按照特征的规则生成张量,输出是一个tensor
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.local_variables_initializer()) # gqr:初始化所有的变量
tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess) # gqr:构建文件队列填充的线程,启动后文件队列才可以进行填充,才可以获取图片数据
for i in range(10):
print(sess.run([images, labels]))
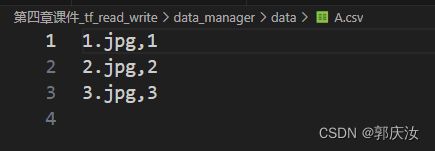
2、读取csv格式类的文件名列表数据形式如下:
import tensorflow as tf
# gqr:Tensorflow对文件数据进行读取
filename = ['data/A.csv', 'data/B.csv', 'data/C.csv']
file_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer(filename,
shuffle=True,
num_epochs=2) # gqr:其输出是一个文件队列,而不是一个tensor
reader = tf.WholeFileReader() # gqr:定义文件读取器,用于从文件队列中进行数据的读取
key, value = reader.read(file_queue) #返回的key是文件的绝对路径,value是这个文件的数据
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.local_variables_initializer()) # gqr:局部变量初始化
tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess) # gqr:构建文件队列填充的线程,启动后文件队列才可以进行填充
for i in range(6):
print(sess.run([key, value]))
3、读取本地图像路径列表数据
import tensorflow as tf
# gqr:Tensorflow对文件数据进行读取
filename = ['data/pictures/3.jpg', 'data/pictures/10.jpg', 'data/pictures/21.jpg']
file_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer(filename,
shuffle=True,
num_epochs=2) # gqr:其输出是一个文件队列,而不是一个tensor
reader = tf.WholeFileReader() # gqr:定义文件读取器,用于从文件队列中进行数据的读取
key, value = reader.read(file_queue) #返回的key是文件的绝对路径,value是这个文件的数据
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.local_variables_initializer()) # gqr:局部变量初始化
tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess) # gqr:构建文件队列填充的线程,启动后文件队列才可以进行填充
i=0
for i in range(6):
image_path,image_data=sess.run([key, value])
with open('data/result/%d.jpg' % i,'wb') as f:
f.write(image_data)
i+=1
##############################################################################################
########如果图片带有标签信息,可以把这里的string_input_producer换成slice_input_producer##########
##############################################################################################
"""
将文件名列表交给tf.train.string_input_producer函数,string_input_producer会生成一个先入先出的队列, 文件阅读器会需要它来读取数据
tf.train.string_input_producer(
string_tensor,
num_epochs=None,
shuffle=True,
seed=None,
capacity=32,
shared_name=None,
name=None,
cancel_op=None
)
string_tensor:传入string_input_producer的张量或文件名列表
num_epochs:ephoch的数量,一个整数,如果指定,string_input_producer在产生OutOfRange错误之前从string_tensor中产生num_epochs次字符串。如果未指定,则可以无限次循环遍历字符串。
shuffle:是否随机打乱数据
seed:随机数种子,配合shuffle = True使用,设定之后每个ephoch的顺序都一样。
capacity:一个整数。设置队列容量。
share_name:如果设置,则此队列将在多个会话的给定名称下共享。对具有此队列的设备打开的所有会话都可以通过shared_name访问它。在分布式设置中使用它意味着只有能够访问此操作的其中一个会话才能看到每个名称。
name:此操作的名称
cancel_op:取消队列的操作
"""
4、读取本地TF-Record格式的数据
