102.【Redis】
Resies集群
- `前言`
- (一)、Nosql概述
-
- 1、为什么要用NoSQL ?
- 2、什么是Nosql
- 3、Nosql特点
- 4、Nosql的四大分类
- 5、阿里巴巴数据结构演进
- (二)、Redis入门
-
- 1.概述
- 2.Redis能干什么?
- 3、Redis的特点
- 4、window安装Redis
- 5、Linux安装Redis
- 6、redis-benchmark性能测试
- 7、Redis基础知识(必须熟练掌握)
-
-
- (1).常用的基本操作命令
- (2)Redis是单线程的,并且是基于内存操作。
- (3)在没有接触redis之前,我们大都会有这样的误区:
-
- (三)、六大基本数据类型
-
- 1、Redis-key(键值对)
- 2、Redis-String (字符串)
- 3、List (列表)
- 4、Set (集合)
- 5、Hash (哈希)
- 6、Zset (有序集合)
- (四)、三种特殊数据类型
-
- 1、Geospatial(地理位置)
- 2、Hyperloglog(基数统计)
- 3、BitMap(位图)
- (五)、事务
-
- 1.正常执行事务
- 2.取消事务
- 3.编译型异常(代码有问题, 命令有错!)
- 4.运行时异常 (错误的不被执行,其他的执行)
- (六)、Redis监控/乐观锁(watch)
-
- 1.正常执行乐观锁
- 2.多线程执行乐观锁
- (七)、Jedis
-
- 1.导入相关的依赖
- 2.测试远程Redis
- 3.事务相关案列
- (八)、SpringBoot整合Redis
-
- 1.导入一个整合包
- 2.源码分析
- 3.导入配置链接
- 4.测试
- 5.设置中文乱码问题展现
- (九)、自定义RedisTemplate
-
- 1.对象通过json传入
- 2.直接传递一个对象
- 3.解决中文乱码问题
- 4.Template自定义的工具类
- (十)、Redis.config
-
-
- 1.容量单位
- 2.包含
- 3.文件
- 4.网络
- 5.通用
- 6.快照
- 7.主从复制
- 8.安全
- 9.客户端
- 10.aof配置
-
- (十一)、Redis持久化
-
- 1.RDB
- 2.AOF (Append only file->每一个动作)
- 3、如何选择 RDB和AOF
- (十二)、Redis订阅
-
- 1.命令
- 2.原理
- 3.缺点
- 4.应用
- (十三)、Redis主从复制
-
- 1.概念
- 2.搭建环境
- 3.使用规则
- 4.复制原理
- 5.宕机后手动配置主机
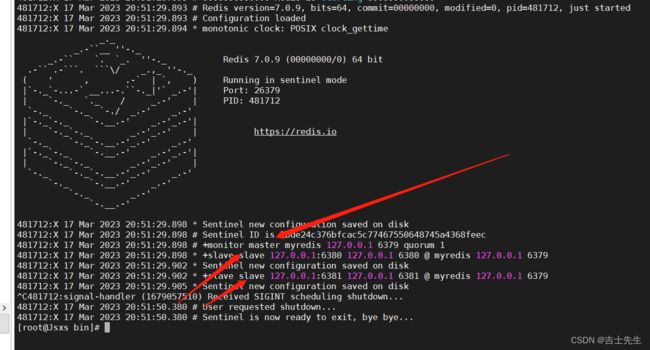
- (十四)、哨兵模式
-
- 1.哨兵概念
- 2. 哨兵的作用
- 3.测试哨兵模式
- 4.哨兵模式优缺点
- 5.哨兵模式全部配置
- (十五)、Redis缓存穿透和雪崩
-
- 1.缓存穿透 (查不到然后高并发)
- 2.缓存穿透解决方案
- 3.缓存击穿 (查得到但超高并发)
- 4.缓存击穿解决方案
- 5.缓存雪崩
- 2.缓存雪崩解决方案
前言
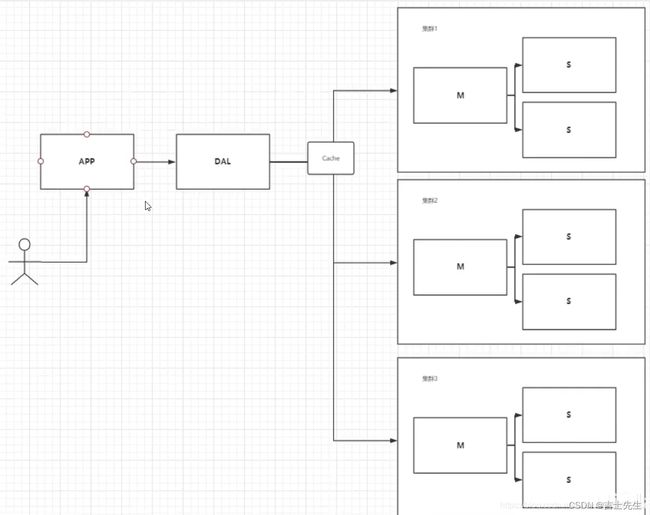
1、单机数据库.90年代,一个网站的访问量一般不会太大,单个数据库完全够用,数据库也没有什么压力。但是,现在我们处于大数据时代;大数据顾名思义数据量很多,那么应用传统的关系型数据库就有可能会出现如下问题:
DAL 数据库访问层

- 数据量增加到一定程度,单机数据库就放不下了。
- 数据的索引(B+ Tree),一个机器内存也存放不下。
- 访问量变大后(读写混合),一台服务器承受不住。
只要发生如上情况之一,那么我们的数据库就必须要晋级
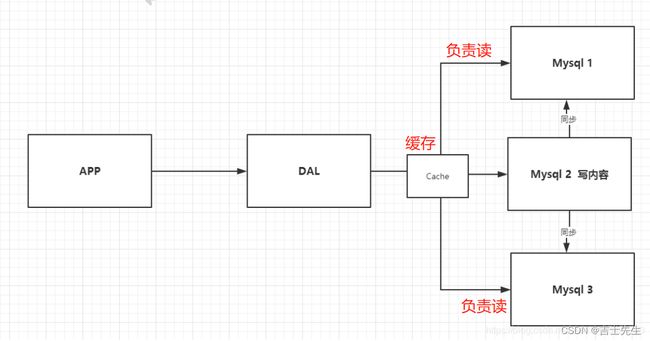
2、Memcache(缓存) + Mysql + 垂直拆分(读写分离)
80%的网站都是在进行读操作,这样的话每次都要去数据库查询就非常麻烦,同时为了能够减轻数据库、服务器的压力,我们可以使用缓存来保证效率!
缓存的出现经历了以下几个过程:
- 优化数据库的数据结构和索引(难度大)。
- 文件缓存,通过IO流获取比每次都访问数据库效率略高,但是流量爆炸式增长时候,IO流也承受不了。
- MemCache,当时最热门的技术,通过在数据库和数据库访问层之间加上一层缓存,第一次访问时查询数据库,将结果保存到缓存,后续的查询先检查缓存,若有直接拿去使用,这样我们的访问效率就会大大提升。
3、(分库分表) + 水平拆分 + MySQL集群
早些年MyISAM: 表锁,十分影响效率!高并发下就会出现严重的锁问题;
于是转战Innodb:行锁,每次查询数据只锁这一行。
慢慢的就开始使用分库分表来解决写的压力! MySQL 在哪个年代推出 了表分区!这个并没有多少公使用!
MySQL 的 集群,很好满足那个年代的所有需求!
MySQL 等关系型数据库就不够用了!数据量很多,变化很快!MySQL 有的使用它来存储一些比较大的文件,博客,图片!数据库表很大,效率就比较低了!
如果有一种据库来专门处理这种数据,MySQL压力就变得十分小(研究如何处理这些问题!)大数据的IO压力下,表几乎没法更大! Nosql的出现就是一种非常好的选择!
5、目前一个基本的互联网项目!
(一)、Nosql概述
1、为什么要用NoSQL ?
用户的个人信息,社交网络,地理位置,自己产生的数据,日志等等爆发式增长!传统的关系型数据库已无法满足这些数据处理的要求,这时我们就需要使用NoSQL数据库,它可以很好的处理上述的情况!
2、什么是Nosql
NoSQL = Not Only SQL(不仅仅是SQL)-----泛指非关系型数据库
这里有两个概念:关系型数据库和菲关系型数据库
- 关系型数据库:列+行,同一个表下数据的结构是一样的。
- 非关系型数据库:数据存储没有固定的格式,并且可以进行横向扩展。
NoSQL泛指非关系型数据库,随着web2.0互联网的诞生,传统的关系型数据库很难对付web2.0时代!尤其是超大规模的高并发的社区,暴露出来很多难以克服的问题,NoSQL在当今大数据环境下发展的十分迅速,Redis是发展最快的。
3、Nosql特点
- 方便扩展(数据之间没有关系,很好扩展!)
- 大数据量高性能(Redis一秒可以写8万次,读11万次,NoSQL的是缓存记录级的,是一种细粒度的缓存,性能会比较高!)
- 数据类型是多样型的!(不需要事先设计数据库,随取随用!如果是数据量十分大的表,很多人很难根据三大范式将其完整的设计出来)
传统的 RDBMS(关系型) 和 NoSQL
传统的 RDBMS(关系型数据库):
- 结构化组织
- SQL
- 数据和关系都存在单独的表中 :行+列
- 操作,数据定义语言
- 严格的一致性
- 基础的事务操作
- …
Nosql:
- 不仅仅是数据
- 没有固定的查询语言
- 键值对存储,列存储,文档存储,图形数据库(社交关系)
- 最终一致性
- CAP定理和BASE
- 高性能,高可用,高扩展
- …
了解:3V + 3高
大数据时代的3V :主要是描述现实问题的
- 海量Velume
- 多样Variety
- 实时Velocity
大数据时代的3高 : 主要是对程序设计的要求
- 高并发 (同时)
- 高可扩 (随时水平拆分)
- 高性能 (用户体验)
真正在公司中的实践:NoSQL + RDBMS(关系型) 一起使用才是最强的。
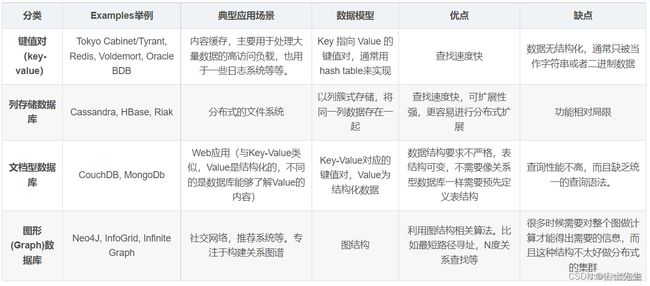
4、Nosql的四大分类
KV键值对:
- 新浪: Redis
- 美团: Redis+tair
- 阿里、百度: Redis +memecache
文档型数据库(bason 格式和json一样)
- MongoDB
-
- MongoDB是一个基于分布式文件存储的数据库,C++编写,主要用来处理大量的文档!
-
- MongoDB是一个介于关系型数据库和非关系数据中中间的产品。MongoDB是非关系型数据库中功能最疯的的,最像关系型数据库的!
列存储数据库
- HBse
- 分布式文件系统
图关系数据库
- 存的是关系,不是图片。比如: 朋友圈社交网络,广告推荐。
- Neo4j,inforGrid
5、阿里巴巴数据结构演进
技术急不得,越是慢慢学,才能越扎实。
技术没有高低之分,就看适应不适用。
开源才是技术的王道。
阿里云-王坚的封神之路
# 1. 商品的基本信息
名称、价格、商家信息:
关系型数据库就可以解决了! MySQL/Orcal. 淘宝用的是自研发的MySQL
#2. 商品的描述、评论(文字比较多)
文档型数据库中: MongoDB
#3. 图片
分布式文件系统: FastDFS
-淘宝自己的TFS
-谷歌自己的 GFS
-hadopp HDFS
-阿里云的 oss
#4. 商品的关键字 (搜索)
-搜索引擎 solr elasticsearch
-ISerach: 多隆
#5.商品人们的波段信息
-内存数据库
-Redis Tair、Memache...
#6.商品的交易,外部的支付接口
-三方应用
所有牛逼的人都有一段苦逼岁月,但是你只要像SB一样的去坚持,终究牛逼。
(二)、Redis入门
1.概述
Redis(Remote Dictionary Server ),即远程字典服务,是一个开源的使用ANSI C语言编写、支持网络、可基于内存亦可持久化的日志型、Key-Value数据库,并提供多种语言的API。
与memcached一样,为了保证效率,数据都是缓存在内存中。区别的是redis会周期性的把更新的数据写入磁盘或者把修改操作写入追加的记录文件,并且还实现了master-slave(主从)同步。
2.Redis能干什么?
- 内存存储、持久化,内存是断电即失的,所以需要持久化(RDB、AOF)
- 高效率、用于高速缓冲
- 发布订阅系统
- 地图信息分析、周围的人…
- 计时器、计数器(浏览量)
3、Redis的特点
- 速度快:Redis是用C语言实现的,所有数据存储在内存中以键值对形式保存。
- 丰富的数据类型 :Redis支持五种数据结构:String、List、Set、Hash、Zset。
- 持久化操作:Redis的所有数据存储在内存中,对数据的更新将异步地保存到磁盘上。
- 主从复制:主服务器上只进行写的操作,在从的服务器上进行读的操作。
- 支持高可用和分布式:使用redis自带的哨兵机制来实现高可用。
- 支持事务
- 集群操作
4、window安装Redis
-
下载安装包 https://github.com/tporadowski/redis/releases?page=1
-
window下使用确实简单,但是Redis 推荐我们使用Linux去开发。
5、Linux安装Redis
(1)解压Redis的安装包!程序一般放在/opt目录下。
# 移动到 /opt
mv redis-7.0.9.tar.gz /opt
#进入到 /opt目录
cd /opt
# 解压redis
tar -zxvf redis-7.0.9.tar.gz
- 安装基本环境
# 安装基本的环境
yum install gcc-c++
# 执行make命令
make
# 安装
make install
- redis默认安装路径 /usr/local/bin
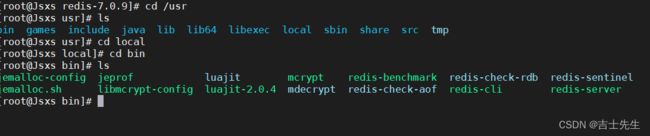
[root@Jsxs redis-7.0.9]# cd /usr
[root@Jsxs usr]# ls
bin games include java lib lib64 libexec local sbin share src tmp
[root@Jsxs usr]# cd local
[root@Jsxs local]# cd bin
[root@Jsxs bin]# ls
jemalloc-config jeprof luajit mcrypt redis-benchmark redis-check-rdb redis-sentinel
jemalloc.sh libmcrypt-config luajit-2.0.4 mdecrypt redis-check-aof redis-cli redis-server
- 在该目录下创建一个文件夹 jconfig,将redis的配置文件复制到/usr/local/bin/zlkconfig
cp /opt/redis-7.0.9/redis.conf jconfig
- redis默认不是后台启动的,需要修改配置文件
- 通过刚刚新定义在 zlkconfig 里面的配置文件启动redis服务
# 回退到bin
cd ..
