SpringBoot的自动装配
前言
众所周知,SpringBoot的自动装配是其核心功能之一,SpringBoot提供了许多自动配置类,我们通常会有这样的一个概念:“当应用程序启动时,SpringBoot会扫描路径上的自动配置类进行加载,从而大大简化了项目配置的工作”,在这里,我们来从代码来学习下自动化装配的原理以及流程;文章将尽力地解答如下两个问题:
- 关于自动装配的bean,尤其是非开发人员所开发的外部资源,是在哪里配置的?
- 而这些配置信息,是在哪里读取解析,并注册到工程中的?
这两个问题很快会有答案~
关于在哪里配置的问题
首先关于第一个问题,我们需要了解下SpringBoot的SpringFactoriesLoader,SpringFactoriesLoader是SpringBoot定义的通用工厂加载机制,我们可以从源码上看下相关的介绍:
/**
* General purpose factory loading mechanism for internal use within the framework.
*
* {@code SpringFactoriesLoader} {@linkplain #loadFactories loads} and instantiates
* factories of a given type from {@value #FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION} files which
* may be present in multiple JAR files in the classpath. The {@code spring.factories}
* file must be in {@link Properties} format, where the key is the fully qualified
* name of the interface or abstract class, and the value is a comma-separated list of
* implementation class names. For example:
*
*
example.MyService=example.MyServiceImpl1,example.MyServiceImpl2
*
* where {@code example.MyService} is the name of the interface, and {@code MyServiceImpl1}
* and {@code MyServiceImpl2} are two implementations.
*
* @author Arjen Poutsma
* @author Juergen Hoeller
* @author Sam Brannen
* @since 3.2
*/即,SpringBoot会在classpath下的多个jar包的特定位置(META-INF目录),读取配置文件spring.factories文件,spring.factories的文件内容需要严格地遵循KV配置文件的格式 ;
有了初步的了解之后,那么SpringFactoriesLoader是在哪里使用的呢?
SpringFactoriesLoader在自动装配中有不止一个地方会使用,两个重要的使用点,其一是在SpringApplication的构造阶段;其二是针对EnableAutoConfiguration注解,在后续的postProcessor处理时(会在问题2进行介绍);
首先是在SpringApplication的构造方法:
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class... primarySources) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}接下来我们追踪到私有方法getSpringFactoriesInstances
private Collection getSpringFactoriesInstances(Class type, Class[] parameterTypes, Object... args) {
ClassLoader classLoader = getClassLoader();
// Use names and ensure unique to protect against duplicates
Set names = new LinkedHashSet<>(SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(type, classLoader));
List instances = createSpringFactoriesInstances(type, parameterTypes, classLoader, args, names);
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(instances);
return instances;
} 这里,我们看到了SpringFactoriesLoader的调用!
接下来我们来到SpringFactoriesLoader的内部看看:
/**
* Load the fully qualified class names of factory implementations of the
* given type from {@value #FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION}, using the given
* class loader.
* @param factoryClass the interface or abstract class representing the factory
* @param classLoader the ClassLoader to use for loading resources; can be
* {@code null} to use the default
* @throws IllegalArgumentException if an error occurs while loading factory names
* @see #loadFactories
*/
public static List loadFactoryNames(Class factoryClass, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
String factoryClassName = factoryClass.getName();
return loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryClassName, Collections.emptyList());
}
private static Map> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) {
MultiValueMap result = cache.get(classLoader);
if (result != null) {
return result;
}
try {
Enumeration urls = (classLoader != null ?
