操作系统实验六 文件管理
文末也可直接获取实验文档
实验六 文件管理
目录
- 1实验目的
- 2实验内容
- 3实验详细操作步骤及程序清单:
- 4相关问题及分析
- 5总结
- 6文件系统的实现
1实验目的
1.加深对文件、目录和文件系统等概念的理解
2.通过设计一个简单的文件系统加深理解操作系统中文件系统的实现
2实验内容
为linux系统设计一个简单的二级文件系统。要求做到以下几点:
(1)可以实现下列几条命令(至少4条);
login 用户登陆
dir 列文件目录
create 创建文件
delete 删除文件
open 打开文件
close 关闭文件
read 读文件
write 写文件
(2)列目录时要列出文件名、物理地址、保护码和文件长度等信息;
(3)源文件可以进行读写保护。
3实验详细操作步骤及程序清单:
一、为Linux系统设计一个简单的二级文件系统。要求做到以下几点:
1.在内存中开辟一个虚拟磁盘空间作为文件存储分区,在其上实现一个简单的基于多级目录的单用户单任务系统中的文件系统。退出该文件系统的使用时,应将该虚拟文件系统以一个Windows文件的方式保存到磁盘上,以便下次可以再将它恢复到内存的虚拟磁盘空间中。
2.文件存储空间的分配可采用显式链接分配或其他的办法。
3.空闲磁盘空间的管理可选择位示图或其他的办法。如果采用位示图来管理文件存储空间,并采用显式链接分配方式,那么可以将位示图合并到FAT中。
4.文件目录结构采用多级目录结构。为了简单起见,可以不使用索引结点,其中的每个目录项应包含文件名、物理地址、长度等信息,还可以通过目录项实现对文件的读和写的保护。
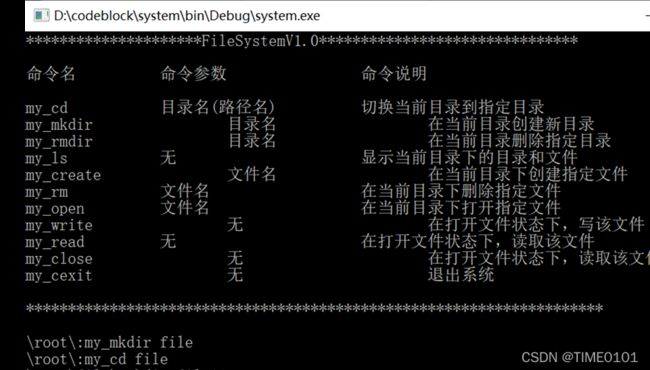
5.要求提供以下操作命令:
(1)my_format:对文件存储器进行格式化,即按照文件系统的结构对虚拟磁盘空间进行布局,并在其上创建根目录以及用于管理文件存储空间等的数据结构。
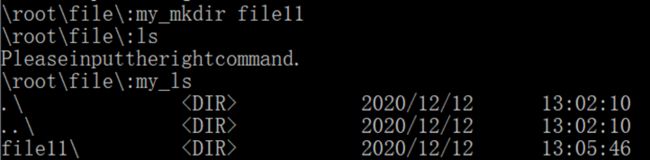
(2)my_mkdir:用于创建子目录。
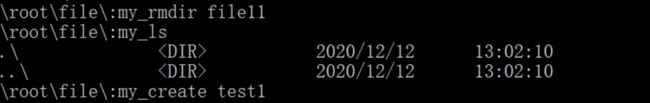
(3)my_rmdir:用于删除子目录。
(4)my_ls:用于显示目录中的内容。
(5)my_cd:用于更改当前目录。
(6)my_create:用于创建文件。
(7)my_open:用于打开文件。
(8)my_close:用于关闭文件。
(9)my_write:用于写文件。
(10)my_read:用于读文件。
(11)my_rm:用于删除文件。
(12)my_exitsys:用于退出文件系统。
4、 删除子目录file11
4相关问题及分析
这次操作系统实验,进一步加深了我对文件属性,文件操作的认识,在文件系统的设计中,难点应该是文件目录的管理,其中文件控制块和索引节点结构起了重要作用。文件控制块中,包含了文件使用,文件管理等信息。在系统中查找文件时,根据文件名找到控制块,再通过控制块获取到文件信息。
5总结
这次实验加深了我对文件、目录和文件系统等概念的理解并通过设计一个简单的文件系统加深理解操作系统中文件文件系统的实现。
但实验是基于参考代码进行的,所以只能对实验进行观看式理解,进行代码读阅和理解相关设计思路,从而理解实验的思路。主要是能通过这次实验理解理论课所讲授内容,在之后的学习生活中还需要继续学习努力。
6文件系统的实现
二、设计思路
1.系统主函数main()
(1)对应命令:无
(2)命令调用格式:无
(3)函数设计格式:voidmain()
(4)功能:系统主函数
(5)输入:无
(6)输出:无
(7)函数需完成的工作:
①对前面定义的全局变量进行初始化;
②调用startsys()进入文件系统;
③列出文件系统提供的各项功能及命令调用格式;
④显示命令行提示符,等待用户输入命令;
⑤将用户输入的命令保存到一个buf中;
⑥对buf中的内容进行命令解析,并调用相应的函数执行用户键入的命令;
⑦如果命令不是“my_exitsys”,则命令执行完毕后转④。
2.进入文件系统函数startsys()
(1)对应命令:无
(2)命令调用格式:无
(3)函数设计格式:voidstartsys()
(4)功能:由main()函数调用,进入并初始化我们所建立的文件系统,以供用户使用。
(5)输入:无
(6)输出:无。
(7)函数需完成的工作:
①申请虚拟磁盘空间;
②使用c语言的库函数fopen()打开myfsys文件:若文件存在,则转③;若文件不存在,则创建之,转⑤
③使用c语言的库函数fread()读入myfsys文件内容到用户空间中的一个缓冲区中,并判断其开始的8个字节内容是否为“10101010”(文件系统魔数),如果是,则转④;否则转⑤;
④将上述缓冲区中的内容复制到内存中的虚拟磁盘空间中;转⑦
⑤在屏幕上显示“myfsys文件系统不存在,现在开始创建文件系统”信息,并调用my_format()对①中申请到的虚拟磁盘空间进行格式化操作。转⑥;
⑥将虚拟磁盘中的内容保存到myfsys文件中;转⑦
⑦使用c语言的库函数fclose()关闭myfsys文件;
⑧初始化用户打开文件表,将表项0分配给根目录文件使用,并填写根目录文件的相关信息,由于根目录没有上级目录,所以表项中的dirno和diroff分别置为5(根目录所在起始块号)和0;并将ptrcurdir指针指向该用户打开文件表项。
⑨将当前目录设置为根目录。
3.磁盘格式化函数my_format()
(1)对应命令:my_format
(2)命令调用格式:my_format
(3)函数设计格式:voidmy_format()
(4)功能:对虚拟磁盘进行格式化,布局虚拟磁盘,建立根目录文件(或根目录区)。
(5)输入:无
(6)输出:无。
(7)函数需完成的工作:
①将虚拟磁盘第一个块作为引导块,开始的8个字节是文件系统的魔数,记为“10101010”;在之后写入文件系统的描述信息,如FAT表大小及位置、根目录大小及位置、盘块大小、盘块数量、数据区开始位置等信息;
②在引导块后建立两张完全一样的FAT表,用于记录文件所占据的磁盘块及管理虚拟磁盘块的分配,每个FAT占据两个磁盘块;对于每个FAT中,前面5个块设置为已分配,后面995个块设置为空闲;
③在第二张FAT后创建根目录文件root,将数据区的第1块(即虚拟磁盘的第6块)分配给根目录文件,在该磁盘上创建两个特殊的目录项:“.”和“…”,其内容除了文件名不同之外,其他字段完全相同。
4.更改当前目录函数my_cd()
(1)对应命令:my_cd
(2)命令调用格式:my_cddirname
(3)函数设计格式:voidmy_cd(chardirname)
(4)功能:改变当前目录到指定的名为dirname的目录。
(5)输入:
dirname:新的当前目录的目录名;
(6)输出:无
(7)函数需完成的工作:
