Spring源码解析(十):spring整合mybatis源码
Spring源码系列文章
Spring源码解析(一):环境搭建
Spring源码解析(二):bean容器的创建、默认后置处理器、扫描包路径bean
Spring源码解析(三):bean容器的刷新
Spring源码解析(四):单例bean的创建流程
Spring源码解析(五):循环依赖
Spring源码解析(六):bean工厂后置处理器ConfigurationClassPostProcessor
Spring源码解析(七):bean后置处理器AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
Spring源码解析(八):bean后置处理器CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
Spring源码解析(九):AOP源码之@Aspect所有相关注解解析
Spring源码解析(十):spring整合mybatis源码
目录
- 一、Mybatis的使用介绍
-
- 1、mybatis框架单独使用
- 2、spring整合mybatis使用
- 二、spring整合mybatis原理
-
- 1、@MapperScan注解原理
-
- 1.1、MapperScannerRegistrar类的核心方法(实现ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar接口方法)
- 1.2、MapperScannerConfigurer类的作用
- 2、SqlSessionFactoryBean类
-
- 2.1、FactoryBean接口
- 3、MapperFactoryBean类
-
- 3.1、FactoryBean接口
- 3.2、DaoSupport抽象类
- 3.3、SqlSessionDaoSupport抽象类
- 3.4、MapperFactoryBean的checkDaoConfig方法
- 4、总结Mapper对象的创建过程
一、Mybatis的使用介绍
1、mybatis框架单独使用
- 通过sqlSession获取对应的代理对象
- 代理对象执行sql完成数据库操作
public class MybatisMain {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
String resource = "mybatis-config.xml";
InputStream resourceAsStream = Resources.getResourceAsStream(resource);
// 1.解析XML配置
SqlSessionFactoryBuilder builder = new SqlSessionFactoryBuilder();
// 2.基于解析好的XML配置创建一个SqlSessionFactory
SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory = builder.build(resourceAsStream);
// 3.通过SqlSessionFactory,创建一个SqlSession
SqlSession sqlSession = sqlSessionFactory.openSession();
// 4.获取一个代理对象
UserMapper mapper = sqlSession.getMapper(UserMapper.class);
// 5.调用代理对象的方法
System.out.println("代理对象查询结果:" + mapper.selectOne(1));
}
}
2、spring整合mybatis使用
- SqlSession对象以及代理对象都交给spring容器来创建
- 直接从容器中获取Mapper接口的实现类(代理对象)即可
@Configuration //声明该类是核心配置类
@ComponentScan("com.xc") //开启spring注解扫描
@MapperScan("com.xc.mapper") //MyBatis扫描Mapper接口
public class MybatisConfig {
@Bean
public DataSource dataSource() {
DriverManagerDataSource driverManagerDataSource = new DriverManagerDataSource();
driverManagerDataSource.setPassword("root");
driverManagerDataSource.setUsername("root");
driverManagerDataSource.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver");
driverManagerDataSource.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mybatis?useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&serverTimezone=GMT%2B8&useSSL=false");
return driverManagerDataSource;
}
@Bean
public SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactoryBean() {
SqlSessionFactoryBean sqlSessionFactoryBean = new SqlSessionFactoryBean();
sqlSessionFactoryBean.setDataSource(dataSource());
return sqlSessionFactoryBean;
}
// 执行操作
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext context = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(MybatisConfig.class);
UserMapper userMapper = context.getBean(UserMapper.class);
User user = userMapper.selectOne(100);
System.out.println(user);
}
}
二、spring整合mybatis原理
- 根据上面spring整合mybatis的配置类的信息,要想清楚Spring是如何整合Mybatis的,我们只要弄明白两点
@MapperScan注解的作用SqlSessionFactoryBean对象的作用
1、@MapperScan注解原理
- 有
@Import注解,那它的作用很明显,就是注册bean
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Documented
@Import(MapperScannerRegistrar.class)
@Repeatable(MapperScans.class)
public @interface MapperScan {
// basePackages属性的别名,等价于basePackages
String[] value() default {};
// 扫描的包名
String[] basePackages() default {};
// 可以提供一个类,以类的包名作为扫描的包
Class<?>[] basePackageClasses() default {};
// BeanName的生成器,一般用默认的就好啦
Class<? extends BeanNameGenerator> nameGenerator() default BeanNameGenerator.class;
// 指定要扫描的注解
Class<? extends Annotation> annotationClass() default Annotation.class;
// 指定标记接口,只有继承了这个接口才会被扫描
Class<?> markerInterface() default Class.class;
