JAVA8 Stream方法使用详解Filter、map等用法(一)
文章目录
-
- 一、筛选和切片
-
- 1、谓词筛选filter
- 2、筛选不同的元素distinct
- 3、截断流limit
- 4、跳过元素
- 二、映射
-
- 1、map对每个元素应用函数
- 2、流的扁平化
- 三、查找和匹配
-
- 1、至少匹配一个
- 2、匹配所有
- 3、查找元素
- 4、查找第一个元素
流可以让我们从外部迭代转向内部迭代,流可以理解为按需加载(只有消费者消费的时候才开始生产),集合是供应商驱动(先把仓库装满,再开始卖)。流可以看作在时间中分布的一组,集合则是在空间中分布的一组。
以下例子都用此数据:
public class Dish {
private final String name;
private final boolean vegetarian;
private final int calories;
private final Type type;
public Dish(String name, boolean vegetarian, int calories, Type type) {
this.name = name;
this.vegetarian = vegetarian;
this.calories = calories;
this.type = type;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public boolean isVegetarian() {
return vegetarian;
}
public int getCalories() {
return calories;
}
public Type getType() {
return type;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return name;
}
}
public enum Type {
MEAT, FISH, OTHER
}
private static List menu = Arrays.asList(
new Dish("pork", false, 800, Type.MEAT),
new Dish("beef", false, 700, Type.MEAT),
new Dish("chicken", false, 400, Type.MEAT),
new Dish("french fries", true, 530, Type.OTHER),
new Dish("rice", true, 350, Type.OTHER),
new Dish("season fruit", true, 120, Type.OTHER),
new Dish("pizza", true, 550, Type.OTHER),
new Dish("prawns", false, 300, Type.FISH),
new Dish("salmon", false, 450, Type.FISH));
一、筛选和切片
用谓词来筛选各不相同的元素,或将流截断指定的长度
1、谓词筛选filter
Stream接口支持filter方法,该方法接受一个谓词(返回Boolean的函数)作为参数,例:
public static void testFilter(){
List collect = menu.stream().filter(dish -> dish.isVegetarian()).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(collect);
}
2、筛选不同的元素distinct
distinct方法,返回一个元素各异的流,说白了就是去重。例:
public static void testDistinct() {
List strings = Arrays.asList("A", "B", "B", "C", "D", "D", "E");
strings.stream().distinct().forEach(System.out::println);
}
3、截断流limit
该方法会给定一个不超过指定长度,所需的长度作为参数传递给limit。例:
public static void testLimit() {
List strings = Arrays.asList("A", "B", "B", "C", "D", "D", "E");
List collect = strings.stream().limit(3).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(collect);
}
4、跳过元素
流还支持跳过元素,返回扔掉前n个元素的流。例:
public static void testSkip() {
List strings = Arrays.asList("A", "B", "B", "C", "D", "D", "E");
List collect = strings.stream().skip(3).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(collect);
}
二、映射
一个非常常见的数据处理就是从某些对象种选择信息,比如在SQL里,你可以从表中选择一列,Stream API也通过map和flatMap提供了类似的方法
1、map对每个元素应用函数
流支持map方法,它接受一个函数作为参数。这个函数会被应用到每个元素上,并映射成新的元素。说白了就是返回一个新的l类型的list集合。例:
map返回的是Stream(String)
public static void testMap() {
List collect = menu.stream().map(Dish::getName).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(collect);
}
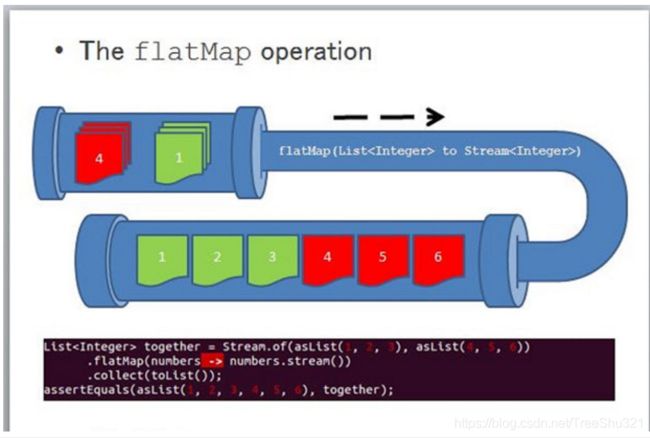
2、流的扁平化
flatMap各个数组并不是分别映射成一个流,而是映射成流的内容,说白了就是把几个小的list转换到一个大的list。例:
public static void testFlatMap() {
String[] array = {"HELLO","WORLD"};
Stream stream = Arrays.stream(array);
stream.forEach(System.out::println);
List strings = Arrays.asList("hello", "world");
List collect = strings.stream().map(w -> w.split("")).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(collect);
Stream> streamStream = collect.stream().map(array1 -> Arrays.stream(array1));
List> collect1 = collect.stream().map(array1 -> Arrays.stream(array1)).collect(Collectors.toList());
collect1.stream().forEach(d -> {
d.forEach(System.out::println);
});
System.out.println(collect1);
Stream stringStream = strings.stream().map(w -> w.split("")).flatMap(Arrays::stream);
List collect2 = strings.stream().map(w -> w.split("")).flatMap(Arrays::stream).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(collect2);
}
给定数字列表1[1,2,3]和列表2[3,4],返回[(1,3),(2,3),(2,3),(2,4),(3,3),(3,4)]
List integers = Arrays.asList(1, 2, 3);
List integers1 = Arrays.asList(3, 4)
List collect3 = integers.stream().flatMap(i -> integers1.stream()
.map(j -> new int[]{i, j})).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(collect3);
三、查找和匹配
另一个常见的数据处理套路是看着数据集中的某些元素是否匹配一个给定属性。
allMatch,、anyMatch、noneMatch、findFirst、findAny
1、至少匹配一个
anyMatch是否有一个元素匹配
if (menu.stream().anyMatch(Dish::isVegetarian)) {
System.out.println("");
}
2、匹配所有
allMatch匹配所有
menu.stream().allMatch(d -> d.getCalories < 1000);
noneMatch和allMatch是相对的没有一个元素匹配
3、查找元素
findAny返回当前流任意元素
public static void testFindAny() {
Optional collect = menu.stream().filter(dish -> dish.getCalories() > 1000).findAny();
System.out.println(collect);
}
返回值是一个Optional,是一个容器代表值存在不存在,这个类我们将在以后章节中详细讲解。
4、查找第一个元素
findFirst
public static void testFindAny() {
Optional collect = menu.stream().filter(dish -> dish.getCalories() > 1000).findFrist();
System.out.println(collect);
}
以上是部分API,我们下一章节继续讲解。