前端面试官:你能实现js数组原型上的方法吗?
有个面试官问我:能不能用for或while将js数组原型上的大部分方法实现一遍?当时我很懵,自己也没试过也不知道能不能,但觉得这些都不算很难,我就说:可以! 很遗憾,后面他也祝我早日找到更匹配的工作了~
后来,我自己就试着实现一遍,在这过程中,有些方法还是比较简单的。如有不足,希望有大佬不吝赐教,而且有些方法我也实现不了:sort、reduce等。但也能实现大部分的。有些方法我写了实现思路可能写得不清楚,,没写实现思路的方法,那就是我解释不了了。你们看代码理解就行!!!
at
官方解释:at()方法接收一个整数值并返回该索引的项目,允许正数和负数。负整数从数组中的最后一个项目开始倒数。大概意思:给一个索引,返回当前索引的值。
思路:
- 当传递的索引大于0时,直接返回当前索引值。
- 当传递的索引小于0时,返回倒数第
i个元素,公式:this.length + i。- 当传递的索引等于0时,直接返回第一个元素。
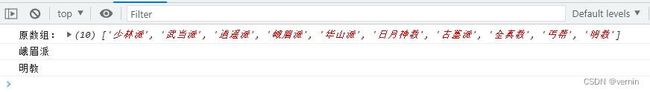
const sect = ['少林派', '武当派', '逍遥派', '峨眉派', '华山派', '日月神教', '古墓派', '全真教', '丐帮', '明教']
Array.prototype.myAt = function(i) {
let index = parseInt(i)
if (index > 0) {
return this[index]
} else if (index < 0) {
return this[this.length + index]
} else {
return this[0]
}
}
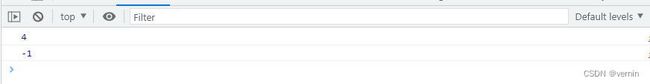
const value = sect.myAt(3)
const value1 = sect.myAt(-1)
console.log('原数组:', sect)
console.log(value)
console.log(value1)
concat
官方解释:concat()方法用于合并两个或多个数组。此方法不会更改现有数组,而是返回一个新数组。
思路:
首先准备一个空数组,然后遍历原数组,把所有的值都放到准备好的空数组中,这个空数组已经跟原数组一模一样了。
- 当不传递参数时(arguments.length < 1),直接返回这个数组
- 当不传递参数时(arguments.length >= 1),遍历实参:
- 当当前实参不是数组时,直接把它插到之前准备好的数组中。
- 当当前实参是数组时,再遍历这个数组,挨个插到之前准备好的数组中。
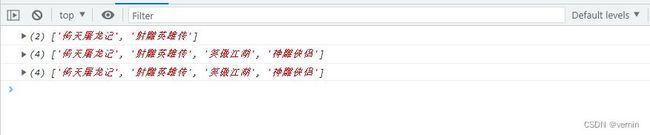
const array1 = ['倚天屠龙记', '射雕英雄传'];
const array2 = ['笑傲江湖', '神雕侠侣'];
Array.prototype.myConcat = function() {
let temp = []
for (let u = 0; u < this.length; u++) {
temp.push(this[u])
}
// 当不传参数时
if (arguments.length < 1) {
return temp;
}
// 如果有参数,遍历实参
for (let i = 0; i < arguments.length; i++) {
// 当前实参
let currentArg = arguments[i]
// 当实参不是数组类型
if (Object.prototype.toString.call(currentArg) !== '[object Array]') {
temp.push(currentArg)
} else {
for (let j = 0; j < currentArg.length; j++) {
temp.push(currentArg[j])
}
}
}
return temp
}
let array3 = array1.myConcat()
let array4 = array1.myConcat(array2)
let array5 = array1.myConcat(array2, '天龙八部')
console.log(array3)
console.log(array4)
console.log(array4)
every
官方解释:every()方法测试一个数组内的所有元素是否都能通过某个指定函数的测试。它返回一个布尔值。
思路:
先判断传进来的是不是一个函数,如果不是函数,抛出错误!如果是一个方法,遍历此数组,执行回调函数并传递当前遍历的值、索引、整个数组。如果回调函数返回
false,直接return false,如果遍历完整个数组就return true
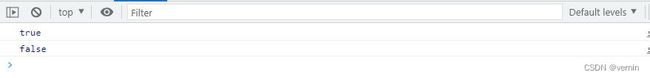
const array1 = [1, 30, 39, 29, 10, 13]
Array.prototype.myEvery = function(fun) {
let isFunction = Object.prototype.toString.call(fun) === '[object Function]'
if (!isFunction) {
throw new Error('请传入一个方法。')
