Ansible-playbook
Ansible之Playbook
1.1 Playbook简介
Playbook与ad-hoc相比,是一种完全不同的运用ansible的方式,类似与saltstack的state状态文件。ad-hoc无法持久使用,playbook可以持久使用。
playbook是由一个或多个play组成的列表,play的主要功能在于将事先归并为一组的主机装扮成事先通过ansible中的task定义好的角色。从根本上来讲,所谓的task无非是调用ansible的一个module。将多个play组织在一个playbook中,即可以让它们联合起来按事先编排的机制完成某一任务
1.2 Playbook核心元素
- Hosts 执行的远程主机列表
- Tasks 任务集
- Varniables 内置变量或自定义变量在playbook中调用
- Templates 模板,即使用模板语法的文件,比如配置文件等
- Handlers 和notity结合使用,由特定条件触发的操作,满足条件方才执行,否则不执行
- tags 标签,指定某条任务执行,用于选择运行playbook中的部分代码。
1.3 Playbook语法
playbook使用yaml语法格式,后缀可以是yaml,也可以是yml。
- 在单一一个
playbook文件中,可以连续三个连子号(---)区分多个play。还有选择性的连续三个点好(...)用来表示play的结尾,也可省略。 - 次行开始正常写
playbook的内容,一般都会写上描述该playbook的功能。 - 使用#号注释代码。
- 缩进必须统一,不能空格和
tab混用。 - 缩进的级别也必须是一致的,同样的缩进代表同样的级别,程序判别配置的级别是通过缩进结合换行实现的。
YAML文件内容和Linux系统大小写判断方式保持一致,是区分大小写的,k/v的值均需大小写敏感k/v的值可同行写也可以换行写。同行使用:分隔。v可以是个字符串,也可以是一个列表- 一个完整的代码块功能需要最少元素包括
name: task
示例:
# 创建playbook文件
[student@ansible ~/ansible]$ cat playbook01.yml
--- #固定格式
- hosts: node1 #定义需要执行主机
remote_user: root #远程用户
vars: #定义变量
http_port: 8088 #变量
tasks: #定义一个任务的开始
- name: create new file #定义任务的名称
file: name=/tmp/playtest.txt state=touch #调用模块,具体要做的事情
- name: create new user
user: name=test02 system=yes shell=/sbin/nologin
- name: install package
yum: name=httpd
- name: config httpd
template: src=./httpd.conf dest=/etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
notify: #定义执行一个动作(action)让handlers来引用执行,与handlers配合使用
- restart apache #notify要执行的动作,这里必须与handlers中的name定义内容一致
- name: copy index.html
copy: src=/var/www/html/index.html dest=/var/www/html/index.html
- name: start httpd
service: name=httpd state=started
handlers: #处理器:更加tasks中notify定义的action触发执行相应的处理动作
- name: restart apache #要与notify定义的内容相同
service: name=httpd state=restarted #触发要执行的动作
1.4 Playbook运行方式
通过ansible-playbook命令运行
格式:ansible-playbook
[student@ansible ~/ansible]$ ansible-playbook -h
#ansible-playbook常用选项:
--check or -C #只检测可能会发生的改变,但不真正执行操作
--list-hosts #列出运行任务的主机
--list-tags #列出playbook文件中定义所有的tags
--list-tasks #列出playbook文件中定义的所以任务集
--limit #主机列表 只针对主机列表中的某个主机或者某个组执行
-f #指定并发数,默认为5个
-t #指定tags运行,运行某一个或者多个tags。(前提playbook中有定义tags)
-v #显示过程 -vv -vvv更详细
1.5 Playbook中元素属性
1.5.1 主机与用户
在一个playbook开始时,最先定义的是要操作的主机和用户
---
- hosts: node1
remote_user: root
除了上面的定义外,还可以在某一个tasks中定义要执行该任务的远程用户
tasks:
- name: run df -h
remote_user: test
shell: name=df -h
还可以定义使用sudo授权用户执行该任务
tasks:
- name: run df -h
sudo_user: test
sudo: yes
shell: name=df -h
1.5.2 tasks任务列表
每一个task必须有一个名称name,这样在运行playbook时,从其输出的任务执行信息中可以很清楚的辨别是属于哪一个task的,如果没有定义 name,action的值将会用作输出信息中标记特定的task。
每一个playbook中可以包含一个或者多个tasks任务列表,每一个tasks完成具体的一件事,(任务模块)比如创建一个用户或者安装一个软件等,在hosts中定义的主机或者主机组都将会执行这个被定义的tasks。
tasks:
- name: create new file
file:
path: /tmp/test01.txt
state: touch
- name: create new user
user:
name: test001
state: present
1.5.3 Handlers与Notify
很多时候当我们某一个配置发生改变,我们需要重启服务,(比如httpd配置文件文件发生改变了)这时候就可以用到handlers和notify了;
(当发生改动时)notify actions会在playbook的每一个task结束时被触发,而且即使有多个不同task通知改动的发生,notify actions知会被触发一次;比如多个resources指出因为一个配置文件被改动,所以apache需要重启,但是重新启动的操作知会被执行一次。
[student@ansible ~/ansible]$ cat httpd.yml
#用于安装httpd并配置启动
---
- hosts: node1
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install httpd
yum:
name: httpd
state: installed
- name: config httpd
template:
src: /root/httpd.conf
dest: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
notify:
- restart httpd
- name: start httpd
service:
name: httpd
state: started
handlers:
- name: restart httpd
service:
name: httpd
state: restarted
#这里只要对httpd.conf配置文件作出了修改,修改后需要重启生效,在tasks中定义了restart httpd这个action,然后在handlers中引用上面tasks中定义的notify。
1.6 Playbook中变量的使用
环境说明:这里配置了两个组,一个apache组和一个nginx组
[student@ansible ~/ansible]$ cat /etc/ansible/hosts
