Python_基于statsmodel包画Bland altman plot (Mean Difference Plot)用于预测结果分析
画Bland Altman plot (Mean Difference Plot)
- API接口介绍
- 使用示例
- 结果
- 自行实现绘制Bland Altman plot的函数
- References:
本文基于Python包——statsmodel的Bland Altman plot的画法,statsmodel的官方介绍参考: https://www.statsmodels.org/stable/index.html
API接口介绍

上图为mean_diff_plot的API接口,其中各个参数:
m1 & m2: 1-d array, 其中一个是estimated value sequence, 另一个是ground-truth value sequence;
ax: 如果ax为None, 则会创建一个figure; 否则,该mean_diff_plot会绘制在该参数指定的axis上;
scatter_kwds: dict format, 指定了 m1和m2中的值组成的点对pair的呈现格式;
mean_line_kwds: dict format, 指定了mean line的呈现格式;
limit_lines_kwds:dict format, 制定了limit line的呈现格式;
使用示例
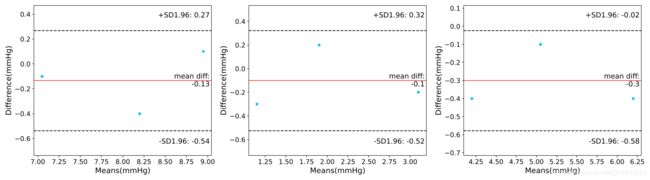
下面的示例代码: 将三张Bland-Altman subplot画在同一张figure中, 并将该figure保存在dir目录下, 保存格式为: jpg和svg.
```python
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
import os
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import statsmodels.api as sm
def bland_altman_plot_wrap(gts, preds, alg_name, dir='../result', random_seed=0, calibration=False):
fig, (ax1, ax2, ax3) = plt.subplots(1, 3, figsize=(18, 5))
sm.graphics.mean_diff_plot(np.array(gts[0]), np.array(preds[0]), ax=ax1, scatter_kwds=dict(color='deepskyblue'), mean_line_kwds=dict(color='red'), limit_lines_kwds=dict(color='black', linewidth=1.5)) # m1, m2: 1-dim vector, modified source file.
sm.graphics.mean_diff_plot(np.array(gts[1]), np.array(preds[1]), ax=ax2, scatter_kwds=dict(color='deepskyblue'), mean_line_kwds=dict(color='red'), limit_lines_kwds=dict(color='black', linewidth=1.5))
sm.graphics.mean_diff_plot(np.array(gts[2]), np.array(preds[2]), ax=ax3, scatter_kwds=dict(color='deepskyblue'), mean_line_kwds=dict(color='red'), limit_lines_kwds=dict(color='black', linewidth=1.5))
fig_name = 'bland-altman-plot_{}_{}_seed-{}'.format(alg_name, calibration, random_seed)
#plt.subplots_adjust(top=0.1, bottom=0, left=0, right=0.1)
plt.savefig(os.path.join(dir, fig_name + '.svg'), format='svg')
plt.savefig(os.path.join(dir, fig_name + '.jpg'))
if __name__ == '__main__':
# 20210419
gts = [[7, 8, 9], [1, 2, 3], [4, 5, 6]]
preds = [[7.1, 8.4, 8.9], [1.3, 1.8, 3.2], [4.4, 5.1, 6.4]]
dir = '../temp'
bland_altman_plot_wrap(gts, preds, 'xx', dir=dir, random_seed=0, calibration=False)
结果
自行实现绘制Bland Altman plot的函数
自行实现函数:sm.graphics.mean_diff_plot, 实现如下:
def bland_altman_plot_my(data1, data2, *args, **kwargs):
'''
'''
data1 = np.asarray(data1)
data2 = np.asarray(data2)
mean = np.mean([data1, data2], axis=0)
diff = data1 - data2 # Difference between data1 and data2
md = np.mean(diff) # Mean of the difference
sd = np.std(diff, axis=0) # Standard deviation of the difference
plt.scatter(mean, diff, *args, **kwargs)
plt.axhline(md, color='gray', linestyle='--')
plt.axhline(md + 1.96*sd, color='gray', linestyle='--')
plt.axhline(md - 1.96*sd, color='gray', linestyle='--')
References:
1.http://www.codesd.com/item/bland-altman-in-python.html
2.https://www.statsmodels.org/stable/index.html