SpringBoot扩展点之EnvironmentPostProcessor
在使用spring boot做开发时,有时我们需要自定义环境变量或者编写第三方扩展点,可以使用EnvironmentPostProcessor,注意如果你只是基本的使用环境,就不需要看此文了 。
1. 属性文件myapp.properties,可以自定义文件名,也可以有多个同名文件
config/myapp.properties文件
app.url=https://github.com/dongguangming/
app.name=dgm
app.desc=dongguangming github
app.customComponentScanPackages=com.spring.mapper,com.spring.mapper
mysqluser=rootroot
mysqlpwd=cstorfscstorfs
app.who=who are youmyapp.properties.文件
app.url=https://github.com/dongguangming//
app.name=dgmdgm
app.desc=dongguangming github
app.customComponentScanPackages=com.spring.mapper,com.spring.mapper
2. 新建java实现类
/**
* @author dgm
* @describe "环境变量扩展点"
* @date 2020年10月12日
*/
@Order(Ordered.LOWEST_PRECEDENCE)
public class MyJsonEnvironmentPostProcessor implements EnvironmentPostProcessor {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory
.getLogger(MyJsonEnvironmentPostProcessor.class);
private static final String DEFAULT_SEARCH_LOCATIONS = "classpath:/,classpath:/config/,file:./,file:./config/";
private static final String DEFAULT_NAMES = "myapp";
private static final String DEFAULT_FILE_EXTENSION = ".properties";
private static final String PREFIX = "com.spring.environmentpostprocessor.";
private static final String CALCUATION_MODE = "calculation_mode";
private static final String GROSS_CALCULATION_TAX_RATE = "gross_calculation_tax_rate";
private static final String CALCUATION_MODE_DEFAULT_VALUE = "NET";
private static final double GROSS_CALCULATION_TAX_RATE_DEFAULT_VALUE = 0;
List names = Arrays.asList(CALCUATION_MODE,
GROSS_CALCULATION_TAX_RATE);
private static Map defaults = new LinkedHashMap<>();
static {
defaults.put(CALCUATION_MODE, CALCUATION_MODE_DEFAULT_VALUE);
defaults.put(GROSS_CALCULATION_TAX_RATE,
GROSS_CALCULATION_TAX_RATE_DEFAULT_VALUE);
}
@Override
public void postProcessEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment,
SpringApplication application) {
/*
* PropertySource system = environment.getPropertySources()
* .get(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME);
*
* Map prefixed = new LinkedHashMap<>();
*
* if (!hasOurPriceProperties(system)) { // Baeldung-internal code so
* this doesn't break other examples logger.error(
* "System environment variables [calculation_mode,gross_calculation_tax_rate] not detected, fallback to default value [calcuation_mode={},gross_calcuation_tax_rate={}]"
* , CALCUATION_MODE_DEFAULT_VALUE,
* GROSS_CALCULATION_TAX_RATE_DEFAULT_VALUE); prefixed = names.stream()
* .collect(Collectors.toMap(this::rename, this::getDefaultValue));
*
* environment.getPropertySources()
* .addAfter(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, new
* MapPropertySource("prefixer", prefixed));
*
* return; }
*
* prefixed = names.stream() .collect(Collectors.toMap(this::rename,
* system::getProperty)); environment.getPropertySources()
* .addAfter(SYSTEM_ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, new
* MapPropertySource("prefixer", prefixed));
*/
List list = Arrays
.asList(StringUtils.trimArrayElements(StringUtils
.commaDelimitedListToStringArray(DEFAULT_SEARCH_LOCATIONS)));
Collections.reverse(list);
Set reversedLocationSet = new LinkedHashSet(list);
System.err.println(reversedLocationSet);
ResourceLoader defaultResourceLoader = new DefaultResourceLoader();
// YamlPropertiesFactoryBean yamlPropertiesFactoryBean = new
// YamlPropertiesFactoryBean();
PropertiesFactoryBean propertiesFactoryBean = new PropertiesFactoryBean();
List loadedProperties = new ArrayList<>(16);
// List propertiesPathList = new ArrayList<>(16);
reversedLocationSet.forEach(location -> {
Resource resource = defaultResourceLoader.getResource(location
+ DEFAULT_NAMES + DEFAULT_FILE_EXTENSION);
System.err.println(location + DEFAULT_NAMES
+ DEFAULT_FILE_EXTENSION);
if (resource == null || !resource.exists()) {
return;
}
System.err.println("################33");
Properties p = new Properties();
try {
InputStream inputStream = resource.getInputStream();
p.load(inputStream);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
loadedProperties.add(p);
});
System.err.println(loadedProperties);
Properties filteredProperties = new Properties();
Set 是一个实现了***PostProcessor 接口的类,此是EnvironmentPostProcessor
3. 配置约定的文件
在class目录下必须要有约定的文件配置META-INF/spring.factories, 必须这样命名,因为
