Java IO流
目录
一,文件
1.基本概念
2.常用文件操作
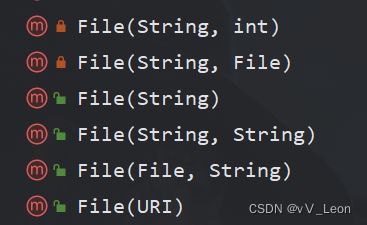
方式 1 new File(String pathname) //根据路径创建
方式 2 new File(File parent,String child) //根据父目录文件+子路径构建
方式 3 new File(String parent,String child) //根据父目录+子路径构建
3.常用获取文件信息方法
4.目录操作
二,IO流原理和流的分类
1.JavaIO流原理
2.流的分类
编辑 3.IO流体系图编辑
三,常用输入输出流
1.FileInputStream&FileOutputStream
==应用FileCopy==
2.FileReader&FileWriter
四,节点流和处理流
1.基本介绍
2.节点流和处理流一览图
3.节点流和处理流的区别和联系
4.处理流的功能
五,缓冲流
BufferedReader&BufferedWriter(InputOutput类似)
===应用(处理流FileCopy)===
六,对象流
*序列化和反序列化
ObjectInputStream&ObjectOutputStream编辑
注意事项
七,标准输入输出流
八,转换流
InputStreamReader&OutputStreamWriter
九,打印流
PrintStream&PrintWriter
十,Properties类
一,文件
1.基本概念
文件
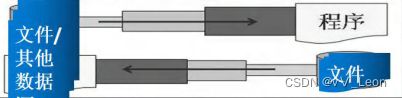
文件是计算机中保存数据的地方,而文件在程序中是以流的形式来操作的
文件流
流:数据在数据源(文件)和程序(内存)之间经历的路径
输入流:数据从数据源(文件)到程序(内存)的路径
输出流:数据从程序(内存)到数据源(文件)的路径
2.常用文件操作
-
方式 1 new File(String pathname) //根据路径创建
String filePath = "e:\\news1.txt";
File file = new File(filePath);
try {
file.createNewFile();
System.out.println("文件创建成功");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}-
方式 2 new File(File parent,String child) //根据父目录文件+子路径构建
File parentFile = new File("e:\\");
String fileName = "news2.txt";
//这里的 file 对象,在 java 程序中,只是一个对象
//只有执行了 createNewFile 方法,才会真正的,在磁盘创建该文件
File file = new File(parentFile, file);
try {
file.createNewFile();
System.out.println("创建成功~");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
-
方式 3 new File(String parent,String child) //根据父目录+子路径构建
String parentPath = "e:\\";
String fileName = "news3.txt";
File file = new File(parentPath, fileName);
try {
file.createNewFile();
System.out.println("创建成功~");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}3.常用获取文件信息方法
File file = new File("e:\\file.txt");
//调用相应的方法,得到对应信息
//getName、getAbsolutePath、getParent、length、exists、isFile、isDirectory
System.out.println("文件名字=" + file.getName());
System.out.println("文件绝对路径=" + file.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.println("文件父级目录=" + file.getParent());
System.out.println("文件大小(字节)=" + file.length());
System.out.println("文件是否存在=" + file.exists());//T
System.out.println("是不是一个文件=" + file.isFile());//T
System.out.println("是不是一个目录=" + file.isDirectory());//F4.目录操作
mkdir()创建一级目录
mkdirs()创建多级目录
delete()删除空目录或文件
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String dirPath="e:\\mytemp";
String filePath="e:\\mytemp\\hello.txt";
File dir = new File(dirPath);
if(!dir.exists()){
System.out.println("mytemp 不存在");
dir.mkdir();
System.out.println("mytemp 已创建");
}else{
System.out.println("mytemp 已存在");
}
File file = new File(filePath);
if (!file.exists()){
System.out.println("file 不存在");
file.createNewFile();
System.out.println("file 已创建");
}else {
System.out.println("file 已存在");
}
System.out.println("over...");
}
二,IO流原理和流的分类
1.JavaIO流原理
- IO即input/output,io技术用于处理数据传输,如读写文件和网络通讯等
- Java程序中,对于数据的输入输出操作以“流(stream)”的方式进行
- java.io 包下提供了各种“流”类和接口,用以获取不同种类的数据,并通过方法输入或输出数据
- 输入:读取外部数据(磁盘,光盘等存储设备的数据)到程序(内存)
- 输出:将程序的数据输出到外部存储设备
2.流的分类
按操作数据单位分为:字节流(8 bit )二进制文件,字符流(按字符)文本文件
按数据流的流向分为:输入流,输出流
按流的角色不同分为:节点流,处理流/包装流

3.IO流体系图
三,常用输入输出流
1.FileInputStream&FileOutputStream
public class fileinputstream {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
@Test
public void readfile() throws IOException {
String filePath="e:\\src.txt";