}
// 遍历当前数组,执行回调函数并传入当前遍历的值
for (let i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
let flag = fun(this[i], i, this)
if (!flag) {
return false
}
}
return true
}
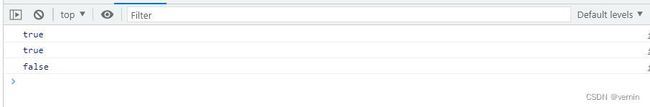
console.log(array1.myEvery(item => item < 50))
console.log(array1.myEvery(item => item < 20))
fill
官方解释:fill()方法用一个固定值填充一个数组中从起始索引到终止索引内的全部元素。不包括终止索引。
思路:
准备一个空数组,遍历此数组:
- 当传一个参数时,把这个参数插入到空数组中,
- 当传递两个参数时,
- 当遍历的值小于第二个参数时,把数组的值插入刚刚准备的数组中。
- 当遍历到的索引等于大于第二个参数时,把第一个参数插入到刚刚准备的数组中.
- 当传递三个参数时,同理!!!
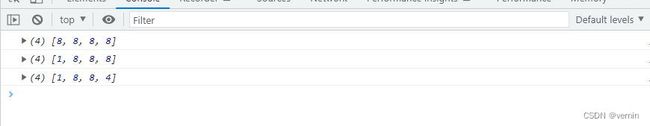
const array1 = [1, 2, 3, 4];
Array.prototype.myFill = function() {
let temp = []
let leng = arguments.length
for (let i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
if (leng === 1) {
temp.push(arguments[0])
} else if (leng === 2) {
let start = parseInt(arguments[1])
if(i < start) {
temp.push(this[i])
} else {
temp.push(arguments[0])
}
} else {
let start = parseInt(arguments[1])
let end = parseInt(arguments[2])
if(i < start || i >= end) {
temp.push(this[i])
} else {
temp.push(arguments[0])
}
}
}
return temp
}
const array2 = array1.myFill(8)
const array3 = array1.myFill(8, 1)
const array4 = array1.myFill(8, 1, 3)
console.log(array2)
console.log(array3)
console.log(array4)
filter
官方解释:filter()方法创建给定数组一部分的浅拷贝,其包含通过所提供函数实现的测试的所有元素。大概意思:从数组中筛选出你想要的数据。
思路:
首先判断参数是不是一个函数,不是函数,抛出错误!如果是函数,遍历此数组,执行回调函数,当回调函数返回
true,则将当前值插入准备好的空数组中,最后返回这个数组。
const sect = ['少林派', '武当派', '逍遥派', '峨眉派', '华山派', '日月神教', '古墓派', '全真教', '丐帮', '明教']
Array.prototype.myFilter = function(fun) {
let isFunction = Object.prototype.toString.call(fun) === '[object Function]'
if (!isFunction) {
throw new Error('请传入一个方法。')
}
let temp = []
for (let i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
let flag = fun(this[i], i, this)
if (flag) {
temp.push(this[i])
}
}
return temp
}
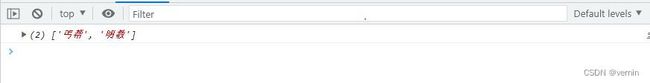
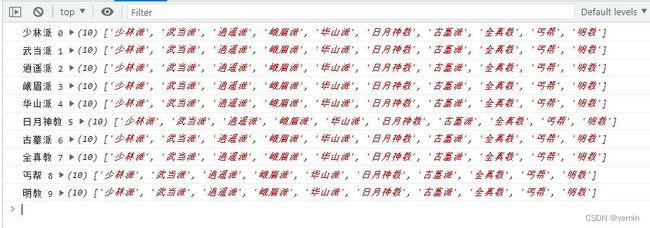
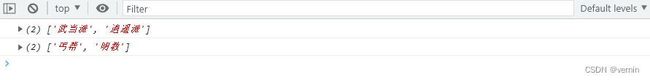
let newSect = sect.myFilter(item => item.length === 2)
console.log(newSect)
find
官方解释:find()方法返回数组中满足提供的测试函数的第一个元素的值。否则返回 undefined。
思路:
首先判断参数是不是一个函数,不是函数,抛出错误!如果是函数,遍历此数组,执行回调函数,如果回调函数返回
true,则return遍历中的当前值。如果遍历完了,回调函数都没有返回true,则return undefined
const array1 = [5, 12, 8, 130, 44];
Array.prototype.myFind = function(fun) {
let isFunction = Object.prototype.toString.call(fun) === '[object Function]'