[apache]
192.168.111.46
192.168.111.43
[nginx]
192.168.111.6[1:2]
1.6.1 命令行指定变量
执行playbook时候通过参数-e传入变量,这样传入的变量在整个playbook中都可以被调用,属于全局变量
[student@ansible ~/ansible]$ cat variables.yml
---
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install pkg
yum:
name: "{{ pkg }}"
#执行playbook 指定pkg
[student@ansible ~/ansible]$ ansible-playbook -e "pkg=httpd" variables.yml
1.6.2 hosts文件中定义变量
在/etc/ansible/hosts文件中定义变量,可以针对每个主机定义不同的变量,也可以定义一个组的变量,然后直接在playbook中直接调用。注意,组中定义的变量没有单个主机中的优先级高。
# 编辑hosts文件定义变量
[student@ansible ~/ansible]$ vim /etc/ansible/hosts
[apache]
192.168.111.46 webdir=/opt/test #定义单个主机的变量
192.168.111.43
[apache:vars] #定义整个组的统一变量
webdir=/web/test
[nginx]
192.168.111.6[1:2]
[nginx:vars]
webdir=/opt/web
# 编辑playbook文件
[student@ansible ~/ansible]$ cat variables.yml
---
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: create webdir
file:
name: "{{ webdir }}"
state: directory #引用变量
# 执行playbook
[student@ansible ~/ansible]$ ansible-playbook variables.yml
1.6.3 playbook文件中定义变量
编写playbook时,直接在里面定义变量,然后直接引用,可以定义多个变量;注意:如果在执行playbook时,又通过-e参数指定变量的值,那么会以-e参数指定的为准。
# 编辑playbook
[student@ansible ~/ansible]$ cat variables.yml
---
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
vars: #定义变量
pkg: nginx #变量1
dir: /tmp/test1 #变量2
tasks:
- name: install pkg
yum:
name: "{{ pkg }} " #引用变量
state: installed
- name: create new dir
file:
name: "{{ dir }}" #引用变量
state: directory
# 执行playbook
[student@ansible ~/ansible]$ ansible-playbook variables.yml
# 如果执行时候又重新指定了变量的值,那么会已重新指定的为准
[student@ansible ~/ansible]$ ansible-playbook -e "dir=/tmp/test2" variables.yml
1.6.4 调用setup模块获取变量
setup模块默认是获取主机信息的,有时候在playbook中需要用到,所以可以直接调用。常用的参数[参考](https://buji595.github.io/2019/05/27/Ansible Ad-hoc常用Module/#setup)
# 编辑playbook文件
[student@ansible ~/ansible]$ cat variables.yml
---
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: create file
file:
name: "{{ ansible_fqdn }}.log " #引用setup中的ansible_fqdn
state: touch
# 执行playbook
[student@ansible ~/ansible]$ ansible-playbook variables.yml
1.6.5 独立的变量YAML文件中定义
为了方便管理将所有的变量统一放在一个独立的变量YAML文件中,laybook文件直接引用文件调用变量即可。
# 定义存放变量的文件
[student@ansible ~/ansible]$ cat var.yml
var1: vsftpd
var2: httpd
# 编写playbook
[student@ansible ~/ansible]$ cat variables.yml
---
- hosts: all
remote_user: root
vars_files: #引用变量文件
- ./var.yml #指定变量文件的path(这里可以是绝对路径,也可以是相对路径)
tasks:
- name: install package
yum:
name: "{{ var1 }}" #引用变量
- name: create file
file:
name: /tmp/{{ var2 }}.log #引用变量
state: touch
# 执行playbook
[student@ansible ~/ansible]$ ansible-playbook variables.yml
1.7 Playbook中标签的使用
一个playbook文件中,执行时如果想执行某一个任务,那么可以给每个任务集进行打标签,这样在执行的时候可以通过-t选择指定标签执行,还可以通过--skip-tags选择除了某个标签外全部执行等。
# 编辑playbook
[student@ansible ~/ansible]$ cat httpd.yml
---
- hosts: 192.168.111.61
remote_user: root
tasks:
- name: install httpd
yum:
name: httpd
state: installed
tags: inhttpd
- name: start httpd
service:
name: httpd
state: started
tags: sthttpd
- name: restart httpd
service:
name: httpd
state: restarted
tags:
- rshttpd
- rs_httpd
# 正常执行的结果
[student@ansible ~/ansible]$ ansible-playbook httpd.yml
PLAY [192.168.111.61] **************************************************************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] ***********************************************************************************************************************
ok: [192.168.111.61]
TASK [install httpd] *************************************************************************************************************************
ok: [192.168.111.61]
TASK [start httpd] ***************************************************************************************************************************
ok: [192.168.111.61]