int readData;
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
try {
//创建流对象,用于读取目的文件
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(filePath);
//从该输出流中读取一个字节的数据,如果没有输出可用,此方法被阻止
//如果返回-1,表示读取完毕
while ((readData=fileInputStream.read())!=-1) {
System.out.print((char) readData);//转成char显示
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
//流是一种资源,如果不关闭,会造成资源浪费
fileInputStream.close();
}
}
@Test// 利用read[byte]优化
public void readfile2() throws IOException {
String filePath="e:\\key.txt";
int readLen;
byte[] buff=new byte[8];//一次读取八个字节
FileInputStream fileInputStream = null;
try {
//创建流对象,用于读取目的文件
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(filePath);
//从该输出流中读取一个字节的数据,如果没有输出可用,此方法被阻止
//如果返回-1,表示读取完毕
//如果读取正常,则返回实际读取的字节数
while ((readLen=fileInputStream.read(buff))!=-1) {
System.out.print(new String(buff,0,readLen));//转成char显示
}
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}finally {
//流是一种资源,如果不关闭,会造成资源浪费
fileInputStream.close();
}
}
}public class fileoutputstream {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
@Test
public void write() throws IOException {
String filePath="E:\\write.txt";
FileOutputStream fileOutputStream=null;
String str="output";//利用getbyte方法将字符串转成字节数组
//如果文件存在就得到输出流
//否则创建文件
try {
fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(filePath,true);
fileOutputStream.write(str.getBytes());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
fileOutputStream.close();
}
// new FileOutputStream(filePath) 创建方式为覆盖模式,写入内容会覆盖原来的内容
// new FileOutputStream(filePath, true) 创建方式为追加模式,写入内容追加到文件后面
}
}==应用FileCopy==
public class filecopy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
1.输入流,将文件读取到Java程序
2.输出流,将文件写入内存
在完成程序时,应该读取部分程序就写入指定位置
使用循环
*/
FileInputStream fileInputStream=null;
FileOutputStream fileOutputStrem=null;
String srcPath="E:\\key.txt";
String destPath="D:\\key.txt";
try {
fileInputStream = new FileInputStream(srcPath);
fileOutputStrem = new FileOutputStream(destPath);
byte[] buf=new byte[1024];
int readLen;
while ((readLen=fileInputStream.read(buf))!=-1){
fileOutputStrem.write(buf,0,readLen);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if(fileInputStream!=null)
fileInputStream.close();
if(fileOutputStrem!=null)
fileOutputStrem.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}2.FileReader&FileWriter
public class filereader {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filePath = "E:\\CODE\\Java_67\\ChangePass\\src\\ChangePassApp.java";
FileReader fileReader = null;
int data;
try {
fileReader = new FileReader(filePath);
while ((data=fileReader.read())!=-1){//可以选择逐字符读入和以字符数组读入
System.out.print((char) data);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (fileReader!=null)
fileReader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
@Test
public void read(){
String filePath = "E:\\CODE\\Java_67\\ChangePass\\src\\ChangePassApp.java";
FileReader fileReader = null;
char[] chars =new char[1024];
int readLen;
try {
fileReader = new FileReader(filePath);
while ((readLen=fileReader.read(chars))!=-1){//可以选择逐字符读入和以字符数组读入
System.out.println(new String(chars,0,readLen));
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
if (fileReader!=null)
fileReader.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
