Python最佳实践-构建自己的第三方库
- 作者简介:大家好,我是Zeeland,全栈领域优质创作者。
- CSDN主页:Zeeland
- 我的博客:Zeeland
- Github主页: Undertone0809 (Zeeland) (github.com)
- 支持我:点赞+收藏⭐️+留言
- 系列专栏:Python系列专栏
- 介绍:The mixture of software dev+Iot+ml+anything
移植自本人博客:Python最佳实践-构建自己的第三方库
Introduction
在写一个项目的时候需要用到发布订阅者模式(又叫广播模式),于是就实现了一下,写完之后感觉可以封装成库,于是查阅了一下如何在python上开发自己的第三方库,并上传至Pypi,让别人可以直接pip下来。该项目目前已封装成第三方库,详细信息可以跳转https://github.com/Undertone0809/broadcast-service
如果你有好的想法,或者在项目开发时遇到了封装了一些不错的功能,笔者也强烈推荐将其封装成第三封库开源出来,造福更多的人。
如何构建?
如何构建自己的第三方库,我将以自己的项目broadcast-service为例一步一步地介绍如何构建一个python第三方库。
First of all,你需要在Pypi注册一个号,用于上传你的第三方库,官网链接。
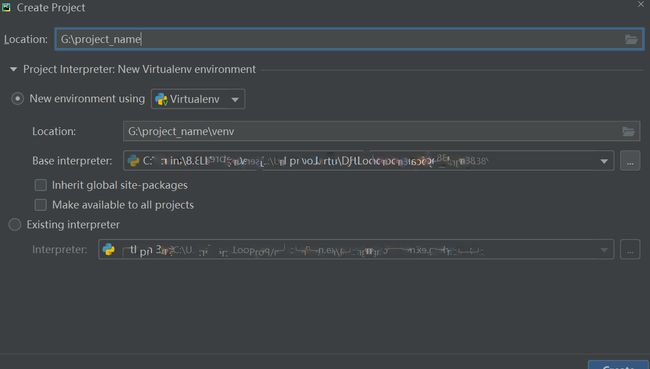
接着,打开pycharm,新建一个项目,然后选择编译器Virtualenv,新建一个虚拟环境。
等待虚拟环境创建完成,如果默认存在main.py,就删除它
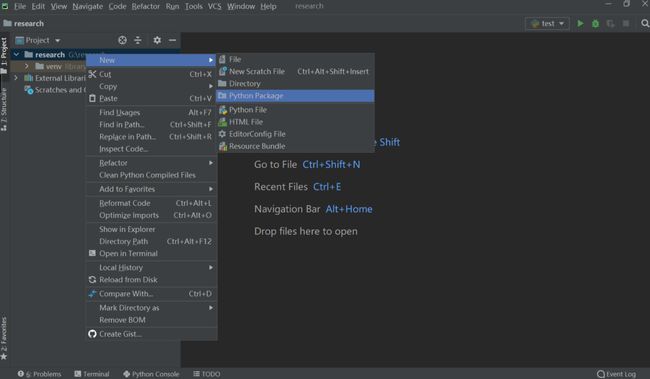
然后,新建一个python package文件夹,取名为你要上传的库的名字。
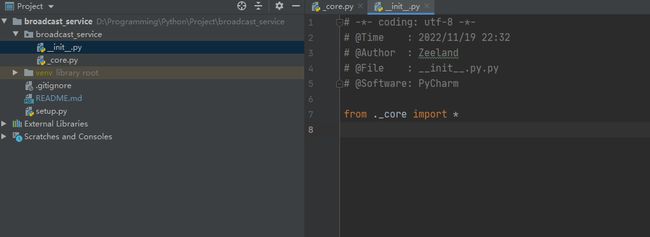
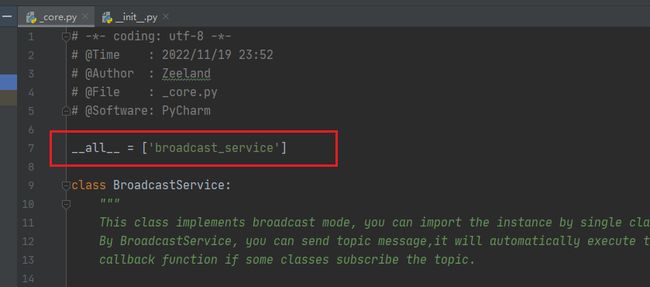
创建后,我们可以看到文件夹中默认有__init__.py,先不用编辑它,紧接着新建一个py文件,名叫_core.py,用于编写我们的核心代码
不是一定要叫_core.py,叫什么都无所谓,至于为什么要取名_core.py,后面会介绍,这是一个不错的实践优化。
此时我们打开init.py,将_core.py导出。
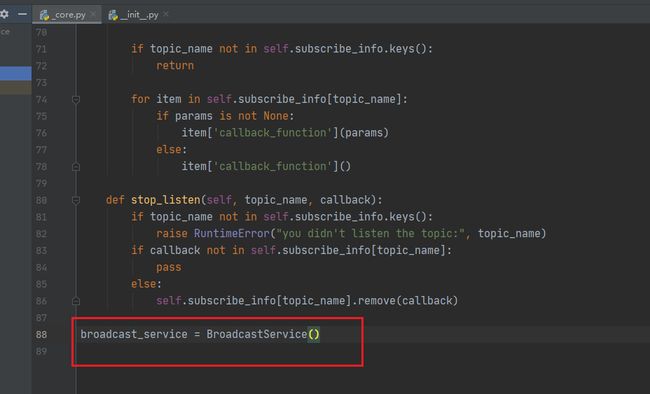
接下来就可以编写核心代码了,笔者在这里实现了一个轻量级的广播模式,不需要创建更多的类,直接引入一个单例类,即可在自己的应用程序中构建其一个完善的消息分发和广播回调模式,因此,我在_core.py实现了一个BroadcastService类,并在结尾将其实例化了一个单例类,并使用__all__ 将其导出。
至此,笔者主要的代码工作已经编写完成,接下来,我们需要做一些配置。在项目根目录下,新建setup.py
setup.py 里面要一些关于这个库的配置文件,这里我直接把官方demo的setup.py拿过来了,全部的详细配置都在里面,大家可以自行配置,或者参考我的配置。
我的配置会更简单一下,去掉了一些没什么必要的东西,大家可以参考一下。
"""A setuptools based setup module.
See:
https://packaging.python.org/guides/distributing-packages-using-setuptools/
https://github.com/pypa/sampleproject
"""
# Always prefer setuptools over distutils
from setuptools import setup, find_packages
import pathlib
here = pathlib.Path(__file__).parent.resolve()
# Get the long description from the README file
long_description = (here / "README.md").read_text(encoding="utf-8")