if (!isFunction) {
throw new Error('请传入一个方法。')
}
for (let i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
let target = fun(this[i], i, this)
if (target) {
return this[i]
}
}
return undefined
}
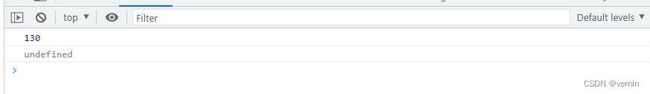
console.log(array1.myFind(item => item > 20));
console.log(array1.myFind(item => item > 200));
findLast
官方解释:findLast()方法返回数组中满足提供的测试函数条件的最后一个元素的值。如果没有找到对应元素,则返回 undefined。
思路:
原理跟
find一样,只不过循环数组的时候,从右往左循环就行了。
const array1 = [5, 12, 8, 130, 44]
Array.prototype.myFindLast = function(fun) {
let isFunction = Object.prototype.toString.call(fun) === '[object Function]'
if (!isFunction) {
throw new Error('请传入一个方法。')
}
for (let i = this.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
let target = fun(this[i], i, this)
if (target) {
return this[i]
}
}
return undefined
}
console.log(array1.myFindLast(item => item > 20))
console.log(array1.myFindLast(item => item > 200))
findIndex
官方解释:findIndex()方法返回数组中满足提供的测试函数的第一个元素的索引。若没有找到对应元素则返回-1。
思路:
首先判断参数是不是一个函数,不是函数,抛出错误!如果是函数,遍历此数组,执行回调函数,如果回调函数返回
true,则return遍历中的当前索引。如果遍历完了,回调函数都没有返回true,则return -1
const array1 = [5, 12, 8, 130, 44]
Array.prototype.myFindIndex = function(fun) {
let isFunction = Object.prototype.toString.call(fun) === '[object Function]'
if (!isFunction) {
throw new Error('请传入一个方法。')
}
for (let i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
let target = fun(this[i], i, this)
if (target) {
return i
}
}
return -1
}
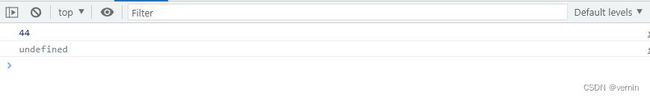
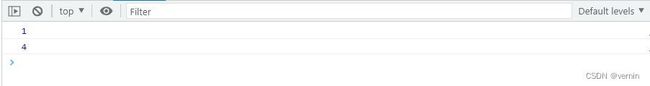
console.log(array1.myFindIndex(item => item > 10));
console.log(array1.myFindIndex(item => item > 1000));
findLastIndex
官方解释:findLastIndex() 方法返回数组中满足提供的测试函数条件的最后一个元素的索引。若没有找到对应元素,则返回 -1。
思路:
原理跟
findIndex一样,只不过循环数组的时候,从右往左循环就行了。
const array1 = [5, 12, 8, 130, 44]
Array.prototype.myFindLastIndex = function(fun) {
let isFunction = Object.prototype.toString.call(fun) === '[object Function]'
if (!isFunction) {
throw new Error('请传入一个方法。')
}
for (let i = this.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
let target = fun(this[i], i, this)
if (target) {
return i
}
}
return -1
}
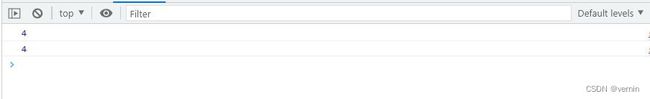
console.log(array1.myFindLastIndex(item => item > 10))
console.log(array1.myFindLastIndex(item => item > 1000))
forEach
官方解释:forEach()方法对数组的每个元素执行一次给定的函数。
const sect = ['少林派', '武当派', '逍遥派', '峨眉派', '华山派', '日月神教', '古墓派', '全真教', '丐帮', '明教']