①调用my_open()打开指定目录名的父目录文件,并调用do_read()读入该父目录文件内容到内存中;
②在父目录文件中检查新的当前目录名是否存在,如果存在则转③,否则返回,并显示出错信息;
③调用my_close()关闭①中打开的父目录文件;
④调用my_close()关闭原当前目录文件;
⑤如果新的当前目录文件没有打开,则打开该目录文件;并将ptrcurdir指向该打开文件表项;
⑥设置当前目录为该目录。
5.创建子目录函数my_mkdir()
(1)对应命令:my_mkdir
(2)命令调用格式:my_mkdirdirname
(3)函数设计格式:voidmy_mkdir(chardirname)
(4)功能:在当前目录下创建名为dirname的子目录。
(5)输入:
dirname:新建目录的目录名。
(6)输出:无。
(7)函数需完成的工作:
①调用do_read()读入当前目录文件内容到内存,检查当前目录下新建目录文件是否重名,若重名则返回,并显示错误信息;
②为新建子目录文件分配一个空闲打开文件表项,如果没有空闲表项则返回-1,并显示错误信息;
③检查FAT是否有空闲的盘块,如有则为新建目录文件分配一个盘块,否则释放①中分配的打开文件表项,返回,并显示错误信息;
④在当前目录中为新建目录文件寻找一个空闲的目录项或为其追加一个新的目录项;需修改当前目录文件的长度信息,并将当前目录文件的用户打开文件表项中的fcbstate置为1;
⑤准备好新建目录文件的FCB的内容,文件的属性为目录文件,以覆盖写方式调用do_write()将其填写到对应的空目录项中;
⑥在新建目录文件所分配到的磁盘块中建立两个特殊的目录项“.”和“…”目录项,方法是:首先在用户空间中准备好内容,然后以截断写或者覆盖写方式调用do_write()将其写到③中分配到的磁盘块中;
⑦返回。
6.删除子目录函数rmdir()
(1)对应命令:my_rmdir
(2)命令调用格式:my_rmdirdirname
(1)函数设计格式:voidmy_rmdir(chardirname)
(2)功能:在当前目录下删除名为dirname的子目录。
(3)输入:
dirname:欲删除目录的目录名。
(4)输出:无。
(5)函数需完成的工作:
①调用do_read()读入当前目录文件内容到内存,检查当前目录下欲删除目录文件是否存在,若不存在则返回,并显示错误信息;
②检查欲删除目录文件是否为空(除了“.”和“…”外没有其他子目录和文件),可根据其目录项中记录的文件长度来判断,若不为空则返回,并显示错误信息;
③检查该目录文件是否已经打开,若已打开则调用my_close()关闭掉;
④回收该目录文件所占据的磁盘块,修改FAT;
⑤从当前目录文件中清空该目录文件的目录项,且free字段置为0:以覆盖写方式调用do_write()来实现;
⑥修改当前目录文件的用户打开表项中的长度信息,并将表项中的fcbstate置为1;
⑦返回。
7.显示目录函数my_ls()
(1)对应命令:my_ls
(2)命令调用格式:my_ls
(3)函数设计格式:voidmy_ls(void)
(4)功能:显示当前目录的内容(子目录和文件信息)。
(5)输入:无
(6)输出:无
(7)函数需完成的工作:
①调用do_read()读出当前目录文件内容到内存;
②将读出的目录文件的信息按照一定的格式显示到屏幕上;
③返回。
8.创建文件函数my_create()
(1)对应命令:my_create
(2)命令调用格式:my_createfilename
(3)函数设计格式:intmy_create(charfilename)
(4)功能:创建名为filename的新文件。
(5)输入:
filename:新建文件的文件名,可能包含路径。
(6)输出:若创建成功,返回该文件的文件描述符(文件打开表中的数组下标);否则返回-1。
(7)函数需完成的工作:
①为新文件分配一个空闲打开文件表项,如果没有空闲表项则返回-1,并显示错误信息;
②若新文件的父目录文件还没有打开,则调用my_open()打开;若打开失败,则释放①中为新建文件分配的空闲文件打开表项,返回-1,并显示错误信息;
③调用do_read()读出该父目录文件内容到内存,检查该目录下新文件是否重名,若重名则释放①中分配的打开文件表项,并调用my_close()关闭②中打开的目录文件;然后返回-1,并显示错误信息;
④检查FAT是否有空闲的盘块,如有则为新文件分配一个盘块,否则释放①中分配的打开文件表项,并调用my_close()关闭②中打开的目录文件;返回-1,并显示错误信息;
⑤在父目录中为新文件寻找一个空闲的目录项或为其追加一个新的目录项;需修改该目录文件的长度信息,并将该目录文件的用户打开文件表项中的fcbstate置为1;
⑥准备好新文件的FCB的内容,文件的属性为数据文件,长度为0,以覆盖写方式调用do_write()将其填写到⑤中分配到的空目录项中;
⑦为新文件填写①中分配到的空闲打开文件表项,fcbstate字段值为0,读写指针值为0;
⑧调用my_close()关闭②中打开的父目录文件;
⑨将新文件的打开文件表项序号作为其文件描述符返回。
9.删除文件函数my_rm()
(1)对应命令:my_rm
(2)命令调用格式:my_rmfilename
(3)函数设计格式:voidmy_rm(charfilename)
(4)功能:删除名为filename的文件。
(5)输入:
filename:欲删除文件的文件名,可能还包含路径。
(6)输出:无。
(7)函数需完成的工作:
①若欲删除文件的父目录文件还没有打开,则调用my_open()打开;若打开失败,则返回,并显示错误信息;
②调用do_read()读出该父目录文件内容到内存,检查该目录下欲删除文件是否存在,若不存在则返回,并显示错误信息;
③检查该文件是否已经打开,若已打开则关闭掉;
④回收该文件所占据的磁盘块,修改FAT;
⑤从文件的父目录文件中清空该文件的目录项,且free字段置为0:以覆盖写方式调用do_write()来实现;;
⑥修改该父目录文件的用户打开文件表项中的长度信息,并将该表项中的fcbstate置为1;
⑦返回。
10.打开文件函数my_open()
(1)对应命令:my_open
(2)命令调用格式:my_openfilename
(3)函数设计格式:intmy_open(charfilename)
(4)功能:打开当前目录下名为filename的文件。
(5)输入:
filename:欲打开文件的文件名
(6)输出:若打开成功,返回该文件的描述符(在用户打开文件表中表项序号);否则返回-1。
(7)函数需完成的工作:
①检查该文件是否已经打开,若已打开则返回-1,并显示错误信息;
②调用do_read()读出父目录文件的内容到内存,检查该目录下欲打开文件是否存在,若不存在则返回-1,并显示错误信息;