具体文件内容设置:
org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessor=com.spring.environmentpostprocessor.MyJsonEnvironmentPostProcessor
4. 测试启动类
/**
* @author dgm
* @describe ""
*/
@EnableConfigurationProperties
// @ComponentScan({"cn.cstor.platform.bdrack.config.druid","com.spring.component"})
@MapperScan(basePackages = "cn.cstor.platform.bdrack.mapper")
@SpringBootApplication(scanBasePackages = {
"cn.cstor.platform.bdrack.config.druid", "com.spring.componentt",
"com.spring.controller", "com.spring.value" })
// (exclude= {DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class})
public class SpringBootCustomStarterApplication implements CommandLineRunner {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory
.getLogger(SpringBootCustomStarterApplication.class);
// @Autowired
// ApplicationProperties appProperties;
public static void main(String[] args) {
// System.setProperty("app.name", "dgm");
// System.setProperty("app.desc", "dongguangming github");
// System.setProperty("logType", "FILE");
String bdrack = System.getenv("BDRACK");
logger.error("配置文件:"
+ (bdrack != null ? ((bdrack.endsWith("/") ? bdrack
+ "conf/config.properties" : bdrack
+ "/conf/config.properties"))
: "conf/config.properties"));
System.setProperty("spring.config.location",
bdrack != null ? ((bdrack.endsWith("/") ? bdrack
+ "conf/config.properties" : bdrack
+ "/conf/config.properties"))
: "conf/config.properties");
logger.error("获取配置文件:" + System.getProperty("spring.config.location"));
// SpringApplication applicationContext = new SpringApplication(
// SpringBootCustomStarterApplication.class);
// app.setBannerMode(Banner.Mode.OFF);
// applicationContext.setLogStartupInfo(false);
// ConfigurableApplicationContext c = applicationContext.run(args);
ApplicationContext applicationContext = SpringApplication.run(
SpringBootCustomStarterApplication.class, args);
List packages = AutoConfigurationPackages
.get(applicationContext);
System.err.println("要扫描的包是packages: " + packages);
String[] beanNames = applicationContext.getBeanDefinitionNames();
List beans = Arrays.asList(beanNames);
System.err.println(beans);
beans.forEach(bean -> {
if (bean.contains("UserDAO") || bean.contains("cacheManager")
|| bean.contains("LogService")) {
System.out.println(bean);
}
});
System.err.println("来自环境变量:");
Environment env = (Environment) applicationContext.getEnvironment();
System.out.println("- connection Name1111: " + env.getProperty("app.name"));
System.out.println("- connection Url111: " + env.getProperty("app.url"));
ApplicationProperties appProperties = (ApplicationProperties) applicationContext
.getBean(ApplicationProperties.class);
System.err.println("Properties Values from Properties File:");
System.out.println("- connection Name: " + appProperties.getName());
System.out.println("- connection Url: " + appProperties.getUrl());
// 我使用的最新版Springboot2.3.0(放弃1版本)启动后,不放心的话可以测试数据库是否连接正常
/*UserMapper userMapper = applicationContext.getBean(UserMapper.class);
Example example = new Example(User.class);
example.createCriteria().andEqualTo("username", "dongguangming");
List userList = userMapper.selectByExample(example);
if (userList.size() > 0) {
User user = userList.get(0);
System.err.println("数据库连接正常,从用户表取用户名是donggguangming的数据,用户:" + user);
}*/
// JdbcUserDAO jdbcUserDAO= (JdbcUserDAO) c.getBean("jdbcUserDAO");
// System.out.println(jdbcUserDAO.getAllUserNames());
// SpringApplication.run(SpringBootTestApplication.class, args);
}
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
System.err.println("输入参数是:" + Arrays.asList(args));
}
} 显示输出结果
[file:./config/, file:./, classpath:/config/, classpath:/]
file:./config/myapp.properties
file:./myapp.properties
classpath:/config/myapp.properties
################33
classpath:/myapp.properties
################33
[{mysqlpwd=cstorfscstorfs, app.desc=dongguangming github, mysqluser=rootroot, app.customComponentScanPackages=com.spring.mapper,com.spring.mapper, app.url=https://github.com/dongguangming/, app.name=dgm, app.who=who are you}, {app.desc=dongguangming github, app.customComponentScanPackages=com.spring.mapper,com.spring.mapper, app.url=https://github.com/dongguangming//, app.name=dgmdgm}]