1、TF-Record数据格式讲述
对于大数据,TensorFlow中都需要转换成TFRecord格式的文件,TFRecord文件同样是以二进制进行存储数据的,适合以串行的方式读取大批量数据。其优势是能更好的利用内存,更方便地复制和移动,这更符合TensorFlow执行引擎的处理方式。通常数据转换成tfrecord格式需要写个小程序将每一个样本组装成protocol buffer定义的Example的对象,序列化成字符串,再由tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter写入文件即可。
这里为了方便快捷我更改了一部分代码直接调用datasets下的flowers模型文件来生成我们的tfrecord格式和labels文件,我们进入我们下载好的slim文件夹下,然后再进入datasets文件夹下
import tensorflow as tf
# tensorflow对TF-Record打包过的数据进行解析
filelist = ['data/train.tfrecord']
# 将文件名列表交给tf.train.string_input_producer函数,string_input_producer会生成一个先入先出的队列, 文件阅读器会需要它来读取数据
file_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer(filelist,
num_epochs=None,
shuffle=True)
reader = tf.TFRecordReader() # gqr:创建TF-record文件读写器
_, ex = reader.read(file_queue) # gqr:得到序列化的数据
# gqr:对序列化后的数据进行解码
# gqr:格式
feature = {
'image':tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string), # gqr:因为将图像数据打包成TF_record时是以byte格式存储的,所以在解码时解码成String类型
'label':tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64) # gqr:label是int型
}
batchsize = 2
batch = tf.train.shuffle_batch([ex], batchsize, capacity=batchsize*10,
min_after_dequeue=batchsize*5) # gqr:capacity:队列的容量;min_after_dequeue:最小的队列容量
# gqr:对batch size的数据进行解码
example = tf.parse_example(batch, features=feature)
image = example['image']
label = example['label']
# 解码操作
image = tf.decode_raw(image, tf.uint8) # gqr:因为image解码格式是字符串,所以需要调用解码函数将其转换成byte格式
image = tf.reshape(image, [-1, 32, 32, 3])
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.local_variables_initializer()) # gqr:初始化所有变量
tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess) # gqr:创建文件填充队列
for i in range(1):
image_bth, _ = sess.run([image,label]) # gqr:获取到图片的数据以及对应的label
import cv2
cv2.imshow("image", image_bth[0,...]) #gqr:因为batchsize为2,所以取第一个
cv2.waitKey(0)
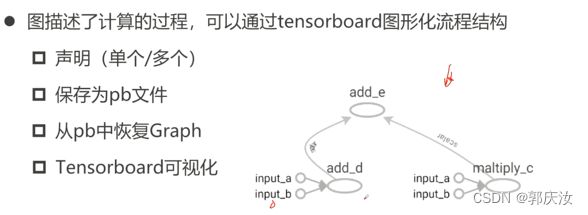
6、Graph的概念
1、声明Graph以及Graph的获取
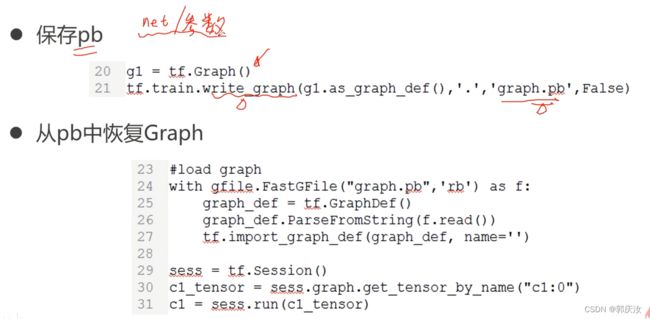
2、保存pb文件以及利用pb文件恢复Graph
3、使用tensorboard可视化计算图结构
7、Session的概念
1、Session的几种创建方式
2、Session的注入机制
3、制定资源设备
4、资源分配
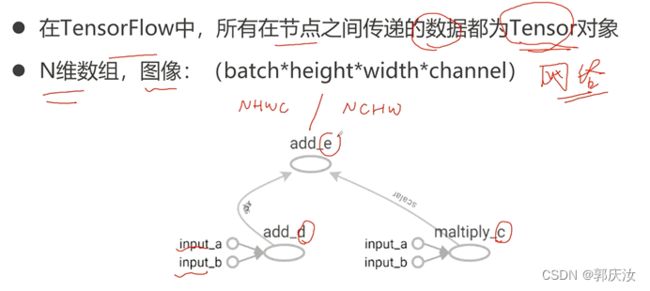
8、Tensor
1、Tensor的定义
9、Operation
10、feed数据的喂入
11、TensorFlow中常用的API
1、tf.nn库
2、tf.train库
定义了模型存储、模型恢复、优化函数以及与学习率相关的设定

关于数据处理相关:

12、TensorFlow中数据的处理方式
1、数据的写入相关API
2、数据读取相关API
13、TensorFlow中的高级API接口------TF-slim
1、slim包参数作用域相关
2、slim包的BatchNorm层相关
定义方式:

例子:
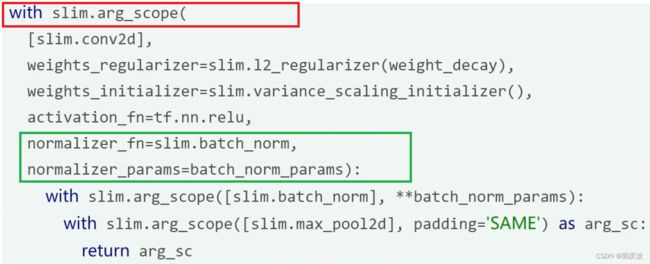
以上定义好batch_norm层后,在网络训练时需要对其进行单独的更新:

3、slim包的net模型
4、slim包的loss损失
5、slim包的学习率
6、slim包的优化器
7、slim包的模型度量
8、slim包的评估
9、slim包的数据操作方法
9、slim数据增强的方法
15、Tensorbord使用
1、tf.summary写入数据方式
16、TensorFlow实战Cifar10图像分类项目代码实现
1、将Cifar10数据打包成TF-record格式