TASK [restart httpd] *************************************************************************************************************************
changed: [192.168.111.61]
PLAY RECAP ***********************************************************************************************************************************
192.168.111.61 : ok=4 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
1)通过-t选项指定tags进行执行
# 通过-t指定tags名称,多个tags用逗号隔开
[root@ansible PlayBook]# ansible-playbook -t rshttpd httpd.yml
PLAY [192.168.111.61] **************************************************************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] ***********************************************************************************************************************
ok: [192.168.111.61]
TASK [restart httpd] *************************************************************************************************************************
changed: [192.168.111.61]
PLAY RECAP ***********************************************************************************************************************************
192.168.111.61 : ok=2 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
2)通过--skip-tags选项排除不执行的tags
[root@ansible PlayBook]# ansible-playbook --skip-tags inhttpd httpd.yml
PLAY [192.168.111.61] **************************************************************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] ***********************************************************************************************************************
ok: [192.168.111.61]
TASK [start httpd] ***************************************************************************************************************************
ok: [192.168.111.61]
TASK [restart httpd] *************************************************************************************************************************
changed: [192.168.111.61]
PLAY RECAP ***********************************************************************************************************************************
192.168.111.61 : ok=3 changed=1 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
1.8 Playbook案例
一、部署web服务器
1、部署yum仓库
2、安装httpd 3、新建/www目录
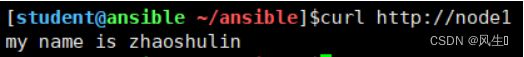
4、在/www中新建index.html,内容为my name is zhaoshulin
5、该web服务器的DocumentRoot为/www
6、实现在ansible中能够使用http://node1访问到该网页内容
[student@ansible ~/ansible]$cat zsl.yml
---
- name: web statin
hosts: node1
tasks:
- name: set repo1
yum_repository:
file: server
name: BaseOS
description: BaseOS
baseurl: file:///mnt/BaseOS
enabled: yes
gpgcheck: no
- name: set repo2
yum_repository:
file: server
name: AppStream
description: AppStream
baseurl: file:///mnt/AppStream
enabled: yes
gpgcheck: no
- name: mount Dev
mount:
src: /dev/cdrom
path: /mnt
fstype: iso9660
state: mounted
- name: install httpd
yum:
name: httpd
state: installed
- name: create link
file:
src: /var/www/html
dest: /www
state: link
- name: create files
file:
path: /www/index.html
state: touch
- name: Add content
lineinfile:
dest: /www/index.html
line: my name is zhaoshulin
- name: set selinux context
file:
path: '/www/index.html'
setype: httpd_sys_content_t
- name: apply context
shell:
cmd: restorecon -Rv /www/index.html
- name: modify apache config1
replace:
path: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
regexp: DocumentRoot "/var/www/html"
replace: DocumentRoot "/www"
- name: modify apache config2
replace:
path: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
regexp:
replace:
- name: restart httpd
service:
name: httpd
state: restarted
enabled: yes
- name: set firewalld for httpd
firewalld:
service: http
state: enabled
permanent: yes
immediate: yes
[student@ansible ~/ansible]$ansible-playbook zsl.yml