*********** end ************
{mysqlpwd=cstorfscstorfs, app.desc=dongguangming github, app.customComponentScanPackages=com.spring.mapper,com.spring.mapper, mysqluser=rootroot, app.url=https://github.com/dongguangming/, app.name=dgm, app.who=who are you}
我们知道程序启动需要准备文件解析,环境变量设置,然后事件发布,缓存,bean生成,最后启动servlet运行环境,当然中间还有其他一系列环节,此文只关注环境设置。
首先springboot应用启动从run开始,
ApplicationContext applicationContext = SpringApplication.run(
SpringBootCustomStarterApplication.class, args);接着 重点来了(定制化springboot启动可以在此发挥)
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
context = createApplicationContext();
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
listeners.started(context);
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
listeners.running(context);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
} 接下来一步一步拆分
第一步:我们第一个要关注的就是spring boot首先初始化了一个全局的事件监听器,这个事件监听器会伴随着springboot的整个生命周期,这个我们以后也会多次接触这个组件,即是
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();初始化全局的事件监听器EventPublishingRunListener,如图
第二步:接下来就是开始准备springboot所有配置文件存储的仓库Environment,这个其实也很好理解,spring是管理bean的,bean里面也有很多属性,所以优先收集整个上下文的配置属性信息,将其放在一个Environment里面,然后以后想要什么,就从环境里面去获取。
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
第三步: 我们进入prepareEnvironment方法,关注它是如何实现。
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// Create and configure the environment,创建环境
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
//配置环境上下文
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader()).convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment,
deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}
我们可以看到首先先调用getOrCreateEnvironment创建好一个上下文环境,接着看下一行的#configureEnvironment方法。
protected void configureEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) {
if (this.addConversionService) {
ConversionService conversionService = ApplicationConversionService.getSharedInstance();
environment.setConversionService((ConfigurableConversionService) conversionService);
}
//加载一些基本的环境变量
configurePropertySources(environment, args);
configureProfiles(environment, args);
}主要是加载如下的配置文件,运行时一般会配置启动参数,其实也就是在这个地方,启动参数被会spring boot解析到作为默认选项,加载到上下文中,作为启动的核心参数启动,但是一般这些参数叫做默认参数,优先级是最低的,如果你在代码有同key值的时候,就会覆盖运行配置的系统级变量值。
[ConfigurationPropertySourcesPropertySource {name='configurationProperties'}, StubPropertySource {name='servletConfigInitParams'}, StubPropertySource {name='servletContextInitParams'}, PropertiesPropertySource {name='systemProperties'}, OriginAwareSystemEnvironmentPropertySource {name='systemEnvironment'}, RandomValuePropertySource {name='random'}, OriginTrackedMapPropertySource {name='applicationConfig: [file:conf/config.properties]'}, PropertiesPropertySource {name='myapp'}]
然后通过: listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
我们可以看到方法名叫做environmentPrepared,调用者是listener,是一个监听器,也就是我们上文说的EventPublishingRunListener监听器。
依次追踪代码到了ConfigFileApplicationListener的监听器实例,它监听的是一个ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent,故其名曰"应用环境准备好事件",虽然有点绕口,也不通顺,但是看到这边我们就动了,springboot是靠一种事件订阅的方式来做解耦合的,源码如下
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (event instanceof ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) {
onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent((ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) event);
}
if (event instanceof ApplicationPreparedEvent) {
onApplicationPreparedEvent(event);
}
}紧接着我们进入onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent这个方法
private void onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event) {
List postProcessors = loadPostProcessors();
postProcessors.add(this);
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(postProcessors);
for (EnvironmentPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
postProcessor.postProcessEnvironment(event.getEnvironment(), event.getSpringApplication());
}
} 继续追查代码怎么拿到postprocessors,
List loadPostProcessors() {
return SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactories(EnvironmentPostProcessor.class, getClass().getClassLoader());
} 然后继续查看SpringFactoriesLoader.java
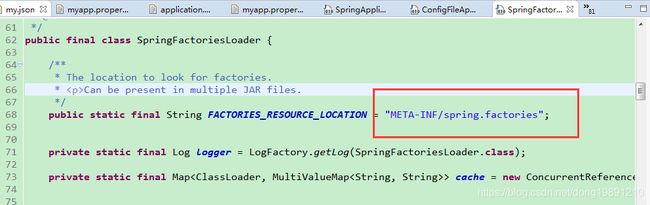
//写死了
public static final String FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories";
private static Map> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
MultiValueMap result = cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
try {
Enumeration urls = (classLoader != null ?
classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION) :
ClassLoader.getSystemResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION));
..........
} 这下知道为啥要把约定配置文件写死了吧,且文件名字必须是META-INF/spring.factories
是不是想到了 SPI ,全称为 Service Provider Interface,是一种服务发现机制。算是技术呢,还是约束呢,因为jdk和dubbo也有类似机制,大同小异,路数一致,怎么现场发挥就看个人了,看到别人的就能完善或仿制出来,记得改名字,别一模一样。
终于看到自定义环境postprocessors
可以看到当loadPostProcessors执行完之后,看方法名我们也是是加载当前项目中EnvironmentPostProcessor,然后排序,最后调用我们刚刚说的postProcessorEnvironment方法
for (EnvironmentPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
postProcessor.postProcessEnvironment(event.getEnvironment(), event.getSpringApplication());
}即案例中的
public class MyJsonEnvironmentPostProcessor implements EnvironmentPostProcessor {
......
@Override
public void postProcessEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment environment,
SpringApplication application) {
//处理逻辑略
}
}
至此,自定义环境变量就可以拿到了,
不过特别注意,此时bean阶段还未到。
总结: 技术是逻辑的规则、权威的典范,算是技术吗???忘了吧,其实是妙想和逻辑,看你会不会想,能不能想得到!!!!!!
附图:
最后上传spring5英文资料电子书(对我来说已没什么鸟用了,逻辑和想法比技术更重要)入github仓库
大功告成!!!!!!!!!
参考:
1. Java System.getProperty vs System.getenv
https://www.baeldung.com/java-system-get-property-vs-system-getenv
2. Spring3.1新属性管理API:PropertySource、Environment、Profile
https://www.iteye.com/blog/jinnianshilongnian-2000183
3. springcloud config配置读取优先级过程详解 http://www.cppcns.com/ruanjian/java/276075.html
4. Spring的Environment应用上下文环境 http://wiliam.me/2017/02/25/20170225125823.html
5. Using & Mocking PropertySource & Environment in Spring3.2 https://blog.jamesdbloom.com/UsingPropertySourceAndEnvironment.html
6. 基于Spring Boot的Environment源码理解实现分散配置详解
https://www.jb51.net/article/145192.htm
7. Customize the Environment or ApplicationContext Before It Starts
https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/htmlsingle/#howto-customize-the-environment-or-application-context
8. 10分钟搞懂SpringBoot的组件EnvironmentPostProcessor使用和原理
https://www.solves.com.cn/it/cxkf/yy/JAVA/2019-10-10/5850.html
9. Properties with Spring and Spring Boot https://www.baeldung.com/properties-with-spring, https://www.baeldung.com/configuration-properties-in-spring-boot
10. EnvironmentPostProcessor in Spring Boot https://www.baeldung.com/spring-boot-environmentpostprocessor
11. Another post-processor for Spring Boot
https://blog.frankel.ch/another-post-processor-for-spring-boot/
12. Application servers and environments supported by Weld https://docs.jboss.org/weld/reference/latest/en-US/html/environments.html