【算法与数据结构】112、LeetCode路径总和
文章目录
- 一、题目
- 二、解法
- 三、完整代码
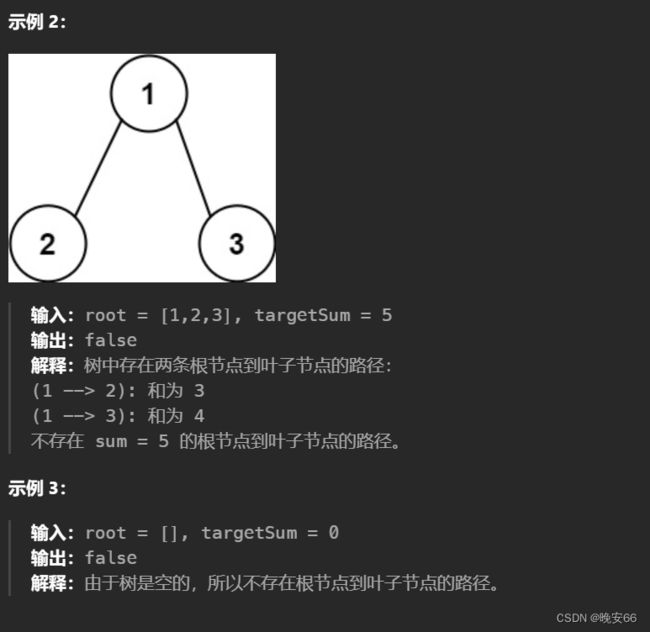
所有的LeetCode题解索引,可以看这篇文章——【算法和数据结构】LeetCode题解。
一、题目
二、解法
思路分析:本题通过计算根节点到叶子节点路径上节点的值之和,然后再对比目标值。利用文章【算法和数据结构】257、LeetCode二叉树的所有路径中的递归算法。这里要注意,默认路径之和是不等于目标值,一旦递归当中出现了等于的情况就直接返回,不必继续算后面的和。因此程序当中将结果result作为引用输入参数,有true出现就直接退出了。
程序如下:
class Solution {
public:
void traversal(TreeNode* root, int sumOfPath, const int targetSum, bool &result) {
// 1.输入参数和返回值
sumOfPath += root->val;
// 2.终止条件:遇到叶子节点
if (!root->left && !root->right) {
if (sumOfPath == targetSum) result = true;
}
// 3.单层递归逻辑:递归+回溯
if (root->left && !result) traversal(root->left, sumOfPath, targetSum, result); // 左
if (root->right && !result) traversal(root->right, sumOfPath, targetSum, result); // 右
}
bool hasPathSum(TreeNode* root, int targetSum) {
bool result = false;
if(root) traversal(root, 0, targetSum, result);
return result;
}
};
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n)。
- 空间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n)。
三、完整代码
# include end