③检查用户打开文件表中是否有空表项,若有则为欲打开文件分配一个空表项,若没有则返回-1,并显示错误信息;
④为该文件填写空白用户打开文件表表项内容,读写指针置为0;
⑤将该文件所分配到的空白用户打开文件表表项序号(数组下标)作为文件描述符fd返回。
11.关闭文件函数my_close()
(1)对应命令:my_close
(2)命令调用格式:my_closefd
(3)函数设计格式:voidmy_close(intfd)
(4)功能:关闭前面由my_open()打开的文件描述符为fd的文件。
(5)输入:
fd:文件描述符。
(6)输出:无。
(7)函数需完成的工作:
①检查fd的有效性(fd不能超出用户打开文件表所在数组的最大下标),如果无效则返回-1;
②检查用户打开文件表表项中的fcbstate字段的值,如果为1则需要将该文件的FCB的内容保存到虚拟磁盘上该文件的目录项中,方法是:打开该文件的父目录文件,以覆盖写方式调用do_write()将欲关闭文件的FCB写入父目录文件的相应盘块中;
③回收该文件占据的用户打开文件表表项(进行清空操作),并将topenfile字段置为0;
④返回。
12.写文件函数my_write()
(1)对应命令:my_write
(2)命令调用格式:my_writefd
(3)函数设计格式:intmy_write(intfd)
(4)功能:将用户通过键盘输入的内容写到fd所指定的文件中。磁盘文件的读写操作都必须以完整的数据块为单位进行,在写操作时,先将数据写在缓冲区中,缓冲区的大小与磁盘块的大小相同,然后再将缓冲区中的数据一次性写到磁盘块中;读出时先将一个磁盘块中的内容读到缓冲区中,然后再传送到用户区。本实例为了简便起见,没有设置缓冲区管理,只是在读写文件时由用户使用malloc()申请一块空间作为缓冲区,读写操作结束后使用free()释放掉。
写操作常有三种方式:截断写、覆盖写和追加写。截断写是放弃原来文件的内容,重新写文件;覆盖写是修改文件在当前读写指针所指的位置开始的部分内容;追加写是在原文件的最后添加新的内容。在本实例中,输入写文件命令后,系统会出现提示让用户选择其中的一种写方式,并将随后键盘输入的内容按照所选的方式写到文件中,键盘输入内容通过CTR+Z键(或其他设定的键)结束。
(5)输入:
fd:open()函数的返回值,文件的描述符;
(6)输出:实际写入的字节数。
(7)函数需完成的工作:
①检查fd的有效性(fd不能超出用户打开文件表所在数组的最大下标),如果无效则返回-1,并显示出错信息;
②提示并等待用户输入写方式:(1:截断写;2:覆盖写;3:追加写)
③如果用户要求的写方式是截断写,则释放文件除第一块外的其他磁盘空间内容(查找并修改FAT表),将内存用户打开文件表项中文件长度修改为0,将读写指针置为0并转④;如果用户要求的写方式是追加写,则修改文件的当前读写指针位置到文件的末尾,并转④;如果写方式是覆盖写,则直接转④;
④提示用户:整个输入内容通过CTR+Z键(或其他设定的键)结束;用户可分多次输入写入内容,每次用回车结束;
⑤等待用户从键盘输入文件内容,并将用户的本次输入内容保存到一临时变量text[]中,要求每次输入以回车结束,全部结束用CTR+Z键(或其他设定的键);
⑥调用do_write()函数将通过键盘键入的内容写到文件中。
⑦如果do_write()函数的返回值为非负值,则将实际写入字节数增加do_write()函数返回值,否则显示出错信息,并转⑨;
⑧如果text[]中最后一个字符不是结束字符CTR+Z,则转⑦继续进行写操作;否则转⑨;
⑨如果当前读写指针位置大于用户打开文件表项中的文件长度,则修改打开文件表项中的文件长度信息,并将fcbstate置1;
⑩返回实际写入的字节数。
13.实际写文件函数do_write()
(1)对应命令:无
(2)命令调用格式:无
(3)函数设计格式:intmy_write(intfd,chartext,intlen,charwstyle)
(4)功能:被写文件函数my_write()调用,用来将键盘输入的内容写到相应的文件中去。
(5)输入:
fd:open()函数的返回值,文件的描述符;
text:指向要写入的内容的指针;
len:本次要求写入字节数
wstyle:写方式
(6)输出:实际写入的字节数。
(7)函数需完成的工作:
①用malloc()申请1024B的内存空间作为读写磁盘的缓冲区buf,申请失败则返回-1,并显示出错信息;
②将读写指针转化为逻辑块块号和块内偏移off,并利用打开文件表表项中的首块号及FAT表的相关内容将逻辑块块号转换成对应的磁盘块块号blkno;如果找不到对应的磁盘块,则需要检索FAT为该逻辑块分配一新的磁盘块,并将对应的磁盘块块号blkno登记到FAT中,若分配失败,则返回-1,并显示出错信息;
③如果是覆盖写,或者如果当前读写指针所对应的块内偏移off不等于0,则将块号为blkno的虚拟磁盘块全部1024B的内容读到缓冲区buf中;否则便用ASCII码0清空buf;
④将text中未写入的内容暂存到缓冲区buff的第off字节开始的位置,直到缓冲区满,或者接收到结束字符CTR+Z为止;将本次写入字节数记录到tmplen中;
⑤将buf中1024B的内容写入到块号为blkno的虚拟磁盘块中;
⑥将当前读写指针修改为原来的值加上tmplen;并将本次实际写入的字节数增加tmplen;
⑦如果tmplen小于len,则转②继续写入;否则转⑧;
⑧返回本次实际写入的字节数。
14.读文件函数my_read()
(1)对应命令:my_read
(2)命令调用格式:my_readfdlen
(3)函数设计格式:intmyread(intfd,intlen)
(4)功能:读出指定文件中从读写指针开始的长度为len的内容到用户空间中。
(5)输入:
fd:open()函数的返回值,文件的描述符;
len:要从文件中读出的字节数。
(6)输出:实际读出的字节数。
(7)函数需完成的工作:
①定义一个字符型数组text[len],用来接收用户从文件中读出的文件内容;
②检查fd的有效性(fd不能超出用户打开文件表所在数组的最大下标),如果无效则返回-1,并显示出错信息;
③调用do_read()将指定文件中的len字节内容读出到text[]中;
④如果do_read()的返回值为负,则显示出错信息;否则将text[]中的内容显示到屏幕上;
⑤返回。
15.实际读文件函数do_read()
(1)对应命令:无
(2)命令调用格式:无
(3)函数设计格式:intdo_read(intfd,intlen,chartext)
(4)功能:被my_read()调用,读出指定文件中从读写指针开始的长度为len的内容到用户空间的text中。
(5)输入:
fd:open()函数的返回值,文件的描述符;
len:要求从文件中读出的字节数。
text:指向存放读出数据的用户区地址