public class filewriter {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String filePath="E:\\writerwriter.txt" ;
FileWriter fileWriter=null;
String str="writer test";
try {
fileWriter=new FileWriter(filePath,true);
fileWriter.write(str.toCharArray(),0,str.length()-3);//字符数组写入
fileWriter.write(str,str.length()-3,3);//字符串写入
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if(fileWriter!=null){
try {
fileWriter.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
}四,节点流和处理流
1.基本介绍
- 节点流可以从一个特定的数据源读写数据,如:FileReader,FileWriter
- 处理流(包装流)是“连接”在已存在的流(节点流或处理流)之上,为程序提供更为强大的读写功能,也更加灵活
2.节点流和处理流一览图
 3.节点流和处理流的区别和联系
3.节点流和处理流的区别和联系
- 节点流是底层流/低级流,直接和数据源相接。
- 处理流(包装流)包装节点流,既可以消除不同节点流的实现差异,也可以提供更方便的方法来完成输入输出
- 处理流对节点流的包装使用了修饰器设计模式,不会直接与数据源相接
4.处理流的功能
性能的提高:利用增加缓冲的方式提高输入输出的效率
操作的便捷:处理流可能提供了一些便捷的方法来一次输入输出大批量数据,使用更加灵活方便
五,缓冲流
BufferedReader&BufferedWriter(InputOutput类似)
public class bufferedreader {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String filePath="e:\\dest.txt";
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(filePath));
String line;
//readLine表示按行读取,当返回空时表示读取结束
while ((line=bufferedReader.readLine())!=null){//高效
System.out.print(line);
}
//关闭流
bufferedReader.close();
}
}
public class bufferedwriter {
public static void main(String[] args)throws IOException {
String filePath="e:\\writerwriter.txt";
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(filePath,true));
bufferedWriter.write("我是熊二");
bufferedWriter.newLine();//添加行
bufferedWriter.close();
}
}===应用(处理流FileCopy)===
public class bufferedcopy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
}
@Test
public void fileCopy()throws IOException{
//buffered是按字符操作的,
// 不要对二进制文件操作(声音,视频,doc,pdf),否则可能造成文件损坏
String srcPath="E:\\src.txt";
String destPath="E:\\dest.txt";
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new FileReader(srcPath));
BufferedWriter bufferedWriter = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(destPath));
String line=null;
while ((line=bufferedReader.readLine())!=null){
bufferedWriter.write(line);
bufferedWriter.newLine();//换行!
}
System.out.println("finish...");
bufferedWriter.close();
bufferedReader.close();
}
@Test
public void streamCopy() throws IOException{
String srcPath="E:\\狗头.png";
String destPath="E:\\狗头副本.png";
BufferedInputStream bufferedInputStream = new BufferedInputStream(new FileInputStream(srcPath));
BufferedOutputStream bufferedOutputStream = new BufferedOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(destPath));
byte[] in=new byte[1024];
int len=0;
while ((len=bufferedInputStream.read(in))!=-1){
bufferedOutputStream.write(in,0,len);
}
System.out.println("Copy finish");
bufferedInputStream.close();
bufferedOutputStream.close();
}
}六,对象流
*序列化和反序列化
- 序列化和反序列化就是在保存和恢复数据时,保存或恢复数据的值和数据类型
- 若要让某个对象支持序列化机制,则必须让其类是可序列化的,为此需要让该类实现两个接口之一:
- Serializable //这是一个标记接口,没有方法
- Externalizable //该接口需要实现抽象方法,因此一般使用第一个接口
ObjectInputStream&ObjectOutputStream
public class objectoutputstream {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String filePath="E:\\obj.dat";
//序列化后,保存的文件格式,不是存文本,而是按照他的格式来保存
ObjectOutputStream objectOutputStream = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream(filePath));
//序列化保存:都实现了Seriaizable
objectOutputStream.writeInt(100);;// int -> Integer
objectOutputStream.writeDouble(1.2);// boolean -> Boolean
