Rabbitmq安装
1、安装说明
安装RabbitMq时需注意,需要先安装Erlang。因为RabbitMq依赖于Erlang,且两者之间的版本是有对应关系的,详细可查看:版本对照表
此外,需要注意的是本教程中采用的安装方式是使用源码安装。非rpm或一键安装方式。目的是避免与服务器中其他版本的冲突或者docker安装的应用冲突,也便于移动或者迁移、自定义安装位置等优点。
2、安装 Erlang
2.1、 第一步:更新yum源
执行:sudo yum update
#更新yum源命令
[aiot@template-CentOS7 ~]$ sudo yum update
#更新过程中,出现是否下载时。输入 y 回车即可
总下载量:277 M
Is this ok [y/d/N]: y
#更新完成后
xz-libs.x86_64 0:5.2.2-2.el7_9
完毕!
[aiot@template-CentOS7 ~]$
2.2、第二步:更新工具与库文件
执行:sudo yum -y install gcc glibc-devel make ncurses-devel openssl-devel xmlto perl wget
[aiot@template-CentOS7 ~]$ sudo yum -y install gcc glibc-devel make ncurses-devel openssl-devel xmlto perl wget
[sudo] aiot 的密码:
已加载插件:fastestmirror
Loading mirror speeds from cached hostfile
* remi-safe: mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn
软件包 gcc-4.8.5-44.el7.x86_64 已安装并且是最新版本
软件包 glibc-devel-2.17-326.el7_9.x86_64 已安装并且是最新版本
软件包 1:make-3.82-24.el7.x86_64 已安装并且是最新版本
软件包 1:openssl-devel-1.0.2k-26.el7_9.x86_64 已安装并且是最新版本
软件包 4:perl-5.16.3-299.el7_9.x86_64 已安装并且是最新版本
软件包 wget-1.14-18.el7_6.1.x86_64 已安装并且是最新版本
正在解决依赖关系
--> 正在检查事务
……………………
作为依赖被安装:
centos-indexhtml.noarch 0:7-9.el7.centos docbook-dtds.noarch 0:1.0-60.el7 docbook-style-xsl.noarch 0:1.78.1-3.el7 flex.x86_64 0:2.5.37-6.el7 lynx.x86_64 0:2.8.8-0.3.dev15.el7 m4.x86_64 0:1.4.16-10.el7
sgml-common.noarch 0:0.6.3-39.el7 xml-common.noarch 0:0.6.3-39.el7
完毕!
[aiot@template-CentOS7 ~]$
2.3、第三步:下载Erlang
2、下载Erlang包
执行:wget http://erlang.org/download/otp_src_24.1.4.tar.gz
[aiot@template-CentOS7 rabbitmq]$ wget http://erlang.org/download/otp_src_24.1.4.tar.gz
--2023-06-26 15:00:46-- http://erlang.org/download/otp_src_24.1.4.tar.gz
正在解析主机 erlang.org (erlang.org)... 192.121.151.106
正在连接 erlang.org (erlang.org)|192.121.151.106|:80... 已连接。
已发出 HTTP 请求,正在等待回应... 200 OK
长度:88865562 (85M) [application/gzip]
正在保存至: “otp_src_24.1.4.tar.gz”
0% [ ] 20,193 --.-K/s 剩余 47h 23m
…………
3、 解压Erlang包
执行:tar -zxvf otp_src_24.1.4.tar.gz
4、进入Erlang目录
5、指定Erlang安装目录
执行:./configure --prefix=[具体安装目录路径]
[aiot@template-CentOS7 otp_src_24.1.4]$ ./configure --prefix=/home/aiot/app/rabbitmq/erlang_24.1.4
=== Running configure in /home/aiot/app/rabbitmq/otp_src_24.1.4/erts ===
./configure '--prefix=/home/aiot/app/rabbitmq/erlang_24.1.4' --disable-option-checking --cache-file=/dev/null --srcdir="/home/aiot/app/rabbitmq/otp_src_24.1.4/erts"
checking build system type... x86_64-pc-linux-gnu
checking host system type... x86_64-pc-linux-gnu
checking for gcc... gcc
checking whether the C compiler works... yes
…………
6、编译安装
执行:make && make install
[aiot@template-CentOS7 otp_src_24.1.4]$ make && make install
Makefile:1235: warning: overriding recipe for target `dialyzer'
Makefile:510: warning: ignoring old recipe for target `dialyzer'
MAKE depend
make[1]: 进入目录“/home/aiot/app/rabbitmq/otp_src_24.1.4/erts/emulator”
MAKE generate
make[2]: 进入目录“/home/aiot/app/rabbitmq/otp_src_24.1.4/erts/emulator”
GEN x86_64-pc-linux-gnu/opt/emu/OPCODES-GENERATED
GEN x86_64-pc-linux-gnu/opt/emu/TABLES-GENERATED
GEN x86_64-pc-linux-gnu/opt/emu/erl_alloc_types.h
GEN x86_64-pc-linux-gnu/erl_version.h
GEN x86_64-pc-linux-gnu/opt/emu/driver_tab.c
make[3]: 进入目录“/home/aiot/app/rabbitmq/otp_src_24.1.4/erts/lib_src”
MAKE opt
make[4]: 进入目录“/home/aiot/app/rabbitmq/otp_src_24.1.4/erts/lib_src”
…………
ln -s ../lib/erlang/bin/escript escript
ln -s ../lib/erlang/bin/ct_run ct_run
[aiot@template-CentOS7 otp_src_24.1.4]$
特别提示:当执行安装目录指定过程中,有提示 err 错误时,需要解决依赖的问题,出现一个解决一个;有info和warn则可直接忽略;有APPLICATIONS INFORMATION及DOCUMENTATION INFORMATION,则没有影响。出现错误安装依赖命令示例:yum install -y [缺少的依赖]
3、安装Rabbitmq
3.1、第一步:下载软件
访问官方开源社区或官方网站下载指定版本的软件包,下载需要的包格式:
下载完成后,将应用软件包上传到服务器指定目录内:
3.2、第二步:解压软件
执行第一次解压:xz -d rabbitmq-server-generic-unix-3.8.16.tar.xz
执行第二次解压:tar -xvf rabbitmq-server-generic-unix-3.8.16.tar
[aiot@template-CentOS7 rabbitmq]$ xz -d rabbitmq-server-generic-unix-3.8.16.tar.xz
[aiot@template-CentOS7 rabbitmq]$ tar -xvf rabbitmq-server-generic-unix-3.8.16.tar
rabbitmq_server-3.8.16/
rabbitmq_server-3.8.16/INSTALL
rabbitmq_server-3.8.16/LICENSE
rabbitmq_server-3.8.16/LICENSE-APACHE2
rabbitmq_server-3.8.16/LICENSE-APACHE2-ExplorerCanvas
rabbitmq_server-3.8.16/LICENSE-APACHE2-excanvas
…………
[aiot@template-CentOS7 rabbitmq]$
3.3、第三步:配置环境变量/etc/profile
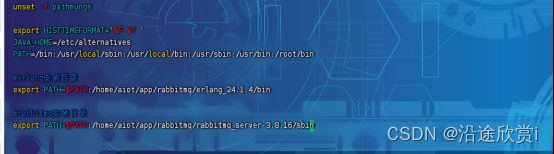
在 /etc/profile 文件中最后加入下面的代码:
#编辑配置文件
[aiot@template-CentOS7 rabbitmq]$ sudo vim /etc/profile
#加入以下配置
#erlang安装目录
export PATH=$PATH:/home/aiot/app/rabbitmq/erlang_24.1.4/bin
#rabbitmq安装目录
export PATH=$PATH:/home/aiot/app/rabbitmq/rabbitmq_server-3.8.16/sbin
执行命令source使配置生效:source /etc/profile
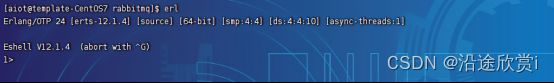
3.4、第四步:验证Erlang是否安装成功
输入erl,若结果会出现版本信息,则Erlang安装成功。如下图:
3.5、第五步:新增RabbitMq服务脚本
#!/bin/sh
#
# rabbitmq-server RabbitMQ broker
#
# chkconfig: 2345 80 05
# description: Enable AMQP service provided by RabbitMQ
#
### BEGIN INIT INFO
# Provides: rabbitmq-server
# Required-Start: $remote_fs $network
# Required-Stop: $remote_fs $network
# Description: RabbitMQ broker
# Short-Description: Enable AMQP service provided by RabbitMQ broker
### END INIT INFO
# Source function library.
. /etc/init.d/functions
#指定rabbitmq安装目录
export HOME=/home/aiot/app/rabbitmq/rabbitmq_server-3.8.16
#指定Erlang安装目录
export PATH=$PATH:/home/aiot/app/rabbitmq/erlang_24.1.4/bin
NAME=rabbitmq-server
#DAEMON=/usr/sbin/${NAME}
#CONTROL=/usr/sbin/rabbitmqctl
DAEMON=/home/aiot/app/rabbitmq/rabbitmq_server-3.8.16/sbin/${NAME}
CONTROL=/home/aiot/app/rabbitmq/rabbitmq_server-3.8.16/sbin/rabbitmqctl
DESC=rabbitmq-server
#指定启动用户
USER=aiot
ROTATE_SUFFIX=
INIT_LOG_DIR=/home/aiot/app/rabbitmq/rabbitmq_server-3.8.16/var/log/rabbitmq
PID_FILE=/home/aiot/app/rabbitmq/rabbitmq_server-3.8.16/var/run/rabbitmq/pid
START_PROG="daemon"
LOCK_FILE=/home/aiot/app/rabbitmq/rabbitmq_server-3.8.16/var/lock/subsys/$NAME
test -x $DAEMON || exit 0
test -x $CONTROL || exit 0
RETVAL=0
set -e
[ -f /etc/default/${NAME} ] && . /etc/default/${NAME}
ensure_pid_dir () {
PID_DIR=`dirname ${PID_FILE}`
if [ ! -d ${PID_DIR} ] ; then
mkdir -p ${PID_DIR}
chown -R ${USER}:${USER} ${PID_DIR}
chmod 755 ${PID_DIR}
fi
if [ ! -d ${INIT_LOG_DIR} ] ; then
mkdir -p ${INIT_LOG_DIR}
chown -R ${USER}:${USER} ${INIT_LOG_DIR}
chmod 755 ${INIT_LOG_DIR}
fi
}
remove_pid () {
rm -f ${PID_FILE}
rmdir `dirname ${PID_FILE}` || :
}
start_rabbitmq () {
status_rabbitmq quiet
if [ $RETVAL = 0 ] ; then
echo RabbitMQ is currently running
else
RETVAL=0
ensure_pid_dir
set +e
RABBITMQ_PID_FILE=$PID_FILE $START_PROG $DAEMON \
> "${INIT_LOG_DIR}/startup_log" \
2> "${INIT_LOG_DIR}/startup_err" \
0<&- &
$CONTROL wait $PID_FILE >/dev/null 2>&1
RETVAL=$?
set -e
case "$RETVAL" in
0)
echo SUCCESS
if [ -n "$LOCK_FILE" ] ; then
touch $LOCK_FILE
fi
;;
*)
remove_pid
echo FAILED - check ${INIT_LOG_DIR}/startup_\{log, _err\}
RETVAL=1
;;
esac
fi
}
stop_rabbitmq () {
status_rabbitmq quiet
if [ $RETVAL = 0 ] ; then
set +e
$CONTROL stop ${PID_FILE} > ${INIT_LOG_DIR}/shutdown_log 2> ${INIT_LOG_DIR}/shutdown_err
RETVAL=$?
set -e
if [ $RETVAL = 0 ] ; then
remove_pid
if [ -n "$LOCK_FILE" ] ; then
rm -f $LOCK_FILE
fi
else
echo FAILED - check ${INIT_LOG_DIR}/shutdown_log, _err
fi
else
echo RabbitMQ is not running
RETVAL=0
fi
}
status_rabbitmq() {
set +e
if [ "$1" != "quiet" ] ; then
$CONTROL status 2>&1
else
$CONTROL status > /dev/null 2>&1
fi
if [ $? != 0 ] ; then
RETVAL=3
fi
set -e
}
rotate_logs_rabbitmq() {
set +e
$CONTROL rotate_logs ${ROTATE_SUFFIX}
if [ $? != 0 ] ; then
RETVAL=1
fi
set -e
}
restart_running_rabbitmq () {
status_rabbitmq quiet
if [ $RETVAL = 0 ] ; then
restart_rabbitmq
else
echo RabbitMQ is not runnning
RETVAL=0
fi
}
restart_rabbitmq() {
stop_rabbitmq
start_rabbitmq
}
case "$1" in
start)
echo -n "Starting $DESC: "
start_rabbitmq
echo "$NAME."
;;
stop)
echo -n "Stopping $DESC: "
stop_rabbitmq
echo "$NAME."
;;
status)
status_rabbitmq
;;
rotate-logs)
echo -n "Rotating log files for $DESC: "
rotate_logs_rabbitmq
;;
force-reload|reload|restart)
echo -n "Restarting $DESC: "
restart_rabbitmq
echo "$NAME."
;;
try-restart)
echo -n "Restarting $DESC: "
restart_running_rabbitmq
echo "$NAME."