(6)输出:实际读出的字节数。
(7)函数需完成的工作:
①使用malloc()申请1024B空间作为缓冲区buf,申请失败则返回-1,并显示出错信息;
②将读写指针转化为逻辑块块号及块内偏移量off,利用打开文件表表项中的首块号查找FAT表,找到该逻辑块所在的磁盘块块号;将该磁盘块块号转化为虚拟磁盘上的内存位置;
③将该内存位置开始的1024B(一个磁盘块)内容读入buf中;
④比较buf中从偏移量off开始的剩余字节数是否大于等于应读写的字节数len,如果是,则将从off开始的buf中的len长度的内容读入到text[]中;否则,将从off开始的buf中的剩余内容读入到text[]中;
⑤将读写指针增加④中已读字节数,将应读写的字节数len减去④中已读字节数,若len大于0,则转②;否则转⑥;
⑥使用free()释放①中申请的buf。
⑦返回实际读出的字节数。
16.退出文件系统函数my_exitsys()
(1)对应命令:my_exitsys
(2)命令调用格式:my_exitsys
(1)函数设计格式:voidmy_exitsys()
(2)功能:退出文件系统。
(3)输入:无
(4)输出:无。
(5)函数需完成的工作:
①使用C库函数fopen()打开磁盘上的myfsys文件;
②将虚拟磁盘空间中的所有内容保存到磁盘上的myfsys文件中;
③使用c语言的库函数fclose()关闭myfsys文件;
④撤销用户打开文件表,释放其内存空间
⑤释放虚拟磁盘空间。
三、主要数据结构
1.文件控制块
typedefstructFCB{
charfilename[8];//文件名
charexname[3];//文件扩展名
unsignedcharattribute;//文件属性字段,值为0时表示目录文件,值为1时表示数据文件
unsignedshorttime;//文件创建时间
unsignedshortdate;//文件创建日期
unsignedshortfirst;//文件起始盘块号
unsignedlonglength;//文件长度
charfree;//表示目录项是否为空,若值为0,表示空,值为1,表示已分配
}fcb;
2.文件分配表
typedefstructFAT
{
unsignedshortid;//磁盘块的状态(空闲的,最后的,下一个)
}fat;
3.用户打开文件表
typedefstructUSEROPEN
{
charfilename[8];//文件名
charexname[3];//文件扩展名
unsignedcharattribute;//文件属性字段,值为0时表示目录文件,值为1时表示数据文件
unsignedshorttime;//文件创建时间
unsignedshortdate;//文件创建日期
unsignedshortfirst;//文件起始盘块号
unsignedlonglength;//文件长度(对数据文件是字节数,对目录文件可以是目录项个数)
charfree;//表示目录项是否为空,若值为0,表示空,值为1,表示已分配
unsignedshortdirno;//相应打开文件的目录项在父目录文件中的盘块号
intdiroff;//相应打开文件的目录项在父目录文件的dirno盘块中的目录项序号
chardir[80];//相应打开文件所在的路径名,这样方便快速检查出指定文件是否已经打开
intfather;//父目录在打开文件表项的位置
intcount;//读写指针在文件中的位置,文件的总字符数
charfcbstate;//是否修改了文件的FCB的内容,如果修改了置为1,否则为0
chartopenfile;//表示该用户打开表项是否为空,若值为0,表示为空,否则表示已被某打开文件占据
}useropen;
4.引导块
typedefstructBLOCK0
{
charmagic[10];//文件系统魔数
charinformation[200];//存储一些描述信息,如磁盘块大小、磁盘块数量、最多打开文件数等
unsignedshortroot;//根目录文件的起始盘块号
unsignedchar*startblock;//虚拟磁盘上数据区开始位置
}block0;
四、主要函数
voidstartsys();//进入文件系统
voidmy_format();//磁盘格式化
voidmy_cd(char*dirname);//更改当前目录
voidmy_mkdir(char*dirname);//创建子目录
voidmy_rmdir(char*dirname);//删除子目录
voidmy_ls();//显示目录
voidmy_create(char*filename);//创建文件
voidmy_rm(char*filename);//删除文件
intmy_open(char*filename);//打开文件
intmy_close(intfd);//关闭文件
intmy_write(intfd);//写文件
intdo_write(intfd,char*text,intlen,charwstyle);//实际写文件
intmy_read(intfd,intlen);//读文件
intdo_read(intfd,intlen,char*text);//实际读文件
voidmy_exitsys();//退出文件系统
unsignedshortfindblock();//寻找空闲盘块
intfindopenfile();//寻找空闲文件表项
五、参考程序
#include\t\t%d/%d/%d\t%02d:%02d:%02d\n" ,fcbptr->filename,(fcbptr->date>>9)+1980,(fcbptr->date>>5)&0x000f,fcbptr->date&0x001f,fcbptr->time>>11,(fcbptr->time>>5)&0x003f,fcbptr->time&0x001f*2);
else
printf("%s.%s\t\t%dB\t\t%d/%d/%d\t%02d:%02d:%02d\t\n",fcbptr->filename,fcbptr->exname,(int)(fcbptr->length),(fcbptr->date>>9)+1980,(fcbptr->date>>5)&0x000f,fcbptr->date&0x1f,fcbptr->time>>11,(fcbptr->time>>5)&0x3f,fcbptr->time&0x1f*2);
}
fcbptr++;
}
}
voidmy_create(char*filename)
{
fcb*fcbptr;
fat*fat1,*fat2;
char*fname,*exname,text[MAXTEXT];
unsignedshortblkno;
intrbn,i;
time_tnow;
