自动化运维工具-----Ansible入门详解
目录
一.Ansible简介
什么是Ansible?
Ansible的特点
Ansible的架构
二.Ansible任务执行解析
ansible任务执行模式
ansible执行流程
ansible命令执行过程
三.Ansible配置解析
ansible的安装方式
ansible的程序结构(yum安装为例)
ansible的配置文件查找顺序
ansible的配置文件
ansible的主机清单
四.部署ansible管理集群
实验环境
实验步骤
五.Ansible常用模块
主机连通性测试
command模块
shell模块
copy模块
file模块
fetch模块
cron模块
yum模块
service模块
六 Ansible常用命令
ansible命令集解释
ansible-doc命令
ansible命令
ansible配置公私钥
一.Ansible简介
什么是Ansible?
- ansible是新出现的自动化运维工具,基于python开发,集合了从多的运维工具(puppet、chef、func、fabric)的优点,实现了批量系统配置、批量程序部署、批量运行命令等功能。
- ansible是基于paramiko开发的,并且基于模块化工作,它本身没有批量部署的能力。真正具有批量部署的是ansible所运行的模块,ansible只是提供一种框架,ansible不需要在远程主机上安装client/agents,因为它们是基于ssh来和远程主机通讯的。ansible目前已经被红帽官方收购,是自动化运维工具认可度最高的。
- 更加详细的资源参考官方文档,如右是Ansible的官方网站:Ansible Documentation
Ansible的特点
- 部署简单,只需要在主控端部署Ansible环境,被控端无需做任何操作;
- 默认使用SSH协议对设备进行管理;
- 有大量的常规运维操作模块,可实现日常绝大部分的操作;
- 配置简单、功能强大、扩展性强;
- 支持API以及自定义模块,可以通过Python轻松扩展;
- 通过Playbooks来定制强大的配置、状态管理;
- 轻量级、无需在客户端安装agent,更新时,只需在操作机上进行一次更新即可;
- 提供一个功能强大、操作性强的web管理界面和REST API接口——AWX平台。
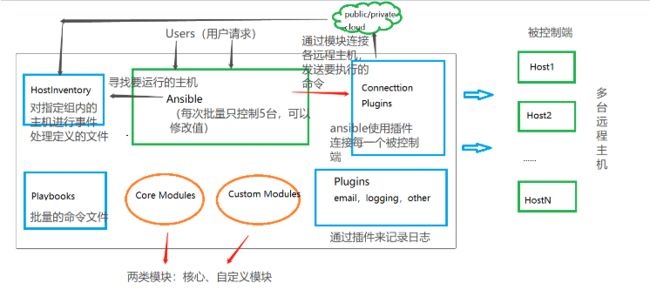
Ansible的架构
- Ansible:Ansible的核心程序
- HostInventory:记录有Ansible管理的主机信息,包括端口、密码、IP地址等
- Playbooks:“剧本”YAML格式的文件,多个任务定义在一个文件中,定义主机需要调用哪些模块来完成的功能。
- CoreModules:核心模块,主要操作是通过调用核心模块来完成管理任务
- CustomModules:自定义模块,完成核心模块无法完成的功能,支持多种语言。
- ConnectionPlugins:连接插件,Ansible和Host通信使用
二.Ansible任务执行解析
ansible任务执行模式
- ansible系统由控制主机被管节点的操作方式可以分为两类,即adhoc和playbook
- ad-hoc模式(点对点模式)
使用单个模块,支持批量执行单条命令。ad-hoc命令是一种可以快速输入的命令,而且不需要保存起来的命令。就相当于bash中的一句话shell
- playbook模式(剧本模式)
剧本模式是Ansible的主要管理方式,也是Ansible功能强大的关键所在。playbook通过多个task(任务)集合完成一类功能,比如web服务的安装部署、数据库服务的批量备份等。可以简单地把playbook理解为通过组合多条ad-hoc操作的配置文件
ansible执行流程
- 简单理解就是Ansible在运行时,首先读取ansible.cfg中的配置,根据规则获取Inventory中的管理主机列表,并行的在这些主机中执行配置的任务,最后等待执行返回结果。
ansible命令执行过程
- 加载自己的配置文件,默认为/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg;
- 查找对应的主机配置文件,找到要执行的主机或者组;
- 加载自己对应的模块文件,如command;
- 通过ansible将模块或者命令生成对应的py文件(python脚本),并且将该文件传输到远程服务器;
- 对应执行用户的家目录.ansible/tmp/xxx/xxx.py文件;
- 给文件添加执行权限;
- 执行并且返回结果;
- 删除临时的py文件, sleep 0退出;
三.Ansible配置解析
ansible的安装方式
- ansible安装常用两种方式,yum安装和pip程序安装。
使用pip(python的包管理模块)安装
- 首先,我们需要安装python-pip包,安装完成之后,则直接使用pip命令来安装我们的包,具体操作过程如下:
yum install python-pip
pip install ansible使用yum安装
- yum安装是我们比较熟悉的安装方式。我们需要先安装一个epel-release包,然后再安装ansible即可。