代码:![]()
import tensorflow as tf
import cv2
import numpy as np
classification = ['airplane',
'automobile',
'bird',
'cat',
'deer',
'dog',
'frog',
'horse',
'ship',
'truck']
import glob
idx = 0
im_data = [] # gqr:总的图像数据路径list
im_labels = [] # 类别标签对对应的id list
for path in classification:
# path = "data/image/train/" + path # gqr:训练数据路径地址
path = "data/image/test/" + path # gqr:测试数据路径地址
im_list = glob.glob(path + "/*")
im_label = [idx for i in range(im_list.__len__())] # gqr:表示对应图片的id标签
idx += 1
im_data += im_list
im_labels += im_label
# print(im_labels)
# print(im_data)
# tfrecord_file = "data/train.tfrecord" # gqr:生成的Tf-record文件存放路径
tfrecord_file = "data/test.tfrecord" # gqr:生成的Tf-record文件存放路径
writer = tf.python_io.TFRecordWriter(tfrecord_file) # gqr:定义Tf-record的写入的实例
index = [i for i in range(im_data.__len__())]
np.random.shuffle(index) # gqr:对打包的数据进行shuffle处理
for i in range(im_data.__len__()):
im_d = im_data[index[i]]
im_l = im_labels[index[i]]
data = cv2.imread(im_d)
#data = tf.gfile.FastGFile(im_d, "rb").read() # gqr:也可以使用该方法读取数据图像,读取到的数据为byte形式,所以以下进行数据封装时不需要再转换成byte形式
# gqr:对一组图片的数据与标签进行封装
ex = tf.train.Example(
features = tf.train.Features(
feature = {
"image":tf.train.Feature(
bytes_list=tf.train.BytesList(
value=[data.tobytes()])), # gqr:图像采用byte格式的形式进行存储
"label": tf.train.Feature(
int64_list=tf.train.Int64List(
value=[im_l])), # gqr:图片的标签数据是一个int型的数据,所以使用int64_list,value为一个列表的形式
}
)
)
# gqr:将封装好的数据进行序列化,写入到TF-Record中
writer.write(ex.SerializeToString())
writer.close()
2、读取Cifar10格式数据与数据增强部分
![]()
import tensorflow as tf
def read(batchsize=64, type=1, no_aug_data=1):
reader = tf.TFRecordReader() # gqr:创建读写器
if type == 0: #train
file_list = ["data/train.tfrecord"]
if type == 1: #test
file_list = ["data/test.tfrecord"]
filename_queue = tf.train.string_input_producer(
file_list, num_epochs=None, shuffle=True
)
_, serialized_example = reader.read(filename_queue) # gqr:得到序列化的数据
batch = tf.train.shuffle_batch([serialized_example], batchsize, capacity=batchsize * 10,
min_after_dequeue= batchsize * 5) # gqr:capacity:队列的容量;min_after_dequeue:最小的队列容量
feature = {'image': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.string),
'label': tf.FixedLenFeature([], tf.int64)}
features = tf.parse_example(batch, features = feature) # gqr:对batch size的数据进行解码
images = features["image"]
img_batch = tf.decode_raw(images, tf.uint8) # gqr:因为image解码格式是字符串,所以需要调用解码函数将其转换成byte格式
img_batch = tf.cast(img_batch, tf.float32)
img_batch = tf.reshape(img_batch, [batchsize, 32, 32, 3])
# gqr:以下为数据增强操作
if type == 0 and no_aug_data == 1:
distorted_image = tf.random_crop(img_batch,