# Arguments marked as "Required" below must be included for upload to PyPI.
# Fields marked as "Optional" may be commented out.
setup(
# This is the name of your project. The first time you publish this
# package, this name will be registered for you. It will determine how
# users can install this project, e.g.:
#
# $ pip install sampleproject
#
# And where it will live on PyPI: https://pypi.org/project/sampleproject/
#
# There are some restrictions on what makes a valid project name
# specification here:
# https://packaging.python.org/specifications/core-metadata/#name
name="sampleproject", # Required
# Versions should comply with PEP 440:
# https://www.python.org/dev/peps/pep-0440/
#
# For a discussion on single-sourcing the version across setup.py and the
# project code, see
# https://packaging.python.org/guides/single-sourcing-package-version/
version="2.0.0", # Required
# This is a one-line description or tagline of what your project does. This
# corresponds to the "Summary" metadata field:
# https://packaging.python.org/specifications/core-metadata/#summary
description="A sample Python project", # Optional
# This is an optional longer description of your project that represents
# the body of text which users will see when they visit PyPI.
#
# Often, this is the same as your README, so you can just read it in from
# that file directly (as we have already done above)
#
# This field corresponds to the "Description" metadata field:
# https://packaging.python.org/specifications/core-metadata/#description-optional
long_description=long_description, # Optional
# Denotes that our long_description is in Markdown; valid values are
# text/plain, text/x-rst, and text/markdown
#
# Optional if long_description is written in reStructuredText (rst) but
# required for plain-text or Markdown; if unspecified, "applications should
# attempt to render [the long_description] as text/x-rst; charset=UTF-8 and
# fall back to text/plain if it is not valid rst" (see link below)
#
# This field corresponds to the "Description-Content-Type" metadata field:
# https://packaging.python.org/specifications/core-metadata/#description-content-type-optional
long_description_content_type="text/markdown", # Optional (see note above)