yum install epel-release -y
yum install ansible -yansible的程序结构(yum安装为例)
- 配置文件目录:/etc/ansible/
- 执行文件目录:/usr/bin/
- Lib库依赖目录:/usr/lib/pyhtonX.X/site-packages/ansible/
- Help文档目录:/usr/share/doc/ansible-X.X.X/
- Man文档目录:/usr/share/man/man1/
ansible的配置文件查找顺序
- ansible与我们其他的服务在这一点上又很大的不同,这里的配置文件查找是从多个地方找的,顺序如下:
1.检查环境变量 ANSIBLE_CONFIG 指向的路径文件(export ANSIBLE_CONFIG=/etc/ansible.cfg);
2. ~/.ansible.cfg,检查当前目录下的ansible.cfg配置文件;
3./etc/ansible.cfg检查etc目录的配置文件。
ansible的配置文件
- ansible的配置文件路径是/etc/ansible/ansible.cfg,ansible许多参数,下面我们列出一些常见的参数:
inventory = /etc/ansible/hoste #这个参数表示资源清单inventory文件的位置
library = /usr/share/ansible #指向存放ansible模块的目录,支持多个目录方式,只要用冒号(:)隔开就行。
fbrks = 5 #并发连接数,默认为5
sudo_user = root #设置默认执行命令的用户
remote_port = 22 #指定连接被管理节点的端口,默认为22端口,为安全考虑,建议修改
host_key_checking = False #设置是否检查SSH主机的密钥,值为True/False,关闭后第一次连接不会提示配置实例
timeout = 60 #设置SSH连接的超时时间,单位为秒
log_path = /var/log/ansible.cfg #指定一个存储ansible日志的文件(默认不记录日志)ansible的主机清单
- 在配置文件中,我们提到了资源清单,这个清单就是主机清单,里面保存的是一些ansible需要连接管理的主机列表。
- 如下是ansible主机清单的定义方式:
1.直接指明主机地址或者主机名:
#green.example.com#
#bule.example.com#
# 192.168.40.170
# 192.168.40.172
2.定义一个主机组(组名)把地址或者主机名加进去
[niuma_mysql]
192.168.40.170
192.168.40.172
192.168.40.17- 需要注意的是,这里的组成员可以使用通配符来匹配,这样对于一些标准化管理就比较方便。我们可以根据实际情况来配置我们的主机列表,具体的操作如下:
vi /etc/ansible/hosts
[web]
192.168.40.16
192.168.40.150四.部署ansible管理集群
实验环境
| 主机名 | IP地址 | 安装包 |
| ansible | 192.168.40.20 | epel-release、ansible |
| node1 | 192.168.40.21 | - |
| node2 | 192.168.40.22 | - |
实验步骤
- 安装ansible
[root@localhost ~]# hostnamectl set-hostname ansible
[root@localhost ~]# su
[root@ansible ~]# yum install epel-release -y
[root@ansible ~]# yum install ansible -y-
添加主机清单
[root@ansible ~]# cd /etc/ansible/
[root@ansible ansible]# ls
ansible.cfg hosts roles
[root@ansible ansible]# vi hosts
[web] ##添加到最后一行
192.168.40.20
192.168.40.21-
配置公私钥
[root@ansible ansible]# ssh-keygen
Generating public/private rsa key pair.
Enter file in which to save the key (/root/.ssh/id_rsa):
Created directory '/root/.ssh'.
Enter passphrase (empty for no passphrase):
Enter same passphrase again:
Your identification has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.
Your public key has been saved in /root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub.
