Spring系列七:声明式事务
声明式事务
和AOP有密切的联系, 是AOP的一个实际的应用.
事务分类简述
●分类
1.编程式事务:
示意代码, 传统方式
Connection connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
try {
//1.先设置事务不要自动提交
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
//2.进行各种crud
//多个表的修改, 添加, 删除
//3.提交
connection.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
//4.回滚
connection.rollback();
}
声明式事务案例
需求分析
我们需要去处理用户购买商品的业务逻辑. 分析: 当一个用户要去购买商品应该包含三个步骤
- 通过商品获取价格
- 购买商品(某人购买商品, 修改用户的余额)
- 修改库存量
其实我们也可以看到, 这时, 需要涉及到三张表: 用户表, 商品表, 商品存量表. 应该使用事务管理.
解决方案分析
1.使用传统的编程事务来处理, 将代码写到一起 [缺点: 代码冗余, 效率低, 不利于扩展, 优点是简单, 好理解]
Connection connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
try {
//1.先设置事务不要自动提交
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
//2.进行各种crud
//多个表的修改, 添加, 删除
select from 商品表 => 获取价格
//修改用户余额 update…
//修改库存量 update
//3.提交
connection.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
//4.回滚
connection.rollback();
}
2.使用Spring的声明式事务处理, 可以将上面三个子步骤分别写成一个方法, 然后统一管理. [这是Spring很牛的地方, 在开发使用很多, 优点是无代码冗余, 效率高, 扩展方便, 缺点是理解较困难 ==> 底层使用AOP(动态代理+动态绑定+反射+注解) => 看Debug源码]
代码实现
1.先创建商品系统的数据库和表
USE spring;
-- 用户表
CREATE TABLE user_account (
user_id INT UNSIGNED PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
user_name VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL DEFAULT '',
money DOUBLE NOT NULL DEFAULT 0.0
)CHARSET=utf8;
INSERT INTO user_account VALUES(1, '张三', 300);
INSERT INTO user_account VALUES(2, '李四', 400);
UPDATE user_account SET money = money - 1 WHERE user_id = '1';
SELECT * FROM user_account;
-- 商品表
CREATE TABLE goods (
goods_id INT UNSIGNED PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
goods_name VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL DEFAULT '',
price DOUBLE NOT NULL DEFAULT 0.0
)CHARSET=utf8;
INSERT INTO goods VALUES(1, '电风扇', '13.5');
INSERT INTO goods VALUES(2, '小台灯', '15.5');
SELECT price FROM goods WHERE goods_id = 1;
-- 商品库存表
CREATE TABLE goods_amount (
goods_id INT UNSIGNED PRIMARY KEY AUTO_INCREMENT,
goods_num INT UNSIGNED DEFAULT 0
)CHARSET=utf8;
INSERT INTO `goods_amount` VALUES(1, 100);
INSERT INTO goods_amount VALUES(2, 200);
INSERT INTO goods_amount VALUES(3, 300);
UPDATE goods_amount SET goods_num = goods_num - 1 WHERE goods_id = '1';
SELECT * FROM goods_amount;
2.在spring项目com.zzw.spring.tx.dao包下新建GoodsDao
@Repository //将GoodsDao-对象 注入到spring容器
public class GoodsDao {
@Resource
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
/**
* 根据商品id返回价格
* @param id
* @return
*/
public Float queryPriceById(Integer goods_id) {
String sql = "SELECT price FROM goods WHERE goods_id = ?";
Float price = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, Float.class, goods_id);
return price;
}
/**
* 修改用户的余额 [减少用户余额]
* @param user_id
* @param money
*/
public void updateBalance(Integer user_id, Float money) {
String sql = "UPDATE user_account SET money = money - ? WHERE user_id = ?";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql, money, user_id);
}
/**
* 修改商品的库存量
* @param goods_id
* @param amount
*/
public void updateAmount(Integer goods_id, Integer amount) {
String sql = "UPDATE goods_amount SET goods_num = goods_num - ? WHERE goods_id = ?";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql, amount, goods_id);
}
}
3.src目录下, 新建容器配置文件 tx_ioc.xml
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.zzw.spring.tx.dao"/>
beans>
4.在com.zzw.spring.tx包下新建测试类TxTest
public class TxTest {
@Test
public void queryPriceById() {
//获取到容器
ApplicationContext ioc =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("tx_ioc.xml");
GoodsDao goodsDao = ioc.getBean(GoodsDao.class);
Float price = goodsDao.queryPriceById(1);
System.out.println("id等于1的价格=" + price);
}
}
结果报错 No qualifying bean of type 'org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate' available
因为没有注入JdbcTemplate对象, 正确配置tx_ioc.xml文件
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.zzw.spring.tx.dao"/>
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
<bean class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource" id="dataSource">
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.user}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.pwd}"/>
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
bean>
<bean class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate" id="jdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
bean>
beans>
再次测试
public class TxTest {
@Test
public void queryPriceById() {
//获取到容器
ApplicationContext ioc =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("tx_ioc.xml");
GoodsDao goodsDao = ioc.getBean(GoodsDao.class);
Float price = goodsDao.queryPriceById(1);
System.out.println("id等于1的价格=" + price);
}
@Test
public void updateBalance() {
//获取到容器
ApplicationContext ioc =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("tx_ioc.xml");
GoodsDao goodsDao = ioc.getBean(GoodsDao.class);
goodsDao.updateBalance(1, 1f);
System.out.println("用户余额减少成功");
}
@Test
public void updateAmount() {
//获取到容器
ApplicationContext ioc =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("tx_ioc.xml");
GoodsDao goodsDao = ioc.getBean(GoodsDao.class);
goodsDao.updateAmount(1, 1);
System.out.println("商品减少库存量成功");
}
}
5.在com.zzw.spring.tx.service包下新建GoodsService, 验证不使用事务就会出现数据不一致现象.