objectOutputStream.writeChar('A');// char -> Character
objectOutputStream.writeUTF("ABC");//double -> Double
objectOutputStream.writeObject(new dog("大黄",3));
objectOutputStream.close();
}
}
class dog implements Serializable {//标记接口
private String name;
private int age;
@Override
public String toString() {
return "dog{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
public dog(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}public class objectinputstream {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException {
String filePath="e:\\obj.dat";
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(filePath));
//反序列化读取
System.out.println(objectInputStream.readInt());
System.out.println(objectInputStream.readDouble());
System.out.println(objectInputStream.readChar());
System.out.println(objectInputStream.readUTF());
Object dog=objectInputStream.readObject();
System.out.println("dog.getclass = " + dog.getClass());
System.out.println("dog = " + dog);
objectInputStream.close();
}
}注意事项
- 读写顺序要一致
- 要求序列化和反序列化的对象要实现接口
- 序列化的类中建议添加SerialVersionUID,提高版本的兼容性
- 序列化对象时,默认将里面的锁属性都序列化,除了static和transient修饰的成员
- 序列化的对象要求里面的属性类型也需要实现序列化接口
- 序列化具有可继承性
七,标准输入输出流
new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print();八,转换流
- InputSreamReader:Reader的子类,可以将InputStream(字节流)包装成(转换)Reader(字符流)
- OutputStreamWriter:Writer的子类,实现将OutputStream包装成Writer
- 当处理纯文本数据时,如果使用字符流效率更高,并且可以有效解决中文乱码问题,所以建议将字节流转换成字符流
- 可以在使用时指定编码格式(UTF-8,GBK,GB2312,ISO8859-1等)
InputStreamReader&OutputStreamWriter
public class inputstreamreader {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String filePath="E:\\key.txt";
String charSet="gbk";
BufferedReader isr = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(filePath), charSet));
String s =isr.readLine();
System.out.println(s);
isr .close();
System.out.println("使用"+charSet+"编码读取成功");
}
}public class outputstreamwriter {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
String filePath="E:\\key.txt";
BufferedWriter osw = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(new FileOutputStream(filePath,true),"gbk"));
osw.write("加入非字节内容");
osw.newLine();
osw.close();
}
}九,打印流
打印流只有输出流
PrintStream&PrintWriter
PrintStream out = System.out;
//在默认情况下,PrintStream 输出数据的位置是 标准输出,即显示器
out.print("Hello");
//因为print底层使用的是write,可以直接调用write进行输出
out.write("Hello");
//我们可以去修改打印流输出的位置/设备
//1. 输出修改成到 "e:\\tt.txt"
//2. "Hello" 就会输出到 e:\tt.txt
//3. public static void setOut(PrintStream out) {
// checkIO();
// setOut0(out); // native 方法,修改了 out
// }
System.setOut(new PrintStream("e:\\tt.txt"));
System.out.println("Hello");十,Properties类
Properties类是专门用于读写配置文件的集合类
*配置文件的格式: 键=值
键=值
...
键值对不需要有空格,值不需要引号,默认类型为String
Properties类的常用方法:
load:加载配置文件键值对到Properties对象
list:将数据下那是到指定设备
getProperty(key):根据键获取值
setProperty(key,value):设置键值对到Properties对象,如果原先不存在就创建,存在就修改
store:将Properties对象中的键值对储存到配置文件(idea默认将中文转为Unicode码)
//使用 Properties 类来读取 mysql.properties 文件
//1. 创建 Properties 对象
Properties properties = new Properties();
//2. 加载指定配置文件
properties.load(new FileReader("src\\mysql.properties"));
//3. 把 k-v 显示控制台
properties.list(System.out);
//4. 根据 key 获取对应的值
String user = properties.getProperty("user");
String pwd = properties.getProperty("pwd");
System.out.println("用户名=" + user);
System.out.println("密码是=" + pwd);