structtm*nowtime;
fat1=(fat*)(myvhard+BLOCKSIZE);
fat2=(fat*)(myvhard+BLOCKSIZE);
fname=strtok(filename,".");
exname=strtok(NULL,".");
if(strcmp(fname,"")==0)
{
printf("Error,creatingfilemusthavearightname.\n");
return;
}
if(!exname)
{
printf("Error,creatingfilemusthaveaexternname.\n");
return;
}
openfilelist[curdir].count=0;
rbn=do_read(curdir,openfilelist[curdir].length,text);
fcbptr=(fcb*)text;
for(i=0;i<rbn/sizeof(fcb);i++)
{
if(strcmp(fcbptr->filename,fname)==0&&strcmp(fcbptr->exname,exname)==0)
{
printf("Error,thefilenameisalreadyexist!\n");
return;
}
fcbptr++;
}
fcbptr=(fcb*)text;
for(i=0;i<rbn/sizeof(fcb);i++)
{
if(fcbptr->free==0)
break;
fcbptr++;
}
blkno=findblock();
if(blkno==-1)
return;
(fat1+blkno)->id=END;
(fat2+blkno)->id=END;
now=time(NULL);
nowtime=localtime(&now);
strcpy(fcbptr->filename,fname);
strcpy(fcbptr->exname,exname);
fcbptr->attribute=0x00;
fcbptr->time=nowtime->tm_hour*2048+nowtime->tm_min*32+nowtime->tm_sec/2;
fcbptr->date=(nowtime->tm_year-80)*512+(nowtime->tm_mon+1)*32+nowtime->tm_mday;
fcbptr->first=blkno;
fcbptr->length=0;
fcbptr->free=1;
openfilelist[curdir].count=i*sizeof(fcb);
do_write(curdir,(char*)fcbptr,sizeof(fcb),2);
fcbptr=(fcb*)text;
fcbptr->length=openfilelist[curdir].length;
openfilelist[curdir].count=0;
do_write(curdir,(char*)fcbptr,sizeof(fcb),2);
openfilelist[curdir].fcbstate=1;
}
voidmy_rm(char*filename)
{
fcb*fcbptr;
fat*fat1,*fat2,*fatptr1,*fatptr2;
char*fname,*exname,text[MAXTEXT];
unsignedshortblkno;
intrbn,i;
fat1=(fat*)(myvhard+BLOCKSIZE);
fat2=(fat*)(myvhard+3*BLOCKSIZE);
fname=strtok(filename,".");
exname=strtok(NULL,".");
if(strcmp(fname,"")==0)
{
printf("Error,removingfilemusthavearightname.\n");
return;
}
if(!exname)
{
printf("Error,removingfilemusthaveaexternname.\n");
return;
}
openfilelist[curdir].count=0;
rbn=do_read(curdir,openfilelist[curdir].length,text);
fcbptr=(fcb*)text;
for(i=0;i<rbn/sizeof(fcb);i++)
{
if(strcmp(fcbptr->filename,fname)==0&&strcmp(fcbptr->exname,exname)==0)
break;
fcbptr++;
}
if(i==rbn/sizeof(fcb))
{
printf("Error,thefileisnotexist.\n");
return;
}
blkno=fcbptr->first;
while(blkno!=END)
{
fatptr1=fat1+blkno;
fatptr2=fat2+blkno;
blkno=fatptr1->id;
fatptr1->id=FREE;
fatptr2->id=FREE;
}
strcpy(fcbptr->filename,"");
fcbptr->free=0;
openfilelist[curdir].count=i*sizeof(fcb);
do_write(curdir,(char*)fcbptr,sizeof(fcb),2);
openfilelist[curdir].fcbstate=1;
}
intmy_open(char*filename)
{
fcb*fcbptr;
char*fname,exname[3],*str,text[MAXTEXT];
intrbn,fd,i;
fname=strtok(filename,".");
str=strtok(NULL,".");
if(str)
strcpy(exname,str);
else
strcpy(exname,"");
for(i=0;i<MAXOPENFILE;i++)//在用户打开文件数组查找看当前文件是否已经打开
{
if(strcmp(openfilelist[i].filename,fname)==0&&strcmp(openfilelist[i].exname,exname)==0&&i!=curdir)
{
printf("Error,thefileisalreadyopen.\n");
return-1;
}
}
openfilelist[curdir].count=0;
rbn=do_read(curdir,openfilelist[curdir].length,text);
fcbptr=(fcb*)text;
for(i=0;i<rbn/sizeof(fcb);i++)//在当前目录下找要打开的文件是否存在
{