@Service //将GoodsService-对象 注入到spring容器
public class GoodsService {
//定义属性GoodsDao
@Resource
private GoodsDao goodsDao;
/**
* 编写一个方法, 完成用户购买商品的业务
* 这里主要是讲解事务管理
* @param userId 用户id
* @param goodsId 商品id
* @param amount 购买数量
*/
public void buyGoods(int userId, int goodsId, int amount) {
//输出购买相关信息
System.out.println("用户购买信息 用户id=" + userId + ", 商品id=" +
goodsId + ", 购买数量=" + amount);
//1.得到商品的价格
Float price = goodsDao.queryPriceById(goodsId);
//2.减少用户的余额
goodsDao.updateBalance(userId, price * amount);
//3.减少库存量
goodsDao.updateAmount(goodsId, amount);
System.out.println("用户购买成功");
}
}
修改xml要扫描的包
<context:component-scan base-package="com.zzw.spring.tx"/>
测试
public class TxTest {
//测试用户购买商品业务
@Test
public void buyGoodsTest() {
//获取到容器
ApplicationContext ioc =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("tx_ioc.xml");
GoodsService goodsService = ioc.getBean(GoodsService.class);
goodsService.buyGoods(1,1,1);
}
}
验证不使用事务就会出现数据不一致现象. 故意修改MonsterDao的updateAmount语句
参考: 家居购, 数据不一致问题
/**
* 修改商品的库存量
* @param goods_id
* @param amount
*/
public void updateAmount(Integer goods_id, Integer amount) {
String sql = "UPDATEX goods_amount SET goods_num = goods_num - ? WHERE goods_id = ?";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql, amount, goods_id);
}
结论:不能出现部分正确的情况, 要成为一个整体, 要有原子性.
6.加入@Transactional注解
@Service //将GoodsService-对象 注入到spring容器
public class GoodsService {
//定义属性GoodsDao
@Resource
private GoodsDao goodsDao;
/**
* @Transactional 注解解读
* 1.使用@Transactional 可以进行声明式事务控制
* 2.即将标识的方法中的对数据库的操作作为一个事务管理
* @param userId
* @param goodsId
* @param amount
*/
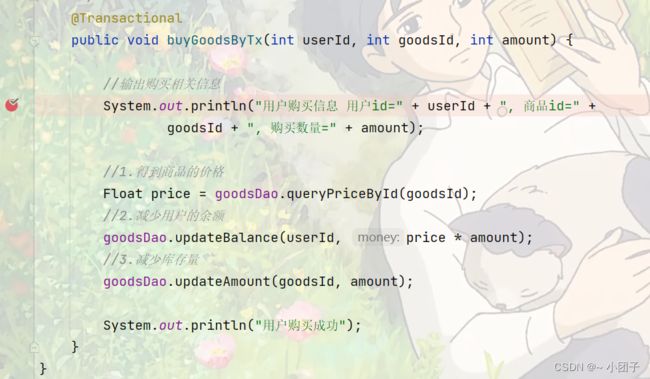
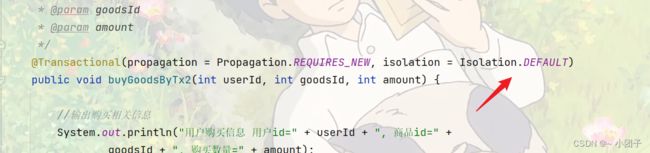
@Transactional
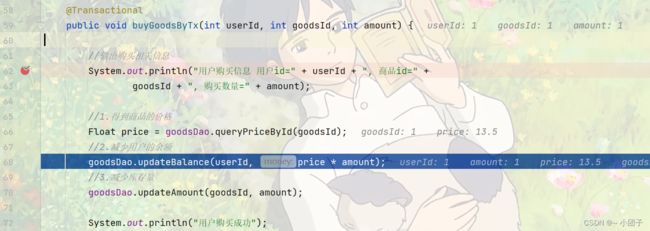
public void buyGoodsByTx(int userId, int goodsId, int amount) {
//输出购买相关信息
System.out.println("用户购买信息 用户id=" + userId + ", 商品id=" +
goodsId + ", 购买数量=" + amount);
//1.得到商品的价格
Float price = goodsDao.queryPriceById(goodsId);
//2.减少用户的余额
goodsDao.updateBalance(userId, price * amount);
//3.减少库存量
goodsDao.updateAmount(goodsId, amount);
System.out.println("用户购买成功");
}
}
测试
public class TxTest {
//测试用户购买商品业务
@Test
public void buyGoodsTestByTx() {
//获取到容器
ApplicationContext ioc =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("tx_ioc.xml");
GoodsService goodsService = ioc.getBean(GoodsService.class);
//这里我们调用的是进行了事务声明的方法
goodsService.buyGoodsByTx(1,1,1);
}
}
发现事务没有发挥作用. 也就是只加一个注解是没有什么作用的.