[batchsize, 28, 28, 3]) # gqr:随机的裁剪
distorted_image = tf.image.random_contrast(distorted_image,
lower=0.8,
upper=1.2) # gqr:随机的对比度
distorted_image = tf.image.random_hue(distorted_image,
max_delta=0.2) # gqr:随机的hsv,饱和度
distorted_image = tf.image.random_saturation(distorted_image,
lower=0.8,
upper=1.2) # gqr:色调
img_batch = tf.clip_by_value(distorted_image, 0, 255) # gqr:对处理过的图像进行取值范围的约束
img_batch = tf.image.resize_images(img_batch, [32, 32]) # gqr:将图像进行尺寸缩放
label_batch = tf.cast(features['label'], tf.int64) # gqr:tf.cast:将张量转换为新类型
#-1,1 # gqr:将图像数据处理到[-1,1]之间
img_batch = tf.cast(img_batch, tf.float32) / 128.0 - 1.0 # gqr:原始数据是0~255,除以128再减去1,就转换到[-1,1]之间
#
return img_batch, label_batch
3、网络结构定义、tensorbord具体使用以及模型训练部分
import tensorflow as tf
import readcifar10
slim = tf.contrib.slim
import os
import resnet
def model(image, keep_prob=0.8, is_training=True):
# gqr:定义batch-norm相关的参数
batch_norm_params = {
"is_training": is_training, # gqr:训练时为True;测试时为False
"epsilon":1e-5, # gqr:防止在进行归一化时除0
"decay":0.997, # gqr:衰减系数
'scale':True,
'updates_collections':tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS # gqr:实现参数的可收集
}
# gqr:设置卷积操作的作用域
with slim.arg_scope(
[slim.conv2d],
weights_initializer = slim.variance_scaling_initializer(), # gqr:采用方差尺度不变的方式进行全局初始化
activation_fn = tf.nn.relu, # gqr:定义卷积层激活函数
weights_regularizer = slim.l2_regularizer(0.0001), # gqr:定义正则化约束,L2正则
normalizer_fn = slim.batch_norm, # gqr:卷积后的Batch-norm
normalizer_params = batch_norm_params): # gqr:定义Batch-norm后指定其参数
# gqr:添加对max_pool2d的约束
with slim.arg_scope([slim.max_pool2d], padding="SAME"): # gqr:将padding设置为“SAME”,保证每次池化等比例
net = slim.conv2d(image, 32, [3, 3], scope='conv1') # gqr:scope:对当前的操作进行命名
net = slim.conv2d(net, 32, [3, 3], scope='conv2')
net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [3, 3], stride=2, scope='pool1')
net = slim.conv2d(net, 64, [3, 3], scope='conv3')
net = slim.conv2d(net, 64, [3, 3], scope='conv4')
net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [3, 3], stride=2, scope='pool2')
net = slim.conv2d(net, 128, [3, 3], scope='conv5')
net = slim.conv2d(net, 128, [3, 3], scope='conv6')
net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [3, 3], stride=2, scope='pool3')
net = slim.conv2d(net, 256, [3, 3], scope='conv7')
net = tf.reduce_mean(net, axis=[1, 2]) #nhwc--n11c # gqr:相当于全局平均池化
net = slim.flatten(net) # gqr:展平操作
net = slim.fully_connected(net, 1024) # 全连接层
slim.dropout(net, keep_prob) # gqr:drop out层
net = slim.fully_connected(net, 10)
return net #10 dim vec
def loss(logits, label):
# gqr:分类的loss
one_hot_label = slim.one_hot_encoding(label, 10) # gqr:对label进行one-hot编码
