C++异常
文章目录
- C++异常
-
- 异常语法
-
- 代码示例
- 栈解旋
-
- 示例代码
- noexcept
-
- 代码示例
- 异常的声明周期
-
- 示例代码
- 异常的多态使用
-
- 代码示例
- C++标准异常库
-
- 代码示例
- 重写自己的异常
-
- 示例代码
C++异常
异常是处理程序中的错误。所谓的错误时指程序运行的过程中发生的一些异常事件(如:除零错误,数组下标越界,所要读取的文件不存在,空指针,内存不足等)
C++异常机制相比C语言异常处理的优势:
- 函数返回值可以忽略,但是异常不可以忽略,并且容易和正常结果混淆;
- 如果程序出现异常,但是没有被捕获,程序就会终止;
异常语法
代码示例
#include 栈解旋
异常抛出后,从try起,到异常被抛出前,这期间在栈上构造的所有对象都会被自动析构。析构的顺序与构造的顺序相反,这一过程称为栈的解旋。
示例代码
#include noexcept
- 为了加强程序可读性,可以在函数声明中指定是否可以抛出异常。
例如:void func() noexcept(true);表示函数函数无法抛出异常, 后面的true可省略
例如:void func() noexcept(false);表示函数函数可能抛出异常
代码示例
#include 异常的声明周期
throw 的异常是有类型的,可以是数字、字符串、类对象。throw的异常是有类型的,catch需要严格匹配异常的类型。
示例代码
#include 注意: 抛出指针的时候记得析构, 推荐test5()的这种方式,可以提高效率。
异常的多态使用
与正常多态使用无差别
代码示例
#include C++标准异常库
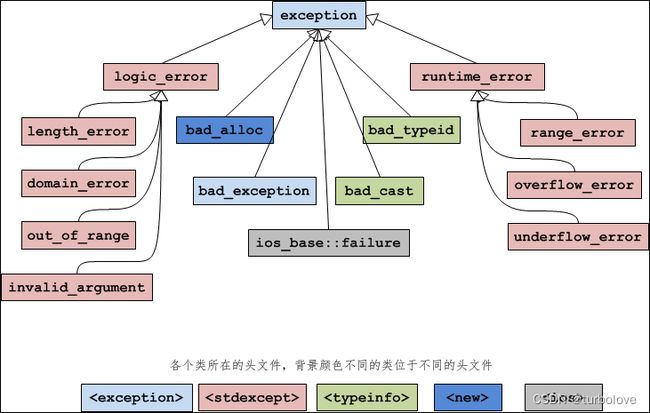
标准库中有很多的异常类,它们是通过类继承组织起来的。
exception 类的直接派生类:
| 异常名称 | 说 明 |
|---|---|
| logic_error | 逻辑错误。 |
| runtime_error | 运行时错误。 |
| bad_alloc | 使用 new 或 new[ ] 分配内存失败时抛出的异常。 |
| bad_typeid | 使用 typeid 操作一个 NULL 指针,而且该指针是带有虚函数的类,这时抛出 bad_typeid 异常。 |
| bad_cast | 使用 dynamic_cast 转换失败时抛出的异常。 |
| ios_base::failure | io 过程中出现的异常。 |
| bad_exception | 这是个特殊的异常,如果函数的异常列表里声明了 bad_exception 异常,当函数内部抛出了异常列表中没有的异常时,如果调用的 unexpected() 函数中抛出了异常,不论什么类型,都会被替换为 bad_exception 类型。 |
logic_error 的派生类:
| 异常名称 | 说 明 |
|---|---|
| length_error | 试图生成一个超出该类型最大长度的对象时抛出该异常,例如 vector 的 resize 操作。 |
| domain_error | 参数的值域错误,主要用在数学函数中,例如使用一个负值调用只能操作非负数的函数。 |
| out_of_range | 超出有效范围。 |
| invalid_argument | 参数不合适。在标准库中,当利用string对象构造 bitset 时,而 string 中的字符不是 0 或1 的时候,抛出该异常。 |
runtime_error 的派生类:
| 异常名称 | 说 明 |
|---|---|
| range_error | 计算结果超出了有意义的值域范围。 |
| overflow_error | 算术计算上溢。 |
| underflow_error | 算术计算下溢。 |
代码示例
#include 重写自己的异常
使用继承实现一个自己的异常(我这里是一个简单的实现)
示例代码
#include