解决方案: 在tx_ioc.xml加入如下配置, 事务得到控制
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="com.zzw.spring.tx"/>
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc.properties"/>
<bean class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource" id="dataSource">
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.user}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.pwd}"/>
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
bean>
<bean class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate" id="jdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
bean>
<bean class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager" id="transactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
bean>
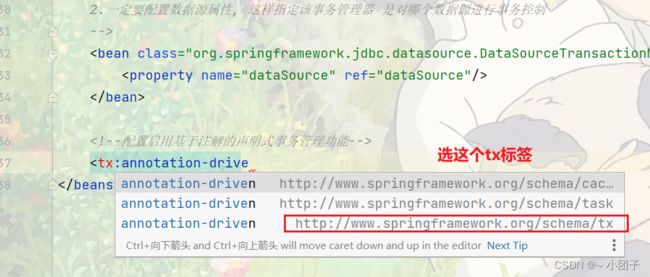
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/>
beans>
7.debug事务管理器
/**
* @Transactional 注解解读
* 1.使用@Transactional 可以进行声明式事务控制
* 2.即将标识的方法中的对数据库的操作作为一个事务管理
* 3.@Transaction 底层使用的仍然是AOP
* 4.底层使用动态代理对象来调用buyGoodsByTx
* 5.在执行buyGoodsByTx()方法时, 先调用 事务管理器的 doBegin(), 再调用buyGoodsByTx()
* 如果执行没有发生异常, 则调用 事务管理器的 doCommit(), 如果发生异常, 调用 事务管理器的
* doRollback()
* @param userId
* @param goodsId
* @param amount
*/
@Transactional
public void buyGoodsByTx(int userId, int goodsId, int amount) {
//输出购买相关信息
System.out.println("用户购买信息 用户id=" + userId + ", 商品id=" +
goodsId + ", 购买数量=" + amount);
//1.得到商品的价格
Float price = goodsDao.queryPriceById(goodsId);
//2.减少用户的余额
goodsDao.updateBalance(userId, price * amount);
//3.减少库存量
goodsDao.updateAmount(goodsId, amount);
System.out.println("用户购买成功");
}
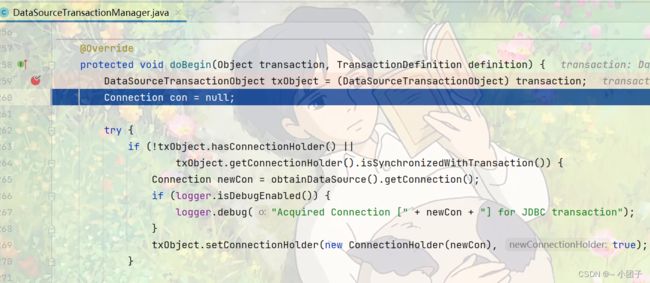
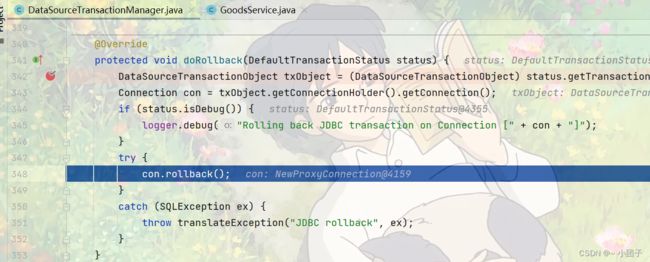
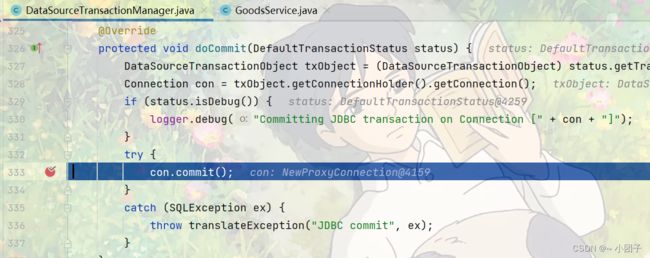
在doBegin方法中将connection设置为不自动提交
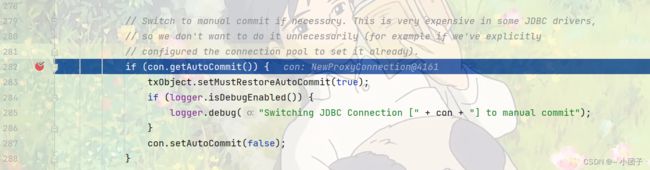
当运行到updateAmount会报错, 出错后进入rollback方法
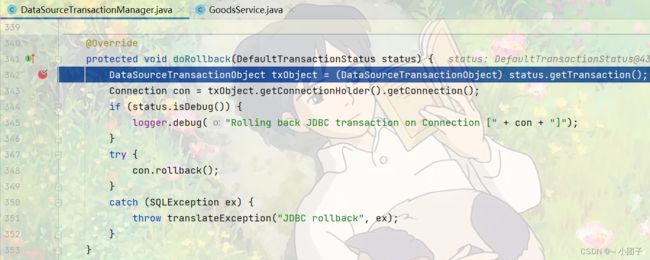
doBegin相当于前置通知
doCommit相当于返回通知
doRollback相当于异常通知
事务传播机制问题
1.当有多个事务处理并存时, 如何控制?