classLoader.getResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION) :
ClassLoader.getSystemResources(FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION));
result = new LinkedMultiValueMap<>();
while (urls.hasMoreElements()) {
URL url = urls.nextElement();
UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url);
Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource);
for (Map.Entry entry : properties.entrySet()) {
String factoryClassName = ((String) entry.getKey()).trim();
for (String factoryName : StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String) entry.getValue())) {
result.add(factoryClassName, factoryName.trim());
}
}
}
cache.put(classLoader, result);
return result;
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [" +
FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION + "]", ex);
}
} 而方法中配置的静态常量,就是META-INF/spring.factories了:
public static final String FACTORIES_RESOURCE_LOCATION = "META-INF/spring.factories";
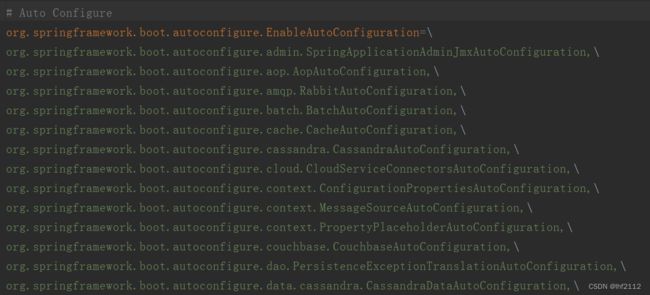
接下来我们可以观察下手中的SpringBoot项目中已经包含的META-INF/spring.factories中配置的内容,我们通常会很容易地找到EnableAutoConfiguration的配置,例如:
不难发现,org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration的values,大多都是SpringBoot的配置类(@Configuration),那么这些配置类,是在哪里被调用,进而对其配置的bean进行加载的呢?下面我们来回答文章开始部分提到的第二个问题。
关于在哪里解析的问题
关于第二个问题,我们先从结论出发,它的实现是在ConfigurationClassPostProcessor这个类中的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法。ConfigurationClassPostProcessor是一个关键的后置处理器,它的主要作用是:能够解析和处理配置类中的注解和配置信息,包括@Bean方法的注册,@Import注解的处理,条件注解的判断和依赖注入的解析。
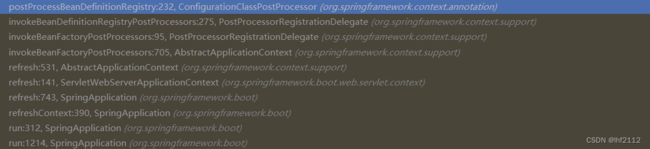
如果我们在SpringBoot的工程中进行断点调试,我们可以发现它的源头其实也是源自Spring/SpringBoot源码中的AbstractApplicationContext#refresh方法,这个大名鼎鼎的refresh方法是spring/springboot源码学习最核心的部分了,其内容十分地丰富,网上也有不少相关的学习资源,关于refresh方法本人在学习的过程中也进行了一些记录 https://mp.csdn.net/mp_blog/creation/editor/104491404;自动化装配,是在refresh方法的invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法中被执行的
refresh方法的源码如下:
@Override
public void refresh() throws BeansException, IllegalStateException {
synchronized (this.startupShutdownMonitor) {
// Prepare this context for refreshing.
prepareRefresh();
// Tell the subclass to refresh the internal bean factory.
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// Prepare the bean factory for use in this context.
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
try {
// Allows post-processing of the bean factory in context subclasses.
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Invoke factory processors registered as beans in the context.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Register bean processors that intercept bean creation.
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
// Initialize message source for this context.
initMessageSource();
// Initialize event multicaster for this context.
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
// Initialize other special beans in specific context subclasses.
onRefresh();
// Check for listener beans and register them.
registerListeners();
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory);
// Last step: publish corresponding event.
finishRefresh();
}
catch (BeansException ex) {
if (logger.isWarnEnabled()) {
logger.warn("Exception encountered during context initialization - " +
"cancelling refresh attempt: " + ex);
}
// Destroy already created singletons to avoid dangling resources.
destroyBeans();
// Reset 'active' flag.
cancelRefresh(ex);
// Propagate exception to caller.
throw ex;
}
finally {
// Reset common introspection caches in Spring's core, since we
// might not ever need metadata for singleton beans anymore...
resetCommonCaches();
}
}
}而自动化装配的核心步骤:invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors方法,我们主要对它来进行跟踪:
/**
* Instantiate and invoke all registered BeanFactoryPostProcessor beans,
* respecting explicit order if given.
* Must be called before singleton instantiation.
*/
protected void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactory, getBeanFactoryPostProcessors());
// Detect a LoadTimeWeaver and prepare for weaving, if found in the meantime
// (e.g. through an @Bean method registered by ConfigurationClassPostProcessor)
if (beanFactory.getTempClassLoader() == null && beanFactory.containsBean(LOAD_TIME_WEAVER_BEAN_NAME)) {
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(new LoadTimeWeaverAwareProcessor(beanFactory));
beanFactory.setTempClassLoader(new ContextTypeMatchClassLoader(beanFactory.getBeanClassLoader()));
}
}
我们发现这个方法直接调用了PostProcessorRegistrationDelegate.invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors
方法;
public static void invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, List beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
// Invoke BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors first, if any.
Set processedBeans = new HashSet<>();
if (beanFactory instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistry) {
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry = (BeanDefinitionRegistry) beanFactory;
List regularPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List registryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
for (BeanFactoryPostProcessor postProcessor : beanFactoryPostProcessors) {
if (postProcessor instanceof BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) {
BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor registryProcessor =
(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor) postProcessor;
registryProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
registryProcessors.add(registryProcessor);
}
else {
regularPostProcessors.add(postProcessor);
}
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
// Separate between BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement
// PriorityOrdered, Ordered, and the rest.
List currentRegistryProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
// First, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// Next, invoke the BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName) && beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
// Finally, invoke all other BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors until no further ones appear.
boolean reiterate = true;
while (reiterate) {
reiterate = false;
postProcessorNames = beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (!processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
currentRegistryProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor.class));
processedBeans.add(ppName);
reiterate = true;
}
}
sortPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, beanFactory);
registryProcessors.addAll(currentRegistryProcessors);
invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry);
currentRegistryProcessors.clear();
}
// Now, invoke the postProcessBeanFactory callback of all processors handled so far.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(registryProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(regularPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
else {
// Invoke factory processors registered with the context instance.
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(beanFactoryPostProcessors, beanFactory);
}
// Do not initialize FactoryBeans here: We need to leave all regular beans
// uninitialized to let the bean factory post-processors apply to them!
String[] postProcessorNames =
beanFactory.getBeanNamesForType(BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class, true, false);
// Separate between BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered,
// Ordered, and the rest.
List priorityOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
List orderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
List nonOrderedPostProcessorNames = new ArrayList<>();
for (String ppName : postProcessorNames) {
if (processedBeans.contains(ppName)) {
// skip - already processed in first phase above
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, PriorityOrdered.class)) {
priorityOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(ppName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
else if (beanFactory.isTypeMatch(ppName, Ordered.class)) {
orderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
else {
nonOrderedPostProcessorNames.add(ppName);
}
}
// First, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement PriorityOrdered.
sortPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(priorityOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Next, invoke the BeanFactoryPostProcessors that implement Ordered.
List orderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
for (String postProcessorName : orderedPostProcessorNames) {
orderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
sortPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(orderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Finally, invoke all other BeanFactoryPostProcessors.
List nonOrderedPostProcessors = new ArrayList<>();
for (String postProcessorName : nonOrderedPostProcessorNames) {
nonOrderedPostProcessors.add(beanFactory.getBean(postProcessorName, BeanFactoryPostProcessor.class));
}
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors(nonOrderedPostProcessors, beanFactory);
// Clear cached merged bean definitions since the post-processors might have
// modified the original metadata, e.g. replacing placeholders in values...
beanFactory.clearMetadataCache();
} 其中有一行方法:invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(currentRegistryProcessors, registry); 我们继续进行跟踪
/**
* Invoke the given BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor beans.
*/
private static void invokeBeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessors(
Collection postProcessors, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
for (BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
postProcessor.postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(registry);
}
}可以发现,这个方法中,会将所有注册的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor类进行遍历,并执行它们的postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法。
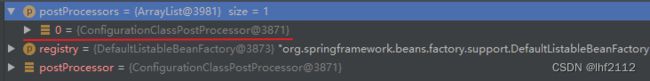
在作者的调试的时候,我们可以看到此处注册的BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor有且只有一个,那就是ConfigurationClassPostProcessor。
在这里,我们成功地跟踪到了BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor#postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry方法
/**
* Derive further bean definitions from the configuration classes in the registry.
*/
@Override
public void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
int registryId = System.identityHashCode(registry);
if (this.registriesPostProcessed.contains(registryId)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry already called on this post-processor against " + registry);
}
if (this.factoriesPostProcessed.contains(registryId)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"postProcessBeanFactory already called on this post-processor against " + registry);
}
this.registriesPostProcessed.add(registryId);
processConfigBeanDefinitions(registry);
}其中在最后,会执行一个processConfigBeanDefinitions方法,而这个方法就是处理配置类的核心方法了。这个方法比较复杂,内容很多,下一篇博文中,我们再来对这个方法进行下更深入的分享。
在前文我们提到@Import注解会在BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor处理,这里有一个关键的注解,相信我们对@EnableAutoConfiguration这个注解并不陌生;
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
String ENABLED_OVERRIDE_PROPERTY = "spring.boot.enableautoconfiguration";
/**
* Exclude specific auto-configuration classes such that they will never be applied.
* @return the classes to exclude
*/
Class[] exclude() default {};
/**
* Exclude specific auto-configuration class names such that they will never be
* applied.
* @return the class names to exclude
* @since 1.3.0
*/
String[] excludeName() default {};
}@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)这里会引入一个AutoConfigurationImportSelector类,我们看下它的getAutoConfigurationEntry方法
protected AutoConfigurationEntry getAutoConfigurationEntry(AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata,
AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return EMPTY_ENTRY;
}
AnnotationAttributes attributes = getAttributes(annotationMetadata);
List configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);
configurations = removeDuplicates(configurations);
Set exclusions = getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes);
checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions);
configurations.removeAll(exclusions);
configurations = filter(configurations, autoConfigurationMetadata);
fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions);
return new AutoConfigurationEntry(configurations, exclusions);
} 它会调用同类的getCandidateConfigurations方法
protected List getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
List configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(),
getBeanClassLoader());
Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you "
+ "are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
} 在这里我们再一次看到了SpringFactoriesLoader的调用,这里要和上一个问题中SpringApplication对象构造时对SpringFactoriesLoader的调用进行区分哦。