PLAY [web statin] ******************************************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *************************************************************************************************
ok: [node1]
TASK [set repo1] *******************************************************************************************************
ok: [node1]
TASK [set repo2] *******************************************************************************************************
ok: [node1]
TASK [mount Dev] *******************************************************************************************************
ok: [node1]
TASK [install httpd] ***************************************************************************************************
ok: [node1]
TASK [create link] *****************************************************************************************************
ok: [node1]
TASK [create files] ****************************************************************************************************
changed: [node1]
TASK [Add content] *****************************************************************************************************
ok: [node1]
TASK [set selinux context] *********************************************************************************************
ok: [node1]
TASK [apply context] ***************************************************************************************************
changed: [node1]
TASK [modify apache config1] *******************************************************************************************
ok: [node1]
TASK [modify apache config2] *******************************************************************************************
ok: [node1]
TASK [restart httpd] ***************************************************************************************************
changed: [node1]
TASK [set firewalld for httpd] *****************************************************************************************
changed: [node1]
PLAY RECAP *************************************************************************************************************
node1 : ok=14 changed=4 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0
二、使用notify…handlers
1、写一个剧本runtime.yml,只对node1操作
2、创建用户aa,该用户不能用于登录,家目录/www
3、在/www创建一个文件html
4、每次执行该剧本时,将系统的当前时间输入到html文件中。
5、如果html中的时间发生变化,那么创建/tmp/kk的文件
[student@ansible ~/ansible]$cat alone.yml
---
- name: time
hosts: node1
tasks:
- name: create user
user:
name: aa
shell: /sbin/nologin
home: /www
- name: create file
file:
path: /www/html
state: touch
- name: date
shell: date > /www/html
notify:
- kk
handlers:
- name: kk
file:
path: /tmp/kk
state: touch
[student@ansible ~/ansible]$ansible-playbook alone.yml
PLAY [time] ************************************************************************************************************
TASK [Gathering Facts] *************************************************************************************************
ok: [node1]
TASK [create user] *****************************************************************************************************
ok: [node1]
TASK [create file] *****************************************************************************************************
changed: [node1]
TASK [date] ************************************************************************************************************
changed: [node1]
RUNNING HANDLER [kk] ***************************************************************************************************
changed: [node1]
PLAY RECAP *************************************************************************************************************
node1 : ok=5 changed=3 unreachable=0 failed=0 skipped=0 rescued=0 ignored=0