# 利用 jconfi/下面的配置文件启动redis 服务端
redis-server jconfig/redis.conf
# 查看自己是否运行
netstat -anp|grep 6379
# 客户端链接redis 客户端
redis-cli -p 6379
9.全部过程
[root@Jsxs redis-7.0.9]# cd /usr
[root@Jsxs usr]# ls
bin games include java lib lib64 libexec local sbin share src tmp
[root@Jsxs usr]# cd local
[root@Jsxs local]# cd bin
[root@Jsxs bin]# ls
jemalloc-config jeprof luajit mcrypt redis-benchmark redis-check-rdb redis-sentinel
jemalloc.sh libmcrypt-config luajit-2.0.4 mdecrypt redis-check-aof redis-cli redis-server
[root@Jsxs bin]# mkdir jconfig
[root@Jsxs bin]# cp /opt/redis-7.0.9/redis.conf j
jconfig/ jemalloc-config jemalloc.sh jeprof
[root@Jsxs bin]# cp /opt/redis-7.0.9/redis.conf jconfig
[root@Jsxs bin]#
[root@Jsxs bin]# cd jconfig/
[root@Jsxs jconfig]# ls
redis.conf
[root@Jsxs jconfig]# vim redis.conf
[root@Jsxs jconfig]# vim redis.conf
[root@Jsxs jconfig]# vim redis.conf
[1]+ Stopped vim redis.conf
[root@Jsxs jconfig]# vim redis.conf
[root@Jsxs jconfig]# vim redis.conf
[root@Jsxs jconfig]# vim redis.conf
[root@Jsxs jconfig]# vim redis.conf
[root@Jsxs jconfig]# vim redis.conf
[root@Jsxs jconfig]# vim redis.conf
[root@Jsxs jconfig]# vi -r redis.conf
[root@Jsxs jconfig]# ls -a
. .. redis.conf .redis.conf.swp
[root@Jsxs jconfig]# rm .redis.conf.swp
rm: remove regular file '.redis.conf.swp'?
[root@Jsxs jconfig]# ls -a
. .. redis.conf .redis.conf.swp
[root@Jsxs jconfig]# rm .redis.conf.swp
rm: remove regular file '.redis.conf.swp'? y
[root@Jsxs jconfig]# ls -a
. .. redis.conf
[root@Jsxs jconfig]# vim redis.conf
[root@Jsxs jconfig]# vim redis.conf
[root@Jsxs jconfig]# clear
[root@Jsxs jconfig]# cd ..
[root@Jsxs bin]# pwd
/usr/local/bin
[root@Jsxs bin]# ls
jconfig jemalloc.sh libmcrypt-config luajit-2.0.4 mdecrypt redis-check-aof redis-cli redis-server
jemalloc-config jeprof luajit mcrypt redis-benchmark redis-check-rdb redis-sentinel
[root@Jsxs bin]# redis-seerver jconfig/redis.conf
-bash: redis-seerver: command not found
[root@Jsxs bin]# redis-server jconfig/redis.conf
[root@Jsxs bin]# netstat -anp|grep 6379
tcp 0 0 127.0.0.1:6379 0.0.0.0:* LISTEN 1726/redis-server 1
[root@Jsxs bin]# ls
jconfig jemalloc.sh libmcrypt-config luajit-2.0.4 mdecrypt redis-check-aof redis-cli redis-server
jemalloc-config jeprof luajit mcrypt redis-benchmark redis-check-rdb redis-sentinel
[root@Jsxs bin]# redis-cli -p 6379
127.0.0.1:6379> ping
PONG
127.0.0.1:6379> set name jsxs
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> get name
"jsxs"
127.0.0.1:6379>
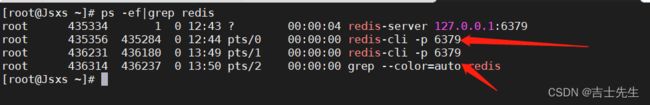
- 查看redis进程是否开启
ps -ef|grep redis
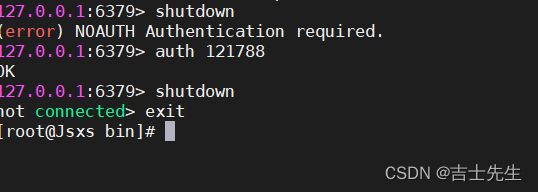
(9)关闭Redis服务 shutdown,并通过exit退出
如果设置了密码,那么我们需要先输入密码
auth 密码
6、redis-benchmark性能测试
在 /usr/local/bin 文件夹下存在Redis官方提供的性能测试工具 redis-benchmark;
cd /usr/local/bin
基本命令:redis-benchmark [option] [option value]
可选参数如下所示:
测试:
100个并发连接 100000请求,实例中主机为 127.0.0.1,端口号为 6379;
redis-benchmark -h localhost -p 6379 -c 100 -n 100000
7、Redis基础知识(必须熟练掌握)
(1).常用的基本操作命令
默认使用第0个,共16个数据库。可以使用select n切换到DB n,dbsize可以查看当前数据库的大小,与key数量相关。
通过配置文件查看数据库的数量:
select n[第几个数据库]
# 切换到第四个数据库
127.0.0.1:6379[3]> select 4
OK
# 查看数据库的条数
127.0.0.1:6379[4]> DBSIZE
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379[4]> set name jsxs
OK
127.0.0.1:6379[4]> DBSIZE
(integer) 1
# 查看数据库的个数
127.0.0.1:6379[4]> config get databases
1) "databases"
2) "16"
# 查看所有的key
127.0.0.1:6379[4]> keys *
1) "name"
# 清除目前所在数据库的
127.0.0.1:6379[4]> flushdb
OK
127.0.0.1:6379[4]> keys *
(empty array)
# 清空全部数据库的信息
flushall
(2)Redis是单线程的,并且是基于内存操作。
所以说。redis所遇到的瓶颈并不是CPU,而是机器的内存和网络的带宽。
(3)在没有接触redis之前,我们大都会有这样的误区:
- 误区一: 高性能的服务器一定就是多线程的?
- 误区二: 多线程(CPU上下文会切换!)一定比单线程效率高?
事实上并不完全是这样,我们的Redis是将所有的数据放在内存中。这样的话使用单线程去操作效率就是最高的,而多线程(CPU上下文会切换:耗时的操作!),对于内存系统来说,如果没有上下文切换效率就是最高的,多次读写都是在一个CPU上的,在内存存储数据情况下,单线程就是最佳的方案。
正常情况下: CPU > 内存 > 硬盘
(三)、六大基本数据类型
官方:
Redis是一个开源(BSD许可),内存存储的数据结构服务器,可用作数据库,高速缓存和消息队列代理。它支持字符串、哈希表、列表、集合、有序集合,位图,hyperloglogs等数据类型。内置复制、Lua脚本、LRU收回、事务以及不同级别磁盘持久化功能,同时通过Redis Sentinel提供高可用,通过Redis Cluster提供自动分区。
1、Redis-key(键值对)
127.0.0.1:6379> keys * # 查看本数据库的全部key
(empty array)
127.0.0.1:6379> set name jsxs # 设置key值为name,值为jsxs
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> set aege 21
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> keys *
1) "name"
2) "aege"
127.0.0.1:6379> EXISTS namE
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> EXISTS name # 判断key值是否存在,存在的话为1,不存在为0
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> move name 1 # 移动key值到指定的index数据库
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> select 1 # 切换到指定数据库
OK
127.0.0.1:6379[1]> keys *
1) "name"
127.0.0.1:6379[1]> select 0
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> set name jsxs
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> keys *
1) "name"
2) "aege"
127.0.0.1:6379> expire name 10 # 设置过期时间 单位是秒
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> ttl name # 查看还剩多少秒过期 -2已经过期 -1 不会过期
(integer) -2
127.0.0.1:6379> ttl name
(integer) -2
127.0.0.1:6379> get name
(nil)
127.0.0.1:6379> type aege # 查看当前key的类型
string
127.0.0.1:6379> rename aege age #修改key值得名字
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> keys *
1) "age"
更多常用的的redis命令,可以参考 redis命令手册
2、Redis-String (字符串)
------------------------------------------
字符串基本设置 追加
127.0.0.1:6379> keys *
1) "age"
2) "key1"
127.0.0.1:6379> exists key1 # 是否存在
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> append key1 "hello" # 追加字符串
(integer) 7
127.0.0.1:6379> get key1
"v1hello"
127.0.0.1:6379> strlen key1 # 查看key得长度
(integer) 7
127.0.0.1:6379> append key1 ",jsxs" #追加字符串
(integer) 12
127.0.0.1:6379> keys *
1) "age"
2) "key1"
127.0.0.1:6379> append jsxs aaa #追加字符串,假如说key值不存在,那么就添加此字符串
(integer) 3
127.0.0.1:6379> keys *
1) "age"
2) "jsxs"
3) "key1"
------------------------------------------
自增变量
127.0.0.1:6379> set views 0 # 初始浏览量为0
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> get views
"0"
127.0.0.1:6379> incr views #字符串自增1
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> incr views
(integer) 2
127.0.0.1:6379> decr views #字符串自减1
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> decr views
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> INCRBY views 10 # 设置自增10
(integer) 10
127.0.0.1:6379> INCRBY views 10
(integer) 20
127.0.0.1:6379> DECRBY views 5 # 自减5
(integer) 15
------------------------------------------
字符串范围 range
127.0.0.1:6379> keys *
(empty array)
127.0.0.1:6379> set key "hello,jsxs"
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> get key
"hello,jsxs"
127.0.0.1:6379> GETRANGE key 0 3 # 截取字符串 [0,3]
"hell"
127.0.0.1:6379> GETRANGE key 0 -1 # 获得全部字符串得信息
"hello,jsxs"
------------------------------------------
替换指定位置得字符串
127.0.0.1:6379> get key2
"abcdsefs"
127.0.0.1:6379> SETRANGE key2 1 xx # 替换key2值中 index为1开始的数据 为xx
(integer) 8
127.0.0.1:6379> get key2
"axxdsefs"
------------------------------------------
setex (set with expire) | 存在的前提下设置过期时间
setnx (set if not exist) | 不存在的前提下再设置 (分布式锁中会常常使用)
127.0.0.1:6379> SETEX key3 30 hello # 假如存在设置过期时间
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> ttl key3 # 查看秒数
(integer) 23
127.0.0.1:6379> SETNX mykey redis #假如不存在就设置 0失败 1成功
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> keys *
1) "key"
2) "mykey"
3) "key2"
127.0.0.1:6379> ttl key3
(integer) -2
127.0.0.1:6379> setnx mykey mongodb # 假如不存在就设置 0失败
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> get mykey
"redis"
------------------------------------------
批量设置键值对 | 批量获取键值对
127.0.0.1:6379> keys *
(empty array)
127.0.0.1:6379> MSET k1 v1 k2 v2 k3 v3 # 批量设置键值对
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> keys *
1) "k3"
2) "k2"
3) "k1"
127.0.0.1:6379> MGET k1 k2 k3 #批量获取键值对
1) "v1"
2) "v2"
3) "v3"
127.0.0.1:6379> MSETNX k1 v1 k4 v4 #批量设置setnx 遵从原子性
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> keys *
1) "k3"
2) "k2"
3) "k1"
------------------------------------------
对象
set user:1{name:jsxs,age:3} # 设置一个user:1对象 值为json字符串来保存一个对象
这里的key是一个巧妙地设计: user:{id}:{files},如此设计再redis中是完全ok了.