The key fingerprint is:
SHA256:Gcx8heCuJ5aTcJMwQ1tkLnTotffs2PgbNUsLX6ZBtn4 root@ansible
The key's randomart image is:
+---[RSA 2048]----+
| oo= .. .. |
| o.*.= .. |
| .*...* . o |
| .=.o.+ o . |
| . +.So. * o |
| o = o* O |
| B .=. * E |
| . +o o. . |
| .o. |
+----[SHA256]-----+
[root@ansible ansible]# ssh-copy-id [email protected]
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: Source of key(s) to be installed: "/root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub"
The authenticity of host '192.168.40.21 (192.168.40.21)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:syLOZP0q9x4iB03a1qJRnxbETn5FsxbZDyKmRRQhvHM.
ECDSA key fingerprint is MD5:1f:c8:9a:d7:df:00:72:14:1b:e3:6b:d5:3f:ae:51:c5.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: attempting to log in with the new key(s), to filter out any that are already installed
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: 1 key(s) remain to be installed -- if you are prompted now it is to install the new keys
[email protected]'s password:
Number of key(s) added: 1
Now try logging into the machine, with: "ssh '[email protected]'"
and check to make sure that only the key(s) you wanted were added.
[root@ansible ansible]# ssh-copy-id [email protected]
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: Source of key(s) to be installed: "/root/.ssh/id_rsa.pub"
The authenticity of host '192.168.40.22 (192.168.40.22)' can't be established.
ECDSA key fingerprint is SHA256:d5GOWyy7Ux6q2Te8f+ibOaZl7r8UvNLF3psHdmC9LG4.
ECDSA key fingerprint is MD5:00:ab:48:63:8b:23:31:7f:07:ca:30:e5:ef:58:6e:a1.
Are you sure you want to continue connecting (yes/no)? yes
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: attempting to log in with the new key(s), to filter out any that are already installed
/usr/bin/ssh-copy-id: INFO: 1 key(s) remain to be installed -- if you are prompted now it is to install the new keys
[email protected]'s password:
Number of key(s) added: 1
Now try logging into the machine, with: "ssh '[email protected]'"
and check to make sure that only the key(s) you wanted were added.