slim.losses.softmax_cross_entropy(logits, one_hot_label) # gqr:使用交叉熵损失
reg_set = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.REGULARIZATION_LOSSES) # gqr:获取正则化的loss的集合
l2_loss = tf.add_n(reg_set) # gqr:将所有的L2 loss相加到一起,得到总体的l2 loss
slim.losses.add_loss(l2_loss) # gqr:将L2 loss添加到loss中
totalloss = slim.losses.get_total_loss() # gqr:将所有的loss合并到一起
return totalloss, l2_loss
def func_optimal(batchsize, loss_val): # gqr:定义优化器
global_step = tf.Variable(0, trainable=False)
# gqr:定义学习率
# gqr:tf.train.exponential_decay:采用指数衰减形式
lr = tf.train.exponential_decay(0.01, # gqr:初始学习率
global_step, # gqr:当前迭代次数
decay_steps= 50000// batchsize, # 每次衰减对应的步长,为 总样本量//batchsize
decay_rate= 0.95, # gqr:每次衰减量
staircase=False) # gqr:staircase:学习率衰减形式,False:为平滑衰减 True:为阶梯衰减
update_ops = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS) # gqr:收集与batch-norm相关的参数,用于对batch-norm进行更新
with tf.control_dependencies(update_ops): # gqr:完成对BN层的更新
op = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(lr).minimize(loss_val, global_step)
return global_step, op, lr
# gqr:定义训练代码
def train():
batchsize = 64
floder_log = 'logdirs-resnet' # gqr:日志存放的目录
floder_model = 'model-resnet' # gqr:模型存放路径
if not os.path.exists(floder_log):
os.mkdir(floder_log)
if not os.path.exists(floder_model):
os.mkdir(floder_model)
tr_summary = set() # gqr:用于记录训练日志
te_summary = set() # gqr:用于记录测试日志
##data # gqr:获取文件队列中的图片与label
tr_im, tr_label = readcifar10.read(batchsize, 0, 1) # batchsize=训练批次, type=训练, no_aug_data=数据增强
te_im, te_label = readcifar10.read(batchsize, 1, 0)
##net # gqr:定义输入数据
input_data = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=[None, 32, 32, 3],
name='input_data') # 定义输入数据
input_label = tf.placeholder(tf.int64, shape=[None],
name='input_label')
keep_prob = tf.placeholder(tf.float32, shape=None,
name='keep_prob')
is_training = tf.placeholder(tf.bool, shape=None,
name='is_training') # gqr:batch-norm中需要用到的参数
logits = model(input_data, keep_prob=keep_prob, is_training=is_training)
# logits = resnet.model_resnet(input_data, keep_prob=keep_prob, is_training=is_training)
##loss
total_loss, l2_loss = loss(logits, input_label) # gqr:定义损失函数
tr_summary.add(tf.summary.scalar('train total loss', total_loss)) # tf.summary.scalar: 这个方法是添加变量到直方图中
tr_summary.add(tf.summary.scalar('test l2_loss', l2_loss))
te_summary.add(tf.summary.scalar('train total loss', total_loss))
te_summary.add(tf.summary.scalar('test l2_loss', l2_loss))
##accurancy 准确率
pred_max = tf.argmax(logits, 1) # gqr:得到最大值对用的索引值
correct = tf.equal(pred_max, input_label) # gqr:得到bool值
accurancy = tf.reduce_mean(tf.cast(correct, tf.float32)) # 得到准确率