127.0.0.1:6379> keys *
(empty array)
127.0.0.1:6379> mset user:1:name jsxs user:1:age 26
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> MGET user:1:name user:1:age
1) "jsxs"
2) "26"
------------------------------------------
getset #先get然后set
127.0.0.1:6379> getset db mysql #getset先get后set
(nil)
127.0.0.1:6379> get db
"mysql"
127.0.0.1:6379> getset db moguodb
"mysql"
127.0.0.1:6379> get db
"moguodb"
String中的value除了是字符串还可以是数字,它更加适合字符串存储,应用场景举例:
- 计数器
- 统计多单位的数量
- 粉丝数
- 对象存储缓存
3、List (列表)
Redis列表是简单的字符串列表,按照插入顺序排序。你可以添加一个元素到列表的头部(左边)或者尾部(右边)。如下Redis中List是可以进行双端操作的,所以命令也就分为了LXXX和RLLL两类。
头部是左边,头部的索引值为0.尾部是右边,尾部的索引值是list.size
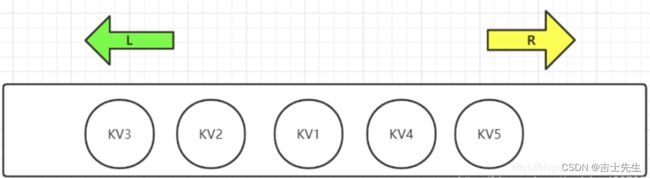
栈: 只在一边进和出。 队列: 一边进另一边出。
在redis里面我们呢可以把List玩成 栈和队列。所有地list命令都是以 L 开头地。
------------------------------------------
向头部插入一个值和向尾部插入一个值
127.0.0.1:6379> keys *
(empty array)
127.0.0.1:6379> LPUSH list one # 将一个值或多个值,从头部插进去
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> LPUSH list two
(integer) 2
127.0.0.1:6379> LPUSH list three
(integer) 3
127.0.0.1:6379> LRANGE list 0 -1 #通过区间获得所有值
1) "three"
2) "two"
3) "one"
127.0.0.1:6379> LRANGE list 0 1
1) "three"
2) "two"
127.0.0.1:6379> RPUSH list four # 向尾部插入一个值
(integer) 4
127.0.0.1:6379> LRANGE list 0 -1
1) "three"
2) "two"
3) "one"
4) "four"
127.0.0.1:6379>
------------------------------------------
移除一个值
127.0.0.1:6379> LRANGE list 0 -1 # 通过范围获得所有值
1) "three"
2) "two"
3) "one"
4) "four"
127.0.0.1:6379> LPOP list # 移除左边地第一个
"three"
127.0.0.1:6379> RPOP list #移除右边地第一个
"four"
127.0.0.1:6379> LRANGE list 0 -1
1) "two"
2) "one"
------------------------------------------
Lindex 通过游标获取值
127.0.0.1:6379> LRANGE list 0 -1
1) "two"
2) "one"
127.0.0.1:6379> LINDEX list 1 # 查看游标为1的值
"one"
127.0.0.1:6379> LINDEX list 0 #查看游标为0的值
"two"
------------------------------------------
Llen 查看链表的长度
127.0.0.1:6379> keys *
(empty array)
127.0.0.1:6379> LPUSH list one # 向key为list的值放进一个值
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> LPUSH list two
(integer) 2
127.0.0.1:6379> LPUSH list three
(integer) 3
127.0.0.1:6379> LRANGE list 0 -1
1) "three"
2) "two"
3) "one"
127.0.0.1:6379> Llen list # 查看指定链表的长度
(integer) 3
------------------------------------------
移除指定的值
127.0.0.1:6379> Llen list
(integer) 3
127.0.0.1:6379> LREM list 1 two # 移除最近添加的1个two
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> LRANGE list 0 -1
1) "three"
2) "one"
127.0.0.1:6379> LPUSH list three
(integer) 3
127.0.0.1:6379> LRANGE list 0 -1
1) "three"
2) "three"
3) "one"
127.0.0.1:6379> LREM list 2 three # 移除最近添加的2个three
(integer) 2
127.0.0.1:6379> LRANGE list 0 -1
1) "one"
------------------------------------------
截取一个值的范围 Ltrim -》保留
127.0.0.1:6379> keys *
(empty array)
127.0.0.1:6379> LPUSH mylist "hello"
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> LPUSH mylist "hello1"
(integer) 2
127.0.0.1:6379> LPUSH mylist "hello13"
(integer) 3
127.0.0.1:6379> LRANGE mylist 0 -1
1) "hello13"
2) "hello1"
3) "hello"
127.0.0.1:6379> LPUSH mylist "hello12"
(integer) 4
127.0.0.1:6379> LTRIM mylist 0 1 # 保留从0到1的字段
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> LRANGE mylist 0 -1
1) "hello12"
2) "hello13"
------------------------------------------
repoplpush #移除列表的最后一个元素并让其添加到一个新列表中
127.0.0.1:6379> LPUSH list "hello"
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> LPUSH list "hello1"
(integer) 2
127.0.0.1:6379> LPUSH list "hello2"
(integer) 3
127.0.0.1:6379> LPUSH list "hello3"
(integer) 4
127.0.0.1:6379> RPOPLPUSH list myotherlist # 移除最右边的元素并移动到新的位置
"hello"
127.0.0.1:6379> LRANGE list 0 -1
1) "hello3"
2) "hello2"
3) "hello1"
127.0.0.1:6379> LRANGE myotherlist 0 -1
1) "hello"
------------------------------------------
lset # 向指定列表的指定位置替换成某个值,前提是存在这个索引
127.0.0.1:6379> EXISTS list
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> lset list 0 item # 如果不存在索引就会报错
(error) ERR no such key
127.0.0.1:6379> lpush list hello1
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> LRANGE list 0 -1
1) "hello1"
127.0.0.1:6379> lset list 0 item # 向0索引处替换成某个值
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> LRANGE list 0 -1
1) "item"
127.0.0.1:6379> lset list 1 item2
(error) ERR index out of range
------------------------------------------
linsert #向指定元素前/或元素后 添加指定元素
127.0.0.1:6379> LPUSH list 0
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> LPUSH list 1
(integer) 2
127.0.0.1:6379> LPUSH list 2
(integer) 3
127.0.0.1:6379> LRANGE list 0 -1
1) "2"
2) "1"
3) "0"
127.0.0.1:6379> LINSERT list before "2" hello #向指定元素前加入某个值
(integer) 4
127.0.0.1:6379> LRANGE list 0 -1
1) "hello"
2) "2"
3) "1"
4) "0"
127.0.0.1:6379> LINSERT list after "2" hello #向指定元素后加入某个值
(integer) 5
127.0.0.1:6379> LRANGE list 0 -1
1) "hello"
2) "2"
3) "hello"
4) "1"
5) "0"
小结:
- list实际上是一个链表,before after , left, right都可以插入值
- 如果key不存在,则创建新的链表
- 如果key存在,则表示新增内容
- 如果移除了所有值,那么list就变成了空链表,也代表不存在
- 对于链表,在两边插入或者改动值,效率最高!修改中间元素,效率相对较低
4、Set (集合)
set中的值是无序不重复集合。
127.0.0.1:6379> sadd myset "hello" # set 集合中添加元素
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> sadd myset "jsxs"
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> sadd myset "love jsxs"
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> SMEMBERS myset # 查看set的所有制
1) "love jsxs"
2) "jsxs"
3) "hello"
127.0.0.1:6379> SISMEMBER myset hello # 判断一个值是否在-集合中
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> SISMEMBER myset jsd
(integer) 0
------------------------------------------
# scard 查看链表的个数
127.0.0.1:6379> sadd myset "love jsxs" # 不能重复,重复报0
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> sadd myset "love jsxs2" #
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> SCARD myset #查看链表的个数
(integer) 4
------------------------------------------
移除某一个元素 srem
127.0.0.1:6379> SCARD myset
(integer) 4
127.0.0.1:6379> srem myset hello # 移除某一个元素
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> SMEMBERS myset
1) "love jsxs2"
2) "love jsxs"
3) "jsxs"
------------------------------------------
随机数: 随机选取一个set值
127.0.0.1:6379> SMEMBERS myset
1) "love jsxs2"
2) "love jsxs"
3) "jsxs"
127.0.0.1:6379> SRANDMEMBER myset #随机抽选出一个元素
"jsxs"
127.0.0.1:6379> SRANDMEMBER myset
"jsxs"
127.0.0.1:6379> SRANDMEMBER myset
"jsxs"
127.0.0.1:6379> SRANDMEMBER myset
"love jsxs2"
127.0.0.1:6379> SRANDMEMBER myset
"jsxs"
127.0.0.1:6379> SRANDMEMBER myset
"love jsxs2"
127.0.0.1:6379> SRANDMEMBER myset
"love jsxs"
127.0.0.1:6379> SRANDMEMBER myset
"jsxs"
127.0.0.1:6379> SRANDMEMBER myset 2 #随机抽选处指定元素的个数
1) "love jsxs2"
2) "jsxs"
------------------------------------------
随机移除一个set值
127.0.0.1:6379> clear
127.0.0.1:6379> SMEMBERS myset
1) "love jsxs2"
2) "love jsxs"
3) "jsxs"
127.0.0.1:6379> SPOP myset #随机移除一个set值
"jsxs"
127.0.0.1:6379> SPOP myset
"love jsxs2"
127.0.0.1:6379> SMEMBERS
(error) ERR wrong number of arguments for 'smembers' command
127.0.0.1:6379> SMEMBERS myset
1) "love jsxs"
------------------------------------------
将一个值移动到另一个set 集合中
127.0.0.1:6379> sadd myset "hello"
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> sadd myset "hello1"
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> sadd myset "hello2"
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> sadd myset "hello3"
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> sadd myset2 "0"
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> SMEMBERS myset
1) "hello3"
2) "hello1"
3) "hello2"
4) "hello"
127.0.0.1:6379> SMEMBERS myset2
1) "0"
127.0.0.1:6379> SMOVE myset myset2 "hello" #将myset集合中的set2移动到myset2
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> SMEMBERS myset2
1) "0"
2) "hello"
127.0.0.1:6379> SMEMBERS myset
1) "hello3"
2) "hello1"
3) "hello2"
------------------------------------------
微博,B站,共同关注(并集)
127.0.0.1:6379> sadd key1 a
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> sadd key1 b
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> sadd key1 c
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> sadd key2 c
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> sadd key2 d
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> sadd key2 e
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> SDIFF key1 key2 # 差集
1) "b"
2) "a"
127.0.0.1:6379> SINTER key1 key2 #交集
1) "c"
127.0.0.1:6379> SUNION key1 key2 #并集
1) "d"
2) "c"
3) "a"
4) "b"
5) "e"
微博,A用户将所有关注的人放在一个set集合中!将他的粉丝也放在一个集合中,实现共同关注模块,二度好友**(六度分隔理论-推荐好友)**。
5、Hash (哈希)
集合中的元素是唯一的,这就意味着集合中不能出现重复的数据。在Redis 中 集合是通过哈希表实现的,所以添加,删除,查找的复杂度都是O(1)。Hash更适合于对象的存储。本质和String类型是没有太大区别的,还是一个简单的key-value.
127.0.0.1:6379> hset myhash filed1 jsxs #设置单个hashMap
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> HGET myhash filed1 #得到一个hashMap
"jsxs"
127.0.0.1:6379> HMSET myhash filed1 "hello" filed2 "world" #设置多个hashMap
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> HGET myhash filed1
"hello"
127.0.0.1:6379> HMGET myhash filed1 filed2 #获取多个hashMap
1) "hello"
2) "world"
127.0.0.1:6379> HGETALL myhash # 获得所有的hashMap
1) "filed1"
2) "hello"
3) "filed2"
4) "world"
------------------------------------------
删除指定的hashMap
127.0.0.1:6379> HDEL myhash filed2 #删除指定的hashmap
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> HGETALL myhash
1) "filed1"
2) "hello"
------------------------------------------
查看有几个键值对
127.0.0.1:6379> HLEN myhash
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> HMSET myhash filed2 world filed3 hh
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> HGETALL myhash
1) "filed1"
2) "hello"
3) "filed2"
4) "world"
5) "filed3"
6) "hh"
127.0.0.1:6379> HLEN myhash # 获取hash表的字段数量
(integer) 3
------------------------------------------
hash中指定字段是否存在
127.0.0.1:6379> HEXISTS myhash files1 #判断hash是否存在
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> HEXISTS myhash filed1
(integer) 1
------------------------------------------
仅仅获取字段和值
127.0.0.1:6379> HKEYS myhash # 单纯获取字段
1) "filed1"
2) "filed2"
3) "filed3"
127.0.0.1:6379> HVALS myhash #单纯获取值
1) "hello"
2) "world"
3) "hh"
------------------------------------------
127.0.0.1:6379> HSET myhash fileds3 5
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> HINCRBY myhash fileds3 1 # 自增1
(integer) 6
127.0.0.1:6379> HINCRBY myhash fileds3 2 #自自增2
(integer) 8
127.0.0.1:6379> HINCRBY myhash fileds3 -1 # 自减1
(integer) 7
127.0.0.1:6379> HSETNX myhash filed4 hello #加入说不存在就创建,存在就不创建
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> HSETNX myhash filed4 hello
(integer) 0
hash变更的数据user name age,尤其是用户信息之类的,经常变动的信息!
127.0.0.1:6379> HSET user:1 name jsxs # 设置id为1 键值对name
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> HGET myhash user:1
(nil)
127.0.0.1:6379> HGET user:1 name #获取id为1 的键值对
"jsxs"
6、Zset (有序集合)
在set基础上,增加一个值。set k1 v1 | zset k1 score1 v1
# 添加值
127.0.0.1:6379> zadd myset 1 one # 添加一个值
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> zadd myset 2 two
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> zadd myset 3 three 4 four #添加多个值
(integer) 2
127.0.0.1:6379> ZRANGE myset 0-1
(error) ERR wrong number of arguments for 'zrange' command
127.0.0.1:6379> ZRANGE myset 0 -1 # 查看添加的值
1) "one"
2) "two"
3) "three"
4) "four"
------------------------------------------
根据score 进行排序
127.0.0.1:6379> ZRANGEBYSCORE salary -inf +inf # 范围是正无穷 到 负无穷升序排序
1) "jsxs"
2) "xiaoming"
3) "zahngsan"
127.0.0.1:6379> ZRANGEBYSCORE salary -inf +inf withscores # 范围是正无穷 到 负无穷升序排序 并显示分数
1) "jsxs"
2) "200"
3) "xiaoming"
4) "2500"
5) "zahngsan"
6) "5000"
127.0.0.1:6379> ZRANGEBYSCORE salary -inf 2500 withscores # 范围是正无穷 到 2500
1) "jsxs"
2) "200"
3) "xiaoming"
4) "2500"
127.0.0.1:6379> ZREVRANGEBYSCORE salary +inf -inf withscores # 范围是正无穷 到 负无穷降序排序 并显示分数
1) "zahngsan"
2) "5000"
3) "xiaoming"
4) "2500"
5) "jsxs"
6) "200"
------------------------------------------
移除指定元素
127.0.0.1:6379> ZRANGE salary 0 -1
1) "jsxs"
2) "xiaoming"
3) "zahngsan"
127.0.0.1:6379> ZREM salary xiaoming # 移除指定的元素
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> ZRANGE salary 0 -1
1) "jsxs"
2) "zahngsan"
127.0.0.1:6379> zcard salary # 查看长度
(integer) 2
------------------------------------------
获取指定区间的个数
127.0.0.1:6379> zadd myset 1 "hello" #
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> zadd myset 2 "world" 3 ".jsxs"
(integer) 2
127.0.0.1:6379> ZCOUNT myset 1 3 # 获取1-3区间之间的数量
(integer) 3
127.0.0.1:6379> ZCOUNT myset 1 2 # 获取1-2区间之间的数量
(integer) 2
应用案例:
set排序 存储班级成绩表 工资表排序!
普通消息1 重要消息 2 ----带权重进行判断!
排行榜应用实现,取Top N测试!
(四)、三种特殊数据类型
1、Geospatial(地理位置)
使用经纬度定位地理坐标,并用一个有序集合Zset进行保存,GEO的底层实现原理就是Zset。
在这里我们先来增加一个经纬度的基本常识:
超链接: 在线经纬度查询工具
- 有效的经度从-180度到180度。
- 有效的纬度从-85.05112878度到85.05112878度。
1.geoAdd 添加地址
添加地理位置:
geoadd key 值(经度,维度,名称)
127.0.0.1:6379> geoadd china:city 116.40 39.90 beijing
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> geoadd china:city 121.47 31.23 shanghai
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> geoadd china:city 106.50 29.53 chongqing
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> geoadd china:city 114.05 22.52 shenzhen
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> geoadd china:city 120.16 30.24 hangzhou 108.96 34.26 xian
(integer) 2
2.geoPos 获取地址
获取指定城市的精度和维度
127.0.0.1:6379> GEOPOS china:city beijing
1) 1) "116.39999896287918091"
2) "39.90000009167092543"
127.0.0.1:6379> GEOPOS china:city beijing chongqing
1) 1) "116.39999896287918091"
2) "39.90000009167092543"
2) 1) "106.49999767541885376"
2) "29.52999957900659211"
3.geoDist 获取两点的距离
- m :米
- km :千米
- mi :英里
- ft :英尺
两点之间的距离
127.0.0.1:6379> GEODIST china:city beijing xian km # 北京到西安的千米
"910.0565"
127.0.0.1:6379> geoadd china:city 114.60 33.53 zhoukou
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> GEODIST china:city beijing zhoukou
"726411.7341"
127.0.0.1:6379> GEODIST china:city beijing zhoukou km #北京到周口的km
"726.4117"
3.geoRadius 以给定的经纬度为中心,找出某一半径的元素
(我附近的人?) 获得所有附件的人的地址,定位! 通过半径来查询。
多用于找朋友
根据经纬度查找附近的城市
127.0.0.1:6379> GEORADIUS china:city 110 30 1000 km # 查找以经度110 维度30 长度为1000km的城市
1) "chongqing"
2) "xian"
3) "shenzhen"
4) "hangzhou"
5) "zhoukou"
127.0.0.1:6379> GEORADIUS china:city 110 30 500 km
1) "chongqing"
2) "xian"
127.0.0.1:6379> GEORADIUS china:city 110 30 500 km withdist # 查找以经度110 维度30 长度为500km的城市 并标出直线距离
1) 1) "chongqing"
2) "341.9374"
2) 1) "xian"
2) "483.8340"
127.0.0.1:6379> GEORADIUS china:city 110 30 500 km withcoord # 查找以经度110 维度30 长度为500km的城市 并标出经纬度
1) 1) "chongqing"
2) 1) "106.49999767541885376"
2) "29.52999957900659211"
2) 1) "xian"
2) 1) "108.96000176668167114"
2) "34.25999964418929977"
127.0.0.1:6379> GEORADIUS china:city 110 30 500 km withdist withcoord count 1# 查找以经度110 维度30 长度为500km的城市 并标出直线距离 经纬度以及最近的一个。
1) 1) "chongqing"
2) "341.9374"
3) 1) "106.49999767541885376"
2) "29.52999957900659211"
- geoRadiusByMber 找出指定范围的元素,中心点是给定的元素
多用于找城市
根据地名向附近查找:
127.0.0.1:6379> GEORADIUSBYMEMBER china:city beijing 1000 km #以北京为中心半径为1000km查找所有的城市
1) "zhoukou"
2) "beijing"
3) "xian"
127.0.0.1:6379> GEORADIUSBYMEMBER china:city shanghai 1000 km
1) "hangzhou"
2) "shanghai"
3) "zhoukou"
5.geoHash 命令- 返回一个或多个位置元素的geoHash表示
该命令将返回11个字符的GeoHash字符串!