2.比如用户去购买两次商品(使用不同的方法), 每个方法都是一个事务, 如何控制呢?
事务传播机制种类
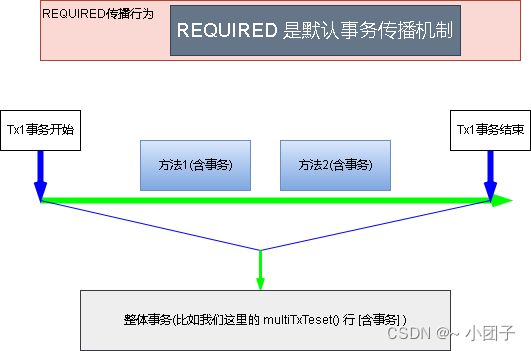
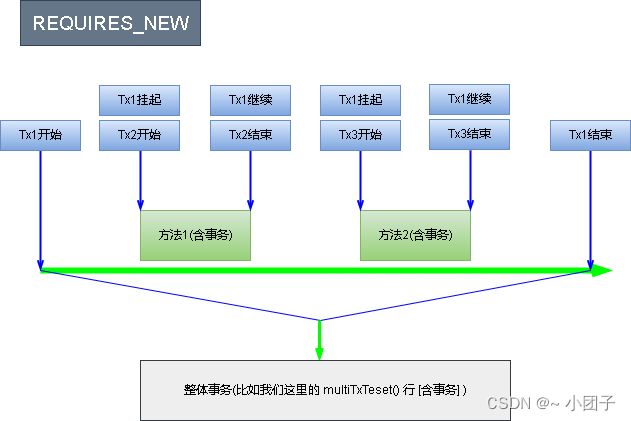
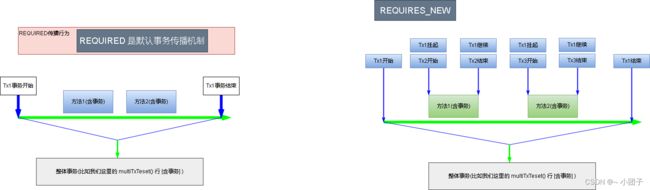
事务传播的属性/种类机制分析, 重点分析 required 和 requires_new 两种事务传播属性, 其它忽略.
| 传播属性 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| REQUIRED | 如果有事务在运行, 当前的方法就在这个事务内运行. 否则, 就启动一个新的事务, 并在自己的事务内运行. |
| REQUIRES_NEW | 当前的方法必须启动新事务, 并在它自己的事务内运行, 如果有事务正在运行, 应该将它挂起 |
事务传播机制图解
1.如果设置为REQUIRES_NEW
buyGoods2如果错误, 不会影响到 buyGoods(), 反之亦然, 即他们的事务是独立的
2.如果设置为REQUIRED
buyGoods2和buyGoods是一个整体, 只要有方法的事务错误, 那么两个方法都不会执行成功.