// 指定SqlSessionTemplate的名称,
// SqlSessionTemplate是Spring对Mybatis中SqlSession的封装
String sqlSessionTemplateRef() default "";
// 指定SqlSessionFactory的名称
String sqlSessionFactoryRef() default "";
// 这个属性是什么意思呢?Spring跟Mybatis整合
// 最重要的事情就是将Mybatis生成的代理对象交由Spring来管理
// 实现这个功能的就是这个MapperFactoryBean
Class<? extends MapperFactoryBean> factoryBean() default MapperFactoryBean.class;
// 是否对mapper进行懒加载,默认为false
String lazyInitialization() default "";
}
1.1、MapperScannerRegistrar类的核心方法(实现ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar接口方法)
- 核心内容就是注册
MapperScannerConfigurer.class的bean - @MapperScan注解中的属性都添加到这个bean中
public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
// 获取到@MapperScan这个注解中的属性
AnnotchaationAttributes mapperScanAttrs = AnnotationAttributes
.fromMap(importingClassMetadata.getAnnotationAttributes(MapperScan.class.getName()));
if (mapperScanAttrs != null) {
// 紧接着开始向Spring容器中注册bd
registerBeanDefinitions(importingClassMetadata, mapperScanAttrs, registry,
generateBaseBeanName(importingClassMetadata, 0));
}
}
void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata annoMeta, AnnotationAttributes annoAttrs,
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, String beanName) {
// 打算注册到容器中的bd的beanClass属性为MapperScannerConfigurer.class
BeanDefinitionBuilder builder = BeanDefinitionBuilder.genericBeanDefinition(MapperScannerConfigurer.class);
builder.addPropertyValue("processPropertyPlaceHolders", true);
// 省略部分代码
// ....
// 这部分代码就是将注解中的属性获取出来
// 放到MapperScannerConfigurer这个beanDefinition中
// 最后将这个beanDefinition注册到容器中
registry.registerBeanDefinition(beanName, builder.getBeanDefinition());
}
1.2、MapperScannerConfigurer类的作用
类图:
- 由图可知,MapperScannerConfigurer是一个
Bean工厂的后置处理器,bean初始化也会做一些事情
初始化操作:
- 内容简单,就是校验下@MapperScan是否有basePackage属性,没有抛异常
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
notNull(this.basePackage, "Property 'basePackage' is required");
}
public static void notNull(Object object, String message) {
if (object == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(message);
}
}
bean工厂后置处理器操作bean定义:
- ClassPathMapperScanner继承ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner
- ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner有扫描包注册bean的功能
- 默认扫描规则@Component的bean,包括@Controller @Service @Repository
- 所以这里需要重新设置扫描规则
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
if (this.processPropertyPlaceHolders) {
// 处理@MaperScan注解属性中的占位符
processPropertyPlaceHolders();
}
// 在这里创建了一个ClassPathMapperScanner
// 这个类继承了ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner,并复写了它的doScan、registerFilters等方法
// 其整体行为跟ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner差不多,
ClassPathMapperScanner scanner = new ClassPathMapperScanner(registry);
scanner.setAddToConfig(this.addToConfig);
scanner.setAnnotationClass(this.annotationClass);
scanner.setMarkerInterface(this.markerInterface);
scanner.setSqlSessionFactory(this.sqlSessionFactory);
scanner.setSqlSessionTemplate(this.sqlSessionTemplate);
scanner.setSqlSessionFactoryBeanName(this.sqlSessionFactoryBeanName);
scanner.setSqlSessionTemplateBeanName(this.sqlSessionTemplateBeanName);
scanner.setResourceLoader(this.applicationContext);
scanner.setBeanNameGenerator(this.nameGenerator);
scanner.setMapperFactoryBeanClass(this.mapperFactoryBeanClass);
if (StringUtils.hasText(lazyInitialization)) {
scanner.setLazyInitialization(Boolean.valueOf(lazyInitialization));
}
// 这里设置了扫描规则
scanner.registerFilters();
scanner.scan(
StringUtils.tokenizeToStringArray(this.basePackage,
ConfigurableApplicationContext.CONFIG_LOCATION_DELIMITERS));
}
- 注册指定包扫描规则(
指定注解、指定接口或全部)
public void registerFilters() {