if(strcmp(fcbptr->filename,fname)==0&&strcmp(fcbptr->exname,exname)==0)
break;
fcbptr++;
}
if(i==rbn/sizeof(fcb))
{
printf("Error,thefileisnotexist.\n");
return-1;
}
fd=findopenfile();//寻找空闲文件表项
if(fd==-1)
return-1;
strcpy(openfilelist[fd].filename,fcbptr->filename);
strcpy(openfilelist[fd].exname,fcbptr->exname);
openfilelist[fd].attribute=fcbptr->attribute;
openfilelist[fd].time=fcbptr->time;
openfilelist[fd].date=fcbptr->date;
openfilelist[fd].first=fcbptr->first;
openfilelist[fd].length=fcbptr->length;
openfilelist[fd].free=fcbptr->free;
openfilelist[fd].dirno=openfilelist[curdir].first;
openfilelist[fd].diroff=i;
strcpy(openfilelist[fd].dir,openfilelist[curdir].dir);
strcat(openfilelist[fd].dir,filename);
if(fcbptr->attribute&0x20)
strcat(openfilelist[fd].dir,"\\");
openfilelist[fd].father=curdir;
openfilelist[fd].count=0;
openfilelist[fd].fcbstate=0;
openfilelist[fd].topenfile=1;
returnfd;
}
intmy_close(intfd)
{
fcb*fcbptr;
intfather;
if(fd<0||fd>=MAXOPENFILE)
{
printf("Error,thefileisnotexist.\n");
return-1;
}
if(openfilelist[fd].fcbstate)
{
fcbptr=(fcb*)malloc(sizeof(fcb));
strcpy(fcbptr->filename,openfilelist[fd].filename);
strcpy(fcbptr->exname,openfilelist[fd].exname);
fcbptr->attribute=openfilelist[fd].attribute;
fcbptr->time=openfilelist[fd].time;
fcbptr->date=openfilelist[fd].date;
fcbptr->first=openfilelist[fd].first;
fcbptr->length=openfilelist[fd].length;
fcbptr->free=openfilelist[fd].free;
father=openfilelist[fd].father;
openfilelist[father].count=openfilelist[fd].diroff*sizeof(fcb);
do_write(father,(char*)fcbptr,sizeof(fcb),2);
free(fcbptr);
openfilelist[fd].fcbstate=0;
}
strcpy(openfilelist[fd].filename,"");
strcpy(openfilelist[fd].exname,"");
openfilelist[fd].topenfile=0;
returnfather;
}
intmy_write(intfd)
{
fat*fat1,*fat2,*fatptr1,*fatptr2;
intwstyle,len,ll,tmp;
chartext[MAXTEXT];
unsignedshortblkno;
fat1=(fat*)(myvhard+BLOCKSIZE);
fat2=(fat*)(myvhard+3*BLOCKSIZE);
if(fd<0||fd>=MAXOPENFILE)
{
printf("Thefileisnotexist!\n");
return-1;
}
while(1)
{
printf("Pleaseenterthenumberofwritestyle:\n1.cutwrite\t2.coverwrite\t3.addwrite\n");
scanf("%d",&wstyle);
if(wstyle>0&&wstyle<4)
break;
printf("InputError!");
}
getchar();
switch(wstyle)
{
case1://截断写把原文件所占的虚拟磁盘空间重置为1
blkno=openfilelist[fd].first;
fatptr1=fat1+blkno;
fatptr2=fat2+blkno;
blkno=fatptr1->id;
fatptr1->id=END;
fatptr2->id=END;
while(blkno!=END)
{
fatptr1=fat1+blkno;
fatptr2=fat2+blkno;
blkno=fatptr1->id;
fatptr1->id=FREE;
fatptr2->id=FREE;
}
openfilelist[fd].count=0;
openfilelist[fd].length=0;
break;
case2:
openfilelist[fd].count=0;
break;
case3:
openfilelist[fd].count=openfilelist[fd].length;
break;
default:
break;
}
ll=0;
printf("pleaseinputwritedata(endwithCtrl+Z):\n");
while(gets(text))
{
len=strlen(text);
text[len++]='\n';
text[len]='\0';
tmp=do_write(fd,text,len,wstyle);
if(tmp!=-1)
ll+=tmp;
if(tmp<len)
{
printf("WirteError!");
break;
}
}
returnll;//实际写的字节数
}
intdo_write(intfd,char*text,intlen,charwstyle)
{