事务传播机制应用实例
需求说明
- 比如用户去购买两次商品(使用不同的方法), 每个方法都是一个事务, 如何控制呢? => 这就是事务的传播机制
案例
GoodsDao
@Repository //将GoodsDao-对象 注入到spring容器
public class GoodsDao {
@Resource
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
/**
* 根据商品id返回价格
* @param id
* @return
*/
public Float queryPriceById(Integer goods_id) {
String sql = "SELECT price FROM goods WHERE goods_id = ?";
Float price = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, Float.class, goods_id);
return price;
}
/**
* 修改用户的余额 [减少用户余额]
* @param user_id
* @param money
*/
public void updateBalance(Integer user_id, Float money) {
String sql = "UPDATE user_account SET money = money - ? WHERE user_id = ?";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql, money, user_id);
}
/**
* 修改商品的库存量
* @param goods_id
* @param amount
*/
public void updateAmount(Integer goods_id, Integer amount) {
String sql = "UPDATE goods_amount SET goods_num = goods_num - ? WHERE goods_id = ?";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql, amount, goods_id);
}
public Float queryPriceById2(Integer goods_id) {
String sql = "SELECT price FROM goods WHERE goods_id = ?";
Float price = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, Float.class, goods_id);
return price;
}
public void updateBalance2(Integer user_id, Float money) {
String sql = "UPDATE user_account SET money = money - ? WHERE user_id = ?";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql, money, user_id);
}
public void updateAmount2(Integer goods_id, Integer amount) {
String sql = "UPDATE goods_amount SET goods_num = goods_num - ? WHERE goods_id = ?";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql, amount, goods_id);
}
}
GoodsService
@Service //将GoodsService-对象 注入到spring容器
public class GoodsService {
//定义属性GoodsDao
@Resource
private GoodsDao goodsDao;
/**
* @Transactional 注解解读
* 1.使用@Transactional 可以进行声明式事务控制
* 2.即将标识的方法中的对数据库的操作作为一个事务管理
* 3.@Transaction 底层使用的仍然是AOP
* 4.底层使用动态代理对象来调用buyGoodsByTx
* 5.在执行buyGoodsByTx()方法时, 先调用 事务管理器的 doBegin(), 再调用buyGoodsByTx()
* 如果执行没有发生异常, 则调用 事务管理器的 doCommit(), 如果发生异常, 调用 事务管理器的
* doRollback()
* @param userId
* @param goodsId
* @param amount
*/
@Transactional
public void buyGoodsByTx(int userId, int goodsId, int amount) {
//输出购买相关信息
System.out.println("用户购买信息 用户id=" + userId + ", 商品id=" +
goodsId + ", 购买数量=" + amount);
//1.得到商品的价格
Float price = goodsDao.queryPriceById(goodsId);
//2.减少用户的余额
goodsDao.updateBalance(userId, price * amount);
//3.减少库存量
goodsDao.updateAmount(goodsId, amount);
System.out.println("用户购买成功");
}
/**
* 这个方法是第二套进行商品购买的方法
* @param userId
* @param goodsId
* @param amount
*/
@Transactional
public void buyGoodsByTx2(int userId, int goodsId, int amount) {
//输出购买相关信息
System.out.println("用户购买信息 用户id=" + userId + ", 商品id=" +
goodsId + ", 购买数量=" + amount);
//1.得到商品的价格
Float price = goodsDao.queryPriceById2(goodsId);
//2.减少用户的余额
goodsDao.updateBalance2(userId, price * amount);
//3.减少库存量
goodsDao.updateAmount2(goodsId, amount);
System.out.println("用户购买成功");
}
}
在com.zzw.spring.tx.service包下新建 MultiplyService
@Service
public class MultiplyService {
@Resource
private GoodsService goodsService;
/**
* 1.multiBuyGoodsByTx 这个方法 有两次购买商品的操作
* 2.buyGoodsByTx 和 buyGoodsByTx2 都是使用了声明式事务
* 3.当前 buyGoodsByTx 和 buyGoodsByTx2 使用的传播属性是默认的, 即REQUIRED
* 即会当做一个整体事务管理, 比如buyGoodsByTx方法成功, 但是buyGoodsByTx2失败,
* 会造成整个事务的回滚, 即会回滚buyGoodsByTx.
*/
public void multiBuyGoodsByTx() {
goodsService.buyGoodsByTx(1, 1, 1);
goodsService.buyGoodsByTx2(1,1,1);
}
}
测试
public class TxTest {
//测试事务的传播机制
@Test
public void multiBuyGoodsByTest() {
//获取到容器
ApplicationContext ioc =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("tx_ioc.xml");
MultiplyService multiplyService = ioc.getBean(MultiplyService.class);
multiplyService.multiBuyGoodsByTx();
System.out.println("ok");
}
}
1.将GoodsDao类下的updateAmount2方法 UPDATE改成UPDATEX, 运行后, 代码回滚, 查看数据库
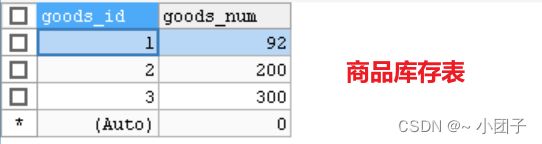
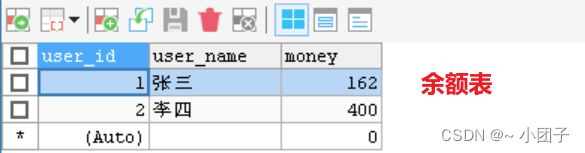
2.在此基础上, 将GoodsService的buyGoodsByTx 和 buyGoodsByTx2 的事务传播属性修改成 REQUIRES_NEW. 查看数据库
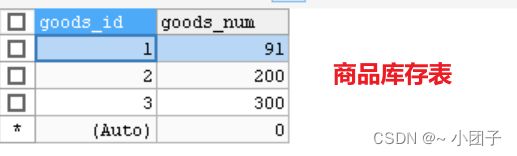
事务隔离级别说明
mysql中的事务隔离级别
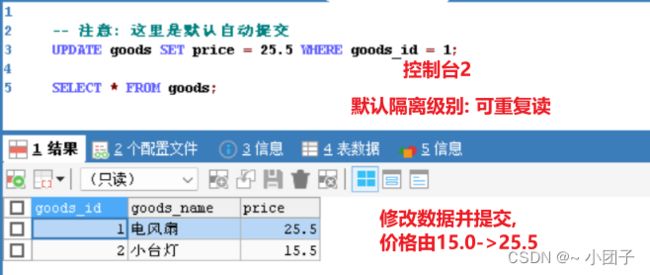
1.声明式事务中, 默认的隔离级别, 就是mysql数据库默认的隔离级别, 一般为 repeatable read
2.看源码可知 Isolation.DEFAULT 是: Use the default isolation level of the underlying datastore.