将二纬的经纬度转换为以为的字符串.如果两个字符串越接近,那么距离越近
127.0.0.1:6379> GEOHASH china:city beijing
1) "wx4fbxxfke0"
127.0.0.1:6379> GEOHASH china:city beijing zhoukou
1) "wx4fbxxfke0"
2) "wtcqxzcnmt0"
GEO 底层的实现原理其实就是 Zset!我们可以使用Zset命令来对其进行相关操作.
验证: 我们可以利用Zset进行删除的操作
移除坐标
127.0.0.1:6379> ZRANGE china:city 0 -1
1) "chongqing"
2) "xian"
3) "shenzhen"
4) "hangzhou"
5) "shanghai"
6) "zhoukou"
7) "beijing"
127.0.0.1:6379> ZREM china:city shenzhen #移除坐标
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> ZRANGE china:city 0 -1
1) "chongqing"
2) "xian"
3) "hangzhou"
4) "shanghai"
5) "zhoukou"
6) "beijing"
2、Hyperloglog(基数统计)
基数就是一个集合中不重复的元素。举一个简单的例子:
- A {1,3,5,7,8,7}
- A(不重复的元素) = (1,3,5,8),可以接受误差!
简介
- Redis HyperLogLog 是用来做基数统计的算法。
- 优点:
-
- 输入元素的数量或者体积非常大时,计算基数所需的空间总是固定的、并且是很小的。
-
- 花费 12 KB 内存,就可以计算接近 2^64 个不同元素的基数。
网页的UV (一个人访问一个网站多次,但是还是算作一个人!)
-
传统的解决方式: 利用set集合不重复的特性。set保存用户的id,然后就可以统计元素数量作为标准判断!
-
如果允许容错,那么一定可以使用 Hyperloglog 。
-
如果不允许容错,就使用传统的 set 或者自己的数据类型即可。
-
HyperLogLog 底层使用string数据类型。
127.0.0.1:6379> PFADD myset a b c d e f g h i j k #设置一个基数统计
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> PFCOUNT myset #统计不重复的数量-基数
(integer) 11
127.0.0.1:6379> PFADD myset2 a b c d e f g h i j k s a a c b
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> PFCOUNT myset
(integer) 11
127.0.0.1:6379> PFCOUNT myset2
(integer) 12
127.0.0.1:6379> PFMERGE mykey3 myset myset2 # 进行多个集合的合并
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> PFCOUNT mykey3
(integer) 12
3、BitMap(位图)
BitMap可以用来干什么呢?
- 签到统计,使用bitmap 来记录 周一到周日的打卡!
- 状态统计
BitMap采用位存储,它是一连串的二进制数字,信息状态只有0和1,每一位所在的位置为(offset)

测试: 假设我们现在的任务是统计从星期一到星期天的打卡情况。0代表未打卡,1代表打卡
------------------------------------------
添加一个
127.0.0.1:6379> setbit sign 0 0 # 假设第一个0是星期1 第二个0 是未打卡
127.0.0.1:6379> setbit sign 1 0
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> setbit sign 2 1
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> setbit sign 3 1
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> setbit sign 4 1
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> setbit sign 5 1
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> setbit sign 6 1
(integer) 0
------------------------------------------
查看某一个具体的
127.0.0.1:6379> GETBIT sign 0
(integer) 0
127.0.0.1:6379> GETBIT sign 3
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:6379> GETBIT sign 6
(integer) 1
------------------------------------------
统计总和就是 0和1 的
127.0.0.1:6379> BITCOUNT sign
(integer) 5
(五)、事务
面试高频:
这里我们一定要知道Redis中的单条命令是保证原子性的,但是redis事务不能保证原子性。
Redis事务的本质
- 一次性
- 顺序性
- 排他性
在Redis事务没有没有隔离级别的概念;所有的命令在事务中,并没有直接被执行!只有发起执行命令Exec的时候才会执行!事务中每条命令都会被序列化,执行过程中按顺序执行,不允许其他命令进行干扰(排他)
redis事务的三大过程
- 开启事务(multi)
- 命令入队(…)
- 执行事务(exec)
1.正常执行事务
127.0.0.1:6379> multi # 开启事务: 代表以下的命令开始进入事务
OK
127.0.0.1:6379(TX)> set k1 v1
QUEUED
127.0.0.1:6379(TX)> set k2 v2
QUEUED
127.0.0.1:6379(TX)> get k2
QUEUED
127.0.0.1:6379(TX)> set k3 v3
QUEUED
127.0.0.1:6379(TX)> exec #提交事务: 代表即将按照事务进行输出
1) OK
2) OK
3) "v2"
4) OK
2.取消事务
取消事务,代表事务里面的数据不奏效。但以前的数据仍然保留。
127.0.0.1:6379> get k2 # 事务
"v2"
127.0.0.1:6379> multi # 开启事务
OK
127.0.0.1:6379(TX)> set k1 v1
QUEUED
127.0.0.1:6379(TX)> set k2 v2
QUEUED
127.0.0.1:6379(TX)> set k4 v4
QUEUED
127.0.0.1:6379(TX)> discard #取消事务
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> get k4 # 事务里面的数据无效
(nil)
127.0.0.1:6379> get k2 # 事务之前的有效
"v2"
3.编译型异常(代码有问题, 命令有错!)
事务中的所有命令都不会被执行
127.0.0.1:6379> multi # 开启事务
OK
127.0.0.1:6379(TX)> set k1 v1
QUEUED
127.0.0.1:6379(TX)> set k2 v2
QUEUED
127.0.0.1:6379(TX)> set k3 v3
QUEUED
127.0.0.1:6379(TX)> getset k3 # 编译型错误
(error) ERR wrong number of arguments for 'getset' command
127.0.0.1:6379(TX)> set k3 v3
QUEUED
127.0.0.1:6379(TX)> set k4 v4
QUEUED
127.0.0.1:6379(TX)> EXEC # 提交事务
(error) EXECABORT Transaction discarded because of previous errors.
127.0.0.1:6379> get k1 # 得不到值
(nil)
4.运行时异常 (错误的不被执行,其他的执行)
如果事务队列中存在错误语法性,那么执行命令的时候,其他命令是可以正常执行的,只有错误命令会抛出异常!
127.0.0.1:6379> flushdb
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> set k1 "v1"
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> multi
OK
127.0.0.1:6379(TX)> incr k1 # 字符串不能自增 会失败
QUEUED
127.0.0.1:6379(TX)> set k2 v2
QUEUED
127.0.0.1:6379(TX)> set k3 v3
QUEUED
127.0.0.1:6379(TX)> EXEC
1) (error) ERR value is not an integer or out of range
2) OK
3) OK
127.0.0.1:6379> get k2
"v2"
127.0.0.1:6379> get k3
"v3"
(六)、Redis监控/乐观锁(watch)
1、悲观锁:顾名思义就是做什么事情都很悲观,无论干什么都要上锁。(影响性能的)
2、乐观锁:做什么事都很乐观,都不会去上锁;只有更新数据的时候去才判断一下version,看一下在此期间是否有人修改过这个数据:
- 获取version
- 更新的时候比较version
使用watch key监控指定数据,相当于乐观锁加锁。
1.正常执行乐观锁
单线程执行成功!
127.0.0.1:6379> set money 100 #设置余额100
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> set out 0 # 发出 0
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> watch money # 开始监视余额
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> multi # 开启事务
OK
127.0.0.1:6379(TX)> decrby money 20 # 画出20
QUEUED
127.0.0.1:6379(TX)> incrby out 20
QUEUED
127.0.0.1:6379(TX)> EXEC #结束
1) (integer) 80
2) (integer) 20
2.多线程执行乐观锁
一个服务器,两个客户端
第一个线程,继续监视money,然后开启事务设置操作**但不提交**
127.0.0.1:6379> watch money
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> multi
OK
127.0.0.1:6379(TX)> DECRBY money 10
QUEUED
127.0.0.1:6379(TX)> INCRBY out 10
QUEUED
127.0.0.1:6379(TX)>
第二个线程 进行充值1000元人民币
127.0.0.1:6379> get money
"80"
127.0.0.1:6379> set money 1000
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> get money
"1000"
然后第一个线程提交事务,发现会出错
127.0.0.1:6379> watch money
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> multi
OK
127.0.0.1:6379(TX)> DECRBY money 10
QUEUED
127.0.0.1:6379(TX)> INCRBY out 10
QUEUED
127.0.0.1:6379(TX)> EXEC # 提交事务,但是出错
(nil)
无论事务是否执行成功,Redis都会取消watch监控
如果发现事务执行失败,我们需要先解锁。
127.0.0.1:6379> unwatch # 解锁
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> watch money # 重新上锁
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> multi
OK
127.0.0.1:6379(TX)> DECRBY money 10
QUEUED
127.0.0.1:6379(TX)> INCRBY out 10
QUEUED
127.0.0.1:6379(TX)> EXEC
1) (integer) 990
2) (integer) 30
注意:
- 如果发现事务执行失败就先解锁 unwatch
- 获取最新的值,再次进行监视 watch key
- 比对监视的值是否发生了变化,如果没有变化那么可以执行成功,反之则会失败。
(七)、Jedis
Jedis是Redis官方推荐使用的Java连接redis的客户端。所以我们在使用Java来操作redis时就要学习Jedis。
1.导入相关的依赖
首先设置一个空项目,然后创建一个Maven项目
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>redis.clientsgroupId>
<artifactId>jedisartifactId>
<version>3.2.0version>
dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>com.alibabagroupId>
<artifactId>fastjsonartifactId>
<version>1.2.70version>
dependency>
dependencies>
2.测试远程Redis
假如说连接Linux系统。
- 注释掉配置文件中的 bind 127.0.0.1
- daemonize 设置为no
- 阿里云开启安全组6379 宝塔也要开启6379
- 要开启服务端的redis
- 一定要设置密码 否则容易被黑。
测试:
package com.jsxs;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
public class testPing {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. new Jedis对象
Jedis jedis = new Jedis("IP", 6379);
jedis.auth("密码");
System.out.println(jedis.ping());
}
}
package com.jsxs;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
public class testPing {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1. new Jedis对象
Jedis jedis = new Jedis("IP", 6379);
jedis.auth("密码");
// 2.测试是否链接成功
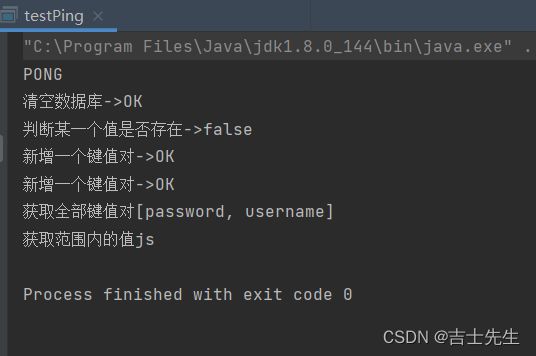
System.out.println(jedis.ping());
System.out.println("清空数据库->"+ jedis.flushDB());
System.out.println("判断某一个值是否存在->"+ jedis.exists("username"));
System.out.println("新增一个键值对->"+jedis.set("username","jsxs"));
System.out.println("新增一个键值对->"+ jedis.set("password","15945"));
System.out.println("获取全部键值对"+jedis.keys("*"));
System.out.println("获取范围内的值"+jedis.getrange("username",0,1));
}
}
3.事务相关案列
事务相关举列
成功案列事务
package com.jsxs;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
import redis.clients.jedis.Transaction;
public class testTX {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Jedis jedis = new Jedis("8.130.48.9", 6379);
jedis.auth("121788");
System.out.println(jedis.ping());
// 设置JSON数据
JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject();
jsonObject.put("hello","world");
jsonObject.put("name","jsxs");
Transaction multi = jedis.multi();//开启事务
String result = jsonObject.toJSONString(); //把JSON数据转换为字符串
try {
multi.set("user1",result);
multi.set("user2",result);
multi.exec(); //假如成功就执行
} catch (Exception e) {
multi.discard(); //假如执行失败,就取消事务
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
System.out.println(jedis.get("user1"));
System.out.println(jedis.get("user2"));
jedis.close(); //最终都关闭客户端
}
}
}
package com.jsxs;
import com.alibaba.fastjson.JSONObject;
import redis.clients.jedis.Jedis;
import redis.clients.jedis.Transaction;
public class testTX {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Jedis jedis = new Jedis("8.130.48.9", 6379);
jedis.auth("121788");
System.out.println(jedis.ping());
jedis.flushDB();
// 设置JSON数据
JSONObject jsonObject = new JSONObject();
jsonObject.put("hello","world");
jsonObject.put("name","jsxs");
Transaction multi = jedis.multi();//开启事务
String result = jsonObject.toJSONString(); //把JSON数据转换为字符串
try {
multi.set("user1",result);
multi.set("user2",result);
int i=1/0;
multi.exec(); //假如成功就执行
} catch (Exception e) {
multi.discard(); //假如执行失败,就取消事务
System.out.println("事务执行失败");
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
System.out.println(jedis.get("user1"));
System.out.println(jedis.get("user2"));
jedis.close(); //最终都关闭客户端
}
}
}
(八)、SpringBoot整合Redis
1.导入一个整合包
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.bootgroupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redisartifactId>
dependency>
说明: 在SpringBoot2.x之后,原来使用的jedis被替换为了lettuce.
- jedis: 采用的是直连,多个线程操作的话,是不安全的,如果想要避免不安全的,使用jedis oppl连接池,更像BIO模式。
- lerruce: 采用netty,实列可以在多个线程中进行共享,不存在线程不安全的情况,可以减少线程数据了,更像NIO模式

2.源码分析
@AutoConfiguration
@ConditionalOnClass(RedisOperations.class)
@EnableConfigurationProperties(RedisProperties.class)
@Import({ LettuceConnectionConfiguration.class, JedisConnectionConfiguration.class })
public class RedisAutoConfiguration {
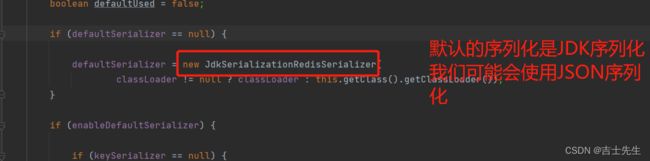
@Bean
//默认的redisTemplate 没有过多的设置,redis对象都是需要序列化。
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = "redisTemplate") //我们可以自定义一个redisTemlate来替换这个默认的。
@ConditionalOnSingleCandidate(RedisConnectionFactory.class)
// 两个泛型都是Object 的类型,我们后面使用的话需要强制转化
public RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
template.setConnectionFactory(redisConnectionFactory);
return template;
}
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
@ConditionalOnSingleCandidate(RedisConnectionFactory.class)
public StringRedisTemplate stringRedisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) {
return new StringRedisTemplate(redisConnectionFactory);
}
}
可以配置的参数
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.redis")
public class RedisProperties {
/**
* Database index used by the connection factory.
*/
private int database = 0;
/**
* Connection URL. Overrides host, port, and password. User is ignored. Example:
* redis://user:[email protected]:6379
*/
private String url;
/**
* Redis server host.