Array.prototype.myForEach = function(fun) {
let isFunction = Object.prototype.toString.call(fun) === '[object Function]'
if (!isFunction) {
throw new Error('请传入一个方法。')
}
for (let i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
fun(this[i], i, this)
}
}
sect.myForEach((item, i, arr) => console.log(item, i, arr))
includes
官方解释:forEach()方法用来判断一个数组是否包含一个指定的值,根据情况,如果包含则返回 true,否则返回 false。
思路:
遍历数组,挨个判断参数和遍历的当前值是否相等,如果相等
return true,否则return false
const sect = ['少林派', '武当派', '逍遥派', '峨眉派', '华山派', '日月神教', '古墓派', '全真教', '丐帮', '明教']
Array.prototype.myIncludes = function(value) {
if (!value) {
return false
}
for (let i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
if (value === this[i]) {
return true
}
}
return false
}
console.log(sect.myIncludes('明教'))
console.log(sect.myIncludes('伊斯兰'))
indexOf
官方解释:indexOf()方法返回在数组中可以找到给定元素的第一个索引,如果不存在,则返回 -1。
const beasts = ['ant', 'bison', 'camel', 'duck', 'bison'];
Array.prototype.myIndexOf = function(target, index) {
if (!target) {
return -1
}
index = parseInt(index)
let i = 0;
if (index && index > 0 && index <= this.length) {
i = index
}
if (index && index < 0 && index >= -(this.length)) {
i = this.length + index
}
for (i; i < this.length; i++) {
if (target === this[i]) {
return i
}
}
return -1
}
console.log(beasts.myIndexOf('bison'))
console.log(beasts.myIndexOf('bison', 4))
lastIndexOf
官方解释:lastIndexOf()方法返回指定元素(也即有效的 JavaScript 值或变量)在数组中的最后一个的索引,如果不存在则返回 -1。从数组的后面向前查找,从 fromIndex 处开始
const beasts = ['ant', 'bison', 'camel', 'duck', 'bison'];
Array.prototype.myLastIndexOf = function(target, index) {
if (!target) {
return -1
}
index = parseInt(index)
let i = this.length - 1;
if (index && index > 0 && index <= this.length) {
i = index
}
if (index && index < 0 && index >= -(this.length)) {
i = this.length + index
}
for (i; i >= 0; i--) {
if (target === this[i]) {
return i
}
}
return -1
}
console.log(beasts.myLastIndexOf('bison'))
console.log(beasts.myLastIndexOf('bison', 4))
join
官方解释:join()方法将一个数组(或一个类数组对象)的所有元素连接成一个字符串并返回这个字符串。如果数组只有一个项目,那么将返回该项目而不使用分隔符。
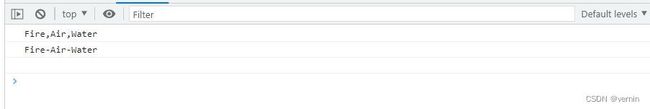
const elements = ['Fire', 'Air', 'Water']
Array.prototype.myJoin = function(target) {
let str = ''
for (let i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
if (!target) {
str += this[i] + ','
} else {
str += this[i] + target