# This should be a valid link to your project's main homepage.
#
# This field corresponds to the "Home-Page" metadata field:
# https://packaging.python.org/specifications/core-metadata/#home-page-optional
url="https://github.com/pypa/sampleproject", # Optional
# This should be your name or the name of the organization which owns the
# project.
author="A. Random Developer", # Optional
# This should be a valid email address corresponding to the author listed
# above.
author_email="[email protected]", # Optional
# Classifiers help users find your project by categorizing it.
#
# For a list of valid classifiers, see https://pypi.org/classifiers/
classifiers=[ # Optional
# How mature is this project? Common values are
# 3 - Alpha
# 4 - Beta
# 5 - Production/Stable
"Development Status :: 3 - Alpha",
# Indicate who your project is intended for
"Intended Audience :: Developers",
"Topic :: Software Development :: Build Tools",
# Pick your license as you wish
"License :: OSI Approved :: MIT License",
# Specify the Python versions you support here. In particular, ensure
# that you indicate you support Python 3. These classifiers are *not*
# checked by 'pip install'. See instead 'python_requires' below.
"Programming Language :: Python :: 3",
"Programming Language :: Python :: 3.7",
"Programming Language :: Python :: 3.8",
"Programming Language :: Python :: 3.9",
"Programming Language :: Python :: 3.10",
"Programming Language :: Python :: 3 :: Only",
],
# This field adds keywords for your project which will appear on the
# project page. What does your project relate to?
#
# Note that this is a list of additional keywords, separated
# by commas, to be used to assist searching for the distribution in a
# larger catalog.
keywords="sample, setuptools, development", # Optional
# When your source code is in a subdirectory under the project root, e.g.
# `src/`, it is necessary to specify the `package_dir` argument.
package_dir={"": "src"}, # Optional
# You can just specify package directories manually here if your project is
# simple. Or you can use find_packages().
#
# Alternatively, if you just want to distribute a single Python file, use
# the `py_modules` argument instead as follows, which will expect a file
# called `my_module.py` to exist:
#
# py_modules=["my_module"],
#
packages=find_packages(where="src"), # Required
# Specify which Python versions you support. In contrast to the
# 'Programming Language' classifiers above, 'pip install' will check this
# and refuse to install the project if the version does not match. See
# https://packaging.python.org/guides/distributing-packages-using-setuptools/#python-requires
python_requires=">=3.7, <4",
# This field lists other packages that your project depends on to run.
# Any package you put here will be installed by pip when your project is
# installed, so they must be valid existing projects.
#
# For an analysis of "install_requires" vs pip's requirements files see:
# https://packaging.python.org/discussions/install-requires-vs-requirements/
install_requires=["peppercorn"], # Optional