fat*fat1,*fat2,*fatptr1,*fatptr2;
unsignedchar*buf,*blkptr;
unsignedshortblkno,blkoff;
inti,ll;
fat1=(fat*)(myvhard+BLOCKSIZE);
fat2=(fat*)(myvhard+3*BLOCKSIZE);
buf=(unsignedchar*)malloc(BLOCKSIZE);
if(buf==NULL)
{
printf("mallocfailed!\n");
return-1;
}
blkno=openfilelist[fd].first;
blkoff=openfilelist[fd].count;
fatptr1=fat1+blkno;
fatptr2=fat2+blkno;
while(blkoff>=BLOCKSIZE)
{
blkno=fatptr1->id;
if(blkno==END)
{
blkno=findblock();
if(blkno==-1)
{
free(buf);
return-1;
}
fatptr1->id=blkno;
fatptr2->id=blkno;
fatptr1=fat1+blkno;
fatptr2=fat2+blkno;
fatptr1->id=END;
fatptr2->id=END;
}
else
{
fatptr1=fat1+blkno;
fatptr2=fat2+blkno;
}
blkoff=blkoff-BLOCKSIZE;//让blkoff定位到文件最后一个磁盘块的读写位置
}
ll=0;//实际写的字节数
while(ll<len)//len是用户输入的字节数
{
blkptr=(unsignedchar*)(myvhard+blkno*BLOCKSIZE);
for(i=0;i<BLOCKSIZE;i++)
buf[i]=blkptr[i];
for(;blkoff<BLOCKSIZE;blkoff++)
{
buf[blkoff]=text[ll++];
openfilelist[fd].count++;
if(ll==len)
break;
}
for(i=0;i<BLOCKSIZE;i++)
blkptr[i]=buf[i];
if(ll<len)//如果一个磁盘块写不下,则再分配一个磁盘块
{
blkno=fatptr1->id;
if(blkno==END)
{
blkno=findblock();
if(blkno==-1)
break;
fatptr1->id=blkno;
fatptr2->id=blkno;
fatptr1=fat1+blkno;
fatptr2=fat2+blkno;
fatptr1->id=END;
fatptr2->id=END;
}
else
{
fatptr1=fat1+blkno;
fatptr2=fat2+blkno;
}
blkoff=0;
}
}
if(openfilelist[fd].count>openfilelist[fd].length)
openfilelist[fd].length=openfilelist[fd].count;
openfilelist[fd].fcbstate=1;
free(buf);
returnll;
}
intmy_read(intfd,intlen)
{
chartext[MAXTEXT];
intll;
if(fd<0||fd>=MAXOPENFILE)
{
printf("TheFileisnotexist!\n");
return-1;
}
openfilelist[fd].count=0;
ll=do_read(fd,len,text);//ll是实际读出的字节数
if(ll!=-1)
printf("%s",text);
else
printf("ReadError!\n");
returnll;
}
intdo_read(intfd,intlen,char*text)
{
fat*fat1,*fatptr;
unsignedchar*buf,*blkptr;
unsignedshortblkno,blkoff;
inti,ll;
fat1=(fat*)(myvhard+BLOCKSIZE);
buf=(unsignedchar*)malloc(BLOCKSIZE);
if(buf==NULL)
{
printf("mallocfailed!\n");
return-1;
}
blkno=openfilelist[fd].first;
blkoff=openfilelist[fd].count;
if(blkoff>=openfilelist[fd].length)
{
puts("Readoutofrange!");
free(buf);
return-1;
}
fatptr=fat1+blkno;
while(blkoff>=BLOCKSIZE)//blkoff为最后一块盘块剩余的容量
{
blkno=fatptr->id;
blkoff=blkoff-BLOCKSIZE;
fatptr=fat1+blkno;
}
ll=0;
while(ll<len)
{
blkptr=(unsignedchar*)(myvhard+blkno*BLOCKSIZE);
for(i=0;i<BLOCKSIZE;i++)//将最后一块盘块的内容读取到buf中
buf[i]=blkptr[i];
for(;blkoff<BLOCKSIZE;blkoff++)
{
text[ll++]=buf[blkoff];
openfilelist[fd].count++;
if(ll==len||openfilelist[fd].count==openfilelist[fd].length)
break;
}
if(ll<len&&openfilelist[fd].count!=openfilelist[fd].length)
{
blkno=fatptr->id;
if(blkno==END)
break;
blkoff=0;
fatptr=fat1+blkno;
}
}
text[ll]='\0';
free(buf);
returnll;
}
voidmy_exitsys()
{
FILE*fp;
while(curdir)
curdir=my_close(curdir);
fp=fopen(myfilename,"w");
fwrite(myvhard,SIZE,1,fp);
fclose(fp);
free(myvhard);
}
unsignedshortfindblock()
{
unsignedshorti;
fat*fat1,*fatptr;
fat1=(fat*)(myvhard+BLOCKSIZE);
for(i=7;i<SIZE/BLOCKSIZE;i++)
{
fatptr=fat1+i;