*/
private String host = "localhost";
/**
* Login username of the redis server.
*/
private String username;
/**
* Login password of the redis server.
*/
private String password;
/**
* Redis server port.
*/
private int port = 6379;
/**
* Whether to enable SSL support.
*/
private boolean ssl;
/**
* Read timeout.
*/
private Duration timeout;
/**
* Connection timeout.
*/
private Duration connectTimeout;
/**
* Client name to be set on connections with CLIENT SETNAME.
*/
private String clientName;
/**
* Type of client to use. By default, auto-detected according to the classpath.
*/
private ClientType clientType;
private Sentinel sentinel;
private Cluster cluster;
3.导入配置链接
application.properties
# 链接远程主机
spring.redis.host=IP
#端口
spring.redis.port=6379
#密码
spring.redis.password=*****
4.测试
package com.jsxs;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnection;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@SpringBootTest
class Redis02SpringBootApplicationTests {
@Resource
RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
// redisTemplate-》操作不同的类型
// 操作字符串opsForValue()
// 操作List opsForList()
// 操作SET opsForSet()
// 操作Hash opsForHash()
// 操作地图 opsForGeo()
// 除了基本的操作,我们常用的方法都可以直接redisTemplate来调用,比如事务和基本的增删改查。
// RedisConnection connection = redisTemplate.getConnectionFactory().getConnection(); 获取链接对象
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("myKey","jsxs");
System.out.println(redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("myKey"));
}
}
5.设置中文乱码问题展现
如果设置中文的话,在控制无误,但是会在redis-cli出错

以下是序列化配置

(九)、自定义RedisTemplate
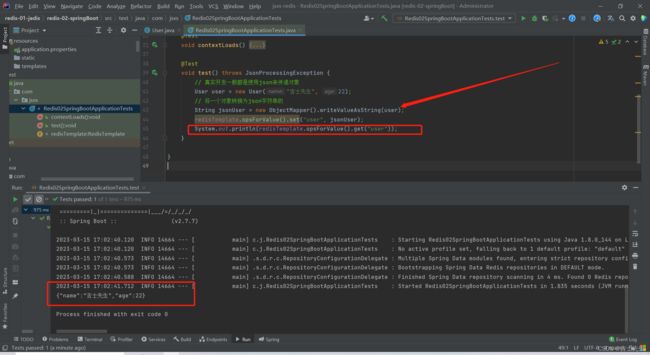
1.对象通过json传入
在企业开发中,对象都是先转换为json字符串再进行传递
@Test
void test() throws JsonProcessingException {
// 真实开发一般都是使用json来传递对象
User user = new User("吉士先生", 22);
// 将一个对象转换为json字符串的
String jsonUser = new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString(user);
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("user", jsonUser);
System.out.println(redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("user"));
}
2.直接传递一个对象
假如我们直接传一个对象就会报错: 没有序列化
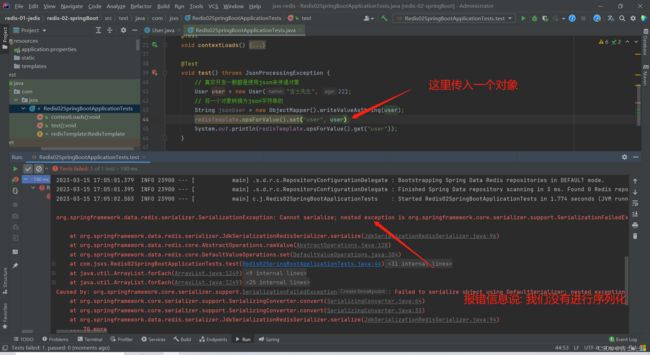
进行序列化之后。
在企业中,我们所有的pojo都会序列化
package com.jsxs.pojo;
import lombok.AllArgsConstructor;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.io.Serializable;
@Component
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
public class User implements Serializable {
private String name;
private int age;
}
3.解决中文乱码问题
我们在config中添加这个配置
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.data.redis.connection.RedisConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.serializer.RedisSerializer;
import java.net.UnknownHostException;
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean
public RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory) throws UnknownHostException {
// 将template 泛型设置为 测试类一定要指向redisTemplate
package com.jsxs;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.core.JsonProcessingException;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.ObjectMapper;
import com.jsxs.pojo.User;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Qualifier;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import javax.annotation.Resource;
@SpringBootTest
class Redis02SpringBootApplicationTests {
@Resource
@Qualifier("redisTemplate") //指向配置类
RedisTemplate redisTemplate;
@Test
void test() throws JsonProcessingException {
// 真实开发一般都是使用json来传递对象
User user = new User("吉士先生", 22);
// 将一个对象转换为json字符串的
String jsonUser = new ObjectMapper().writeValueAsString(user);
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set("user", user);
System.out.println(redisTemplate.opsForValue().get("user"));
}
}
4.Template自定义的工具类
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.util.CollectionUtils;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
@Component
public final class RedisUtil {
@Autowired
private RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
// =============================common============================
/**
* 指定缓存失效时间
* @param key 键
* @param time 时间(秒)
*/
public boolean expire(String key, long time) {
try {
if (time > 0) {
redisTemplate.expire(key, time, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
/**
* 根据key 获取过期时间
* @param key 键 不能为null
* @return 时间(秒) 返回0代表为永久有效
*/
public long getExpire(String key) {
return redisTemplate.getExpire(key, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
}
/**
* 判断key是否存在
* @param key 键
* @return true 存在 false不存在
*/
public boolean hasKey(String key) {
try {
return redisTemplate.hasKey(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
/**
* 删除缓存
* @param key 可以传一个值 或多个
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public void del(String... key) {
if (key != null && key.length > 0) {
if (key.length == 1) {
redisTemplate.delete(key[0]);
} else {
redisTemplate.delete(String.valueOf(CollectionUtils.arrayToList(key)));
}
}
}
// ============================String=============================
/**
* 普通缓存获取
* @param key 键
* @return 值
*/
public Object get(String key) {
return key == null ? null : redisTemplate.opsForValue().get(key);
}
/**
* 普通缓存放入
* @param key 键
* @param value 值
* @return true成功 false失败
*/
public boolean set(String key, Object value) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, value);
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
/**
* 普通缓存放入并设置时间
* @param key 键
* @param value 值
* @param time 时间(秒) time要大于0 如果time小于等于0 将设置无限期
* @return true成功 false 失败
*/
public boolean set(String key, Object value, long time) {
try {
if (time > 0) {
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, value, time, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
} else {
set(key, value);
}
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
/**
* 递增
* @param key 键
* @param delta 要增加几(大于0)
*/
public long incr(String key, long delta) {
if (delta < 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("递增因子必须大于0");
}
return redisTemplate.opsForValue().increment(key, delta);
}
/**
* 递减
* @param key 键
* @param delta 要减少几(小于0)
*/
public long decr(String key, long delta) {
if (delta < 0) {
throw new RuntimeException("递减因子必须大于0");
}
return redisTemplate.opsForValue().increment(key, -delta);
}
// ================================Map=================================
/**
* HashGet
* @param key 键 不能为null
* @param item 项 不能为null
*/
public Object hget(String key, String item) {
return redisTemplate.opsForHash().get(key, item);
}
/**
* 获取hashKey对应的所有键值
* @param key 键
* @return 对应的多个键值
*/
public Map<Object, Object> hmget(String key) {
return redisTemplate.opsForHash().entries(key);
}
/**
* HashSet
* @param key 键
* @param map 对应多个键值
*/
public boolean hmset(String key, Map<String, Object> map) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForHash().putAll(key, map);
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
/**
* HashSet 并设置时间
* @param key 键
* @param map 对应多个键值
* @param time 时间(秒)
* @return true成功 false失败
*/
public boolean hmset(String key, Map<String, Object> map, long time) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForHash().putAll(key, map);
if (time > 0) {
expire(key, time);
}
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
/**
* 向一张hash表中放入数据,如果不存在将创建
*
* @param key 键
* @param item 项
* @param value 值
* @return true 成功 false失败
*/
public boolean hset(String key, String item, Object value) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForHash().put(key, item, value);
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
/**
* 向一张hash表中放入数据,如果不存在将创建
*
* @param key 键
* @param item 项
* @param value 值
* @param time 时间(秒) 注意:如果已存在的hash表有时间,这里将会替换原有的时间
* @return true 成功 false失败
*/
public boolean hset(String key, String item, Object value, long time) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForHash().put(key, item, value);
if (time > 0) {
expire(key, time);
}
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
/**
* 删除hash表中的值
*
* @param key 键 不能为null
* @param item 项 可以使多个 不能为null
*/
public void hdel(String key, Object... item) {
redisTemplate.opsForHash().delete(key, item);
}
/**
* 判断hash表中是否有该项的值
*
* @param key 键 不能为null
* @param item 项 不能为null
* @return true 存在 false不存在
*/
public boolean hHasKey(String key, String item) {
return redisTemplate.opsForHash().hasKey(key, item);
}
/**
* hash递增 如果不存在,就会创建一个 并把新增后的值返回
*
* @param key 键
* @param item 项
* @param by 要增加几(大于0)
*/
public double hincr(String key, String item, double by) {
return redisTemplate.opsForHash().increment(key, item, by);
}
/**
* hash递减
*
* @param key 键
* @param item 项
* @param by 要减少记(小于0)
*/
public double hdecr(String key, String item, double by) {
return redisTemplate.opsForHash().increment(key, item, -by);
}
// ============================set=============================
/**
* 根据key获取Set中的所有值
* @param key 键
*/
public Set<Object> sGet(String key) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForSet().members(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* 根据value从一个set中查询,是否存在
*
* @param key 键
* @param value 值
* @return true 存在 false不存在
*/
public boolean sHasKey(String key, Object value) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForSet().isMember(key, value);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
/**
* 将数据放入set缓存
*
* @param key 键
* @param values 值 可以是多个
* @return 成功个数
*/
public long sSet(String key, Object... values) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForSet().add(key, values);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return 0;
}
}
/**
* 将set数据放入缓存
*
* @param key 键
* @param time 时间(秒)
* @param values 值 可以是多个
* @return 成功个数
*/
public long sSetAndTime(String key, long time, Object... values) {
try {
Long count = redisTemplate.opsForSet().add(key, values);
if (time > 0)
expire(key, time);
return count;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return 0;
}
}
/**
* 获取set缓存的长度
*
* @param key 键
*/
public long sGetSetSize(String key) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForSet().size(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return 0;
}
}
/**
* 移除值为value的
*
* @param key 键
* @param values 值 可以是多个
* @return 移除的个数
*/
public long setRemove(String key, Object... values) {
try {
Long count = redisTemplate.opsForSet().remove(key, values);
return count;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return 0;
}
}
// ===============================list=================================
/**
* 获取list缓存的内容
*
* @param key 键
* @param start 开始
* @param end 结束 0 到 -1代表所有值
*/
public List<Object> lGet(String key, long start, long end) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForList().range(key, start, end);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* 获取list缓存的长度
*
* @param key 键
*/
public long lGetListSize(String key) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForList().size(key);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return 0;
}
}
/**
* 通过索引 获取list中的值
*
* @param key 键
* @param index 索引 index>=0时, 0 表头,1 第二个元素,依次类推;index<0时,-1,表尾,-2倒数第二个元素,依次类推
*/
public Object lGetIndex(String key, long index) {
try {
return redisTemplate.opsForList().index(key, index);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return null;
}
}
/**
* 将list放入缓存
*
* @param key 键
* @param value 值
*/
public boolean lSet(String key, Object value) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPush(key, value);
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
/**
* 将list放入缓存
* @param key 键
* @param value 值
* @param time 时间(秒)
*/
public boolean lSet(String key, Object value, long time) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPush(key, value);
if (time > 0)
expire(key, time);
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
/**
* 将list放入缓存
*
* @param key 键
* @param value 值
* @return
*/
public boolean lSet(String key, List<Object> value) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPushAll(key, value);
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
/**
* 将list放入缓存
*
* @param key 键
* @param value 值
* @param time 时间(秒)
* @return
*/
public boolean lSet(String key, List<Object> value, long time) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForList().rightPushAll(key, value);
if (time > 0)
expire(key, time);
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
/**
* 根据索引修改list中的某条数据
*
* @param key 键
* @param index 索引
* @param value 值
* @return
*/
public boolean lUpdateIndex(String key, long index, Object value) {
try {
redisTemplate.opsForList().set(key, index, value);
return true;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return false;
}
}
/**
* 移除N个值为value
*
* @param key 键
* @param count 移除多少个
* @param value 值
* @return 移除的个数
*/
public long lRemove(String key, long count, Object value) {
try {
Long remove = redisTemplate.opsForList().remove(key, count, value);
return remove;
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return 0;
}
}
}
(十)、Redis.config
- redis在启动的时候,就通过配置文件来启动!
- 工作中,一些小小的配置,可以让你脱颖而出!
1.容量单位
配置文件 unit单位 对大小写不敏感!