;;
*)
echo "Usage: $0 {start|stop|status|rotate-logs|restart|condrestart|try-restart|reload|force-reload}" >&2
RETVAL=1
;;
esac
exit $RETVAL
3.6、第六步:配置并开启服务
1、将服务脚本移动到 /etc/init.d/ 路径下:
[aiot@template-CentOS7 rabbitmq]$ sudo mv ./rabbitmq /etc/init.d/
[sudo] aiot 的密码:
[aiot@template-CentOS7 rabbitmq]$
2、添加执行权限
[aiot@template-CentOS7 rabbitmq]$ sudo chmod u+x /etc/init.d/rabbitmq
[aiot@template-CentOS7 rabbitmq]$
3、将脚本添加到服务列表
[aiot@template-CentOS7 rabbitmq]$ sudo chkconfig rabbitmq on
[aiot@template-CentOS7 rabbitmq]$
3.7、第七步:启动Rabbitmq管控台插件
执行:rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_management
[aiot@template-CentOS7 rabbitmq]$ rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_management
Enabling plugins on node rabbit@template-CentOS7:
rabbitmq_management
The following plugins have been configured:
rabbitmq_management
rabbitmq_management_agent
rabbitmq_web_dispatch
Applying plugin configuration to rabbit@template-CentOS7...
The following plugins have been enabled:
rabbitmq_management
rabbitmq_management_agent
rabbitmq_web_dispatch
set 3 plugins.
Offline change; changes will take effect at broker restart.
[aiot@template-CentOS7 rabbitmq]$
3.8、第八步:放行端口
# 查看防火墙放行的端口
[root@centos01 rabbitmq]# sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --list-ports
8091/tcp
# 放行15672端口
[root@centos01 rabbitmq]# sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=15672/tcp --permanent
success
# 使刚刚配置的防火墙生效
[root@centos01 rabbitmq]# sudo firewall-cmd --reload
success
[root@centos01 rabbitmq]# sudo firewall-cmd --zone=public --list-ports
8091/tcp 15672/tcp
[root@centos01 rabbitmq]#
提示:这边放行的端口根据配置文件里,配置的不同端口来放行。
3.9、第九步:创建Rabbitmq配置文件
官方配置文件示例:
## This example configuration file demonstrates various settings
## available via rabbitmq.conf. It primarily focuses core broker settings
## but some tier 1 plugin settings are also covered.
##
## This file is AN EXAMPLE. It is NOT MEANT TO BE USED IN PRODUCTION. Instead of
## copying the entire (large!) file, create or generate a new rabbitmq.conf for the target system
## and populate it with the necessary settings.
##
## See https://rabbitmq.com/configure.html to learn about how to configure RabbitMQ,
## the ini-style format used by rabbitmq.conf, how it is different from `advanced.config`,
## how to verify effective configuration, and so on.
##
## See https://rabbitmq.com/documentation.html for the rest of RabbitMQ documentation.
##
## In case you have questions, please use RabbitMQ community Slack and the rabbitmq-users Google group
## instead of GitHub issues.
# ======================================
# Core broker section
# ======================================
## Networking
## ====================
##
## Related doc guide: https://rabbitmq.com/networking.html.
##
## By default, RabbitMQ will listen on all interfaces, using
## the standard (reserved) AMQP 0-9-1 and 1.0 port.
##
# listeners.tcp.default = 5672
## To listen on a specific interface, provide an IP address with port.
## For example, to listen only on localhost for both IPv4 and IPv6:
##
# IPv4
# listeners.tcp.local = 127.0.0.1:5672
# IPv6
# listeners.tcp.local_v6 = ::1:5672
## You can define multiple listeners using listener names
# listeners.tcp.other_port = 5673
# listeners.tcp.other_ip = 10.10.10.10:5672
## TLS listeners are configured in the same fashion as TCP listeners,
## including the option to control the choice of interface.
##
# listeners.ssl.default = 5671
## It is possible to disable regular TCP (non-TLS) listeners. Clients
## not configured to use TLS and the correct TLS-enabled port won't be able
## to connect to this node.
# listeners.tcp = none
## Number of Erlang processes that will accept connections for the TCP
## and TLS listeners.
##
# num_acceptors.tcp = 10
# num_acceptors.ssl = 10
## Socket writer will force GC every so many bytes transferred.
## Default is 1 GiB (`1000000000`). Set to 'off' to disable.
##
# socket_writer.gc_threshold = 1000000000
#
## To disable:
# socket_writer.gc_threshold = off
## Maximum amount of time allowed for the AMQP 0-9-1 and AMQP 1.0 handshake
## (performed after socket connection and TLS handshake) to complete, in milliseconds.
##
# handshake_timeout = 10000
## Set to 'true' to perform reverse DNS lookups when accepting a
## connection. rabbitmqctl and management UI will then display hostnames
## instead of IP addresses. Default value is `false`.
##
# reverse_dns_lookups = false
##
## Security, Access Control
## ==============
##
## Related doc guide: https://rabbitmq.com/access-control.html.
## The default "guest" user is only permitted to access the server
## via a loopback interface (e.g. localhost).
## {loopback_users, [<<"guest">>]},
##
# loopback_users.guest = true
## Uncomment the following line if you want to allow access to the
## guest user from anywhere on the network.
# loopback_users.guest = false
## TLS configuration.
##
## Related doc guide: https://rabbitmq.com/ssl.html.
##
# listeners.ssl.1 = 5671
#
# ssl_options.verify = verify_peer
# ssl_options.fail_if_no_peer_cert = false
# ssl_options.cacertfile = /path/to/cacert.pem
# ssl_options.certfile = /path/to/cert.pem
# ssl_options.keyfile = /path/to/key.pem
#
# ssl_options.honor_cipher_order = true
# ssl_options.honor_ecc_order = true
#
## These are highly recommended for TLSv1.2 but cannot be used
## with TLSv1.3. If TLSv1.3 is enabled, these lines MUST be removed.
# ssl_options.client_renegotiation = false
# ssl_options.secure_renegotiate = true
#
## Limits what TLS versions the server enables for client TLS
## connections. See https://www.rabbitmq.com/ssl.html#tls-versions for details.
##
## Cutting edge TLS version which requires recent client runtime
## versions and has no cipher suite in common with earlier TLS versions.
# ssl_options.versions.1 = tlsv1.3
## Enables TLSv1.2 for best compatibility
# ssl_options.versions.2 = tlsv1.2
## Older TLS versions have known vulnerabilities and are being phased out
## from wide use.
## Limits what cipher suites the server will use for client TLS
## connections. Narrowing this down can prevent some clients
## from connecting.
## If TLSv1.3 is enabled and cipher suites are overridden, TLSv1.3-specific
## cipher suites must also be explicitly enabled.
## See https://www.rabbitmq.com/ssl.html#cipher-suites and https://wiki.openssl.org/index.php/TLS1.3#Ciphersuites
## for details.
#
## The example below uses TLSv1.3 cipher suites only
#
# ssl_options.ciphers.1 = TLS_AES_256_GCM_SHA384
# ssl_options.ciphers.2 = TLS_AES_128_GCM_SHA256
# ssl_options.ciphers.3 = TLS_CHACHA20_POLY1305_SHA256
# ssl_options.ciphers.4 = TLS_AES_128_CCM_SHA256
# ssl_options.ciphers.5 = TLS_AES_128_CCM_8_SHA256
#
## The example below uses TLSv1.2 cipher suites only
#
# ssl_options.ciphers.1 = ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384
# ssl_options.ciphers.2 = ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384
# ssl_options.ciphers.3 = ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384
# ssl_options.ciphers.4 = ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384
# ssl_options.ciphers.5 = ECDH-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384
# ssl_options.ciphers.6 = ECDH-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384
# ssl_options.ciphers.7 = ECDH-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384
# ssl_options.ciphers.8 = ECDH-RSA-AES256-SHA384
# ssl_options.ciphers.9 = DHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384
# ssl_options.ciphers.10 = DHE-DSS-AES256-GCM-SHA384
# ssl_options.ciphers.11 = DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA256
# ssl_options.ciphers.12 = DHE-DSS-AES256-SHA256
# ssl_options.ciphers.13 = ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256
# ssl_options.ciphers.14 = ECDHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256
# ssl_options.ciphers.15 = ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256
# ssl_options.ciphers.16 = ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
# ssl_options.ciphers.17 = ECDH-ECDSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256
# ssl_options.ciphers.18 = ECDH-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256
# ssl_options.ciphers.19 = ECDH-ECDSA-AES128-SHA256
# ssl_options.ciphers.20 = ECDH-RSA-AES128-SHA256
# ssl_options.ciphers.21 = DHE-RSA-AES128-GCM-SHA256
# ssl_options.ciphers.22 = DHE-DSS-AES128-GCM-SHA256
# ssl_options.ciphers.23 = DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA256
# ssl_options.ciphers.24 = DHE-DSS-AES128-SHA256
# ssl_options.ciphers.25 = ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA
# ssl_options.ciphers.26 = ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA
# ssl_options.ciphers.27 = DHE-RSA-AES256-SHA
# ssl_options.ciphers.28 = DHE-DSS-AES256-SHA
# ssl_options.ciphers.29 = ECDH-ECDSA-AES256-SHA
# ssl_options.ciphers.30 = ECDH-RSA-AES256-SHA
# ssl_options.ciphers.31 = ECDHE-ECDSA-AES128-SHA
# ssl_options.ciphers.32 = ECDHE-RSA-AES128-SHA
# ssl_options.ciphers.33 = DHE-RSA-AES128-SHA
# ssl_options.ciphers.34 = DHE-DSS-AES128-SHA
# ssl_options.ciphers.35 = ECDH-ECDSA-AES128-SHA
# ssl_options.ciphers.36 = ECDH-RSA-AES128-SHA
# ssl_options.bypass_pem_cache = true
## Select an authentication/authorisation backend to use.