3.查看数据库的默认隔离级别 selec t @@global.tx_isolation;
事务隔离级别应用实例
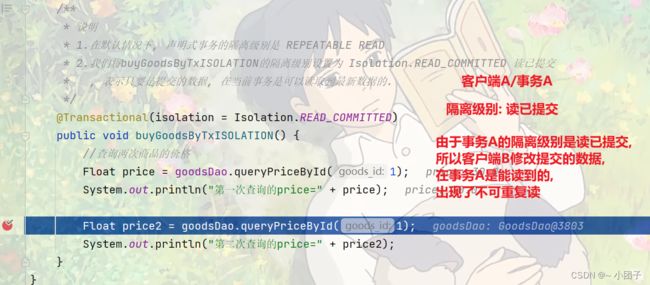
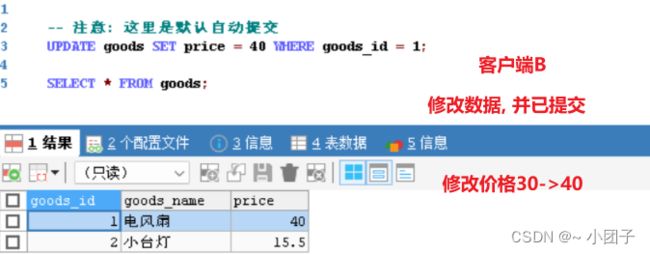
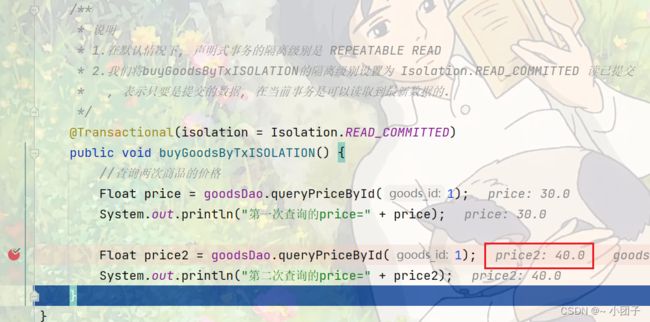
1.修改GoodsService.java, 先测默认隔离级别, 增加方法 buyGoodsByTxISOLATION()
@Service //将GoodsService-对象 注入到spring容器
public class GoodsService {
//定义属性GoodsDao
@Resource
private GoodsDao goodsDao;
/**
* 说明
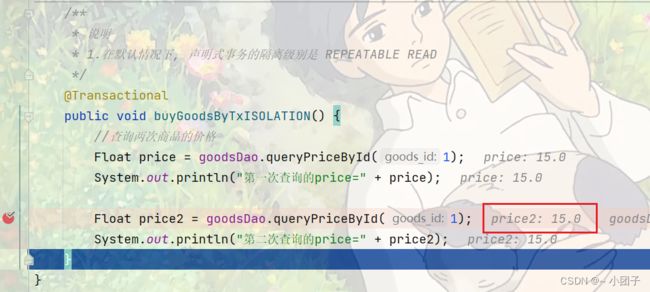
* 1.在默认情况下, 声明式事务的隔离级别是 REPEATABLE READ
*/
@Transactional
public void buyGoodsByTxISOLATION() {
//查询两次商品的价格
Float price = goodsDao.queryPriceById(1);
System.out.println("第一次查询的price=" + price);
Float price2 = goodsDao.queryPriceById(1);
System.out.println("第二次查询的price=" + price2);
}
}
public class TxTest {
//测试声明式事务的隔离级别
@Test
public void buyGoodsByTxISOLATIONTest() {
//获取到容器
ApplicationContext ioc =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("tx_ioc.xml");
GoodsService goodsService = ioc.getBean(GoodsService.class);
goodsService.buyGoodsByTxISOLATION();
}
}
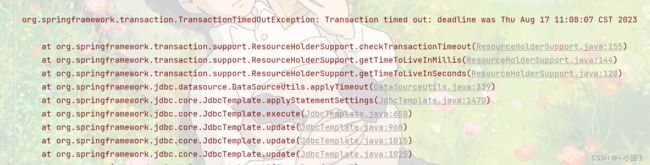
事务超时回滚
●基本介绍
1.如果一个事务执行的时间超过某个时间限制, 就让该事务回滚
2.可以通过设置事务超时回滚来实现
案例
1.修改GoodsService.java, 增加buyGoodsByTxTimeout()
@Service //将GoodsService-对象 注入到spring容器
public class GoodsService {
//定义属性GoodsDao
@Resource
private GoodsDao goodsDao;
/**
* 解读
* 1.@Transactional(timeout = 2)
* 2.timeout = 2 表示 buyGoodsByTxTimeout方法 如果执行时间执行了2秒钟
* , 该事务就进行回滚.