boolean acceptAllInterfaces = true;
// 第一步,判断是否要扫描指定的注解
// 也就是判断在@MapperScan注解中是否指定了要扫描的注解
if (this.annotationClass != null) {
addIncludeFilter(new AnnotationTypeFilter(this.annotationClass));
acceptAllInterfaces = false;
}
// 第二步,判断是否要扫描指定的接口
// 同样也是根据@MapperScan注解中的属性做判断
if (this.markerInterface != null) {
addIncludeFilter(new AssignableTypeFilter(this.markerInterface) {
@Override
protected boolean matchClassName(String className) {
return false;
}
});
acceptAllInterfaces = false;
}
// 如果既没有指定注解也没有指定标记接口
// 那么所有.class文件都会被扫描
if (acceptAllInterfaces) {
addIncludeFilter((metadataReader, metadataReaderFactory) -> true);
}
// 排除package-info文件
addExcludeFilter((metadataReader, metadataReaderFactory) -> {
String className = metadataReader.getClassMetadata().getClassName();
return className.endsWith("package-info");
});
}
- 扫描指定package的类路径下的接口
- ClassPathMapperScanner重新ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner的doScan方法
- 调用父类doScan方法、对扫描出来的BeanDefinition做处理
- super.doScan以前讲过Spring源码解析(二):bean容器的创建、默认后置处理器、扫描包路径bean
- 核心内容就是扫描指定包将符合要求Class注册bean定义
# ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner类方法
public int ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner.scan(String... basePackages) {
//获取容器中已经注册BeanDefinition数量
int beanCountAtScanStart = this.registry.getBeanDefinitionCount();
//扫描
doScan(basePackages);
// Register annotation config processors, if necessary.
//是否需要注册注解后置处理,比如注册ConfigurationClassPostProcessor,AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor等
//但其实这些处理器已经注册了,这里也不需要再注册了
if (this.includeAnnotationConfig) {
AnnotationConfigUtils.registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(this.registry);
}
//注册了多少mapper
return (this.registry.getBeanDefinitionCount() - beanCountAtScanStart);
}
# ClassPathMapperScanner类方法
public Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> doScan(String... basePackages) {
//调用父类的扫描方法
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions = super.doScan(basePackages);
if (beanDefinitions.isEmpty()) {
logger.warn("No MyBatis mapper was found in '" + Arrays.toString(basePackages) + "' package. Please check your configuration.");
} else {
//对扫描出来的BeanDefinition做属性处理,比如添加SqlSessionFactory等
processBeanDefinitions(beanDefinitions);
}
return beanDefinitions;
}
- 扫描出的BeanDefinition修改
- 核心内容:将真实的BeanClass属性设置为
MapperFactoryBean.class- BeanDefinition当初创建赋值:beanClass = “com.xc.UserMapper”
- BeanDefinition的beanName依然是“
userMapper”
- BeanDefinition的构造函数添加mapperInterface参数
// 主要做了这么几件事
// 1.将扫描出来的BeanDefinition的beanClass属性设置为MapperFactoryBeanClass.class
// 2.在BeanDefinition的ConstructorArgumentValues添加一个参数
// 限定实例化时使用MapperFactoryBeanClass的带参构造函数
private void processBeanDefinitions(Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefinitions) {
GenericBeanDefinition definition;
for (BeanDefinitionHolder holder : beanDefinitions) {
definition = (GenericBeanDefinition) holder.getBeanDefinition();
String beanClassName = definition.getBeanClassName();
// 往构造函数的参数集合中添加了一个值,那么在实例化时就会使用带参的构造函数
// 等价于在XML中配置了
// 2、SqlSessionFactoryBean类
类图:
- FactoryBean接口:意味着由 Spring 最终创建的 bean 并不是
SqlSessionFactoryBean本身,而是工厂类(SqlSessionFactoryBean)的getObject()方法的返回结果 - InitializingBean:bean初始化时候做一些操作
2.1、FactoryBean接口
FactoryBean定义了三个方法,其源码如下:
public interface FactoryBean<T> {
// 当IoC容器通过getBean方法来创建FactoryBean的实例时实际获取的不是FactoryBean 本身
// 而是具体创建的T泛型实例。
@Nullable
T getObject() throws Exception;
// 返回FactoryBean创建的bean类型。
@Nullable
Class<?> getObjectType();
// 返回由FactoryBean创建的bean实例的作用域是singleton还是prototype。
default boolean isSingleton() {
return true;
}
}
SqlSessionFactoryBean类中对于FactoryBean的实现:
进入afterPropertiesSet方法