全程是只需要在ansible上面操作就行
五.Ansible常用模块
主机连通性测试
- 使用下列命令对主机清单中的资源进行连通性测试,出现下列信息说明主机处于连通状态
#ansible 主机清单组名 -m(指定模块名字)
[root@localhost ansible]# ansible web -m ping
192.168.40.21 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}
192.168.40.22 | SUCCESS => {
"ansible_facts": {
"discovered_interpreter_python": "/usr/bin/python"
},
"changed": false,
"ping": "pong"
}command模块
- command模块可以直接在远程主机上执行命令,并且结果返回打印出来,举例如下:
##-m 指定执行模块
##-a 指定命令执行
[root@ansible ansible]# ansible web -m command -a 'date'
192.168.40.22 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
2023年 08月 28日 星期一 13:47:45 CST
192.168.40.21 | CHANGED | rc=0 >>
2023年 08月 28日 星期一 13:47:45 CST
- 命令模块接受命令名称,后面是空格分隔的列表参数。给定的命令将在所有选定的节点上执行,它不会通过shell进行处理,比如$HOME和操作如“<”,">","| ", " ; " ," & " (需要使用 shell模块实现这些功能)。注意,command模块不支持 | 管道命令。
- 下面是command模块常用的几个命令:
chdir:在执行命令之前,先切换到该目录
execurable:切换shell来执行命令,需要使用命令的绝对路径
free_form:要执行的Linux指令,一般使用Ansible的-a参数代替
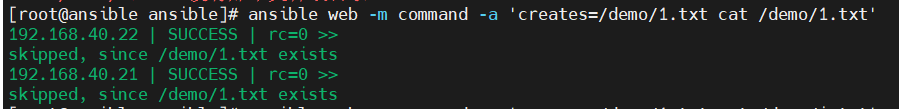
creates:一个文件名,当这个文件存在,则该命令不执行,可以用来做判断
removes:一个文件名,这个文件不存在,则该命令不执行
- 以下是这些命令的效果
shell模块
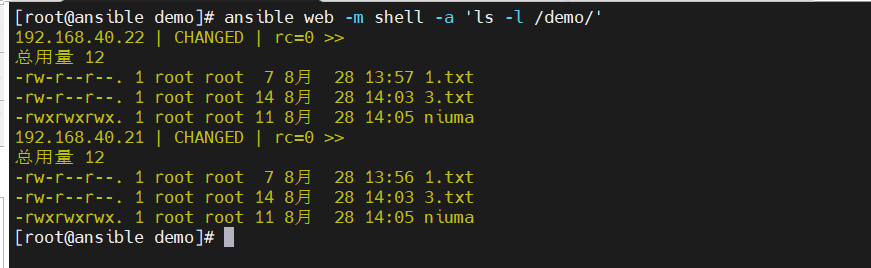
- shell模块可以在远程主机上调用shell解释器运行命令,支持shell的各种功能,例如管道等
- 只要是shell命令都可以在通过这个模块在远程主机里面运行
[root@ansible ~]# ansible web -m shell -a 'cat /etc/passwd | grep zhangsan'
由于command不支持 管道符,所以它只会支持cat /etc/passwd命令
copy模块
- 这个模块用于将文件复制到远程主机上,同时支持给定的内容生成文件和修改权限等
- copy模块的相关选项如下:
src:被复制到远程主机的本地文件。可以是绝对路径,也可以是相对路径。如果路径是一个目录,则会递归复制,用法类似于“rsync”。
content:用于替换“src”,可以直接指定文件的值。
dest:必选项,将源文件复制到远程主机的绝对路径。
backup:当文件内容发生改变之后,在覆盖之前,把源文件备份,备份文件包含时间信息
directory_mode:递归设定目录的权限,默认为系统默认权限。
force:当目标主机包含该文件,但是内容不同时,设定为“yes”,表示强制覆盖;设定为“no”表示目标主机的目标位置不存在该文件才复制。默认为“yes”
others:所有的file模块中的选项可以在这里使用
- 实例如下:复制文件
- 给定内容生成文件,并且制定权限
-
备份源文件,并且覆盖源文件
file模块
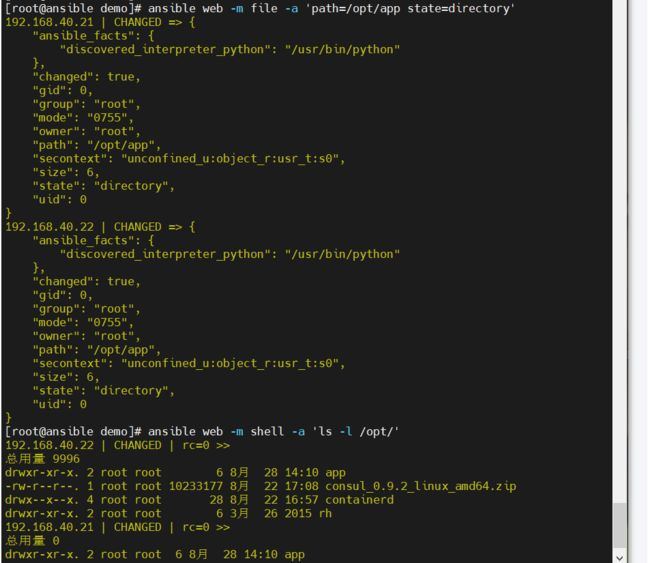
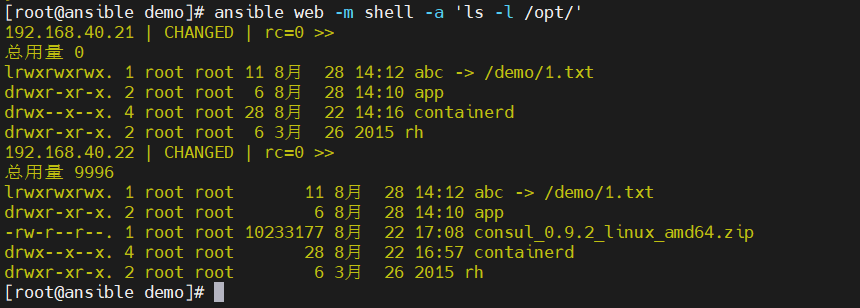
- file模块主要用于设置文件的属性,比如创建文件、创建连接文件、删除文件等,如下为常见的命令:
force:需要两种情况下强制创建软连接,一种是源文件不存在,但是之后会建立的情况下;另外一种是目标软链接已存在,需要取消之前的软链接,然后创建新的,有两个选项:yes|no。
group:定义文件/目录的属组。后面可以加上mode:定义文件/目录的权限。
owner:定义文件/目录的属主,后面必须加上path:定义文件/目录的路径。