* 3.如果你没有设置 timeout, 默认是-1, 表示使用事务的默认超时时间
* 或者不支持
*/
@Transactional(timeout = 2)
public void buyGoodsByTxTimeout(int userId, int goodsId, int amount) {
//输出购买相关信息
System.out.println("用户购买信息 用户id=" + userId + ", 商品id=" +
goodsId + ", 购买数量=" + amount);
//1.得到商品的价格
Float price = goodsDao.queryPriceById2(goodsId);
//2.减少用户的余额
goodsDao.updateBalance2(userId, price * amount);
//3.减少库存量
goodsDao.updateAmount2(goodsId, amount);
System.out.println("用户购买成功");
}
}
测试代码是否正确
public class TxTest {
//测试timeout 属性
@Test
public void buyGoodsByTxTimeoutTest() {
//获取到容器
ApplicationContext ioc =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("tx_ioc.xml");
GoodsService goodsService = ioc.getBean(GoodsService.class);
goodsService.buyGoodsByTxTimeout(1,1,1);
}
}
模拟超时
/**
* 解读
* 1.@Transactional(timeout = 2)
* 2.timeout = 2 表示 buyGoodsByTxTimeout方法 如果执行时间执行了2秒钟
* , 该事务就进行回滚.
* 3.如果你没有设置 timeout, 默认是-1, 表示使用事务的默认超时时间
* 或者不支持
*/
@Transactional(timeout = 2)
public void buyGoodsByTxTimeout(int userId, int goodsId, int amount) {
//输出购买相关信息
System.out.println("用户购买信息 用户id=" + userId + ", 商品id=" +
goodsId + ", 购买数量=" + amount);
//1.得到商品的价格
Float price = goodsDao.queryPriceById2(goodsId);
//2.减少用户的余额
goodsDao.updateBalance2(userId, price * amount);
//模拟超时
System.out.println("========超时开始========");
try {
Thread.sleep(4000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
System.out.println("========超时结束========");
//3.减少库存量
goodsDao.updateAmount2(goodsId, amount);
System.out.println("用户购买成功");
}
课后练习
模拟一个用户, 进行银行转账购买淘宝商品的业务, 数据表/dao/service自己设计, 保证数据一致性.
1)seller[卖家]
2)buyer[买家]
3)goods[商品表(库存量)]
4)taoBao[提取入账成交额的10%]
5)简单实现, 使用声明式事务完成
6)要求创建一个新的spring容器配置文件 shopping_ioc.xml, 完成测试
1.sql代码
-- create database spring_homework;
USE spring_homework;
-- 删除表
DROP TABLE goods;
DROP TABLE seller;
DROP TABLE buyer;
DROP TABLE taoBao;
-- 买家表
CREATE TABLE buyer (
id INT UNSIGNED AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
`name` VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL DEFAULT '',
balance DOUBLE NOT NULL DEFAULT 0.0
)CHARSET=utf8;
INSERT INTO buyer VALUES(1, '小明', 500);
-- update buyer set balance = balance + 1 where id = 1;
SELECT * FROM buyer;
-- 卖家表
CREATE TABLE seller (
id INT UNSIGNED AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
`name` VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL DEFAULT '',
balance DOUBLE NOT NULL DEFAULT 0.0
)CHARSET=utf8;
INSERT INTO seller VALUES(1, '王守义', 500);
-- update seller set balance = balance + 1 where id = 1;
SELECT * FROM seller;
-- 商品表
CREATE TABLE goods (
id INT UNSIGNED AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
seller_id INT UNSIGNED,
`name` VARCHAR(32) NOT NULL DEFAULT '',
price DOUBLE NOT NULL DEFAULT 0.0,
inventory INT UNSIGNED
)CHARSET=utf8;
INSERT INTO goods VALUES(1, 1, '王守义十三香', 10, 5000);
-- update goods set inventory = inventory - 1 where id = 1;
SELECT * FROM goods WHERE id = 1;
-- taoBao表
CREATE TABLE taoBao (
id INT UNSIGNED AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
scale DOUBLE NOT NULL DEFAULT 0.1,
balance DOUBLE NOT NULL DEFAULT 0.0
)CHARSET=utf8;
INSERT INTO taoBao VALUES(1, 0.1, 500);
-- update taoBao set balance = balance + 1 where id = 1;
SELECT * FROM taoBao WHERE id = 1;
2.com.zzw.spring.tx.homework.dao包
@Repository
public class GoodsDao {
@Resource
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
/**
* 查询商品价格. 根据商品id, 查询商品价格
* @param id
* @return price
*/
public Double queryPrice(int id) {
String sql = "SELECT price FROM goods WHERE id = ?";
Double price = jdbcTemplate.queryForObject(sql, Double.class, id);
return price;
}
/**
* 更新商品库存. 根据商品id, 减去库存
* @param id
* @param count
*/
public void updateInventory(int id, int count) {
String sql = "update goods set inventory = inventory - ? where id = ?";
int affected = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, count, id);