##
## Alternative backends are provided by plugins, such as rabbitmq-auth-backend-ldap.
##
## NB: These settings require certain plugins to be enabled.
##
## Related doc guides:
##
## * https://rabbitmq.com/plugins.html
## * https://rabbitmq.com/access-control.html
##
# auth_backends.1 = rabbit_auth_backend_internal
## uses separate backends for authentication and authorisation,
## see below.
# auth_backends.1.authn = rabbit_auth_backend_ldap
# auth_backends.1.authz = rabbit_auth_backend_internal
## The rabbitmq_auth_backend_ldap plugin allows the broker to
## perform authentication and authorisation by deferring to an
## external LDAP server.
##
## Relevant doc guides:
##
## * https://rabbitmq.com/ldap.html
## * https://rabbitmq.com/access-control.html
##
## uses LDAP for both authentication and authorisation
# auth_backends.1 = rabbit_auth_backend_ldap
## uses HTTP service for both authentication and
## authorisation
# auth_backends.1 = rabbit_auth_backend_http
## uses two backends in a chain: HTTP first, then internal
# auth_backends.1 = rabbit_auth_backend_http
# auth_backends.2 = rabbit_auth_backend_internal
## Authentication
## The built-in mechanisms are 'PLAIN',
## 'AMQPLAIN', and 'EXTERNAL' Additional mechanisms can be added via
## plugins.
##
## Related doc guide: https://rabbitmq.com/authentication.html.
##
# auth_mechanisms.1 = PLAIN
# auth_mechanisms.2 = AMQPLAIN
## The rabbitmq-auth-mechanism-ssl plugin makes it possible to
## authenticate a user based on the client's x509 (TLS) certificate.
## Related doc guide: https://rabbitmq.com/authentication.html.
##
## To use auth-mechanism-ssl, the EXTERNAL mechanism should
## be enabled:
##
# auth_mechanisms.1 = PLAIN
# auth_mechanisms.2 = AMQPLAIN
# auth_mechanisms.3 = EXTERNAL
## To force x509 certificate-based authentication on all clients,
## exclude all other mechanisms (note: this will disable password-based
## authentication even for the management UI!):
##
# auth_mechanisms.1 = EXTERNAL
## This pertains to both the rabbitmq-auth-mechanism-ssl plugin and
## STOMP ssl_cert_login configurations. See the RabbitMQ STOMP plugin
## configuration section later in this file and the README in
## https://github.com/rabbitmq/rabbitmq-auth-mechanism-ssl for further
## details.
##
## To use the TLS cert's CN instead of its DN as the username
##
# ssl_cert_login_from = common_name
## TLS handshake timeout, in milliseconds.
##
# ssl_handshake_timeout = 5000
## Cluster name
##
# cluster_name = dev3.eng.megacorp.local
## Password hashing implementation. Will only affect newly
## created users. To recalculate hash for an existing user
## it's necessary to update her password.
##
## To use SHA-512, set to rabbit_password_hashing_sha512.
##
# password_hashing_module = rabbit_password_hashing_sha256
## When importing definitions exported from versions earlier
## than 3.6.0, it is possible to go back to MD5 (only do this
## as a temporary measure!) by setting this to rabbit_password_hashing_md5.
##
# password_hashing_module = rabbit_password_hashing_md5
##
## Default User / VHost
## ====================
##
## On first start RabbitMQ will create a vhost and a user. These
## config items control what gets created.
## Relevant doc guide: https://rabbitmq.com/access-control.html
##
# default_vhost = /
# default_user = guest
# default_pass = guest
# default_permissions.configure = .*
# default_permissions.read = .*
# default_permissions.write = .*
## Tags for default user
##
## For more details about tags, see the documentation for the
## Management Plugin at https://rabbitmq.com/management.html.
##
# default_user_tags.administrator = true
## Define other tags like this:
# default_user_tags.management = true
# default_user_tags.custom_tag = true
##
## Additional network and protocol related configuration
## =====================================================
##
## Set the server AMQP 0-9-1 heartbeat timeout in seconds.
## RabbitMQ nodes will send heartbeat frames at roughly
## the (timeout / 2) interval. Two missed heartbeats from
## a client will close its connection.
##
## Values lower than 6 seconds are very likely to produce
## false positives and are not recommended.
##
## Related doc guides:
##
## * https://rabbitmq.com/heartbeats.html
## * https://rabbitmq.com/networking.html
##
# heartbeat = 60
## Set the max permissible size of an AMQP frame (in bytes).
##
# frame_max = 131072
## Set the max frame size the server will accept before connection
## tuning occurs
##
# initial_frame_max = 4096
## Set the max permissible number of channels per connection.
## 0 means "no limit".
##
# channel_max = 128
## Customising TCP Listener (Socket) Configuration.
##
## Related doc guides:
##
## * https://rabbitmq.com/networking.html
## * https://www.erlang.org/doc/man/inet.html#setopts-2
##
# tcp_listen_options.backlog = 128
# tcp_listen_options.nodelay = true
# tcp_listen_options.exit_on_close = false
#
# tcp_listen_options.keepalive = true
# tcp_listen_options.send_timeout = 15000
#
# tcp_listen_options.buffer = 196608
# tcp_listen_options.sndbuf = 196608
# tcp_listen_options.recbuf = 196608
##
## Resource Limits & Flow Control
## ==============================
##
## Related doc guide: https://rabbitmq.com/memory.html.
## Memory-based Flow Control threshold.
##
# vm_memory_high_watermark.relative = 0.4
## Alternatively, we can set a limit (in bytes) of RAM used by the node.
##
# vm_memory_high_watermark.absolute = 1073741824
## Or you can set absolute value using memory units (with RabbitMQ 3.6.0+).
## Absolute watermark will be ignored if relative is defined!
##
# vm_memory_high_watermark.absolute = 2GB
##
## Supported unit symbols:
##
## k, kiB: kibibytes (2^10 - 1,024 bytes)
## M, MiB: mebibytes (2^20 - 1,048,576 bytes)
## G, GiB: gibibytes (2^30 - 1,073,741,824 bytes)
## kB: kilobytes (10^3 - 1,000 bytes)
## MB: megabytes (10^6 - 1,000,000 bytes)
## GB: gigabytes (10^9 - 1,000,000,000 bytes)
## Fraction of the high watermark limit at which queues start to
## page message out to disc in order to free up memory.
## For example, when vm_memory_high_watermark is set to 0.4 and this value is set to 0.5,
## paging can begin as early as when 20% of total available RAM is used by the node.
##
## Values greater than 1.0 can be dangerous and should be used carefully.
##
## One alternative to this is to use durable queues and publish messages
## as persistent (delivery mode = 2). With this combination queues will
## move messages to disk much more rapidly.
##
## Another alternative is to configure queues to page all messages (both
## persistent and transient) to disk as quickly
## as possible, see https://rabbitmq.com/lazy-queues.html.
##
# vm_memory_high_watermark_paging_ratio = 0.5
## Selects Erlang VM memory consumption calculation strategy. Can be `allocated`, `rss` or `legacy` (aliased as `erlang`),