recurse:递归设置文件的属性,只对目录有效,后面跟上src:被链接的源文件路径,只应用于state=link的情况
dest:被链接到的路径,只应用于state=link的情况
sate:状态,有如下选项
directory:如果目录不存在,就创建目录
file:即使文件不存在,也不会被创建
link:创建软链接
hard:创建硬链接
touch:如果文件不存在,则会创建一个新的文件,如果文件或者目录已经存在,则更新其最后修改时间
absent:删除目录、文件或者取消链接文件创建目录,实例如下:
- 创建链接文件,实例如下:
-
删除文件如下所示:
fetch模块
- fetch模块用于从远程某个主机获取(复制)文件到本地来
dest:用来存在文件的目录。
src:在远程拉取的文件,并且是一个file,不能是目录
-
具体实例如下:
cron模块
- cron模块用于管理crontab计划性任务的,它的语法和crontab中的语法一致
day= :日应该运行的工作( 1-31, *, */2, )
hour= :小时 ( 0-23, *, */2, )
minute= :分钟( 0-59, *, */2, )
month= :月( 1-12, *, /2, )
weekday= : 周 ( 0-6 for Sunday-Saturday,, )
job= :指明运行的命令是什么
name= :定时任务描述
reboot :任务在重启时运行,不建议使用,建议使用special_time
special_time :特殊的时间范围,参数:reboot(重启时),annually(每年),monthly(每月),weekly(每周),daily(每天),hourly(每小时)
state :指定状态,present表示添加定时任务,也是默认设置,absent表示删除定时任务
user :以哪个用户的身份执行
- 添加计划性任务如下,实例如下:
- 删除计划性任务,比如我们计划任务添加错误,则可以执行以下命令删除计划任务
yum模块
- yum模块主要用于软件的安装,它的选项如下
name= :所安装的软件包的名称
state= :present--》安装,latest--》安装最新的,absent--》卸载软件
update_cache :强制更新yum的缓存
conf_file :指定远程yum安装时所依赖的配置文件(安装本地已有的包)。
disable_pgp_check :是否禁止GPG checking,只用于present 或者 latest。
disablerepo :临时禁止使用yum库。只用于安装或者更新时。
enablerepo :临时使用的yum库。只用于安装或者更新时。
- 如下演示安装 tree软件包
service模块
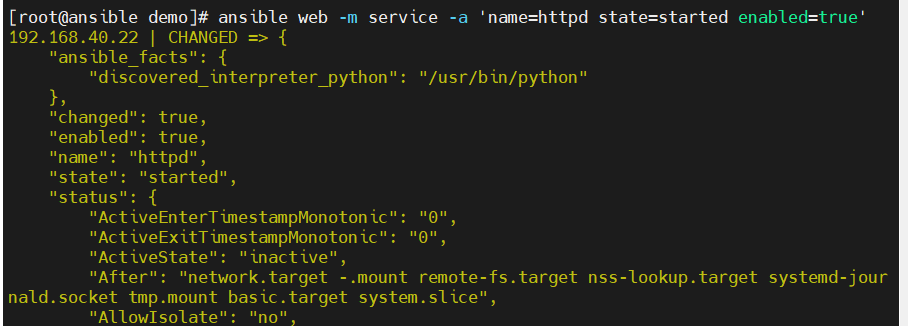
- service模块用于服务程序的管理,它的主要选项如下:
arguments:命令行提供额外的参数
enabled:设置开机自启
name:服务名称
runlevel:开机启动的级别,一般不用指定。
sleep:在重启服务的过程中,是否等待。如在服务关闭以后等待2秒在启动。(定义在剧本当中)
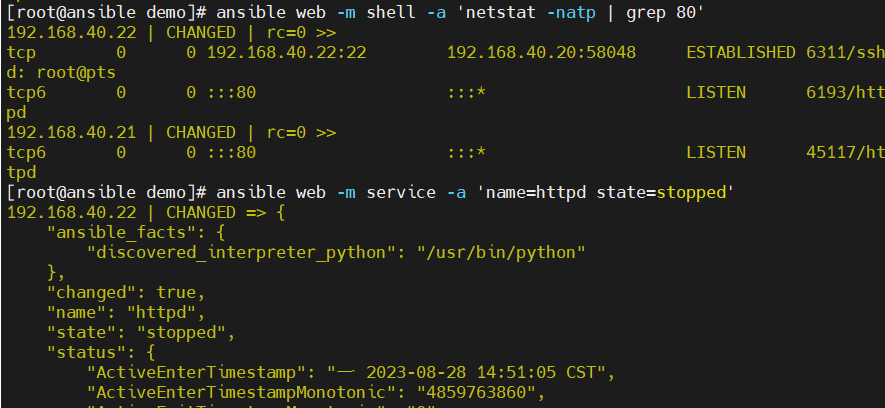
state:有四种状态分别为:started(启动服务),stopped(停止服务),restart(重启服务),reload(重载服务)
-
开启httpd服务并且设置开启自启
-
通过service模块关闭httpd服务
六 Ansible常用命令
ansible命令集解释
- /usr/bin/ansible,Ansible AD-Hoc临时命令执行工具,常用于临时命令的执行
- /usr/bin/ansible-doc,Ansible模块功能查看工具
- /usr/bin/ansible-galaxy,下载上传优秀的代码或者Roles模块的官网平台,基于网络的
- /usr/bin/ansible-playbook,Ansible定制自动化的任务集编排工具
- /usr/bin/ansible-pull,Ansible远程执行命令的工具,拉取配置而非推送配置(使用较少,海量机器时使用,对运维架构能力要求高)
- /usr/bin/ansible-vault,Ansible文件加密工具
- /usr/bin/ansible-console,Ansible基于Linux Consoble界面可与用户交互的命令执行工具
较为常用的是/usr/bin/ansible和/usr/bin/ansible-playbook
ansible-doc命令
- ansible-doc命令常用于获取模板块信息及其适用帮助,一般用法如下:
ansible-doc -l ##获取全部模块信息
ansible-doc -s MOD_NAME #获取指定模块的使用帮助-