System.out.println("affected=" + affected);
}
}
@Repository
public class BuyerDao {
@Resource
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
/**
* 更新买家余额. 从买家表中, 扣除金额
* @param id
* @param money
*/
public void updateBalance(int id, double money) {
String sql = "UPDATE buyer SET balance = balance - ? WHERE id = ?";
int affected = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, money, id);
System.out.println("affected=" + affected);
}
}
@Repository
public class SellerDao {
@Resource
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
/**
* 更新卖家余额. 对卖家账号, 增加金额
* @param id
* @param money
*/
public void updateBalance(int id, double money) {
String sql = "UPDATE seller SET balance = balance + ? WHERE id = ?";
int affected = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, money, id);
System.out.println("affected=" + affected);
}
}
@Repository
public class TaobaoDao {
@Resource
private JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
/**
* 更新淘宝余额. 给id等于1的淘宝账号, 增加金额
* @param id
* @param count
*/
public void updateBalance(int id, double money) {
String sql = "UPDATE taoBao SET balance = balance + ? WHERE id = ?";
int affected = jdbcTemplate.update(sql, money, id);
System.out.println("affected=" + affected);
}
}
3.com.zzw.spring.tx.homework.service
@Service
public class GoodsService {
@Resource
private BuyerDao buyerDao;
@Resource
private SellerDao sellerDao;
@Resource
private GoodsDao goodsDao;
@Resource
private TaobaoDao taobaoDao;
//用户购买商品的行为涉及多张表, 视为一个事务进行管理
@Transactional
public void buyGoods(int buyerId, int taoBaoId, int sellerId, int goodsId, int count) {
//1.查询商品价格
Double price = goodsDao.queryPrice(goodsId);
//计算花费多少钱
double money = price * count;
//2.更新买家余额
buyerDao.updateBalance(buyerId, money);
3.更新卖家余额. 将成交额的90%转入卖家余额
sellerDao.updateBalance(sellerId, money * 0.9);
//4.更新淘宝余额. 将成交额的10%转入淘宝余额
taobaoDao.updateBalance(taoBaoId, money * 0.1);
//5.更新商品库存
goodsDao.updateInventory(goodsId, count);
System.out.println("用户 id=" + buyerId + " 在平台 id=" + taoBaoId + " 商家 id=" + sellerId
+ " 购买了商品 id=" + goodsId + " 数量 count=" + count);
}
}
4.配置文件
jdbc_homework.properties
jdbc.user=root
jdbc.pwd=zzw
jdbc.driver=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbc.url=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/spring_homework
shopping_ioc.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:tx="http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context https://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx http://www.springframework.org/schema/tx/spring-tx.xsd">
<!--配置扫描包-->
<context:component-scan base-package="com.zzw.spring.tx.homework"/>
<!--引入外部文件 jdbc.properties-->
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:jdbc_homework.properties"/>
<!--配置数据源-->
<bean class="com.mchange.v2.c3p0.ComboPooledDataSource" id="dataSource">
<!--给数据源对象配置属性值-->
<property name="user" value="${jdbc.user}"/>
<property name="password" value="${jdbc.pwd}"/>
<property name="driverClass" value="${jdbc.driver}"/>
<property name="jdbcUrl" value="${jdbc.url}"/>
</bean>
<!--配置JdbcTemplate-->
<bean class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate" id="jdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!--配置事务管理器-对象
1.DataSourceTransactionManager 这个对象是进行事务管理的
2.一定要配置数据源属性 这样指定这个事务管理器 是对哪个数据源进行事务控制
-->
<bean class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DataSourceTransactionManager" id="transactionManager">
<property name="dataSource" ref="dataSource"/>
</bean>
<!--启用基于注解的声明式事务管理功能-->
<tx:annotation-driven transaction-manager="transactionManager"/>
</beans>
5.测试
public class buyGoodsTest {
@Test
public void buyGoods() {
//获取容器
ApplicationContext ioc =
new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("shopping_ioc.xml");
GoodsService goodsService = ioc.getBean(GoodsService.class);
goodsService.buyGoods(1,1,1,1,2);
}
}