## Introduced in 3.6.11. `rss` is the default as of 3.6.12.
## See https://github.com/rabbitmq/rabbitmq-server/issues/1223 and rabbitmq/rabbitmq-common#224 for background.
# vm_memory_calculation_strategy = rss
## Interval (in milliseconds) at which we perform the check of the memory
## levels against the watermarks.
##
# memory_monitor_interval = 2500
## The total memory available can be calculated from the OS resources
## - default option - or provided as a configuration parameter.
# total_memory_available_override_value = 2GB
## Set disk free limit (in bytes). Once free disk space reaches this
## lower bound, a disk alarm will be set - see the documentation
## listed above for more details.
##
## Absolute watermark will be ignored if relative is defined!
# disk_free_limit.absolute = 50000
## Or you can set it using memory units (same as in vm_memory_high_watermark)
## with RabbitMQ 3.6.0+.
# disk_free_limit.absolute = 500KB
# disk_free_limit.absolute = 50mb
# disk_free_limit.absolute = 5GB
## Alternatively, we can set a limit relative to total available RAM.
##
## Values lower than 1.0 can be dangerous and should be used carefully.
# disk_free_limit.relative = 2.0
##
## Clustering
## =====================
##
# cluster_partition_handling = ignore
## Pauses all nodes on the minority side of a partition. The cluster
## MUST have an odd number of nodes (3, 5, etc)
# cluster_partition_handling = pause_minority
## pause_if_all_down strategy require additional configuration
# cluster_partition_handling = pause_if_all_down
## Recover strategy. Can be either 'autoheal' or 'ignore'
# cluster_partition_handling.pause_if_all_down.recover = ignore
## Node names to check
# cluster_partition_handling.pause_if_all_down.nodes.1 = rabbit@localhost
# cluster_partition_handling.pause_if_all_down.nodes.2 = hare@localhost
## Mirror sync batch size, in messages. Increasing this will speed
## up syncing but total batch size in bytes must not exceed 2 GiB.
## Available in RabbitMQ 3.6.0 or later.
##
# mirroring_sync_batch_size = 4096
## Make clustering happen *automatically* at startup. Only applied
## to nodes that have just been reset or started for the first time.
##
## Relevant doc guide: https://rabbitmq.com//cluster-formation.html
##
# cluster_formation.peer_discovery_backend = rabbit_peer_discovery_classic_config
#
# cluster_formation.classic_config.nodes.1 = rabbit1@hostname
# cluster_formation.classic_config.nodes.2 = rabbit2@hostname
# cluster_formation.classic_config.nodes.3 = rabbit3@hostname
# cluster_formation.classic_config.nodes.4 = rabbit4@hostname
## DNS-based peer discovery. This backend will list A records
## of the configured hostname and perform reverse lookups for
## the addresses returned.
# cluster_formation.peer_discovery_backend = rabbit_peer_discovery_dns
# cluster_formation.dns.hostname = discovery.eng.example.local
## This node's type can be configured. If you are not sure
## what node type to use, always use 'disc'.
# cluster_formation.node_type = disc
## Interval (in milliseconds) at which we send keepalive messages
## to other cluster members. Note that this is not the same thing
## as net_ticktime; missed keepalive messages will not cause nodes
## to be considered down.
##
# cluster_keepalive_interval = 10000
##
## Statistics Collection
## =====================
##
## Statistics collection interval (in milliseconds). Increasing
## this will reduce the load on management database.
##
# collect_statistics_interval = 5000
## Fine vs. coarse statistics
#
# This value is no longer meant to be configured directly.
#
# See https://www.rabbitmq.com/management.html#fine-stats.
##
## Ra Settings
## =====================
##
# raft.segment_max_entries = 65536
# raft.wal_max_size_bytes = 1048576
# raft.wal_max_batch_size = 4096
# raft.snapshot_chunk_size = 1000000
##
## Misc/Advanced Options
## =====================
##
## NB: Change these only if you understand what you are doing!
##
## Timeout used when waiting for Mnesia tables in a cluster to
## become available.
##
# mnesia_table_loading_retry_timeout = 30000
## Retries when waiting for Mnesia tables in the cluster startup. Note that
## this setting is not applied to Mnesia upgrades or node deletions.
##
# mnesia_table_loading_retry_limit = 10
## Size in bytes below which to embed messages in the queue index.
## Related doc guide: https://rabbitmq.com/persistence-conf.html
##
# queue_index_embed_msgs_below = 4096
## You can also set this size in memory units
##
# queue_index_embed_msgs_below = 4kb
## Whether or not to enable background periodic forced GC runs for all
## Erlang processes on the node in "waiting" state.
##
## Disabling background GC may reduce latency for client operations,
## keeping it enabled may reduce median RAM usage by the binary heap
## (see https://www.erlang-solutions.com/blog/erlang-garbage-collector.html).
##
## Before trying this option, please take a look at the memory
## breakdown (https://www.rabbitmq.com/memory-use.html).
##
# background_gc_enabled = false
## Target (desired) interval (in milliseconds) at which we run background GC.
## The actual interval will vary depending on how long it takes to execute
## the operation (can be higher than this interval). Values less than
## 30000 milliseconds are not recommended.
##
# background_gc_target_interval = 60000
## Whether or not to enable proxy protocol support.
## Once enabled, clients cannot directly connect to the broker
## anymore. They must connect through a load balancer that sends the
## proxy protocol header to the broker at connection time.
## This setting applies only to AMQP clients, other protocols
## like MQTT or STOMP have their own setting to enable proxy protocol.
## See the plugins documentation for more information.
##
# proxy_protocol = false
## Overriden product name and version.
## They are set to "RabbitMQ" and the release version by default.
# product.name = RabbitMQ
# product.version = 1.2.3
## "Message of the day" file.
## Its content is used to expand the logged and printed banners.
## Default to /etc/rabbitmq/motd on Unix, %APPDATA%\RabbitMQ\motd.txt
## on Windows.
# motd_file = /etc/rabbitmq/motd
## Consumer timeout
## If a message delivered to a consumer has not been acknowledge before this timer
## triggers the channel will be force closed by the broker. This ensure that
## faultly consumers that never ack will not hold on to messages indefinitely.
##
# consumer_timeout = 900000
## ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
## Advanced Erlang Networking/Clustering Options.
##
## Related doc guide: https://rabbitmq.com/clustering.html
## ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# ======================================
# Kernel section
# ======================================
## Timeout used to detect peer unavailability, including CLI tools.
## Related doc guide: https://www.rabbitmq.com/nettick.html.
##
# net_ticktime = 60
## Inter-node communication port range.
## The parameters inet_dist_listen_min and inet_dist_listen_max
## can be configured in the classic config format only.
## Related doc guide: https://www.rabbitmq.com/networking.html#epmd-inet-dist-port-range.
## ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
## RabbitMQ Management Plugin
##
## Related doc guide: https://rabbitmq.com/management.html.
## ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# =======================================
# Management section
# =======================================
## Preload schema definitions from the following JSON file.
## Related doc guide: https://rabbitmq.com/management.html#load-definitions.
##
# management.load_definitions = /path/to/exported/definitions.json
## Log all requests to the management HTTP API to a file.
##
# management.http_log_dir = /path/to/access.log
## HTTP listener and embedded Web server settings.
# ## See https://rabbitmq.com/management.html for details.