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
//dataSource是必须要配置的
notNull(dataSource, "Property 'dataSource' is required");
notNull(sqlSessionFactoryBuilder, "Property 'sqlSessionFactoryBuilder' is required");
state((configuration == null && configLocation == null) || !(configuration != null && configLocation != null),
"Property 'configuration' and 'configLocation' can not specified with together");
//主要逻辑都在buildSqlSessionFactory方法,创建sqlSessionFactory,getObject就是返回的sqlSessionFactory
this.sqlSessionFactory = buildSqlSessionFactory();
}
- 创建SqlSessionFactory
protected SqlSessionFactory buildSqlSessionFactory() throws IOException {
// 定义了一个Configuration,叫做targetConfiguration。
final Configuration targetConfiguration;
XMLConfigBuilder xmlConfigBuilder = null;
// 判断 Configuration 对象是否已经存在,也就是是否已经解析过。如果已经有对象,就覆盖一下属性
if (this.configuration != null) {
targetConfiguration = this.configuration;
if (targetConfiguration.getVariables() == null) {
targetConfiguration.setVariables(this.configurationProperties);
} else if (this.configurationProperties != null) {
targetConfiguration.getVariables().putAll(this.configurationProperties);
}
// 如果 Configuration 不存在,但是配置了 configLocation 属性,
// 就根据mybatis-config.xml的文件路径,构建一个xmlConfigBuilder对象。
} else if (this.configLocation != null) {
xmlConfigBuilder = new XMLConfigBuilder(this.configLocation.getInputStream(), null, this.configurationProperties);
targetConfiguration = xmlConfigBuilder.getConfiguration();
// 否则,Configuration 对象不存在,configLocation 路径也没有,
// 只能使用默认属性去构建去给configurationProperties赋值。
} else {
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Property 'configuration' or 'configLocation' not specified,using default MyBatis Configuration");
targetConfiguration = new Configuration();
Optional.ofNullable(this.configurationProperties).ifPresent(targetConfiguration::setVariables);
}
// configuration的属性赋值
...
// 如果xmlConfigBuilder 不为空,也就是上面的第二种情况,
if (xmlConfigBuilder != null) {
try {
// 调用了xmlConfigBuilder.parse()去解析配置文件,最终会返回解析好的Configuration对象
xmlConfigBuilder.parse();
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Parsed configuration file: '" + this.configLocation + "'");
} catch (Exception ex) {
throw new NestedIOException("Failed to parse config resource: " + this.configLocation, ex);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
// 如果没有明确指定事务工厂 ,默认使用pringManagedTransactionFactory。
// 它创建的 SpringManagedTransaction 也有getConnection()和close()方法
// 总结:
SqlSessionFactoryBean就是创建SqlSessionFactory,为以后创建SqlSession做准备
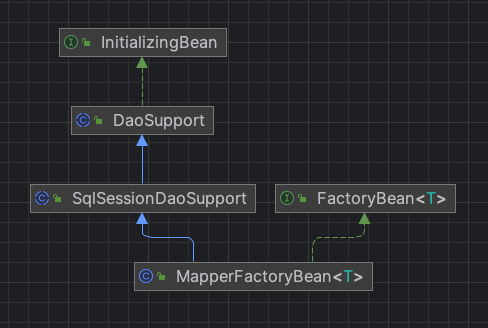
3、MapperFactoryBean类
MapperFactoryBean即创建 mapper接口的 bean 定义被替换的类型
类图:
3.1、FactoryBean接口
- 创建 Mapper的 bean 定义时候将 Class 类型修改为
MapperFactoryBean - 实际它是
FactoryBean对象,真正返回的对象为getObject()的结果
3.2、DaoSupport抽象类
- 初始化时候执行的操作,调用checkDaoConfig方法
public abstract class DaoSupport implements InitializingBean {
@Override
public final void afterPropertiesSet() throws IllegalArgumentException, BeanInitializationException {
// 子类可以实现这个方法去检查相关的配置信息
checkDaoConfig();
// 子类实现,目前没有实现的子类
try {
initDao();
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new BeanInitializationException("Initialization of DAO failed", ex);
}
}
protected abstract void checkDaoConfig() throws IllegalArgumentException;
protected void initDao() throws Exception {
}
}
3.3、SqlSessionDaoSupport抽象类
public abstract class SqlSessionDaoSupport extends DaoSupport {
private SqlSessionTemplate sqlSessionTemplate;
// 这个是核心方法
public void setSqlSessionFactory(SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory) {
if (this.sqlSessionTemplate == null || sqlSessionFactory != this.sqlSessionTemplate.getSqlSessionFactory()) {