# Note on units: when memory size is needed, it is possible to specify
# it in the usual form of 1k 5GB 4M and so forth:
单位
# 1k => 1000 bytes
# 1kb => 1024 bytes
# 1m => 1000000 bytes
# 1mb => 1024*1024 bytes
# 1g => 1000000000 bytes
# 1gb => 1024*1024*1024 bytes
对大小写不敏感
# units are case insensitive so 1GB 1Gb 1gB are all the same.
2.包含
就相当于import,可以把其他的配置文件配置过来
################################## INCLUDES ###################################
# Include one or more other config files here. This is useful if you
# have a standard template that goes to all Redis servers but also need
# to customize a few per-server settings. Include files can include
# other files, so use this wisely.
#
# Note that option "include" won't be rewritten by command "CONFIG REWRITE"
# from admin or Redis Sentinel. Since Redis always uses the last processed
# line as value of a configuration directive, you'd better put includes
# at the beginning of this file to avoid overwriting config change at runtime.
#
# If instead you are interested in using includes to override configuration
# options, it is better to use include as the last line.
#
# Included paths may contain wildcards. All files matching the wildcards will
# be included in alphabetical order.
# Note that if an include path contains a wildcards but no files match it when
# the server is started, the include statement will be ignored and no error will
# be emitted. It is safe, therefore, to include wildcard files from empty
# directories.
可以引入配置
# include /path/to/local.conf
# include /path/to/other.conf
# include /path/to/fragments/*.conf
3.文件
################################## MODULES #####################################
# Load modules at startup. If the server is not able to load modules
# it will abort. It is possible to use multiple loadmodule directives.
加载一些so文件
# loadmodule /path/to/my_module.so
# loadmodule /path/to/other_module.so
4.网络
################################## NETWORK #####################################
# By default, if no "bind" configuration directive is specified, Redis listens
# for connections from all available network interfaces on the host machine.
# It is possible to listen to just one or multiple selected interfaces using
# the "bind" configuration directive, followed by one or more IP addresses.
# Each address can be prefixed by "-", which means that redis will not fail to
# start if the address is not available. Being not available only refers to
# addresses that does not correspond to any network interface. Addresses that
# are already in use will always fail, and unsupported protocols will always BE
# silently skipped.
#
# Examples:
#
# bind 192.168.1.100 10.0.0.1 # listens on two specific IPv4 addresses
# bind 127.0.0.1 ::1 # listens on loopback IPv4 and IPv6
# bind * -::* # like the default, all available interfaces
#
# ~~~ WARNING ~~~ If the computer running Redis is directly exposed to the
# internet, binding to all the interfaces is dangerous and will expose the
# instance to everybody on the internet. So by default we uncomment the
# following bind directive, that will force Redis to listen only on the
# IPv4 and IPv6 (if available) loopback interface addresses (this means Redis
# will only be able to accept client connections from the same host that it is
# running on).
#
# IF YOU ARE SURE YOU WANT YOUR INSTANCE TO LISTEN TO ALL THE INTERFACES
# COMMENT OUT THE FOLLOWING LINE.
#
# You will also need to set a password unless you explicitly disable protected
# mode.
如果我们需要允许远程访问,我们需要把bind 给注释掉
bind 127.0.0.1 -::1
# By default, outgoing connections (from replica to master, from Sentinel to
# instances, cluster bus, etc.) are not bound to a specific local address. In
# most cases, this means the operating system will handle that based on routing
# and the interface through which the connection goes out.
#
# Using bind-source-addr it is possible to configure a specific address to bind
# to, which may also affect how the connection gets routed.
# Example:
#
# bind-source-addr 10.0.0.1
# Protected mode is a layer of security protection, in order to avoid that
# Redis instances left open on the internet are accessed and exploited.
#
# When protected mode is on and the default user has no password, the server
# only accepts local connections from the IPv4 address (127.0.0.1), IPv6 address
# (::1) or Unix domain sockets.
#
# By default protected mode is enabled. You should disable it only if
# you are sure you want clients from other hosts to connect to Redis
# even if no authentication is configured.
保护模式: 假如我们需要远程就设置no ,本地就yes
protected-mode no
# no - Block for any connection (remain immutable)
# yes - Allow for any connection (no protection)
# local - Allow only for local connections. Ones originating from the
# IPv4 address (127.0.0.1), IPv6 address (::1) or Unix domain sockets.
#
# enable-protected-configs no
# enable-debug-command no
# enable-module-command no
# Accept connections on the specified port, default is 6379 (IANA #815344).
# If port 0 is specified Redis will not listen on a TCP socket.
端口号:
port 5555
5.通用
################################# GENERAL #####################################
# By default Redis does not run as a daemon. Use 'yes' if you need it.
# Note that Redis will write a pid file in /var/run/redis.pid when daemonized.
# When Redis is supervised by upstart or systemd, this parameter has no impact.
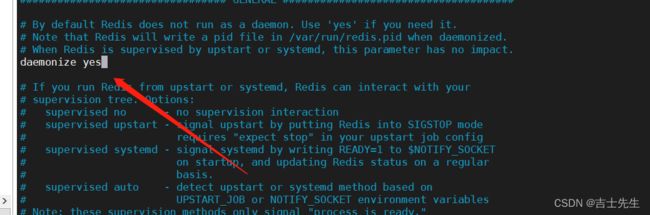
保护进程: 默认是no ,我们需要开启yes
daemonize yes
# If you run Redis from upstart or systemd, Redis can interact with your
# supervision tree. Options:
# supervised no - no supervision interaction
# supervised upstart - signal upstart by putting Redis into SIGSTOP mode
# requires "expect stop" in your upstart job config
# supervised systemd - signal systemd by writing READY=1 to $NOTIFY_SOCKET
# on startup, and updating Redis status on a regular
# basis.
# supervised auto - detect upstart or systemd method based on
# UPSTART_JOB or NOTIFY_SOCKET environment variables
# Note: these supervision methods only signal "process is ready."
# They do not enable continuous pings back to your supervisor.
#
# The default is "no". To run under upstart/systemd, you can simply uncomment
# the line below:
# If you run Redis from upstart or systemd, Redis can interact with your
# supervision tree. Options:
# supervised no - no supervision interaction
# supervised upstart - signal upstart by putting Redis into SIGSTOP mode
# requires "expect stop" in your upstart job config
# supervised systemd - signal systemd by writing READY=1 to $NOTIFY_SOCKET
# on startup, and updating Redis status on a regular
# basis.
# supervised auto - detect upstart or systemd method based on
# UPSTART_JOB or NOTIFY_SOCKET environment variables
# Note: these supervision methods only signal "process is ready."
# They do not enable continuous pings back to your supervisor.
#
# The default is "no". To run under upstart/systemd, you can simply uncomment
# the line below:
管理守护进程的,默认为no.我们不用管
# supervised auto
# If a pid file is specified, Redis writes it where specified at startup
# and removes it at exit.
#
# When the server runs non daemonized, no pid file is created if none is
# specified in the configuration. When the server is daemonized, the pid file
# is used even if not specified, defaulting to "/var/run/redis.pid".
#
# Creating a pid file is best effort: if Redis is not able to create it
# nothing bad happens, the server will start and run normally.
#
# Note that on modern Linux systems "/run/redis.pid" is more conforming
# and should be used instead.
如果以后台的方式运行,我们就需要指定一个pid --进程文件
pidfile /var/run/redis_6379.pid
# Specify the server verbosity level.
# This can be one of:
# debug (a lot of information, useful for development/testing)
# verbose (many rarely useful info, but not a mess like the debug level)
# notice (moderately verbose, what you want in production probably)
# warning (only very important / critical messages are logged)
日志级别: debug测试和开发 (一般不用配置)
loglevel notice
# Specify the log file name. Also the empty string can be used to force
# Redis to log on the standard output. Note that if you use standard
# output for logging but daemonize, logs will be sent to /dev/null
日志生成的文件位置,如果为null,那么就是控制台输出
logfile ""
# To enable logging to the system logger, just set 'syslog-enabled' to yes,
# and optionally update the other syslog parameters to suit your needs.
# syslog-enabled no
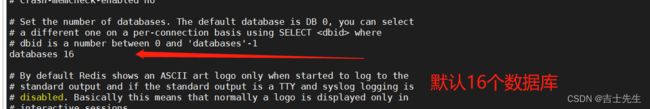
# Set the number of databases. The default database is DB 0, you can select
# a different one on a per-connection basis using SELECT where
# dbid is a number between 0 and 'databases'-1
默认有16个数据库
databases 16
# However it is possible to force the pre-4.0 behavior and always show a
# ASCII art logo in startup logs by setting the following option to yes.
是否显示Redis的log
always-show-logo no
# By default, Redis modifies the process title (as seen in 'top' and 'ps') to
# provide some runtime information. It is possible to disable this and leave
# the process name as executed by setting the following to no.
6.快照
持久化,在规定的时间内执行了多少次操作,则会持久化到文件 .rdb .aof
Redis是内存数据库,如果没有持久化,那么数据就会断电就失去
################################ SNAPSHOTTING ################################
# Save the DB to disk.
#
# save [ ...]
#
# Redis will save the DB if the given number of seconds elapsed and it
# surpassed the given number of write operations against the DB.
#
# Snapshotting can be completely disabled with a single empty string argument
# as in following example:
#
# save ""
#
# Unless specified otherwise, by default Redis will save the DB:
# * After 3600 seconds (an hour) if at least 1 change was performed
# * After 300 seconds (5 minutes) if at least 100 changes were performed
# * After 60 seconds if at least 10000 changes were performed
#
# You can set these explicitly by uncommenting the following line.
如果 3600秒内,如果至少有一个key进行了修改。那么我们就进行持久化操作
如果在300秒内,至少有100个key进行了修改。那么我们就进行持久化操作
如果在60秒内,有10000个key进行了修改。那么我们就进行持久化操作
# save 3600 1 300 100 60 10000
# If the background saving process will start working again Redis will
# automatically allow writes again.
#
# However if you have setup your proper monitoring of the Redis server
# and persistence, you may want to disable this feature so that Redis will
# continue to work as usual even if there are problems with disk,
# permissions, and so forth.
持久化如果出错,是否还需要继续工作
stop-writes-on-bgsave-error yes
# Compress string objects using LZF when dump .rdb databases?
# By default compression is enabled as it's almost always a win.
# If you want to save some CPU in the saving child set it to 'no' but
# the dataset will likely be bigger if you have compressible values or keys.
是否压缩rdb文件,如果yes会消耗cpu
rdbcompression yes
# RDB files created with checksum disabled have a checksum of zero that will
# tell the loading code to skip the check.
保存rdb文件的时候,是否进行检查校验
rdbchecksum yes
# Enables or disables full sanitization checks for ziplist and listpack etc when
# loading an RDB or RESTORE payload. This reduces the chances of a assertion or
# crash later on while processing commands.
# Options:
# no - Never perform full sanitization
# yes - Always perform full sanitization
# clients - Perform full sanitization only for user connections.
# Excludes: RDB files, RESTORE commands received from the master
# connection, and client connections which have the
# skip-sanitize-payload ACL flag.
# The default should be 'clients' but since it currently affects cluster
# resharding via MIGRATE, it is temporarily set to 'no' by default.
#
# sanitize-dump-payload no
# The filename where to dump the DB
dbfilename dump.rdb
# Remove RDB files used by replication in instances without persistence
# enabled. By default this option is disabled, however there are environments
# where for regulations or other security concerns, RDB files persisted on
# disk by masters in order to feed replicas, or stored on disk by replicas
# in order to load them for the initial synchronization, should be deleted
# ASAP. Note that this option ONLY WORKS in instances that have both AOF
# and RDB persistence disabled, otherwise is completely ignored.
#
# An alternative (and sometimes better) way to obtain the same effect is
# to use diskless replication on both master and replicas instances. However
# in the case of replicas, diskless is not always an option.
rdb-del-sync-files no
# The working directory.
#
# The DB will be written inside this directory, with the filename specified
# above using the 'dbfilename' configuration directive.
#
# The Append Only File will also be created inside this directory.
#
# Note that you must specify a directory here, not a file name.
文件保存的目录
dir ./
7.主从复制
# 2) If replica-serve-stale-data is set to 'no' the replica will reply with error
# "MASTERDOWN Link with MASTER is down and replica-serve-stale-data is set to 'no'"
# to all data access commands, excluding commands such as:
# INFO, REPLICAOF, AUTH, SHUTDOWN, REPLCONF, ROLE, CONFIG, SUBSCRIBE,
# UNSUBSCRIBE, PSUBSCRIBE, PUNSUBSCRIBE, PUBLISH, PUBSUB, COMMAND, POST,
# HOST and LATENCY.
#
是否只保存一些数据
replica-serve-stale-data yes
# You can configure a replica instance to accept writes or not. Writing against
# a replica instance may be useful to store some ephemeral data (because data
# written on a replica will be easily deleted after resync with the master) but
# may also cause problems if clients are writing to it because of a
# misconfiguration.
#
# Since Redis 2.6 by default replicas are read-only.
#
# Note: read only replicas are not designed to be exposed to untrusted clients
# on the internet. It's just a protection layer against misuse of the instance.
# Still a read only replica exports by default all the administrative commands
# such as CONFIG, DEBUG, and so forth. To a limited extent you can improve
# security of read only replicas using 'rename-command' to shadow all the
# administrative / dangerous commands.
是否只读
replica-read-only yes
8.安全
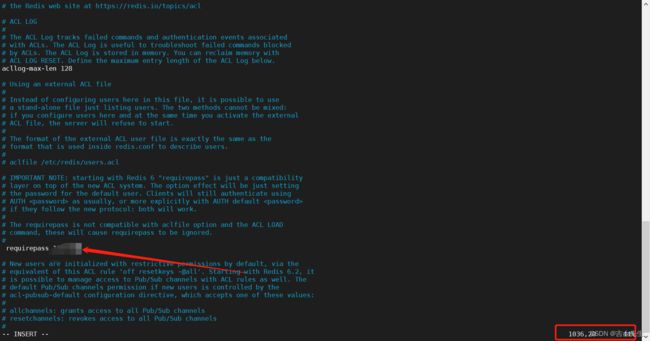
acllog-max-len 128
# Using an external ACL file
#
# Instead of configuring users here in this file, it is possible to use
# a stand-alone file just listing users. The two methods cannot be mixed:
# if you configure users here and at the same time you activate the external
# ACL file, the server will refuse to start.
#
# The format of the external ACL user file is exactly the same as the
# format that is used inside redis.conf to describe users.
#
# aclfile /etc/redis/users.acl
# IMPORTANT NOTE: starting with Redis 6 "requirepass" is just a compatibility
# layer on top of the new ACL system. The option effect will be just setting
# the password for the default user. Clients will still authenticate using
# AUTH as usually, or more explicitly with AUTH default
# if they follow the new protocol: both will work.
#
# The requirepass is not compatible with aclfile option and the ACL LOAD
# command, these will cause requirepass to be ignored.
#
在这里设置密码
requirepass ******
9.客户端
################################### CLIENTS ####################################
# Set the max number of connected clients at the same time. By default
# this limit is set to 10000 clients, however if the Redis server is not
# able to configure the process file limit to allow for the specified limit
# the max number of allowed clients is set to the current file limit
# minus 32 (as Redis reserves a few file descriptors for internal uses).
#
# Once the limit is reached Redis will close all the new connections sending
# an error 'max number of clients reached'.
#
# IMPORTANT: When Redis Cluster is used, the max number of connections is also
# shared with the cluster bus: every node in the cluster will use two
# connections, one incoming and another outgoing. It is important to size the
# limit accordingly in case of very large clusters.
设置redis最大连接服务端的数量为1000
# maxclients 10000
############################## MEMORY MANAGEMENT ################################
# Set a memory usage limit to the specified amount of bytes.
# When the memory limit is reached Redis will try to remove keys
# according to the eviction policy selected (see maxmemory-policy).
#
# If Redis can't remove keys according to the policy, or if the policy is
# set to 'noeviction', Redis will start to reply with errors to commands
# that would use more memory, like SET, LPUSH, and so on, and will continue
# to reply to read-only commands like GET.
#
# This option is usually useful when using Redis as an LRU or LFU cache, or to
# set a hard memory limit for an instance (using the 'noeviction' policy).
#
# WARNING: If you have replicas attached to an instance with maxmemory on,
# the size of the output buffers needed to feed the replicas are subtracted
# from the used memory count, so that network problems / resyncs will
# not trigger a loop where keys are evicted, and in turn the output
# buffer of replicas is full with DELs of keys evicted triggering the deletion
# of more keys, and so forth until the database is completely emptied.
#
# In short... if you have replicas attached it is suggested that you set a lower
# limit for maxmemory so that there is some free RAM on the system for replica
# output buffers (but this is not needed if the policy is 'noeviction').
Redis 配置的最大内存容量
# maxmemory 10.aof配置
############################## APPEND ONLY MODE ###############################
# By default Redis asynchronously dumps the dataset on disk. This mode is
# good enough in many applications, but an issue with the Redis process or
# a power outage may result into a few minutes of writes lost (depending on
# the configured save points).
#
# The Append Only File is an alternative persistence mode that provides
# much better durability. For instance using the default data fsync policy
# (see later in the config file) Redis can lose just one second of writes in a
# dramatic event like a server power outage, or a single write if something
# wrong with the Redis process itself happens, but the operating system is
# still running correctly.
#
# AOF and RDB persistence can be enabled at the same time without problems.
# If the AOF is enabled on startup Redis will load the AOF, that is the file
# with the better durability guarantees.
#
# Please check https://redis.io/topics/persistence for more information.
默认aof不开启,默认使用rdb进行持久化的
appendonly no
# - appendonly.aof.1.base.rdb as a base file.
# - appendonly.aof.1.incr.aof, appendonly.aof.2.incr.aof as incremental files.
# - appendonly.aof.manifest as a manifest file.
持久化文件的饿名字
appendfilename "appendonly.aof"
# For convenience, Redis stores all persistent append-only files in a dedicated
# directory. The name of the directory is determined by the appenddirname
# configuration parameter.
持久化文件目录的名字
appenddirname "appendonlydir"
每次修改都会同步
# appendfsync always
每秒执行一次同步,但可能会丢失这一秒的数据
appendfsync everysec
每次修改都不会同步
# appendfsync no
(十一)、Redis持久化
Redis 是内存数据库,如果不将内存中的数据库状态保存到磁盘,那么一旦服务器进程退出,服务器中的数据库状态也会消失。所以 Redis 提供了持久化的功能
1.RDB
什么是RDB
工作原理:
fork()函数用于从一个已经存在的进程内创建一个新的进程,称为“子进程”。
在指定的时间间隔内将内存中的数据集快照写入磁盘,也就是行话讲的Snapshot快照,它恢复时是将快照文件直接读到内存里。
Redis会单独创建(fork)一个子进程来进行持久化,会先将数据写入到一个临时文件中,待持久化过程都结束了,再用这个临时文件替换上次持久化好的文件。整个过程中,主进程是不进行任何IO操作的。
这就确保了极高的性能。如果需要进行大规模数据的恢复,且对于数据恢复的完整性不是非常敏感,那RDB方式要比AOF方式更加的高效。RDB的缺点是最后一次持久化后的数据可能丢失。我们默认的就是RDB,一般情况下不需要修改这个配置!