#
# management.tcp.port = 15672
# management.tcp.ip = 0.0.0.0
#
# management.tcp.shutdown_timeout = 7000
# management.tcp.max_keepalive = 120
# management.tcp.idle_timeout = 120
# management.tcp.inactivity_timeout = 120
# management.tcp.request_timeout = 120
# management.tcp.compress = true
## HTTPS listener settings.
## See https://rabbitmq.com/management.html and https://rabbitmq.com/ssl.html for details.
##
# management.ssl.port = 15671
# management.ssl.cacertfile = /path/to/ca_certificate.pem
# management.ssl.certfile = /path/to/server_certificate.pem
# management.ssl.keyfile = /path/to/server_key.pem
## More TLS options
# management.ssl.honor_cipher_order = true
# management.ssl.honor_ecc_order = true
## These are highly recommended for TLSv1.2 but cannot be used
## with TLSv1.3. If TLSv1.3 is enabled, these lines MUST be removed.
# management.ssl.client_renegotiation = false
# management.ssl.secure_renegotiate = true
## Supported TLS versions
# management.ssl.versions.1 = tlsv1.2
## Cipher suites the server is allowed to use
# management.ssl.ciphers.1 = ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384
# management.ssl.ciphers.2 = ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384
# management.ssl.ciphers.3 = ECDHE-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384
# management.ssl.ciphers.4 = ECDHE-RSA-AES256-SHA384
# management.ssl.ciphers.5 = ECDH-ECDSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384
# management.ssl.ciphers.6 = ECDH-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384
# management.ssl.ciphers.7 = ECDH-ECDSA-AES256-SHA384
# management.ssl.ciphers.8 = ECDH-RSA-AES256-SHA384
# management.ssl.ciphers.9 = DHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384
## URL path prefix for HTTP API and management UI
# management.path_prefix = /a-prefix
## One of 'basic', 'detailed' or 'none'. See
## https://rabbitmq.com/management.html#fine-stats for more details.
# management.rates_mode = basic
## Configure how long aggregated data (such as message rates and queue
## lengths) is retained. Please read the plugin's documentation in
## https://rabbitmq.com/management.html#configuration for more
## details.
## Your can use 'minute', 'hour' and 'day' keys or integer key (in seconds)
# management.sample_retention_policies.global.minute = 5
# management.sample_retention_policies.global.hour = 60
# management.sample_retention_policies.global.day = 1200
# management.sample_retention_policies.basic.minute = 5
# management.sample_retention_policies.basic.hour = 60
# management.sample_retention_policies.detailed.10 = 5
## ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
## RabbitMQ Shovel Plugin
##
## Related doc guide: https://rabbitmq.com/shovel.html
## ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
## See advanced.config.example for a Shovel plugin example
## ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
## RabbitMQ STOMP Plugin
##
## Related doc guide: https://rabbitmq.com/stomp.html
## ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# =======================================
# STOMP section
# =======================================
## See https://rabbitmq.com/stomp.html for details.
## TCP listeners.
##
# stomp.listeners.tcp.1 = 127.0.0.1:61613
# stomp.listeners.tcp.2 = ::1:61613
## TCP listener settings
##
# stomp.tcp_listen_options.backlog = 2048
# stomp.tcp_listen_options.recbuf = 131072
# stomp.tcp_listen_options.sndbuf = 131072
#
# stomp.tcp_listen_options.keepalive = true
# stomp.tcp_listen_options.nodelay = true
#
# stomp.tcp_listen_options.exit_on_close = true
# stomp.tcp_listen_options.send_timeout = 120
## Proxy protocol support
##
# stomp.proxy_protocol = false
## TLS listeners
## See https://rabbitmq.com/stomp.html and https://rabbitmq.com/ssl.html for details.
# stomp.listeners.ssl.default = 61614
#
# ssl_options.cacertfile = path/to/cacert.pem
# ssl_options.certfile = path/to/cert.pem
# ssl_options.keyfile = path/to/key.pem
# ssl_options.verify = verify_peer
# ssl_options.fail_if_no_peer_cert = true
## Number of Erlang processes that will accept connections for the TCP
## and TLS listeners.
##
# stomp.num_acceptors.tcp = 10
# stomp.num_acceptors.ssl = 1
## Additional TLS options
## Extract a name from the client's certificate when using TLS.
##
# stomp.ssl_cert_login = true
## Set a default user name and password. This is used as the default login
## whenever a CONNECT frame omits the login and passcode headers.
##
## Please note that setting this will allow clients to connect without
## authenticating!
##
# stomp.default_user = guest
# stomp.default_pass = guest
## If a default user is configured, or you have configured use TLS client
## certificate based authentication, you can choose to allow clients to
## omit the CONNECT frame entirely. If set to true, the client is
## automatically connected as the default user or user supplied in the
## TLS certificate whenever the first frame sent on a session is not a
## CONNECT frame.
##
# stomp.implicit_connect = true
## Whether or not to enable proxy protocol support.
## Once enabled, clients cannot directly connect to the broker
## anymore. They must connect through a load balancer that sends the
## proxy protocol header to the broker at connection time.
## This setting applies only to STOMP clients, other protocols
## like MQTT or AMQP have their own setting to enable proxy protocol.
## See the plugins or broker documentation for more information.
##
# stomp.proxy_protocol = false
## ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
## RabbitMQ MQTT Adapter
##
## See https://github.com/rabbitmq/rabbitmq-mqtt/blob/stable/README.md
## for details
## ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# =======================================
# MQTT section
# =======================================
## TCP listener settings.
##
# mqtt.listeners.tcp.1 = 127.0.0.1:61613
# mqtt.listeners.tcp.2 = ::1:61613
## TCP listener options (as per the broker configuration).
##
# mqtt.tcp_listen_options.backlog = 4096
# mqtt.tcp_listen_options.recbuf = 131072
# mqtt.tcp_listen_options.sndbuf = 131072
#
# mqtt.tcp_listen_options.keepalive = true
# mqtt.tcp_listen_options.nodelay = true
#
# mqtt.tcp_listen_options.exit_on_close = true
# mqtt.tcp_listen_options.send_timeout = 120
## TLS listener settings
## ## See https://rabbitmq.com/mqtt.html and https://rabbitmq.com/ssl.html for details.
#
# mqtt.listeners.ssl.default = 8883
#
# ssl_options.cacertfile = /path/to/tls/ca_certificate_bundle.pem
# ssl_options.certfile = /path/to/tls/server_certificate.pem
# ssl_options.keyfile = /path/to/tls/server_key.pem
# ssl_options.verify = verify_peer
# ssl_options.fail_if_no_peer_cert = true
#
## Number of Erlang processes that will accept connections for the TCP
## and TLS listeners.
##
# mqtt.num_acceptors.tcp = 10
# mqtt.num_acceptors.ssl = 10
## Whether or not to enable proxy protocol support.
## Once enabled, clients cannot directly connect to the broker
## anymore. They must connect through a load balancer that sends the
## proxy protocol header to the broker at connection time.
## This setting applies only to STOMP clients, other protocols
## like STOMP or AMQP have their own setting to enable proxy protocol.
## See the plugins or broker documentation for more information.
##
# mqtt.proxy_protocol = false
## Set the default user name and password used for anonymous connections (when client
## provides no credentials). Anonymous connections are highly discouraged!
##
# mqtt.default_user = guest
# mqtt.default_pass = guest
## Enable anonymous connections. If this is set to false, clients MUST provide
## credentials in order to connect. See also the mqtt.default_user/mqtt.default_pass
## keys. Anonymous connections are highly discouraged!
##
# mqtt.allow_anonymous = true
## If you have multiple vhosts, specify the one to which the
## adapter connects.