this.sqlSessionTemplate = createSqlSessionTemplate(sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
// 省略一些getter/setter方法
// 在初始化时要检查sqlSessionTemplate,确保其不为空
@Override
protected void checkDaoConfig() {
notNull(this.sqlSessionTemplate, "Property 'sqlSessionFactory' or 'sqlSessionTemplate' are required");
}
}
- 创建sqlSessionTemplate对象
- Session的代理对象
sqlSessionProxy的 invoke 方法
private class SqlSessionInterceptor implements InvocationHandler {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// 第一步,获取一个sqlSession
SqlSession sqlSession = getSqlSession(SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory,
SqlSessionTemplate.this.executorType, SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator);
try {
// 第二步,调用sqlSession对应的方法
Object result = method.invoke(sqlSession, args);
// 检查是否开启了事务,如果没有开启事务那么强制提交
if (!isSqlSessionTransactional(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory)) {
sqlSession.commit(true);
}
return result;
} catch (Throwable t) {
// 处理异常
Throwable unwrapped = unwrapThrowable(t);
if (SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator != null && unwrapped instanceof PersistenceException) {
closeSqlSession(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory);
sqlSession = null;
Throwable translated = SqlSessionTemplate.this.exceptionTranslator
.translateExceptionIfPossible((PersistenceException) unwrapped);
if (translated != null) {
unwrapped = translated;
}
}
throw unwrapped;
} finally {
// 关闭sqlSession
if (sqlSession != null) {
closeSqlSession(sqlSession, SqlSessionTemplate.this.sqlSessionFactory);
}
}
}
}
- SqlSession的获取,熟悉的味道:
sessionFactory.openSession()
public static SqlSession getSqlSession(SqlSessionFactory sessionFactory, ExecutorType executorType,
PersistenceExceptionTranslator exceptionTranslator) {
notNull(sessionFactory, NO_SQL_SESSION_FACTORY_SPECIFIED);
notNull(executorType, NO_EXECUTOR_TYPE_SPECIFIED);
SqlSessionHolder holder = (SqlSessionHolder) TransactionSynchronizationManager.getResource(sessionFactory);
SqlSession session = sessionHolder(executorType, holder);
if (session != null) {
return session;
}
// 看到了吧,在这里调用了SqlSessionFactory创建了一个sqlSession
LOGGER.debug(() -> "Creating a new SqlSession");
session = sessionFactory.openSession(executorType);
// 如果开启了事务的话并且事务是由Spring管理的话,会将sqlSession绑定到当前线程上
registerSessionHolder(sessionFactory, executorType, exceptionTranslator, session);
return session;
}
3.4、MapperFactoryBean的checkDaoConfig方法
- 创建 Mapper接口代理对象初始化时候,会调用此方法
- 这里就会进入 mybatis 的源码了Mybatis源码解析(八):Mapper代理原理
// 之前分析过了,这个方法会在MapperFactoryBean进行初始化的时候调用
protected void checkDaoConfig() {
super.checkDaoConfig();
Configuration configuration = getSqlSession().getConfiguration();
//addToConfig默认为true的,将mapper接口添加到mybatis的配置信息中
if (this.addToConfig && !configuration.hasMapper(this.mapperInterface)) {
try {
configuration.addMapper(this.mapperInterface);
} catch (Exception e)
throw new IllegalArgumentException(e);
} finally {
ErrorContext.instance().reset();
}
}
}
// 直接调用了mybatis中现成的方法获取一个代理对象然后放入到容器中
@Override
public T getObject() throws Exception {
return getSqlSession().getMapper(this.mapperInterface);
}
4、总结Mapper对象的创建过程
- 根据@MapperScan注解扫描指定路径下接口
- 创建BeanDefinition,beanName 为“userMapper”
- beanClass 修改为
MapperFactoryBean.class
- 实例化 userMapper也就是MapperFactoryBean
- 属性注入SqlSessionFactory(由
SqlSessionFactoryBean创建而来)
- 属性注入SqlSessionFactory(由
- 初始化 userMapper 会调用上面的checkDaoConfig方法
- mybatis 源码内容,将接口创建代理对象
- 代理对象统一放入SqlSession的Configuration对象中
- 对于context.getBean(UserMapper.class);
- 由于userMapper的代理对象是
MapperFactoryBean即FactoryBean - 获取对象时候,实际是获取
getObject()返回的结果 - 此时会从SqlSession的Configuration中获取mybatis生成的代理对象
- 由于userMapper的代理对象是