有时候在生产环境我们会对这个文件进行备份!
rdb保存的文件默认是dump.rdb,都是在我们的配置文件中进行配置的,一般不需要改动!
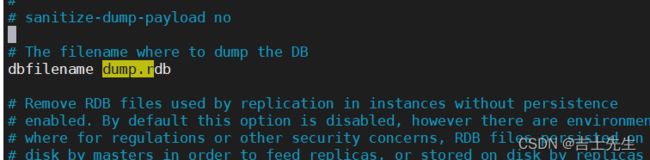
vim 搜索
/ 搜索的内容 然后回车
触发机制:
- save的规则满足的情况下,会自动触发rdb规则
- 执行 flushall 命令,也会触发我们的rdb规则!
- 退出redis,也会产生 rdb 文件!
- 备份就自动生成一个 dump.rdb
如何恢复rdb文件
只需要将rdb文件放在我们的redis启动目录下就可以,redis在启动时就会自动检查dump.rdb并恢复其中的数据。
查看 dump.rdb 需要存放的位置 。
config get dir
优点:
- 适合大规模的数据恢复!
- 对数据的完整性要不高!
缺点:
- 需要一定的时间间隔进行操作!如果redis意外宕机了,这个最后一次修改数据就没有了!
- fork进程的时候,会占用一定的内存空间。
2.AOF (Append only file->每一个动作)
什么是AOF?
将我们执行的所有命令都记录下来,类似于history,恢复的时候就把这个文件全部再执行一遍!
工作原理:
以日志的形式来记录每个写操作,将Redis执行过的所有指令记录下来(读操作不记录),只许追加文件而不可以改写文件,redis启动之初会读取该文件重新构建数据。换言之,redis重启的话就根据日志文件的内容将写指令从前到后执行一次以完成数据的恢复工作。Aof保存的是 appendonly.aof 文件。
如何使用?
如果要使用AOF,需要修改配置文件:
- AOF默认不开启,我们需要手动进行配置!我们只需要将 appendonly 改为yes就开启了 aof!
- 重启,redis 就可以生效
- 如果这个 aof 文件有错误,那么这时候的 redis 是启动不起来的,我们需要修复这个aof文件
配置文件说明:
aof 默认就是文件的无限追加,这样导致的结果就是文件会越来越大。
优点:
- 每一次修改都同步。
- 每秒同步一次,最多可能会丢失一秒的数据。
缺点:
- 相对于数据文件来说,aof远远大于 rdb,修复的速度也比 rdb慢!
- aof运行效率也要比 rdb 慢,所以redis默认的配置就是rdb持久化!
扩展:
- rdb持久化能够在指定的时间间隔内对数据进行快照存储。
- aof持久化记录每次对服务器的写操作,每当服务器重启时都会执行这些命令以此来恢复数据
- aof方式追加每次写操作到文件的末尾,同时在redis配置文件中还设置了对aof文件进行后台重写,使得aof文件不至于过大。
- 同时开启两种持久化方式
-
- 这种情况下redis在重启时会先载入aof文件来恢复原始数据(因为aof文件保存的数据比rdb文件保存的数据更完整)
-
- 建议不要只开启aof持久化,因为rdb更适合用于数据库的备份,同时可以快速重启
- 性能建议
-
- 建议只开启rdb文件,而且只要15分钟备份一次就可以,只保留 save 900 1
-
- 如果使用aof,带来的好处是即使在最恶劣的情况下也不会丢失超过2秒的数据,在重启时只加载自己的aof文件即可。坏处是带来了持续的IO,二是aof重写过程中产生的新数据写到新文件造成的阻塞几乎是不可避免的,只要硬盘许可,应该尽量减少aof重写的频率,AOF重写的基础大小默认值64M太小了,可以设到5G以上。
-
- 如果不使用aof,仅用rdb实现高可用性也可以,这样可以省掉一大笔 IO,也减少了重写时带来的系统波动。代价是如果Master/Slave宕机,这样就会丢失十几分钟的数据。
3、如何选择 RDB和AOF
- 如果想达到足以媲美 PostgreSQL 的数据安全性, 你应该同时使用两种持久化功能。
- 如果你非常关心你的数据, 但仍然可以承受数分钟以内的数据丢失, 那么你可以只使用 RDB 持久化。
- 有很多用户都只使用 AOF 持久化, 但并不推荐这种方式: 因为定时生成 RDB 快照(snapshot)非常便于进行数据库备份, 并且 RDB 恢复数据集的速度也要比 AOF 恢复的速度要快。
(十二)、Redis订阅
Redis 发布订阅(pub/sub)是一种消息通信模式:发送者(pub)发送消息,订阅者(sub)接收消息。
第一个: 消息发布者。第二个频道。第三个:消息订阅者
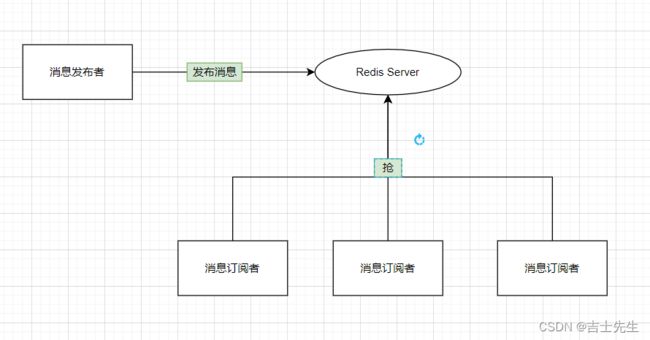
当有新消息通过 PUBLISH 命令发送给频道 channel1 时, 这个消息就会被发送给订阅它的三个客户端:
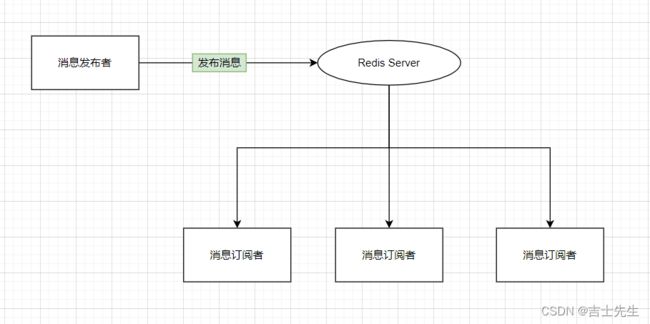
1.命令
- 订阅-个或多个给定模式的频道: PSUBSCRIBE 【预定节目】
- 退阅-个或多个给定模式的频道: PunsubScribe 【表演节目】
- 查看订阅/发布系统状态:PUBSUB
- 向指定频道发布消息: PUBLISH 【发送者】
- 订阅一个或多个频道: SUBSCRIBE
- 退订一个或多个频道: UNSUBSCRIBE 【退订】
我们先开启订阅端,然后再开启推送端
订阅者
127.0.0.1:1245> SUBSCRIBE jsxs # 订阅的频道名字是: jsxs
Reading messages... (press Ctrl-C to quit)
1) "subscribe"
2) "jsxs"
3) (integer) 1 # 以上说: 我们订阅成功!
1) "message"
2) "jsxs"
3) "hello jsxs" #以上是: 说哪一个频道给我们发送了消息
1) "message"
2) "jsxs"
3) "hello redis" #以上是: 说哪一个频道给我们发送了消息
推送者:
127.0.0.1:17> PUBLISH jsxs "hello jsxs" #向jsxs这个频道推送一个消息
(integer) 1
127.0.0.1:17> PUBLISH jsxs "hello redis"
(integer) 1
目前活跃的频道
127.0.0.1:17> PUBSUB CHANNELS
1) "jsxs"
2.原理
每个 Redis 服务器进程都维持着一个表示服务器状态的 redis.h/redisServer 结构, 结构的 pubsub_channels 属性是一个字典, 这个字典就用于保存订阅频道的信息,其中,字典的键为正在被订阅的频道, 而字典的值则是一个链表, 链表中保存了所有订阅这个频道的客户端。
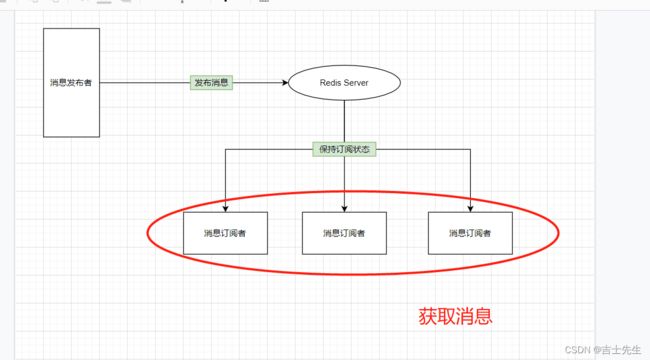
客户端订阅,就被链接到对应频道的链表的尾部,退订则就是将客户端节点从链表中移除。
3.缺点
- 如果一个客户端订阅了频道,但自己读取消息的速度却不够快的话,那么不断积压的消息会使redis输出缓冲区的体积变得越来越大,这可能使得redis本身的速度变慢,甚至直接崩溃。
- 这和数据传输可靠性有关,如果在订阅方断线,那么他将会丢失所有在短线期间发布者发布的消息。
4.应用
- 消息订阅:公众号订阅,微博关注等等(起始更多是使用消息队列来进行实现)
- 多人在线聊天室。
(十三)、Redis主从复制
1.概念
主从复制,是指将一台Redis服务器的数据,复制到其他的Redis服务器。前者称为主节点(Master/Leader),后者称为从节点(Slave/Follower), 数据的复制是单向的!只能由主节点复制到从节点(主节点以写为主、从节点以读为主)。
默认情况下,每台Redis服务器都是主节点,一个主节点可以有0个或者多个从节点,但每个从节点只能有一个主节点。
作用
- 数据冗余:主从复制实现了数据的热备份,是持久化之外的一种数据冗余的方式。
- 故障恢复:当主节点故障时,从节点可以暂时替代主节点提供服务,是一种服务冗余的方式
-负载均衡:在主从复制的基础上,配合读写分离,由主节点进行写操作,从节点进行读操作,分担服务器的负载;尤其是在多读少写的场景下,通过多个从节点分担负载,提高并发量。 - 高可用基石:主从复制还是哨兵和集群能够实施的基础。
2.搭建环境
只配置从节点的库,不配置主节点的库。
查看当前库的信息:
127.0.0.1:1217> info replication
# Replication
role:master # 默认是主分支
connected_slaves:0
master_failover_state:no-failover
master_replid:638a5e8b3d24d6f67fe30fe351452573b1470827
master_replid2:0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
master_repl_offset:0
second_repl_offset:-1
repl_backlog_active:0
repl_backlog_size:1048576
repl_backlog_first_byte_offset:0
repl_backlog_histlen:0
既然需要启动多个服务,就需要多个配置文件。每个配置文件对应修改以下信息:
- 端口号 【port】
- pid文件名 【pid】
- 日志文件名 【logfile】
- rdb文件名 【dump.rdb】
`复制三个配置文件`
[root@Jsxs jconfig]# cp redis.conf redis79.conf
[root@Jsxs jconfig]# cp redis.conf redis80.conf
[root@Jsxs jconfig]# cp redis.conf redis81.conf
[root@Jsxs jconfig]# ls
redis79.conf redis80.conf redis81.conf redis.conf
启动单机多服务集群:
一主二从配置
默认情况下,每台Redis服务器都是主节点; 我们一般情况下只用配置从机就好了!