}
}
return str.slice(0, str.length - 1)
}
console.log(elements.myJoin())
console.log(elements.myJoin('-'))
console.log([].myJoin()) // ''
map
官方解释:map()方法创建一个新数组,这个新数组由原数组中的每个元素都调用一次提供的函数后的返回值组成。
思路:
首先判断参数是不是一个函数,不是函数,抛出错误!如果是函数,遍历此数组,执行回调函数传入遍历的当前值、索引、这个数组,将回调函数的返回值插入临时的空数组中,最后
return这个临时数组。
const array1 = [5, 12, 8, 130, 44];
Array.prototype.myMap = function(fun) {
let isFunction = Object.prototype.toString.call(fun) === '[object Function]'
if (!isFunction) {
throw new Error('请传入一个方法。')
}
let temp = []
for (let i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
let value = fun(this[i], i, this)
temp.push(value)
}
return temp
}
let map1 = array1.myMap(item => item + 2)
let map2 = array1.myMap(item => item / 2)
console.log('array1:', array1)
console.log(map1)
console.log(map2)
reverse
官方解释:reverse()方法将数组中元素的位置颠倒,并返回该数组。数组的第一个元素会变成最后一个,数组的最后一个元素变成第一个。该方法会改变原数组。
const sect = ['少林派', '武当派', '逍遥派', '峨眉派', '华山派', '日月神教', '古墓派', '全真教', '丐帮', '明教']
Array.prototype.myReverse = function () {
for (let i = 0; i < this.length / 2; i++) {
let temp = this[i]
let lastIndex = this.length - 1 - i
this[i] = this[lastIndex]
this[lastIndex] = temp
}
return this
}
let reSect = sect.myReverse()
console.log('改变后的数组:', sect)
console.log(reSect)
slice
官方解释:slice()方法返回一个新的数组对象,这一对象是一个由 begin 和 end 决定的原数组的浅拷贝(包括 begin,不包括end)。原始数组不会被改变。
const sect = ['少林派', '武当派', '逍遥派', '峨眉派', '华山派', '日月神教', '古墓派', '全真教', '丐帮', '明教']
Array.prototype.mySlice = function(begin, end) {
let start = begin || 0
let ending = end || this.length
if (begin < 0) {
start = this.length + begin
}
if (end < 0) {
ending = this.length + end
}
let temp = []
for (let i = start; i < ending; i++) {
temp.push(this[i])
}
return temp
}
console.log(sect.mySlice(1, 3))
console.log(sect.mySlice(-2))
some
官方解释:some()方法测试数组中是不是至少有 1 个元素通过了被提供的函数测试。它返回的是一个 Boolean 类型的值。
const array1 = [5, 12, 8, 130, 44]
Array.prototype.mySome = function(fun) {
let isFunction = Object.prototype.toString.call(fun) === '[object Function]'
if (!isFunction) {
throw new Error('请传入一个方法。')
}
for (let i = 0; i < this.length; i++) {
let flag = fun(this[i], i, this)
if (flag) {
return true
}
}
return false
}
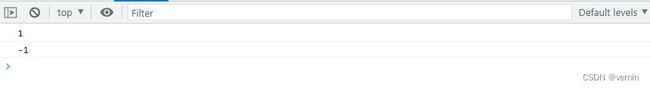
console.log(array1.mySome(item => item === 130))
console.log(array1.mySome(item => item > 100))
console.log(array1.mySome(item => item > 200))