##
# mqtt.vhost = /
## Specify the exchange to which messages from MQTT clients are published.
##
# mqtt.exchange = amq.topic
## Specify TTL (time to live) to control the lifetime of non-clean sessions.
##
# mqtt.subscription_ttl = 1800000
## Set the prefetch count (governing the maximum number of unacknowledged
## messages that will be delivered).
##
# mqtt.prefetch = 10
## Sets the durable queue type to be used for QoS 1 subscriptions.
##
## Supported types are:
##
## * classic
## * quorum
##
## IMPORTANT: changing this setting requires all existing queues used by
## the MQTT plugin to be DELETED or clients will fail to subscribe.
## So this setting should be used for new clusters.
##
# mqtt.durable_queue_type = classic
## ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
## RabbitMQ AMQP 1.0 Support
##
## See https://github.com/rabbitmq/rabbitmq-amqp1.0/blob/stable/README.md.
## ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# =======================================
# AMQP 1.0 section
# =======================================
## Connections that are not authenticated with SASL will connect as this
## account. See the README for more information.
##
## Please note that setting this will allow clients to connect without
## authenticating!
##
# amqp1_0.default_user = guest
## Enable protocol strict mode. See the README for more information.
##
# amqp1_0.protocol_strict_mode = false
## Logging settings.
##
## See https://rabbitmq.com/logging.html for details.
##
## Log directory, taken from the RABBITMQ_LOG_BASE env variable by default.
##
# log.dir = /var/log/rabbitmq
## Logging to file. Can be false or a filename.
## Default:
# log.file = rabbit.log
## To disable logging to a file
# log.file = false
## Log level for file logging
##
# log.file.level = info
## File rotation config. No rotation by default.
## DO NOT SET rotation date to ''. Leave the value unset if "" is the desired value
# log.file.rotation.date = $D0
# log.file.rotation.size = 0
## Logging to console (can be true or false)
##
# log.console = false
## Log level for console logging
##
# log.console.level = info
## Logging to the amq.rabbitmq.log exchange (can be true or false)
##
# log.exchange = false
## Log level to use when logging to the amq.rabbitmq.log exchange
##
# log.exchange.level = info
## ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
## RabbitMQ LDAP Plugin
##
## Related doc guide: https://rabbitmq.com/ldap.html.
##
## ----------------------------------------------------------------------------
# =======================================
# LDAP section
# =======================================
##
## Connecting to the LDAP server(s)
## ================================
##
## Specify servers to bind to. You *must* set this in order for the plugin
## to work properly.
##
# auth_ldap.servers.1 = your-server-name-goes-here
## You can define multiple servers
# auth_ldap.servers.2 = your-other-server
## Connect to the LDAP server using TLS
##
# auth_ldap.use_ssl = false
## Specify the LDAP port to connect to
##
# auth_ldap.port = 389
## LDAP connection timeout, in milliseconds or 'infinity'
##
# auth_ldap.timeout = infinity
## Or number
# auth_ldap.timeout = 500
## Enable logging of LDAP queries.
## One of
## - false (no logging is performed)
## - true (verbose logging of the logic used by the plugin)
## - network (as true, but additionally logs LDAP network traffic)
##
## Defaults to false.
##
# auth_ldap.log = false
## Also can be true or network
# auth_ldap.log = true
# auth_ldap.log = network
##
## Authentication
## ==============
##
## Pattern to convert the username given through AMQP to a DN before
## binding
##
# auth_ldap.user_dn_pattern = cn=${username},ou=People,dc=example,dc=com
## Alternatively, you can convert a username to a Distinguished
## Name via an LDAP lookup after binding. See the documentation for
## full details.
## When converting a username to a dn via a lookup, set these to
## the name of the attribute that represents the user name, and the
## base DN for the lookup query.
##
# auth_ldap.dn_lookup_attribute = userPrincipalName
# auth_ldap.dn_lookup_base = DC=gopivotal,DC=com
## Controls how to bind for authorisation queries and also to
## retrieve the details of users logging in without presenting a
## password (e.g., SASL EXTERNAL).
## One of
## - as_user (to bind as the authenticated user - requires a password)
## - anon (to bind anonymously)
## - {UserDN, Password} (to bind with a specified user name and password)
##
## Defaults to 'as_user'.
##
# auth_ldap.other_bind = as_user
## Or can be more complex:
# auth_ldap.other_bind.user_dn = User
# auth_ldap.other_bind.password = Password
## If user_dn and password defined - other options is ignored.
# -----------------------------
# Too complex section of LDAP
# -----------------------------
##
## Authorisation
## =============
##
## The LDAP plugin can perform a variety of queries against your
## LDAP server to determine questions of authorisation.
##
## Related doc guide: https://rabbitmq.com/ldap.html#authorisation.
## Following configuration should be defined in advanced.config file
## DO NOT UNCOMMENT THESE LINES!
## Set the query to use when determining vhost access
##
## {vhost_access_query, {in_group,
## "ou=${vhost}-users,ou=vhosts,dc=example,dc=com"}},
## Set the query to use when determining resource (e.g., queue) access
##
## {resource_access_query, {constant, true}},
## Set queries to determine which tags a user has
##
## {tag_queries, []}
# ]},
# -----------------------------
修改对应信息后上传到服务器rabbitmq安装目录的/etc/rabbitmq 目录下:
3.10、第十步:创建Rabbitmq超管用户
启动Rabbitmq后,执行以下命令查看当前rabbitmq服务已存在的用户列表:
由于guest用户默认只能在服务器本机登录,无法远程登录。因此需要单独创建一个管理员账号:
[aiot@template-CentOS7 rabbitmq_server-3.8.16]$ rabbitmqctl add_user admin admin_hckj
Adding user "admin" ...
Done. Don't forget to grant the user permissions to some virtual hosts! See 'rabbitmqctl help set_permissions' to learn more.
[aiot@template-CentOS7 rabbitmq_server-3.8.16]$ rabbitmqctl set_user_tags admin administrator
Setting tags for user "admin" to [administrator] ...
[aiot@template-CentOS7 rabbitmq_server-3.8.16]$ rabbitmqctl list_users
Listing users ...
user tags
admin [administrator]
guest [administrator]
[aiot@template-CentOS7 rabbitmq_server-3.8.16]$
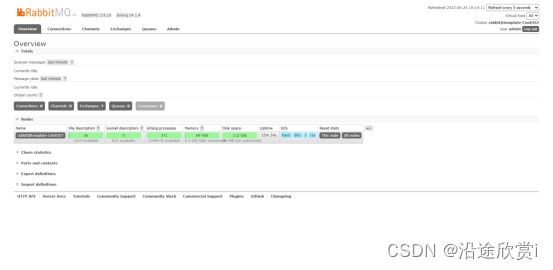
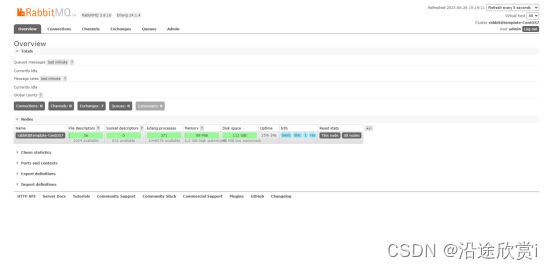
3.11、第十一步:登录管控台
访问部署rabbitmq的管控台端口(这里是:http://10.55.21.232:9995/#/),使用刚刚创建的管理员账号登录:
3.12、常用命令
| 命令用途 | 命令 |
|---|---|
| 启动服务 | service rabbitmq start |
| 查看服务状态 | service rabbitmq status |
| 停止服务 | service rabbitmq stop |
| 启用插件 | rabbitmq-plugins enable [具体插件] |
| 移除服务 | rabbitmq-service remove |
| 安装服务 | rabbitmq-service install |
| 重启服务 | rabbitmq-server restart |
| 启用日志插件 | rabbitmq-plugins enable rabbitmq_tracing |
| 查看集群状态 | rabbitmqctl cluster_status |
| 查看策略 | rabbitmqctl list_policies |
| 设置集群名称 | rabbitmqctl set_cluster_name cluster_name |
| 手动同步queue | rabbitmqctl sync_queue name |
| 取消queue同步 | rabbitmqctl cancel_sync_queue name |
| 查看所有队列消息 | rabbitmqctl list_queues |
| 获取队列消息 | rabbitmqctl list_queues[-p vhostpath] [queueinfoitem …] |
| 新增用户 | rabbitmqctl add_user username password |
| 删除用户 | rabbitmqctl delete_user username |
| 查看用户列表 | rabbitmqctl list_users |
| 修改用户密码 | rabbitmqctl change_password username newpassword |
| 清除密码 | rabbitmqctl clear_password {userName} |
| 设置用户角色 | rabbitmqctl set_user_tags zhaojigang administrator |
| 查看主机列表 | rabbitmqctl list_vhosts |
| 添加主机 | rabbitmqctl add_vhost vhostname |
| 删除主机 | rabbitmqctl delete_vhost vhostname |
| 查看所有连接 | rabbitmqadmin list connections |
| 查看概览 | rabbitmqadmin show overview |
| 查看所有节点 | rabbitmqadmin list nodes |
| 查看所有通道 Channel | rabbitmqadmin list channels |
| 查看所有消费者 | rabbitmqadmin list consumers |
| 查看所有交换机 | rabbitmqadmin list exchanges |
| 查看所有路由与队列的关系绑定 | rabbitmqadmin list bindings |