认老大!一主(79)二从(80,81)
SLAVEOF xxx.xxx.xxx.xxx(主机号) 6379(端口号)
假如主机设置的有密码,那么在从机中添加配置.并且从机不能设置Requiress
masterauth zn20011007(参数根据自己主机密码来)
注意在linux的个人ip(8.xxxx),在本地控制台就是127.0.0.1。
# Replication
role:master # 当前的角色是主机
connected_slaves:2 #发现有两个从机
slave0:ip=127.0.0.1,port=6380,state=online,offset=280,lag=1
slave1:ip=127.0.0.1,port=6381,state=online,offset=280,lag=0
master_failover_state:no-failover
master_replid:9ac622bf6137444efe7c2d93b3b70d8eb4e0df09
master_replid2:0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
master_repl_offset:280
second_repl_offset:-1
repl_backlog_active:1
repl_backlog_size:1048576
repl_backlog_first_byte_offset:1
repl_backlog_histlen:280
SLAVEOF NO ONE
我们这里是使用命令搭建,是暂时的,真实开发中应该在从机的配置文件中进行配置,这样的话是永久的。
3.使用规则
- 从机只能读,不能写,主机可读可写但是多用于写。
- 当主机断电宕机后,默认情况下从机的角色不会发生变化 ,集群中只是失去了写操作,当主机恢复以后,又会连接上从机恢复原状。
- 当从机断电宕机后,若不是使用配置文件配置的从机,再次启动后作为主机。是无法获取之前主机的数据的。若此时重新配置成从机,又可以获取到主机的所有数据。这里就要提到一个同步原理(从机会复制其他从机数据)
4.复制原理
Slave 启动成功连接到master后会送一个sync命令。
Master 接收到命令,启动后台的存盘进程,同时收集所有接收到的用于修改数据集命令,在后台进程执行完毕之后,master将传送整个数据文件到slave,并完成一次同步。
全量复制: 而Slave服务在接收到数据库文件数据后,将其存盘加载到内存中。
增量复制: Master继续将所有收集到的修改命令依次传给slave,完成同步。
但是只要重新连接master,一次完全同步(全量复制)将自动执行。
5.宕机后手动配置主机
层层链路
第三个节点隶属于第二个节点,第二个节点隶属于第一个节点。第二个节点依旧是从节点。

- 第二条中提到,默认情况下,主机故障后,不会出现新的主机,有两种方式可以产生新的主机:从机手动执行命令slaveof no one,这样执行以后从机会独立出来成为一个主机。假如使用哨兵模式(自动选举) 我们就不用手动改了。
slaveof no one
如果主机断开了连接,我们可以使用SLAVEOF no one让自己变成主机!其他的节点就可以手动连接到最新的主节点(手动)!如果这个时候老大修复了,那么就只能手动重新设置隶属关系!(如果配置到配置文件,那么宕机我们就要去修改配置文件)
(十四)、哨兵模式
1.哨兵概念
主从切换技术的方法是:当主服务器宕机后,需要手动把一台从服务器切换为主服务器,这就需要人工干预,费事费力,还会造成一段时间内服务不可用。
谋朝篡位的自动版,能够监控主机是否故障,如果故障了根据投票票数自动从机转换为主机
首先Redis提供了哨兵的命令,哨兵是一个独立的进程,作为进程,他会独立运行。其原理是哨兵通过发送命令,等待Redis服务器响应,从而监控运行多个Redis实列。
所有我们推荐使用哨兵模式
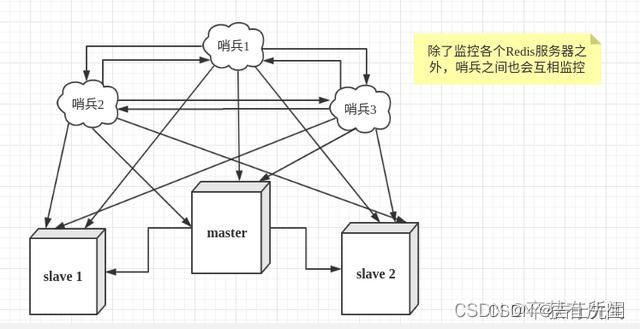
假设主机服务器宕机,哨兵1会先检测到这个结果,系统并不会马上进行Fallove过程,仅仅是哨兵1主观的认为主服务器不可用,这个现象称为主观下线,当后面的哨兵也检测到主服务器不可用,并且数量达到一定值时,那么哨兵之间就会进行一次投票,投票的结果由一个哨兵发起,进行fallover故障转移操作。切换成功后,就会通过发布订阅模式,让各个哨兵把自己监控的从服务器实现切换主机,这个过程称为 客观下线
2. 哨兵的作用
- 通过发送命令,让Redis服务器返回监控其运行状态,包括主服务器和从服务器。
- 当哨兵监测到master宕机,会自动将slave切换成master,然后通过发布订阅模式通知其他的从服务器,修改配置文件,让它们切换主机。
哨兵的核心配置
3.测试哨兵模式
1.配置sentinel.conf 文件
vim sentinel.conf
#编写以下代码:
sentinel monitor 被监控的名称(自定义) 127.0.0.1 6379 1
sentinel auth-pass 被监控的名称(自定义) 主机密码
#保存退出
(数字1表示 :当一个哨兵主观认为主机断开,就可以客观认为主机故障,然后开始选举新的主机)
当从机代替主机之后,之前被替换掉的主机重新加入不能再继续当主机了
2.启动哨兵
redis-sentinel jconfig/sentinel.conf
主机
127.0.0.1:6379> keys *
(empty array)
127.0.0.1:6379> set k1 v1 #没有关机前设置一个值
OK
127.0.0.1:6379> keys *
1) "k1"
127.0.0.1:6379> shutdown
not connected> exit #宕机
[root@Jsxs bin]#
127.0.0.1:6379> info replication #选票后再次上限,发现变成从机
# Replication
role:slave
master_host:127.0.0.1
master_port:6380
master_link_status:up
master_last_io_seconds_ago:2
master_sync_in_progress:0
slave_read_repl_offset:47756
slave_repl_offset:47756
slave_priority:100
slave_read_only:1
replica_announced:1
connected_slaves:0
master_failover_state:no-failover
master_replid:8685054d0c09b9acbf671e46ef7dc8cbf78e64fe
master_replid2:0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
master_repl_offset:47756
second_repl_offset:-1
repl_backlog_active:1
repl_backlog_size:1048576
repl_backlog_first_byte_offset:30884
repl_backlog_histlen:16873
从机1
127.0.0.1:6380> keys *
1) "k1"
127.0.0.1:6380> info replication #宕机第一时刻检查身份
# Replication
role:slave
master_host:127.0.0.1
master_port:6379
master_link_status:down
master_last_io_seconds_ago:-1
master_sync_in_progress:0
slave_read_repl_offset:8204
slave_repl_offset:8204
master_link_down_since_seconds:12
slave_priority:100
slave_read_only:1
replica_announced:1
connected_slaves:0
master_failover_state:no-failover
master_replid:7e5a072e0c62282eebc95446c11aec16f4fd0cf4
master_replid2:0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
master_repl_offset:8204
second_repl_offset:-1
repl_backlog_active:1
repl_backlog_size:1048576
repl_backlog_first_byte_offset:5209
repl_backlog_histlen:2996
127.0.0.1:6380> info replication #宕机第二时刻检查身份
# Replication
role:master # 身份转换
connected_slaves:1
slave0:ip=127.0.0.1,port=6379,state=online,offset=32650,lag=1
master_failover_state:no-failover
master_replid:8685054d0c09b9acbf671e46ef7dc8cbf78e64fe
master_replid2:2b5748a94339ef2150e52b85651d9f7bb441792d
master_repl_offset:32650
second_repl_offset:18175
repl_backlog_active:1
repl_backlog_size:1048576
repl_backlog_first_byte_offset:5209
repl_backlog_histlen:27442
从机2
127.0.0.1:6381> keys *
1) "k1"
127.0.0.1:6381> info replication #宕机第一时刻检查身份
# Replication
role:slave
master_host:127.0.0.1
master_port:6379
master_link_status:down
master_last_io_seconds_ago:-1
master_sync_in_progress:0
slave_read_repl_offset:8204
slave_repl_offset:8204
master_link_down_since_seconds:23
slave_priority:100
slave_read_only:1
replica_announced:1
connected_slaves:0
master_failover_state:no-failover
master_replid:7e5a072e0c62282eebc95446c11aec16f4fd0cf4
master_replid2:0000000000000000000000000000000000000000
master_repl_offset:8204
second_repl_offset:-1
repl_backlog_active:1
repl_backlog_size:1048576
repl_backlog_first_byte_offset:5223
repl_backlog_histlen:2982
127.0.0.1:6381> info replication #宕机第二时刻检查身份
# Replication
role:slave
master_host:127.0.0.1
master_port:6380
master_link_status:down
master_last_io_seconds_ago:-1
master_sync_in_progress:0
slave_read_repl_offset:18174
slave_repl_offset:18174
master_link_down_since_seconds:291
slave_priority:100
slave_read_only:1
replica_announced:1
connected_slaves:0
master_failover_state:no-failover
master_replid:2b5748a94339ef2150e52b85651d9f7bb441792d
master_replid2:7e5a072e0c62282eebc95446c11aec16f4fd0cf4
master_repl_offset:18174
second_repl_offset:8205
repl_backlog_active:1
repl_backlog_size:1048576
repl_backlog_first_byte_offset:5223
repl_backlog_histlen:12952
4.哨兵模式优缺点
- 哨兵集群,基于主从复制模式,所有主从复制的优点,它都有
- 主从可以切换,故障可以转移,系统的可用性更好
- 哨兵模式是主从模式的升级,手动到自动,更加健壮
缺点:
- Redis不好在线扩容,集群容量一旦达到上限,在线扩容就十分麻烦
- 实现哨兵模式的配置其实是很麻烦的,里面有很多配置项
5.哨兵模式全部配置
# 哨兵 sentinel 实例运行的端口 默认 26379
port 26379 # 如果哨兵集群,则要配置多个哨兵端口
# 哨兵 sentinel 的工作目录
dir /tmp
# 哨兵 sentinel 监控的 redis 主节点的 ip port
# master-name 可以自己命名的主节点名字:只能由字母 A-z、数字 0-9、".-_"这三个字符组成。
# quorum 配置多少个 sentinel 哨兵统一认为 master 主节点失联那么这时客观上认为主节点失联了
# sentinel monitor
sentinel monitor mymaster 127.0.0.1 6379 2
# 当在 Redis 实例中开启了 requirepass foobared 授权密码 这样所有连接 Redis 实例的客户端都要提供密码
# 设置哨兵 sentinel 连接主从的密码,注意必须为主从设置一样的验证密码
# sentinel auth-pass
sentinel auth-pass mymaster 密码
# 指定多少毫秒之后,主节点没有应答哨兵 sentinel,此时,哨兵主观上认为主节点下线,默认 30 秒
# sentinel down-after-milliseconds
sentinel down-after-milliseconds mymaster 30000
# 这个配置项指定了在发生 failover 主备切换时最多可以有多少个 slave 同时对新的 master 进行同步
# 这个数字越小,完成 failover 所需的时间就越长
# 但是如果这个数字越大,就意味着越多的 slave 因为 replication 而不可用
# 可以通过将这个值设为 1 来保证每次只有一个 slave 处于不能处理命令请求的状态
# sentinel parallel-syncs
sentinel parallel-syncs mymaster 1
# 故障转移的超时时间 failover-timeout 可以用在以下这些方面:
# 1. 同一个 sentinel 对同一个 master 两次 failover 之间的间隔时间
# 2. 当一个 slave 从一个错误的 master 那里同步数据开始计算时间。直到 slave 被纠正为向正确的 master 那里同步数据时。
# 3. 当想要取消一个正在进行的 failover 所需要的时间。
# 4. 当进行 failover 时,配置所有 slaves 指向新的 master 所需的最大时间。
# 不过,即使过了这个超时,slaves 依然会被正确配置为指向 master,但是就不按 parallel-syncs 所配置的规则来了
# 默认三分钟
# sentinel failover-timeout
sentinel failover-timeout mymaster 180000
# SCRIPTS EXECUTION
# 配置当某一事件发生时所需要执行的脚本,可以通过脚本来通知管理员,例如当系统运行不正常时发邮件通知相关人员。
# 对于脚本的运行结果有以下规则:
# 若脚本执行后返回 1,那么该脚本稍后将会被再次执行,重复次数目前默认为 10
# 若脚本执行后返回 2,或者比 2 更高的一个返回值,脚本将不会重复执行。
# 如果脚本在执行过程中由于收到系统中断信号被终止了,则同返回值为 1 时的行为相同。
# 一个脚本的最大执行时间为 60s,如果超过这个时间,脚本将会被一个 SIGKILL 信号终止,之后重新执行。
# 通知型脚本:当 sentinel 有任何警告级别的事件发生时(比如说 redis 实例的主观失效和客观失效等),将会去调用这个脚本
# 这时这个脚本应该通过邮件,SMS 等方式去通知系统管理员关于系统不正常运行的信息。
# 调用该脚本时,将传给脚本两个参数,一个是事件的类型,一个是事件的描述。
# 如果 sentinel.conf 配置文件中配置了这个脚本路径,那么必须保证这个脚本存在于这个路径,并且是可执行的,否则 sentinel 无法正常启动成功。
# 通知脚本
# sentinel notification-script
sentinel notification-script mymaster /var/redis/notify.sh
# 客户端重新配置主节点参数脚本
# 当一个 master 由于 failover 而发生改变时,这个脚本将会被调用,通知相关的客户端关于 master 地址已经发生改变的信息。
# 以下参数将会在调用脚本时传给脚本:
#
# 目前 总是 “failover”, 是 “leader” 或者 “observer” 中的一个。
# 参数 from-ip,from-port,to-ip,to-port是用来和旧的 master 和新的 master (即旧的 slave)通信的
# 这个脚本应该是通用的,能被多次调用,不是针对性的。
# sentinel client-reconfig-script
sentinel client-reconfig-script mymaster /var/redis/reconfig.sh
(十五)、Redis缓存穿透和雪崩
1.缓存穿透 (查不到然后高并发)
概念
在默认情况下,用户请求数据时,会先在缓存(Redis)中查找,若没找到即缓存未命中,再在数据库中进行查找,数量少可能问题不大,可是一旦大量的请求数据(例如秒杀场景)缓存都没有命中的话,就会全部转移到数据库上,造成数据库极大的压力,就有可能导致数据库崩溃,出现了缓存穿透。网络安全中也有人恶意使用这种手段进行攻击被称为洪水攻击。
2.缓存穿透解决方案
解决方案-两个
布隆过滤器
是一种数据结构,对所有可能查询的参数以hash形式进行存储,在控制层先进行校验,不符合则丢弃,从而避免了对底层存储系统的压力。

缓存空对象
一次请求若在缓存和数据库中都没找到,就在缓存中放一个空对象用于处理后续这个请求。
这样做有一个缺陷:存储空对象也需要空间,大量的空对象会耗费一定的空间,存储效率并不高。解决这个缺陷的方式就是设置较短过期时间
即使对空值设置了过期时间,还是会存在缓存层和存储层的数据会有一段时间窗口的不一致,这对于需要保持一致性的业务会有影响。
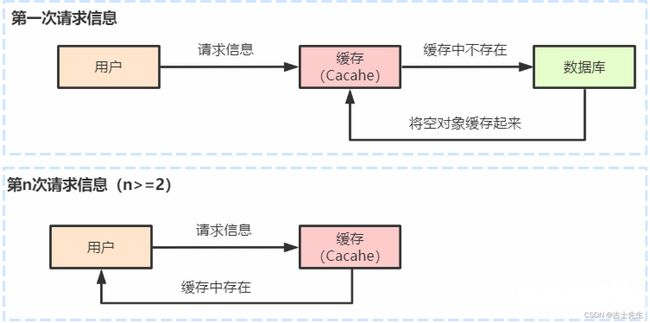
3.缓存击穿 (查得到但超高并发)
概念
相较于缓存穿透,缓存击穿的目的性更强,一个存在的key非常热点,在不停的扛着大并发,大并发集中对这个点进行访问,在缓存过期的一刻,持续大量的请求,这些请求都会击穿缓存到DB,造成瞬时DB请求量大、压力骤增。这就是缓存击穿,只是针对其中某个key的缓存不可用而导致击穿,但是其他的key依然可以使用缓存响应。
比如热搜排行上,一个热点新闻被同时大量访问就可能导致缓存击穿。
4.缓存击穿解决方案
解决方案- 两个
1、设置热点数据永不过期
这样就不会出现热点数据过期的情况,但是当Redis内存空间满的时候也会清理部分数据,而且此种方案会占用空间,一旦热点数据多了起来,就会占用部分空间。
分布式锁: 使用分布式锁,保证对于每个key同时只有一个线程去查询后端服务,其他线程没有获得分布式锁的权限,因此只需要等待即可。这种方式将高并发的压力转移到了分布式锁,因此对分布式锁的考验很大。
5.缓存雪崩
概念
大量的key设置了相同的过期时间,导致在缓存在同一时刻全部失效,造成瞬时DB请求量大、压力骤增,引起雪崩。
双11,热点的数据一定要放在缓存。

2.缓存雪崩解决方案
解决方案-三个
redis高可用
这个思想的含义是,既然redis有可能挂掉,那我多增设几台redis,这样一台挂掉之后其他的还可以继续工作,其实就是搭建的集群
限流降级
这个解决方案的思想是,在缓存失效后,通过加锁或者队列来控制读数据库写缓存的线程数量。比如对某个key只允许一个线程查询数据和写缓存,其他线程等待。
数据预热
数据加热的含义就是在正式部署之前,我先把可能的数据先预先访问一遍,这样部分可能大量访问的数据就会加载到缓存中。在即将发生大并发访问前手动触发加载缓存不同的key,设置不同的过期时间,让缓存失效的时间点尽量均匀。