tr_summary.add(tf.summary.scalar('train accurancy', accurancy)) # gqr:tf.summary.scalar:tensorbord绘制网格图的方式
te_summary.add(tf.summary.scalar('test accurancy', accurancy))
##op定义优化器,将loss传入其中
global_step, op, lr = func_optimal(batchsize, total_loss)
tr_summary.add(tf.summary.scalar('train lr', lr))
te_summary.add(tf.summary.scalar('test lr', lr))
tr_summary.add(tf.summary.image('train image', input_data * 128 + 128))
te_summary.add(tf.summary.image('test image', input_data * 128 + 128))
with tf.Session() as sess:
sess.run(tf.group(tf.global_variables_initializer(),tf.local_variables_initializer())) # gqr:进项参数的初始化,初始化全局变量与局部变量
# gqr:启动文件队列写入线程
tf.train.start_queue_runners(sess=sess,
coord=tf.train.Coordinator()) # gqr:coord=tf.train.Coordinator():表示启动多线程管理器
# gqr:加载预训练模型的操作
saver = tf.train.Saver(tf.global_variables(), max_to_keep=5) # gqr:定义模型存储对象
ckpt = tf.train.latest_checkpoint(floder_model) # gqr: 获取模型文件中最新的文件
if ckpt: # gqr:判断是否存在最先的model,如果存在,则恢复当前的session,传去session和模型
saver.restore(sess, ckpt)
epoch_val = 100 # gqr:训练的epoch
tr_summary_op = tf.summary.merge(list(tr_summary)) # gqr:合并日志信息
te_summary_op = tf.summary.merge(list(te_summary))
summary_writer = tf.summary.FileWriter(floder_log, sess.graph) # gqr:定义summary.FileWriter
for i in range(50000 * epoch_val): # gqr:样本总量 x epoch
train_im_batch, train_label_batch = \
sess.run([tr_im, tr_label]) # gqr:获取batchsize的训练样本、训练标签
# gqr:喂入数据字典
feed_dict = {
input_data:train_im_batch,
input_label:train_label_batch,
keep_prob:0.8,
is_training:True
}
# gqr:完成对网络参数的更新
_, global_step_val, \
lr_val, \
total_loss_val, \
accurancy_val, tr_summary_str = sess.run([op,
global_step,
lr,
total_loss,
accurancy, tr_summary_op],
feed_dict=feed_dict)
summary_writer.add_summary(tr_summary_str, global_step_val) # gqr:写入训练集对应的日志信息
if i % 100 == 0:
print("{},{},{},{}".format(global_step_val,
lr_val, total_loss_val,
accurancy_val)) # gqr:accurancy_val:为当前batch-size的精度,非总体精度
# gqr:测试
if i % (50000 // batchsize) == 0:
test_loss = 0
test_acc = 0
for ii in range(10000//batchsize):
test_im_batch, test_label_batch = \
sess.run([te_im, te_label])
feed_dict = {
input_data: test_im_batch,
input_label: test_label_batch,
keep_prob: 1.0, # gqr:测试期间,dropout为保留率1
is_training: False # gqr:测试期间,BN参数为False
}
total_loss_val, global_step_val, \
accurancy_val, te_summary_str = sess.run([total_loss,global_step,
accurancy, te_summary_op],
feed_dict=feed_dict)
summary_writer.add_summary(te_summary_str, global_step_val) # gqr:写入测试集对应的日志信息
test_loss += total_loss_val
test_acc += accurancy_val
print('test:', test_loss * batchsize / 10000,