if(fatptr->id==FREE)
returni;
}
printf("Error,Can'tfindfreeblock!\n");
return-1;
}
intfindopenfile()
{
inti;
for(i=0;i<MAXTEXT;i++)
{
if(openfilelist[i].topenfile==0)
returni;
}
printf("Error,opentoomanyfiles!\n");
return-1;
}
intmain()
{
charcmd[15][10]={"cd","mkdir","rmdir","ls","create","rm","open","close","write","read","exit"};
chars[30],*sp;
intcmdn,flag=1,i;
startsys();
printf("*********************FileSystemV1.0*******************************\n\n");
printf("命令名\t\t命令参数\t\t命令说明\n\n");
printf("cd\t\t目录名(路径名)\t\t切换当前目录到指定目录\n");
printf("mkdir\t\t目录名\t\t\t在当前目录创建新目录\n");
printf("rmdir\t\t目录名\t\t\t在当前目录删除指定目录\n");
printf("ls\t\t无\t\t\t显示当前目录下的目录和文件\n");
printf("create\t\t文件名\t\t\t在当前目录下创建指定文件\n");
printf("rm\t\t文件名\t\t\t在当前目录下删除指定文件\n");
printf("open\t\t文件名\t\t\t在当前目录下打开指定文件\n");
printf("write\t\t无\t\t\t在打开文件状态下,写该文件\n");
printf("read\t\t无\t\t\t在打开文件状态下,读取该文件\n");
printf("close\t\t无\t\t\t在打开文件状态下,读取该文件\n");
printf("exit\t\t无\t\t\t退出系统\n\n");
printf("*********************************************************************\n\n");
while(flag)
{
printf("%s>",openfilelist[curdir].dir);
gets(s);
cmdn=-1;
if(strcmp(s,""))
{
sp=strtok(s,"");
for(i=0;i<15;i++)
{
if(strcmp(sp,cmd[i])==0)
{
cmdn=i;
break;
}
}
// printf("%d\n",cmdn);
switch(cmdn)
{
case0:
sp=strtok(NULL,"");
if(sp&&(openfilelist[curdir].attribute&0x20))
my_cd(sp);
else
printf("Pleaseinputtherightcommand.\n");
break;
case1:
sp=strtok(NULL,"");
if(sp&&(openfilelist[curdir].attribute&0x20))
my_mkdir(sp);
else
printf("Pleaseinputtherightcommand.\n");
break;
case2:
sp=strtok(NULL,"");
if(sp&&(openfilelist[curdir].attribute&0x20))
my_rmdir(sp);
else
printf("Pleaseinputtherightcommand.\n");
break;
case3:
if(openfilelist[curdir].attribute&0x20)
my_ls();
else
printf("Pleaseinputtherightcommand.\n");
break;
case4:
sp=strtok(NULL,"");
if(sp&&(openfilelist[curdir].attribute&0x20))
my_create(sp);
else
printf("Pleaseinputtherightcommand.\n");
break;
case5:
sp=strtok(NULL,"");
if(sp&&(openfilelist[curdir].attribute&0x20))
my_rm(sp);
else
printf("Pleaseinputtherightcommand.\n");
break;
case6:
sp=strtok(NULL,"");
if(sp&&(openfilelist[curdir].attribute&0x20))
{
if(strchr(sp,'.'))//查找sp中'.'首次出现的位置
curdir=my_open(sp);
else
printf("theopenfileshouldhaveexname.\n");
}
else
printf("Pleaseinputtherightcommand.\n");
break;
case7:
if(!(openfilelist[curdir].attribute&0x20))
curdir=my_close(curdir);
else
printf("Nofilesopened.\n");
break;
case8:
if(!(openfilelist[curdir].attribute&0x20))
my_write(curdir);
else
printf("Nofilesopened.\n");
break;
case9:
if(!(openfilelist[curdir].attribute&0x20))
my_read(curdir,openfilelist[curdir].length);
else
printf("Nofilesopened.\n");
break;
case10:
if(openfilelist[curdir].attribute&0x20)
{
my_exitsys();
flag=0;
}
else
printf("Pleaseinputtherightcommand.\n");
break;
default:
printf("Pleaseinputtherightcommand.\n");
break;
}
}
}
return0;
}
关注公众号:Time木
回复:操作系统实验
可获得相关代码,数据,文档
回复:操作系统试卷
可获取操作系统试卷整理
更多大学课业实验实训可关注公众号回复相关关键词
学艺不精,若有错误还望指点