# List additional groups of dependencies here (e.g. development
# dependencies). Users will be able to install these using the "extras"
# syntax, for example:
#
# $ pip install sampleproject[dev]
#
# Similar to `install_requires` above, these must be valid existing
# projects.
extras_require={ # Optional
"dev": ["check-manifest"],
"test": ["coverage"],
},
# If there are data files included in your packages that need to be
# installed, specify them here.
package_data={ # Optional
"sample": ["package_data.dat"],
},
# Although 'package_data' is the preferred approach, in some case you may
# need to place data files outside of your packages. See:
# http://docs.python.org/distutils/setupscript.html#installing-additional-files
#
# In this case, 'data_file' will be installed into '/my_data'
data_files=[("my_data", ["data/data_file"])], # Optional
# To provide executable scripts, use entry points in preference to the
# "scripts" keyword. Entry points provide cross-platform support and allow
# `pip` to create the appropriate form of executable for the target
# platform.
#
# For example, the following would provide a command called `sample` which
# executes the function `main` from this package when invoked:
entry_points={ # Optional
"console_scripts": [
"sample=sample:main",
],
},
# List additional URLs that are relevant to your project as a dict.
#
# This field corresponds to the "Project-URL" metadata fields:
# https://packaging.python.org/specifications/core-metadata/#project-url-multiple-use
#
# Examples listed include a pattern for specifying where the package tracks
# issues, where the source is hosted, where to say thanks to the package
# maintainers, and where to support the project financially. The key is
# what's used to render the link text on PyPI.
project_urls={ # Optional
"Bug Reports": "https://github.com/pypa/sampleproject/issues",
"Funding": "https://donate.pypi.org",
"Say Thanks!": "http://saythanks.io/to/example",
"Source": "https://github.com/pypa/sampleproject/",
},
)
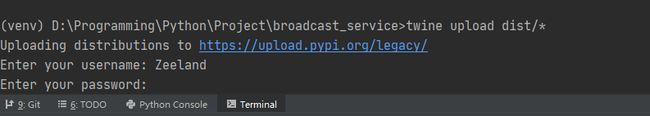
接下来,我们打开终端,将目录切换至该项目目录下,输入python setup.py sdist 项目就会进行打包。打包之后,可以看到项目目录下多了两个文件。
最后我们输入命令twine upload dist/*,然后输入Pypi的帐号密码,就可以对项目进行打包。
这个时候你会发现,你的第三方库已经传到Pypi上面了,也就是说,现在你可以直接使用pip install来下载导入你的包了。
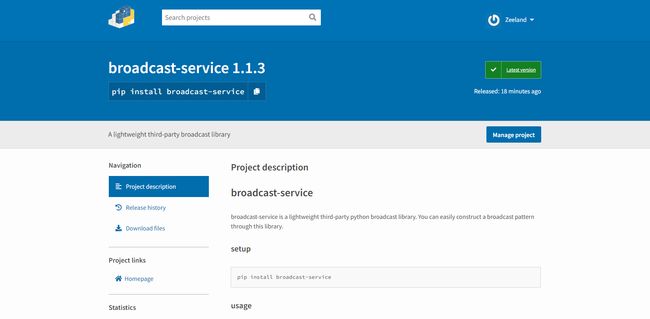
我们现在随便在其他的项目下新建个py测试一下,首先pip install 导入刚才上传的库,这里导入我的库
pip install broadcast-service
体验一波,诶嘿。
至此,关于构建自己的第三方库的教程就结束了。
为什么用_core.py
这里说一下为什么我将代码写在_core.py的目的,如果init.py里面是空的话,我写代码的时候就要像下面这样:
from broadcast_service._core import broadcast_service
# do something
实际上_core.py 里面最重要的代码是 __all__ = ['broadcast_service'] ,通过这个代码,我在init.py中使用from ._core import * 就可以很顺利的将broadcast_service这个单例导出。导出之后,我导包的时候就会更简洁一些, 可读性更好,如下所示:
from broadcast_service import broadcast_service
# do something
Python开源项目
下面是本人通过pypi和github开源的项目,欢迎star!
- 【prompt-me】一个专为Prompt Engineer设计LLM Prompt Layer框架,支持连续对话、角色预设、提供缓存的功能,可以记录历史对话等功能,可以无需代理直接访问,开箱即用。 通过 prompt-me,你可以轻松构建起属于自己的GPT应用程序。
- 【cushy-storage】一个基于磁盘缓存的Python框架
- 【cushy-socket】 一款轻量级的Python Socket框架
- 【cushy-serial】 一个轻量级Python serial库
- 【broadcast-service】一个轻量级Python发布订阅者框架
- 【Python实战】从架构设计到实现:一个Powerful的图书管理系统
References
- https://packaging.python.org/en/latest/guides/distributing-packages-using-setuptools/
- 编写属于自己的Python第三方库
- 如何制作自己的python库 -csdn
- setup.py github demo
- Python单例模式4种方式