test_acc* batchsize / 10000)
if i % 1000 == 0:
saver.save(sess, "{}/model.ckpt{}".format(floder_model, str(global_step_val))) # gqr:保存模型
return
if __name__ == '__main__':
train()
4、更换另一个骨干网络——ResNet网络模型骨干网络定义
import tensorflow as tf
slim = tf.contrib.slim
# gqr:设置ResNet残差单元
def resnet_blockneck(net, numout, down, stride, is_training):
"""
net:特征图
numout:输出的channel的数量
down:在残差模块中,1x1卷积核下采样的倍率
stride:步长,用于判断是否进行下采样
is_training:BN参数
"""
batch_norm_params = {
'is_training': is_training,
'decay': 0.997,
'epsilon': 1e-5,
'scale': True,
'updates_collections': tf.GraphKeys.UPDATE_OPS,
}
with slim.arg_scope( # gqr:卷积作用率
[slim.conv2d],
weights_regularizer=slim.l2_regularizer(0.0001),
weights_initializer=slim.variance_scaling_initializer(),
activation_fn=tf.nn.relu,
normalizer_fn=slim.batch_norm,
normalizer_params=batch_norm_params):
with slim.arg_scope([slim.batch_norm], **batch_norm_params):
with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d, slim.max_pool2d], padding='SAME') as arg_sc:
shortcut = net # gqr:将输入的特征图进行备份
if numout != net.get_shape().as_list()[-1]: # gqr:判断输入特征图与输出特征图通道是否一致,不一致,则用1x1卷积核调整
shortcut = slim.conv2d(net, numout, [1, 1])
if stride != 1: # gqr:如果strde为2,则进行下采样
shortcut = slim.max_pool2d(shortcut, [3, 3],
stride=stride)
net = slim.conv2d(net, numout // down, [1, 1]) # gqr:调整通道的数量
net = slim.conv2d(net, numout // down, [3, 3])
net = slim.conv2d(net, numout, [1, 1]) # # gqr:调整通道的数量
if stride != 1: # gqr:为True则进行下采样处理
net = slim.max_pool2d(net, [3, 3], stride=stride)
net = net + shortcut # gqr:残差链接
return net
def model_resnet(net, keep_prob=0.5, is_training = True):
with slim.arg_scope([slim.conv2d, slim.max_pool2d], padding='SAME') as arg_sc:
net = slim.conv2d(net, 64, [3, 3], activation_fn=tf.nn.relu)
net = slim.conv2d(net, 64, [3, 3], activation_fn=tf.nn.relu)
net = resnet_blockneck(net, 128, 4, 2, is_training)
net = resnet_blockneck(net, 128, 4, 1, is_training)
net = resnet_blockneck(net, 256, 4, 2, is_training)
net = resnet_blockneck(net, 256, 4, 1, is_training)
net = resnet_blockneck(net, 512, 4, 2, is_training)
net = resnet_blockneck(net, 512, 4, 1, is_training)
net = tf.reduce_mean(net, [1, 2])
net = slim.flatten(net)
net = slim.fully_connected(net, 1024, activation_fn=tf.nn.relu, scope='fc1')
net = slim.dropout(net, keep_prob, scope='dropout1')
net = slim.fully_connected(net, 10, activation_fn=None, scope='fc2')
return net
5、保存的文件详解
1、checkpoint:文件记录了最新的模型
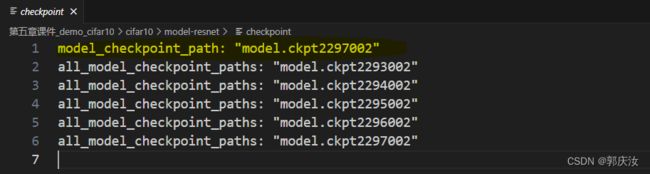
2、.meta文件定义的是graph结构
3、.data文件存放了网络具体参数值
17、TensorFlow-slim包进行图像数据集分类—具体流程
查看已写博文:https://blog.csdn.net/guoqingru0311/article/details/132514699