ansible-doc的全部用法:
[root@localhost ~]# ansible-doc
usage: ansible-doc [-h] [--version] [-v] [-M MODULE_PATH]
...
optional arguments:
--metadata-dump **For internal testing only** Dump json metadata for
all plugins.
--playbook-dir BASEDIR
Since this tool does not use playbooks, use this as a
substitute playbook directory.This sets the relative
path for many features including roles/ group_vars/
etc.
--version show program's version number, config file location,
configured module search path, module location,
executable location and exit
-F, --list_files Show plugin names and their source files without
summaries (implies --list)
##-M,指定模块的路径
-M MODULE_PATH, --module-path MODULE_PATH
prepend colon-separated path(s) to module library (def
ault=~/.ansible/plugins/modules:/usr/share/ansible/plu
gins/modules)
##-h,显示命令参数API文档
-h, --help show this help message and exit
##输出为json格式
-j, --json Change output into json format.
##-l,列出可用模块
-l, --list List available plugins
##-s,显示剧本指定模块的用法
-s, --snippet Show playbook snippet for specified plugin(s)ansible命令
- ansible命令的具体格式如下
ansible <-f forks> [-m module_name] [-a args]
-
如下
使用ansible -h来查看帮助
-a,MODULE_ARGS #模块的参数,如果执行默认COMMAND的模块,即是命令参数,如:“date”,"pwd"。
-k,--ask-pass #ask for SSH password。登录密码,提示输入SSH密码而不是假设基于密钥的验证
--ask-pass #ask for SSH。su切换密码
-K,--ask-sudo-pass #ask for sudo password。提示密码使用sudo,sudo表示提权操作
--ask-vault-pass #ask for vault password。 假设我们设定了加密的密码,则用该选项进行访问
-B SECONDS #后台超时时间
-C #模拟运行环境并且进行预运行,可以进行查错测试
-c CONNECTION #连接类型使用
-f FORKS #并行任务数,默认为5
-i INVENTORY #指定主机清单的路径,默认为/etc/ansible/hosts
--list-hosts #查看有哪些主机组
-m MODULE_NAME #执行模块的名字,默认使用command模块,所以如果只执行单一命令可以不用 -m 参数
-o #压缩输出,尝试讲所有结果在一行输出,一般针对收集工具使用
-S #用su命令
-R SU_USER #指定su的用户,默认为root用户
-s #用sudo的命令
-U SUDO_USERSUDO #指定sudo到哪个用户,默认为root用户
-T TIMEOUT #指定ssh默认超时时间,默认为10s,也可以在配置文件中修改
-u REMOTE_USER #远程用户,默认为root用户
-v #查看详细信息,同时支持 -vvv,-vvvv可以查看更加详细的信息ansible配置公私钥
- 上面已经提到ansible是基于ssh协议实现管理主机的,所以ansible配置公私钥的方式与ssh协议的方式相同,具体操作步骤如下:
1.生产私钥
ssh-keygen
2.向被管理主机分发私钥
ssh-copy-id [email protected]
ssh-copy-id [email protected]